Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Lee, J.; Rossi, F.; 児玉 有; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 佐野 忠史*; 松尾 泰典*; 堀 順一*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.111017_1 - 111017_7, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Silica glass has been used as a base and host material in vitrified radioactive waste and lithium glass scintillator for neutron detection because of its superb transparency, high heat resistance, and excellent chemical inertness. Therefore, an accurate total cross section of the silica glass is important to evaluate the criticality safety for the vitrified wastes and to understand the neutron response for lithium glass scintillators accurately. In the present study, to provide the accurate total cross section in the thermal and epithermal energy range, the neutron transmission measurements were carried out by a pulsed neutron beam with the time-of-flight method at the Kyoto University Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science - Linear Accelerator. We obtained the neutron total cross section of the silica glass in the energy region from 0.002 eV to 25 eV. The obtained results were compared and discussed with the previous results and the evaluated data.
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Wei, T.*; 余語 覚文*; et al.
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2024/11
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a non-destructive method applicable for measuring nuclear material using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. To realize a high resolution compact NRTA system, use of a short-pulsed neutron source is essential. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) are well-suit for generating such neutron beams due to their short pulse width. The advances in laser technology will further reduce the system's size and improve practicality. In this study, we demonstrate the measurement of a neutron transmission TOF spectrum of a sample containing indium and silver using the LDNS of the Osaka University. The obtained spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, showcasing for the first time the potential of an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Lan, Z.*; Wei, T.*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.21916_1 - 21916_9, 2024/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) can generate strong short-pulse neutron beams, which are valuable for scientific studies and engineering applications. Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a nondestructive technique used for determining the areal density of each nuclide in a material sample using pulsed thermal and epithermal neutrons. Herein, we report the first successful NRTA performed using an LDNS driven by the Laser for Fast Ignition Experiment at the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. The key challenge was achieving a well-resolved resonance transmission spectrum for material analysis using an LDNS with a limited number of laser shots in the presence of strong background noise. We addressed this by employing a time-gated  Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to
Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to  In and
In and  Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Morace, A.*; 早川 岳人*; 佐藤 博隆*; 加美山 隆*; Wei, T.*; 巽 湧太*; 小泉 光生; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5365_1 - 5365_7, 2024/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:79.20(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The temperature measurement of material inside of an object is one of the key technologies for control of dynamical processes. For this purpose, various techniques such as laser-based thermography and phase-contrast imaging thermography have been studied. However, it is, in principle, impossible to measure the temperature of an element inside of an object using these techniques. One of the possible solutions is measurements of Doppler brooding effect in neutron resonance absorption (NRA). Here we present a method to measure the temperature of an element or an isotope inside of an object using NRA with a single neutron pulse of approximately 100 ns width provided from a high-power laser. We demonstrate temperature measurements of a tantalum (Ta) metallic foil heated from the room temperature up to 617 K. Although the neutron energy resolution is fluctuated from shot to shot, we obtain the temperature dependence of resonance Doppler broadening using a reference of a silver (Ag) foil kept to the room temperature. A free gas model well reproduces the results. This method enables element(isotope)-sensitive thermometry to detect the instantaneous temperature rise in dynamical processes.
 Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence method
Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence method伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 持丸 貴則*; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*; 小泉 光生
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1064, p.169465_1 - 169465_9, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The response of a gamma-ray spectrometer is generally determined by analyzing full-energy peaks. However, full-energy peaks cannot be measured easily in the case of scintillation detectors that consist of light elements, such as glass scintillators. Only a strong Compton plateau appears in the spectrum of such detectors. Therefore, Compton edgers were used to evaluate the response of these detectors. The response of a low-resolution  Li-glass detector to gamma rays was measured for the first time by a coincidence method with a high-resolution LaBr
Li-glass detector to gamma rays was measured for the first time by a coincidence method with a high-resolution LaBr :Ce detector using cascade gamma rays (2.75 and 1.37 MeV) from a
:Ce detector using cascade gamma rays (2.75 and 1.37 MeV) from a  Na source. Coincidence gates were applied at the peaks of the spectrum of the LaBr
Na source. Coincidence gates were applied at the peaks of the spectrum of the LaBr :Ce detector at the 0.51 MeV annihilation peak, and the sum peaks of a gamma ray and a backscattered gamma ray. By analyzing the gated spectra of the
:Ce detector at the 0.51 MeV annihilation peak, and the sum peaks of a gamma ray and a backscattered gamma ray. By analyzing the gated spectra of the  Li-glass detector, the energy-dependent detector response (i.e., the output strength and its dispersion) was determined.
Li-glass detector, the energy-dependent detector response (i.e., the output strength and its dispersion) was determined.
Rossi, F.; Lee, J.; 児玉 有; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*; 佐野 忠史*
Proceedings of 65th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07
Various non-destructive assay techniques are being used to verify different nuclear material. However, one of the difficulties of current NDA is the measurement of highly radioactive materials. Since 2015, the JAEA has been working on the development of various active non-destructive assay techniques to address some of the current challenges in nuclear safeguards. Among the various technologies proposed, the Neutron Resonance Analysis system combines signatures from NRTA, NRCA and the newly proposed NRFNA. The combination of those techniques can provide accurate information on the small fissile content in a sample. Neutrons are generated by a pulsed neutron source and slowed down into the moderator. Neutrons are collimated using lead and borated polyethylene to reach the sample, where various neutron-induced reactions occur. n/g PSD plastic scintillators are used to measure the captured gamma rays and fission neutrons at sample location. GS20 is used to collect the transmitted neutrons downstream of the source-sample beamline. A first measurement campaign was performed using natural uranium sample. The possibility of using NRFNA to identify fissile materials within a sample was clearly demonstrated, but the detectors used were not sufficient to achieve a good n/g PSD. New PSD scintillators were introduced. A first measurement campaign was performed in 2023. The acquired data are currently being analyzed, but preliminary results show distinct fission resonance peaks of increasing intensity with varying thicknesses of the same natural uranium samples. Currently, an assembly of multiple scintillators is being investigated to provide a better signal. The new setup will be tested starting in early 2024. In this paper, we will describe in detail the NRA project development and the latest results from experimental campaign. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like"
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(18), p.184903_1 - 184903_10, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)We report on the findings of a quantitative nondestructive analysis of the natural isotopic abundances of hafnium and tungsten elements using nuclear resonance fluorescence. Commercial samples of hafnium and tungsten were irradiated to six quasi-monochromatic  -ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering in the energy range of 2.4-3.2 MeV. Multiple nuclei were simultaneously excited at each of the six
-ray beams generated by laser Compton scattering in the energy range of 2.4-3.2 MeV. Multiple nuclei were simultaneously excited at each of the six  -ray beam energies. A high-purity germanium detector array detected deexcitations of the nuclei. In total,
-ray beam energies. A high-purity germanium detector array detected deexcitations of the nuclei. In total, 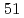 transitions were unprecedentedly employed to estimate the isotopic abundances of heavy elements nondestructively. The estimated abundances of three hafnium isotopes and three tungsten isotopes are consistent with standard known natural abundances within the experimental uncertainties. The deviation from the standard values ranges from 0.18% to 1.36%. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
transitions were unprecedentedly employed to estimate the isotopic abundances of heavy elements nondestructively. The estimated abundances of three hafnium isotopes and three tungsten isotopes are consistent with standard known natural abundances within the experimental uncertainties. The deviation from the standard values ranges from 0.18% to 1.36%. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
 Ta
Ta静間 俊行*; Omer, M.; 羽島 良一*; 小泉 光生
Physical Review C, 109(5), p.054320_1 - 054320_8, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying levels in the odd-mass nucleus  Ta have been populated via nuclear resonance fluorescence using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam at the High Intensity
Ta have been populated via nuclear resonance fluorescence using a quasi-monoenergetic, linearly polarized photon beam at the High Intensity  -ray Source (HI
-ray Source (HI S) facility at Duke University. The spin and parity of the levels were determined from the azimuthal intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
S) facility at Duke University. The spin and parity of the levels were determined from the azimuthal intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole strengths were obtained for excitation energies from 2.2 to 3.2 MeV. The results are discussed in terms of the nuclear scissors mode. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The electric and magnetic dipole strengths were obtained for excitation energies from 2.2 to 3.2 MeV. The results are discussed in terms of the nuclear scissors mode. This work is a contribution of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband). This work was a part of a study of the nuclear resonance fluorescence aiming at nuclear security and safeguards applications, being supported by the subsidiary for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security or the like" of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 伊藤 史哲*; 小泉 光生; 堀 順一*; 佐野 忠史*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.23 - 30, 2024/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:73.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the short-distance time-of-flight (TOF) measurements, the background events increase exponentially with decreasing the distance, and the high background increases the uncertainty of the measurement data. The moderated neutron beam includes the time-dependent background originating from the neutron moderator, such as 2.2 MeV gamma rays emitted by  H(n,
H(n, ) reaction in the moderator. In this paper, to achieve a compact neutron resonance transmission analysis system with high accuracy, we studied the relationship between the moderator and time-dependent background due to gamma rays. Monte Carlo simulations were carried out with the PHITS and the JENDL-4.0 to investigate the time distributions of neutrons and gamma rays emitted from the moderator. Ratios of the gamma-ray intensity to neutron intensity (S
) reaction in the moderator. In this paper, to achieve a compact neutron resonance transmission analysis system with high accuracy, we studied the relationship between the moderator and time-dependent background due to gamma rays. Monte Carlo simulations were carried out with the PHITS and the JENDL-4.0 to investigate the time distributions of neutrons and gamma rays emitted from the moderator. Ratios of the gamma-ray intensity to neutron intensity (S /S
/S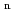 ratio) were calculated for various moderators and flight distances. From the obtained results, moderator designs for maintaining low S
ratio) were calculated for various moderators and flight distances. From the obtained results, moderator designs for maintaining low S /S
/S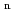 ratio were discussed.
ratio were discussed.
 -ray elastic scattering
-ray elastic scatteringOmer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 小泉 光生; 羽島 良一*; 橋本 智*; 宮本 修治*
LASTI Annual Report, 24, p.20 - 22, 2023/12
Nondestructive elemental analysis is highly valued in many fields such as archeology, paleontology, space sciences, nuclear security, and nuclear nonproliferation. These fields usually impose estimating the elemental composition of bulk, large, and inhomogeneous samples nondestructively. Common elemental analysis techniques such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) may fail in such situations due to self-absorption of low energy X-rays within thin layers of the sample. In the present study, we propose a novel nondestructive method that may be useful in distinguishing the elemental composition of a given sample based on the elastic scattering of linearly polarized and high-energy  -rays. Linear polarization of
-rays. Linear polarization of  -rays causes asymmetry of the elastic scattering cross sections with respect to the polarization plane of the incident
-rays causes asymmetry of the elastic scattering cross sections with respect to the polarization plane of the incident  -rays. At specific
-rays. At specific  -ray energies and scattering angles, the asymmetry ratio, R, of the cross sections in two orthogonal planes is characteristic of each element. The measurement of asymmetry ratio of 1.62 MeV linearly polarized
-ray energies and scattering angles, the asymmetry ratio, R, of the cross sections in two orthogonal planes is characteristic of each element. The measurement of asymmetry ratio of 1.62 MeV linearly polarized  -rays at NewSUBARU facility is presented. This work is a contribution of the JAEA to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband).
-rays at NewSUBARU facility is presented. This work is a contribution of the JAEA to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) under the agreement of the coordinated research program (CRP), J02015 (Facilitation of Safe and Secure Trade Using Nuclear Detection Technology - Detection of RN and Other Contraband).
高橋 時音; 山口 郁斗*; 弘中 浩太*; 持丸 貴則*; 小泉 光生; 山西 弘城*; 若林 源一郎*
第44回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2023/11
原子力機構では、大規模公共イベント等におけるテロ対策強化のため、会場周辺の広い範囲で核・放射性物質を迅速に検知するためのモニタリング技術開発を行っている。本プロジェクトでは、放射線検出器を測位センサや通信機器と組み合わせ、様々な場面で使用可能なマッピング装置を開発を進めている。屋内外でマッピング試験を実施し、放射線量の高い場所を特定できることを確認した。あわせて、核物質を含む中性子線源を探索するための高速中性子検出技術開発を行っている。2本のロッド型検出器を十字に組み合わせた装置を用いて測定を行い、1本の時に比べて線源方向をより精度よく特定することができることを確認した。本稿では、プロジェクトの近況について報告する。
Lee, J.; 児玉 有; Rossi, F.; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 堀 順一*; 佐野 忠史*
第44回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2023/11
核不拡散・核セキュリティ総合支援センターでは、試料中に含まれる少量の核分裂性物質を特定し定量する能力を向上させるための技術として、中性子飛行時間法を用いた中性子共鳴核分裂中性子分析(Neutron Resonance Fission Neutron Analysis: NRFNA)の技術開発を進めている。本発表会では、核分裂性物質の非破壊分析のために進めているNRFNA技術の紹介及びその基礎実験の結果について報告する。
弘中 浩太; Lee, J.; 小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*; 佐野 忠史*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1054, p.168467_1 - 168467_5, 2023/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:62.75(Instruments & Instrumentation)We propose neutron resonance fission neutron analysis (NRFNA), an active nondestructive assay (NDA) technique, to improve the capability to identify and quantify a small amount of fissile material in a sample. NRFNA uses pulsed neutrons to induce fission reactions in the sample. Fission neutrons are detected by a neutron-gamma pulse shape discrimination (PSD) scintillation detector with time-of-flight (TOF) technique. The obtained nuclide-specific resonance peaks in the neutron energy spectrum provide information to identify and quantify a fissile material in the sample. The possibility of using PSD for NRFNA was confirmed through a test experiment using a natural uranium sample. We successfully observed the resonance peaks from  U(n,f) reaction and showed that NRFNA would be useful for measuring a small amount of fissile material in a sample.
U(n,f) reaction and showed that NRFNA would be useful for measuring a small amount of fissile material in a sample.
Omer, M.; 静間 俊行*; 小泉 光生; 平 義隆*; Zen, H.*; 大垣 英明*; 羽島 良一
UVSOR-50, P. 37, 2023/08
核共鳴蛍光(NRF)を用いた非破壊分析において、試料温度によるドップラー効果による影響を調べることを目的とした研究を開始した。今回は、波長1980nmのファイバーレーザーを加速エネルギー746MeVの電子ビームと衝突させて生成した最大エネルギー5.54MeVのレーザーコンプトンガンマ線を Pb標的に照射し、共鳴散乱ガンマ線を3台の高純度ゲルマニウム検出器を用いて測定した。その結果、レーザーコンプトンガンマ線最大エネルギーよりも高いエネルギーで、複数のガンマ線ピークが観測された。これらのガンマ線は、実験室内の制動放射線によって発生した中性子が測定装置の周囲の物質と反応した後に放出された中性子捕獲即発ガンマ線であると考えられる。そのため、バックグラウンドガンマ線の低減のため、ゲルマニウム検出器の周囲を厚さ10cmの鉛を用いて遮蔽した。その結果、即発ガンマ線のバックグラウンドは抑制され、
Pb標的に照射し、共鳴散乱ガンマ線を3台の高純度ゲルマニウム検出器を用いて測定した。その結果、レーザーコンプトンガンマ線最大エネルギーよりも高いエネルギーで、複数のガンマ線ピークが観測された。これらのガンマ線は、実験室内の制動放射線によって発生した中性子が測定装置の周囲の物質と反応した後に放出された中性子捕獲即発ガンマ線であると考えられる。そのため、バックグラウンドガンマ線の低減のため、ゲルマニウム検出器の周囲を厚さ10cmの鉛を用いて遮蔽した。その結果、即発ガンマ線のバックグラウンドは抑制され、 Pbの共鳴散乱ガンマ線を観測することができた。
Pbの共鳴散乱ガンマ線を観測することができた。
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; Bertolotti, D.*; Bonaldi, C.*; Fontana, C.*; 藤本 正己*; Geerts, W.*; 小泉 光生; Macias, M.*; Nonneman, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/05
Under the MEXT subsidy to improve nuclear security related activities, we present the overview of the JAEA-JRC delayed gamma-ray spectroscopic analysis project. We describe past results, recent joint experiments, and the final goals for this project.
小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 弘中 浩太; 持丸 貴則*; 山口 郁斗*; 木村 祥紀; 谷垣 実*; 正木 弘子*; 原田 博司*; 後藤 淳*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
Development of radiation detector systems are essential to prevent nuclear terrorism in major public events. They are required to find nuclear and radioactive materials effectively at gates and in event sites. Overview of such detector system development program is given. (1) Broad area survey system: Broad area survey measurements are usually implemented to ensure radioactive materials, such as dirty bomb, are not placed in a site. To carry out the surveillance efficiently, combination of radioactive detector and mapping system is required. We are, therefore, developing a gamma-ray detector with a GPS system and a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) system to cover outdoor and indoor surveillance. A secure low-power and long-range network system using Wi-SUN FAN is being tested. It would be beneficial to coordinate detector systems, to correct information. They are monitored in an operation center. An artificial intelligent (AI) program is also under development to eliminate false alert from an obtained gamma-ray spectrum. A compact Compton camera would be applicable to figure out the location of hidden radioactive materials. A system with GAGG crystals is being tested. (2) Neutron detector system using plastic scintillation detectors: Neutron detection would be useful to find out nuclear materials and neutron sources shielded in heavy-element materials. A plastic scintillation detector is chosen as a detector material, because that is low-cost, sensitive to fast neutrons, easy to handle, and thus easy to be deployed. Gamma-ray background can be reduced by employing a Pulse Shape Discrimination (PSD) technique to enhance the sensitivity to fast neutrons. Developments of systems using PSD plastic scintillation detectors are in progress.
Rossi, F.; 小泉 光生; Rodriguez, D.; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/05
Since 2015, the Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Nonproliferation and Nuclear Security (ISCN) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been working on the development of the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopy non-destructive assay technique for the quantification of fissile-nuclide content in mixed nuclear materials. Thanks to the efforts and lessons learned from past experiments, the ISCN has successfully designed and fabricated a final integrated instrument. The instrument is composed of a moderator and dose shield where different neutron sources, like Cf-252 and neutron generators, can be inserted to irradiate the sample. Within the moderator, a series of neutron detectors are installed for perform prompt neutron analysis and continuous monitoring of the neutron source emission. Thanks to an innovative transfer system, the sample is then moved to the gamma-ray detector in less than 1.5s providing a fast and reliable movement while being safe from possible contamination. In this work, we will describe the design details of this new instrument. This work is supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like".
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; 森 隆人*; Golovin, D.*; 早川 岳人*; 岩田 夏弥*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:96.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutrons are powerful tools for investigating the structure and properties of materials used in science and technology. Recently, laser-driven neutron sources (LDNS) have attracted the attention of different communities, from science to industry, in a variety of applications, including radiography, spectroscopy, security, and medicine. However, the laser-driven ion acceleration mechanism for neutron generation and for establishing the scaling law on the neutron yield is essential to improve the feasibility of LDNS. In this paper, we report the mechanism that accelerates ions with spectra suitable for neutron generation. We show that the neutron yield increases with the fourth power of the laser intensity, resulting in the neutron generation of 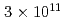 in
in 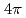 at a maximum, with
at a maximum, with 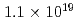 Wcm
Wcm , 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub-
, 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub- s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 余語 覚文*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.137 - 140, 2023/01
中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)は、パルス中性子を計量したい核物質に照射し、飛行時間(TOF)法を用いて測定核物質を非破壊測定する手法であるが、小型・高精度化には短パルスな小型中性子源が必要となる。近年発展著しいレーザー技術を用いたレー ザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)は、そのような中性子源として将来を期待されている。そこで我々はLDNSを用いたNRTAの技術開発を行い、実証実験を行った。その結果について報告する。
Lee, J.; 伊藤 史哲*; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 小泉 光生
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(12), p.1546 - 1557, 2022/12
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:79.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Compact time-of-flight (TOF) measurement systems are desirable for easy installation in various facilities. To achieve such compact systems, one of the key considerations is the design of the neutron moderator. However, there are only a few reports on systematic studies on moderators considering both neutron energy resolution as well as a neutron intensity. In this paper, to design an epithermal neutron moderator for short-distance TOF measurements, the neutron intensity and energy resolution of epithermal neutrons have been studied using the Monte Carlo simulation code PHITS with JENDL-4.0 for various types of moderators. The neutronic characteristics of a moderator comprising several components were evaluated. The relationships between the moderator dimensions and both the energy resolution and intensity of the epithermal neutrons were determined. From the obtained results, the appropriate high resolution moderator designs for the short-distance TOF measurements were proposed.