Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*; 伊東 達矢; 山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)An ultrafine-grained 304 austenitic stainless steel exhibited pronounced serrated Luders deformation at 20 K, with stress and temperature oscillations reaching 200 MPa and 20 K.  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Incorporating solute hydrogen into Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic stainless steels enhances both strength and ductility, providing a promising solution to hydrogen embrittlement by causing solid-solution strengthening and assisting deformation twinning. However, its impacts on the relevant lattice defects evolution ( , dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using
, dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using  neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
伊東 達矢; Xu, S.*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
Shape Memory and Superelasticity, 9 Pages, 2025/00
The microstructure, crystal structures, cold workability, and martensitic transformation temperatures of several Cu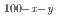 Mn
Mn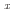 Al
Al (40
(40 
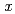
 55; 10
55; 10 
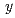
 13; at%) alloys were analyzed. For the first time, martensitic transformation was revealed Mn-rich Cu-Mn-Al alloys. The surface relief of the martensite phase reversibly appeared and disappeared during cooling and heating, along with small thermal hysteresis, implying a thermoelastic transformation. The crystal structures of the parent and martensite phases are B2 and 2M(BCT), respectively, with c
13; at%) alloys were analyzed. For the first time, martensitic transformation was revealed Mn-rich Cu-Mn-Al alloys. The surface relief of the martensite phase reversibly appeared and disappeared during cooling and heating, along with small thermal hysteresis, implying a thermoelastic transformation. The crystal structures of the parent and martensite phases are B2 and 2M(BCT), respectively, with c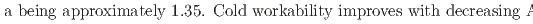 Mn
Mn Al
Al (at%) sample. This alloy demonstrates moderate cold workability and cost-effectiveness, exhibiting potential as an alternative for conventional shape memory alloys in various applications.
(at%) sample. This alloy demonstrates moderate cold workability and cost-effectiveness, exhibiting potential as an alternative for conventional shape memory alloys in various applications.
 neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Hydrogen embrittlement has long been an obstacle to the development of safe infrastructure. However, in contrast to hydrogen's embrittling effect, recent research has revealed that the addition of hydrogen improves both the strength and uniform elongation of AISI Type 310S austenitic stainless steel. A detailed understanding of how hydrogen affects the deformation mechanism of this steel could pave the way for the development of more advanced materials with superior properties. In the present study,  neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:96.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using a hybrid method of in situ neutron diffraction and digital image correlation, we found that ultrafine-grained 304 stainless steel exhibits Luders deformation after yielding, in which the deformation behavior changes from a cooperation mechanism involving dislocation slip and martensitic transformation to one primarily governed by martensitic transformation, as the temperature decreases from 295 K to 77 K. Such martensitic transformation-governed Luders deformation delays the activation of plastic deformation in both the austenite parent and martensite product, resulting in delayed strain hardening. This preserves the strain-hardening capability for the later stage of deformation, thereby maintaining a remarkable elongation of 29% while achieving a high tensile strength of 1.87 GPa at 77 K.
今富 大介*; 石川 遼典*; 仲田 玲*; 伊東 達矢; Han, K.*; 長迫 実*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
Journal of Phase Equilibria and Diffusion, 45(1), p.3 - 17, 2024/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:11.66(Chemistry, Physical)Mn-Zn二元系における相平衡を、組成分析、結晶構造解析、熱分析により実験的に決定した。これまでの報告と比較し、 相、
相、 相、
相、 相の存在領域に違いが見られた。
相の存在領域に違いが見られた。 相の領域から急冷した試料で
相の領域から急冷した試料で Mn相と同じ不規則な体心立方構造が確認されたため、
Mn相と同じ不規則な体心立方構造が確認されたため、 -B2の単相域は確認できなかった。先行研究において、
-B2の単相域は確認できなかった。先行研究において、 相が
相が ,
,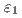 ,
,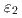 相に分離しているかどうかが論争になっていきたが、拡散対といくつかの合金組成の調査により、
相に分離しているかどうかが論争になっていきたが、拡散対といくつかの合金組成の調査により、 相、
相、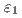 相、
相、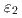 相は分離しておらず、単一の
相は分離しておらず、単一の 相となっていることが示された。さらに、熱分析によって対応する不変系反応が検出されなかったことから、
相となっていることが示された。さらに、熱分析によって対応する不変系反応が検出されなかったことから、 相はZn過剰領域には存在しない。
相はZn過剰領域には存在しない。
 MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発
MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発伊東 達矢; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
物性研だより, 63(3), p.8 - 10, 2023/10
メタ磁性形状記憶合金は磁場により駆動することが出来る形状記憶合金であり、センサーやアクチュエーター等での応用が期待されている。しかし、これまでに開発されてきた合金系ではマルテンサイト変態に伴うエネルギーロスが大きいという問題点があった。近年、我々の研究グループではPd MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Mao, W.; 伊東 達矢; 相澤 一也; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Mechanical properties, as the principal properties of structural metallic materials, are governed by the microstructures. To track the structure-property relationship associated with various solid-solid reactions such as phase transformation and plastic deformation, is crucial for the development of structural metallic materials. TAKUMI, an engineering materials neutron diffractometer at MLF, J-PARC, covering a large d-range with a good balance between high neutron flux and high resolution is reliable to investigate various dynamic phenomena associated with microstructure evolution and deformation behavior. In addition, a variety of specifical sample environments at TAKUMI allow the in-situ studies under extreme environments such as cryogenic deformation (10K~), thermomechanical controlled process (~1473K), fatigue, etc. Crystallographic information including phase fraction, lattice strain (stress), texture, dislocation density, etc. as obtained by neutron diffraction can uniquely provide insights into microstructure evolution and deformation mechanisms in bulky materials. In the presentation, several recent studies on microstructure evolution and deformation mechanisms in metallic materials including steels, high-entropy alloys, magnesium alloys using in-situ neutron diffraction via TAKUMI will be introduced.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
近年、高圧ガス環境中で均一に水素を固溶させたオーステナイト系ステンレス鋼SUS310Sにおいて、強度・延性が共に向上することが報告された。これは水素による固溶強化と双晶変形の促進によると説明されているが、転位密度や積層欠陥など、個々の因子に対する水素の影響の詳細は明らかとなっていない。本研究では、J-PARCの工学材料回折装置「匠」での引張試験中その場中性子回折により、変形メカニズムを明らかにすることを試みた。得られた中性子回折パターンから、水素による体積変化や固溶強化の存在を確認した。更に、転位密度、積層欠陥密度、双晶変形開始ひずみ・応力を評価した。これらの解析により、水素が変形メカニズムに与える影響を明らかにした。
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Hydrogen is being considered as an alternative energy carrier to fossil fuels to achieve the goal of Carbon Neutrality. While hydrogen has historically been associated with causing steel embrittlement, Ogawa et al. reported that the introduction of hydrogen to a Fe-24Cr-19Ni-based (mass%) austenitic stainless steel (AISI Type 310S) enhances both strength and ductility, thus counteracts the embrittlement effect. Although this phenomenon was qualitatively explained by the hydrogen-induced solid-solution strengthening and the promotion of deformation twinning, the influence of hydrogen on the development of dislocations and stacking faults ( , twin nuclei) during deformation remains less understood. The aim of this work is to investigate the effects of hydrogen on the evolution of these crystal defects and overall deformation mechanisms by using
, twin nuclei) during deformation remains less understood. The aim of this work is to investigate the effects of hydrogen on the evolution of these crystal defects and overall deformation mechanisms by using  neutron diffraction measurements.
neutron diffraction measurements.
川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Neutrons offer a unique capability to probe stresses and crystallographic microstructures within engineering materials, thanks to their significant penetrating power and the ability to discern atomic arrangements through diffraction techniques. Pulsed neutron diffraction, employing the time-of-flight method, stands out for its capacity to provide microscopic structural insights, capturing bulk average behaviors via simultaneous measurement of multiple Bragg peaks. Detailed analysis of these peaks within a neutron diffraction pattern unveils crucial structural aspects of sample materials, including internal stresses, phase conditions, dislocations, and texture. The substantial penetrating power of neutrons facilitates in-situ investigations of crystallographic information within engineering materials across diverse environments. This presentation will provide an overview of a diffractometer at J-PARC dedicated for the above purposes, along with highlighting some notable achievements.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
オーステナイト系ステンレス鋼の変形メカニズムに対する固溶水素の影響は、長年研究がなされてきた。先行研究において、水素は積層欠陥エネルギーを低下させ、積層欠陥密度を増加させると考えられてきた。しかし近年、著者らによるその場中性子回折実験の結果から、オーステナイト系ステンレス鋼の一つであるSUS310Sの積層欠陥密度には水素の影響が見られないことが明らかとなった。水素と積層欠陥密度の関係を理解するためには、更なる実験が必要であると考えられる。本講演では、SUS310Sに対して種々の温度で引張変形その場中性子回折実験を行い、積層欠陥密度に対する変形温度と水素の影響を調査した結果を報告する。
Gong, W.; 伊東 達矢; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
優れた特性を有する材料開発のためには変形中に生じる組織変化と力学特性の関係を理解することが重要であるが、従来の技術では極限環境下でのその場観察手法は限られていた。J-PARC MLFに設置された飛行時間型工学材料回折装置「匠」では、工学材料研究に適した波長レンジ、高中性子束と高分解能をバランスよく備えている。さらに、多様な試料環境下に対応した設備を備えており、極低温(15K )から高温(
)から高温( 1473K)までの変形中その場中性子回折実験が可能である。当日は、試料環境装置の整備状況に加え、極限環境下における鉄鋼、マグネシウム合金、ハイエントロピー合金の力学特性と組織変化(マルテンサイト相変態、双晶、積層欠陥、転位など)の関係に関する最新の研究成果を紹介する。
1473K)までの変形中その場中性子回折実験が可能である。当日は、試料環境装置の整備状況に加え、極限環境下における鉄鋼、マグネシウム合金、ハイエントロピー合金の力学特性と組織変化(マルテンサイト相変態、双晶、積層欠陥、転位など)の関係に関する最新の研究成果を紹介する。
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Hydrogen is attracting attention as an alternative energy carrier to fossil fuels to establish a sustainable society. However, hydrogen is considered to cause embrittlement in steel, which has been a longstanding issue known as hydrogen embrittlement. In contrast to the embrittlement, recently, Ogawa 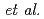 , reported that the addition of hydrogen improved both strength and ductility in SUS310S (Fe-24Cr-19Ni mass%) steel. This phenomenon is attributed to hydrogen-induced solid solution strengthening and the promotion of twinning deformation. These approaches are gaining attention as effective ways to utilize hydrogen, which has long been considered harmful. However, the impact of hydrogen on crystal defects (dislocations, stacking faults) and the mechanisms behind enhanced twinning in SUS310S steel remain unclear. In this work, we investigated the deformation mechanisms of hydrogen-charged SUS310S steel by
, reported that the addition of hydrogen improved both strength and ductility in SUS310S (Fe-24Cr-19Ni mass%) steel. This phenomenon is attributed to hydrogen-induced solid solution strengthening and the promotion of twinning deformation. These approaches are gaining attention as effective ways to utilize hydrogen, which has long been considered harmful. However, the impact of hydrogen on crystal defects (dislocations, stacking faults) and the mechanisms behind enhanced twinning in SUS310S steel remain unclear. In this work, we investigated the deformation mechanisms of hydrogen-charged SUS310S steel by  neutron diffraction measurement conducted by TAKUMI (MLF-BL19) of J-PARC.
neutron diffraction measurement conducted by TAKUMI (MLF-BL19) of J-PARC.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
持続可能な社会の構築に向け、国を挙げて水素社会の実現に向けた研究が行われている。水素インフラを構築するために、水素環境で強度・延性に優れる鉄鋼材料が求められているが、一般的に水素は脆化を引き起こすと考えられてきた。しかし近年、SUS310S (Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%))において、水素により強度・延性が共に向上することが報告され、注目を集めている。これには水素由来の固溶強化と双晶変形の促進が寄与していると考えられているが、転位密度や積層欠陥など、個々の因子に対する水素の影響の詳細は明らかとなっていない。そこで本研究では、MLFの工学材料回折装置 「匠」を利用した引張変形中その場中性子回折実験を行い、変形メカニズムに及ぼす水素の影響を定量的に評価した。
川崎 卓郎; 伊東 達矢; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
J-PARC物質・生命科学実験施設のBL19に設置された「匠」は、材料工学や機械工学に関する研究を目的とした飛行時間型中性子回折装置である。匠は工学研究に適した波長レンジ、高中性子束と高分解能をバランスよく備えている。加えて、測定部位を絞るスリットやラジアルコリメータ等の光学機器、変形試験機、高温・低温機器などの多様な試料環境が利用可能であり、構造物の残留応力マッピングや様々な工学プロセス中での材料挙動の時分割観察を行うことができる。主として格子ひずみ(応力)、相分率、転位組織、集合組織などの材料の力学特性に影響する結晶学的情報の定量評価が行われており、鉄鋼・軽金属・形状記憶合金・ハイエントロピー合金などの金属構造材料を中心に多くの成果を挙げている。本発表では、最近の利用状況や試料環境装置の整備状況を報告するとともに、匠を活用して行われた最新の研究成果を紹介する。
Mao, W.*; 伊東 達矢; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
大量に発生する変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(相転移)は、一般的に準安定オーステナイト鋼の伸びを大幅に低下させ、特に低温ではその影響が顕著である。しかし、超微細粒304ステンレス鋼では例外であることを明らかにした。その場中性子回折とデジタル画像相関を組み合わせたハイブリッド手法を用いて、この材料が降伏後にリューダス変形を示すことを確認した。さらに、温度が295Kから77Kに低下するにつれ、変形挙動が転位すべりとマルテンサイト変態の協調的メカニズムから、主にマルテンサイト変態に支配されるメカニズムへと変化することを明らかにした。このマルテンサイト変態支配のリューダス変形は、オーステナイト母相及びマルテンサイト生成相の塑性変形の発現を遅らせ、加工硬化の遅延を引き起こす。その結果、変形の後半段階においても加工硬化能力が維持され、77Kで29%の顕著な伸びと1.9GPaという高い引張強度を実現した。本研究の成果は、超微細粒材料の変形モードを再編成することで、高強度と高延性を同時に達成するための有望なアプローチを示唆している。
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
持続可能な社会の構築に向け、国を挙げて水素社会の実現を目指した研究が行われている。水素社会を実現するためには、安全性と信頼性を両立した水素インフラの構築が必要不可欠であり、そこで用いられる鉄鋼材料の変形メカニズムに対する水素の影響を明らかにすることは極めて重要である。多くの場合、水素は鉄鋼材料を脆化させ、機械特性を低下させると考えられてきた。しかし近年、小川らにより、SUS310S(Fe-24Cr-19Ni, mass%)に水素を均一に添加することで強度・延性が共に向上することが報告された)。これは、これまで材料特性を悪化させると考えられてきた水素を有効利用することが出来る手法として、注目を集めている。これには、水素由来の固溶強化と双晶変形の促進が寄与していると考えられている。しかし、転位密度や積層欠陥密度など、材料特性を司る個々の因子に対する水素の影響の詳細は明らかになっていない。そこで本研究では水素チャージを施したSUS310Sに対して「匠」を用いた引張試験中その場中性子回折実験を行い、変形メカニズムに及ぼす固溶水素の影響を調査した。
 neutron diffraction study of stacking fault energy in hydrogen-charged Type 310S austenitic steel at low temperatures
neutron diffraction study of stacking fault energy in hydrogen-charged Type 310S austenitic steel at low temperatures伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Stacking fault energy ( ) plays a crucial role in various deformation processes of austenitic steel, such as dislocation motion, deformation twinning, and martensitic transformation. Several previous studies have reported that hydrogen reduces
) plays a crucial role in various deformation processes of austenitic steel, such as dislocation motion, deformation twinning, and martensitic transformation. Several previous studies have reported that hydrogen reduces  . However, our recent in situ neutron diffraction experiment has shown that hydrogen has minimal effect on the
. However, our recent in situ neutron diffraction experiment has shown that hydrogen has minimal effect on the  of Fe-24Cr-19Ni (AISI Type 310S) steel during tensile deformation at room temperature, despite significant reductions in
of Fe-24Cr-19Ni (AISI Type 310S) steel during tensile deformation at room temperature, despite significant reductions in  due to hydrogen reported for a similar composition steel. Moreover, a recent study analyzing the work-hardening behavior of several hydrogen-charged austenitic stainless steels has suggested that hydrogen may have only a limited impact on
due to hydrogen reported for a similar composition steel. Moreover, a recent study analyzing the work-hardening behavior of several hydrogen-charged austenitic stainless steels has suggested that hydrogen may have only a limited impact on  . These findings indicate the need for further research to clarify the influence of hydrogen on
. These findings indicate the need for further research to clarify the influence of hydrogen on  . In this study, we investigated the effect of hydrogen on the
. In this study, we investigated the effect of hydrogen on the  of Type 310S austenitic steel at low temperatures using in situ neutron diffraction.
of Type 310S austenitic steel at low temperatures using in situ neutron diffraction.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
近年、水素添加によりSUS310Sの強度と延性が共に向上することが報告された。本研究では、「匠」を利用した引張試験中その場中性子回折実験を行い、転位密度や積層欠陥密度など、個々の因子に対する水素の影響を定量的に解明することを試みた。