Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
長谷 竹晃; 小菅 義広*; 相楽 洋*; 中岫 翔; 能見 貴佳; 奥村 啓介
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.41 - 46, 2025/05
This paper provides an overview of plutonium quantification in irradiated fuel including fuel debris at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, named Dual Time Measurement (DTM) method. Spontaneous fission nuclides in irradiated fuel decrease exponentially with the passage of time according to the mainly half-life of Cm-244 (half-life of about 18.11 years). By measuring neutrons two times with long time intervals, Pu-240 effective mass (half-life of about 6,500 years) and Cm-244 mass can be quantified. Pu mass can be quantified by utilizing the correlation between ratio of Cm-244/ Pu-240 effective mass and Pu/ Pu-240 effective mass. The applicability of DTM method was evaluated numerically. The results show that long time interval was required to reduce the random errors. In the case that the interval between the first and second measurements is 32 years, Pu-240 effective mass and Pu can be quantified with uncertainties of 10-50% depending on the presence of water in storage canister and the burnup condition of irradiated fuel including the mixture of several burnup compositions in fuel debris.
三星 夏海; 長谷 竹晃; 小菅 義広*; 鈴木 梨沙; 岡田 豊史
第44回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2023/11
中性子計測による燃料デブリ中の核燃料物質定量において、性状によって変化する中性子漏れ増倍率の評価が課題の一つである。本試験では、中性子吸収材等をMOX試料の周囲に配置し、燃料デブリを模擬した試料を中性子測定装置にて測定した結果、DDSI(Differential Die-away Self-Interrogation)法は、中性子漏れ増倍率の評価に有効であることを明らかにした。
長谷 竹晃; 相樂 洋*; 小菅 義広*; 能見 貴佳; 奥村 啓介
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.460 - 472, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:14.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper provides an overview of the applicability of the Differential Die-Away Self-Interrogation (DDSI) technique for quantification of spontaneous fissile nuclides in fuel debris at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants. In this research, massive fuel debris stored in a canister was evaluated, and the void space of the canister was assumed to be filled with water for wet storage and air for dry storage. The composition of fuel debris was estimated based on elements such as the inventory in the reactor core and operation history. The simulation results show that for wet storage, the DDSI technique can properly evaluate the neutron leakage multiplication and quantify spontaneous fissile nuclides with a total measurement uncertainty (TMU) of approximately 8%. For dry storage, the known-alpha technique, which was previously established, can be applied to quantify spontaneous fissile nuclides with a TMU of approximately 4%. In both cases, the largest uncertainty factor is the variation in water content in the canister. In the case of wet storage, the uncertainty could be significantly increased in cases where the fuel debris is extremely unevenly distributed in the canister.
長谷 竹晃; 相楽 洋*; 小菅 義広*; 中岫 翔; 能見 貴佳; 奥村 啓介
第43回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 3 Pages, 2022/11
Neutrons emitted from fuel debris are dominated by Cm-244, and plutonium cannot be quantified only by nondestructive measurements based on the neutron measurements. In this paper, focusing on the difference in half-lives of Cm-244 and plutonium, we devised a method to quantify the Pu-240 effective mass in fuel debris by measuring it two times and evaluated numerically its applicability. As the results, it was confirmed that long time interval, more than five years, will be required to evaluate the Pu-240 effective mass accurately. It was also confirmed that for fuel debris with high burnup, the Pu-240 effective mass will be overestimated by Cm-246, and we devised a method to correct for this.
名内 泰志*; 能見 貴佳; 鈴木 梨沙; 小菅 義広*; 芝 知宙; 高田 映*; 冠城 雅晃; 奥村 啓介
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
As one of the identification techniques for materials in fuel debris, the neutron induced gamma ray spectroscopy (NIGS) is focused on since the gamma ray spectrum is intrinsic to isotopes. The energy of the target gamma ray in NIGS is often higher than that of most of fission products. To demonstrate feasibility of NIGS for the identification, we have measured and analyzed the HPGe response of isotopes for Cf-252 neutron irradiation for plutonium samples and several structural materials. As a result, we confirmed the possibility to identify light water, boron, concrete, sea water, structural material, signal lines and coils, fuel cladding, gadolinium, uranium, and plutonium contained in the retrieved materials from Fukushima Daiichi NPPs.
芝 知宙; 冠城 雅晃; 能見 貴佳; 鈴木 梨沙; 小菅 義広*; 名内 泰志*; 高田 映*; 長谷 竹晃; 奥村 啓介
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/10
A technique that can easily determine the presence of nuclear material in removed object from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant site is important from the viewpoint of sorting fuel debris from radioactive waste. In the case of fresh uranium, the amount of nuclear material in the waste generated from nuclear facilities can be determined by measuring 1001 keV gamma-rays emitted by 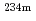 Pa, which is a daughter nuclide of
Pa, which is a daughter nuclide of  U. However, it has been pointed out that such gamma-ray measurement cannot be used for fuel debris that contains a large portion of fission products (FPs) emitting various energies of gamma-rays. In this study, we focus on prompt fission gamma-rays that are directly emitted from nuclear materials and those energy exists in a higher energy region than those of FPs, and aim to measure them in simple manners.
U. However, it has been pointed out that such gamma-ray measurement cannot be used for fuel debris that contains a large portion of fission products (FPs) emitting various energies of gamma-rays. In this study, we focus on prompt fission gamma-rays that are directly emitted from nuclear materials and those energy exists in a higher energy region than those of FPs, and aim to measure them in simple manners.
長谷 竹晃; 米田 政夫; 芝 知宙; 名内 泰志*; 前田 亮; 相楽 洋*; 小菅 義広*; 呉田 昌俊; 富川 裕文; 奥村 啓介; et al.
Energy Procedia, 131, p.258 - 263, 2017/12
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:97.40(Energy & Fuels)This paper provides an interim report for characterization study of four candidate technologies for nuclear material quantification in fuel debris at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F). The severe loss-of-coolant accidents of 1F produced fuel debris in the reactor cores of Units 1-3. Because the fuel debris would contain unknown amounts of minor actinides, fission products and neutron absorbers and the mixing rate of them would vary significantly, accurate quantification of nuclear material in fuel debris would be difficult by applying a single measurement technology. Therefore, we consider that an integrated measurement system that combines several measurement technologies would be required to complement the weakness of each technology. For consideration of an integrated measurement system, we conducted a characterization study for each technology. In order to compare the results of applicability evaluation of each technology, common set of simulation models for fuel debris and canister were developed. These models were used for the applicability evaluation of each technology. Then, the comparative evaluation of the result of applicability evaluation among four technologies was conducted.
長谷 竹晃; 小菅 義広*; 白戸 篤仁*; 佐藤 隆*; 白茂 英雄; 浅野 隆
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Under the collaborative program with United States Department of Energy (DOE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI) have surveyed technologies for nuclear material quantification of fuel debris at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) since 2012. Four research groups in JAEA and CRIEPI have evaluated independently the applicability for four technologies. We, Plutonium Fuel Development Center of JAEA, are in charge of development of the passive neutron technique. All parties recognized the importance of the characterization study on each candidate technology for establishment of the concept of integrated measurement system that combines several measurement technologies for accurate quantification. For the characterization study, standard fuel debris and canister models were developed. In order to perform the characterization study consistent with the other technologies, we evaluated the applicability of the passive neutron technique for nuclear material quantification of fuel debris based on the standard models. In this study, we performed the optimization of detector configuration and measurement parameter for passive neutron detector and then evaluated measurement accuracy. This paper provides the results of applicability evaluation on passive neutron technique for nuclear material quantification in fuel debris at 1F.
長谷 竹晃; 米田 政夫; 芝 知宙; 前田 亮; 名内 泰志*; 相楽 洋*; 小菅 義広*; 呉田 昌俊; 富川 裕文; 奥村 啓介; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
This paper provides an interim report for characterization study of four candidate technologies for nuclear material quantification in fuel debris at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F). The severe loss-of-coolant accidents of 1F produced fuel debris in the reactor cores of Units 1-3. Because the fuel debris would contain unknown amounts of minor actinides, fission products and neutron absorbers and the mixing rate of them would vary significantly, accurate quantification of nuclear material in fuel debris would be difficult by applying a single measurement technology. Therefore, we consider that an integrated measurement system that combines several measurement technologies would be required to complement the weakness of each technology. For consideration of an integrated measurement system, we conducted a characterization study for each technology. In order to compare the results of applicability evaluation of each technology, common set of simulation models for fuel debris and canister were developed. These models were used for the applicability evaluation of each technology. Then, the comparative evaluation of the result of applicability evaluation among four technologies was conducted.
長谷 竹晃; 白戸 篤仁*; 小菅 義広*; 佐藤 隆*; 川久保 陽子; 白茂 英雄; 浅野 隆
Proceedings of INMM 56th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2015/07
福島第一原子力発電所内に発生した燃料デブリの測定技術の候補の一つとして、パッシブ中性子法の適用を提案している。本試験は、前回の米国核物質管理学会にて報告したシミュレーションによるパッシブ中性子法の燃料デブリ測定への適用性を実証するために実施した。本試験では、未照射のMOX試料, 中性子吸収剤, カリフォルニウム線源等を組み合わせた燃料デブリを模擬した試料を既存の中性子測定装置にて測定した。試料中の核分裂性核種の量、試料の周辺に配置する中性子吸収剤の量及びカリフォルニウム線源の強度を変化させ、中性子消滅時間差自己問いかけ法(DDSI法)の計数値と中性子漏れ増倍の相関を確認した。試験結果は、前回報告したシミュレーションによる評価結果の傾向とよく一致した。これは、DDSI法が、燃料デブリのように未知の核分裂性核種及び中性子吸収剤を含む試料に対する中性子漏れ増倍を評価する能力を有することを示唆する。本報は、福島第一原子力発電所の燃料デブリへのパッシブ中性子法を用いた実証研究についてまとめたものである。
長谷 竹晃; 中島 真司; 小菅 義広*; 白茂 英雄; 浅野 隆
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2014/07
福島第一原子力発電所では、2011年3月の炉心溶融事故により、炉内に燃料デブリが発生している。燃料デブリは、マイナーアクチニド、核分裂生成物、中性子吸収剤等を含んでいることから、従来の計量管理・保障措置分野に適用されている自発核分裂性核燃料物質を定量するパッシブ中性子法の適用が困難である。このため、我々は、Differential Die-away Self-Interrogation法やPassive Neutron Albedo Reactivity法のような誘発核分裂性核燃料物質の定量に着目したパッシブ中性子法が燃料デブリへの適用性が高いと考え、その概念をまとめ、前回の米国核物質管理学会にて報告した。我々は、これらの測定技術の燃料デブリへの適用性をより詳細に評価するため、モンテカルロ・シミュレーション・コードを用いた燃料デブリ中の中性子挙動の評価を行った。本評価にあたっては、福島第一原子力発電所で発生した燃料デブリの性状が明らかになっていないため、スリーマイル島原子力発電所事故の燃料デブリや貯蔵容器の情報を基に製作したソースタームを用いた。本稿では、シミュレーションによるパッシブ中性子法の燃料デブリへの適用性評価結果について、報告する。
長谷 竹晃; 米田 政夫; 芝 知宙; 名内 泰志*; 相樂 洋*; 小菅 義広*; 奥村 啓介; 前田 亮; 藤 暢輔; 堀 啓一郎
no journal, ,
福島第一原子力発電所における燃料デブリ中の核燃料物質定量のため、パッシブ中性子法, パッシブ 法, アクティブ中性子法, アクティブ
法, アクティブ中性子法, アクティブ 法の適用を検討している。燃料デブリは、燃焼度の異なる燃料, 構造材, 制御棒, コンクリートなどから構成されており、それらの構成比は収納容器毎に変動し、中性子・
法の適用を検討している。燃料デブリは、燃焼度の異なる燃料, 構造材, 制御棒, コンクリートなどから構成されており、それらの構成比は収納容器毎に変動し、中性子・ 線の計測条件が変動すると想定されるため、1つの技術の適用のみでは、正確性・信頼性の確保は困難である。よって、我々は、いくつかの候補技術を組み合わせた統合型測定システムの開発の検討のため、候補技術の特性研究を開始した。本発表では、本研究の手法と現状を紹介する。
線の計測条件が変動すると想定されるため、1つの技術の適用のみでは、正確性・信頼性の確保は困難である。よって、我々は、いくつかの候補技術を組み合わせた統合型測定システムの開発の検討のため、候補技術の特性研究を開始した。本発表では、本研究の手法と現状を紹介する。
長谷 竹晃; 米田 政夫; 芝 知宙; 名内 泰志*; 相樂 洋*; 小菅 義広*; 奥村 啓介; 前田 亮; 藤 暢輔; 堀 啓一郎
no journal, ,
This paper provides an interim report for characterization study of four candidate technologies for nuclear material quantification in fuel debris at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F). The severe loss-of-coolant accidents of 1F produced fuel debris in the reactor cores of Units 1-3. Because the fuel debris would contain unknown amounts of minor actinides, fission products and neutron absorbers and the mixing rate of them would vary significantly, accurate quantification of nuclear material in fuel debris would be difficult by applying a single measurement technology. Therefore, we consider that an integrated measurement system that combines several measurement technologies would be required to complement the weakness of each technology. For consideration of an integrated measurement system, we conducted a characterization study for each technology. In order to compare the results of applicability evaluation of each technology, common set of simulation models for fuel debris and canister were developed. These models were used for the applicability evaluation of each technology. Then, the comparative evaluation of the result of applicability evaluation among four technologies was conducted.
長谷 竹晃; 米田 政夫; 芝 知宙; 名内 泰志*; 相樂 洋*; 小菅 義広*; 宮地 紀子; 奥村 啓介
no journal, ,
非破壊測定により、燃料デブリ中の核燃料物質を正確に定量することは難しい。これは、マイナーアクチニド及び核分裂生成物を含む使用済み燃料の測定が困難であることに加え、燃料デブリ中には、構造材、制御棒及びコンクリートがなど混入し、これらの構成比が変動するとともに、水分含有率・燃料デブリの配置位置が収納容器毎に変動することにより、収納容器毎に中性子・ 線の計測条件が変化するためである。我々は、パッシブ中性子法, パッシブ
線の計測条件が変化するためである。我々は、パッシブ中性子法, パッシブ 法, アクティブ中性子法, アクティブ
法, アクティブ中性子法, アクティブ 法を候補技術として、不確かさのより小さい測定技術の選定・信頼性確保に向けた複数の技術の組み合わせの検討のため、計算コードにより、候補技術の特性研究を開始した。本報告は、2017年春の年会の報告に続くものである。
法を候補技術として、不確かさのより小さい測定技術の選定・信頼性確保に向けた複数の技術の組み合わせの検討のため、計算コードにより、候補技術の特性研究を開始した。本報告は、2017年春の年会の報告に続くものである。
 線測定
線測定芝 知宙; 冠城 雅晃; 小菅 義広*; 名内 泰志*; 高田 映*; 鈴木 梨沙; 能見 貴佳; 長谷 竹晃; 奥村 啓介
no journal, ,
プルトニウム燃料技術開発センターの有するPuO のうち、本シリーズ発表の研究に供した試料において、核分裂で生じる即発
のうち、本シリーズ発表の研究に供した試料において、核分裂で生じる即発 線を、LYSO検出器を用いて測定した。測定したスペクトルは、HPGe検出器で測定したスペクトルと比較された。また、環境
線を、LYSO検出器を用いて測定した。測定したスペクトルは、HPGe検出器で測定したスペクトルと比較された。また、環境 線を大きく上回る
線を大きく上回る Tlの2614keVの
Tlの2614keVの 線が観測され、これは
線が観測され、これは Puの子孫核種であることが示唆された。
Puの子孫核種であることが示唆された。
冠城 雅晃; 芝 知宙; 能見 貴佳; 鈴木 梨沙; 小菅 義広*; 名内 泰志*; 奥村 啓介
no journal, ,
福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉加速に資するために開発を進めている高線量率下の測定に特化したCeBr シンチレーション検出器(CeBr
シンチレーション検出器(CeBr 検出器)を利用し、原子力機構プルトニウム燃料技術開発センターが有する核燃料物質試料のガンマ線スペクトル測定を実施した。さらに、HPGe検出器による測定も実施し、結果を比較した。
検出器)を利用し、原子力機構プルトニウム燃料技術開発センターが有する核燃料物質試料のガンマ線スペクトル測定を実施した。さらに、HPGe検出器による測定も実施し、結果を比較した。
鈴木 梨沙; 能見 貴佳; 長谷 竹晃; 白茂 英雄; 芝 知宙; 冠城 雅晃; 奥村 啓介; 小菅 義広*; 高田 映*; 名内 泰志*
no journal, ,
燃料デブリ中に含まれる核燃料物質の非破壊測定による定量において、核燃料物質以外の物質の組成・量を得ることで、測定精度の向上が期待できる。プルトニウム燃料技術開発センターでは、プルトニウム試料から発生したガンマ線のスペクトルを解析することにより、当該試料中に含まれる不純物成分を把握・評価する試験を実施した。その結果、プルトニウム試料中に含まれるフッ素とアルファ線の核反応により生成される Na由来のガンマ線を検出するとともに、当該ガンマ線の発生率から、当該試料中の軽元素不純物とアルファ線の核反応由来の中性子の主要な発生源がフッ素とアルファ線の核反応であることを特定した。
Na由来のガンマ線を検出するとともに、当該ガンマ線の発生率から、当該試料中の軽元素不純物とアルファ線の核反応由来の中性子の主要な発生源がフッ素とアルファ線の核反応であることを特定した。
 線スペクトル測定の応答
線スペクトル測定の応答名内 泰志*; 能見 貴佳; 鈴木 梨沙; 小菅 義広*; 芝 知宙; 高田 映*; 冠城 雅晃; 奥村 啓介
no journal, ,
福島第一原子力発電所1 3号機の格納容器から回収される燃料デブリ・廃棄物を中性子照射ガンマ線スペクトル測定(NIGS)により仕分ける手法の開発を進めている。回収物中の核燃料物質量を評価する際、ジルコニウムやホウ素等の非核燃料物質量が核燃料物質量評価に影響する。そこで、これらの非核燃料物質に対するNIGSの応答を原子力機構・プルトニウム燃料技術開発センターで測定した。その結果、
3号機の格納容器から回収される燃料デブリ・廃棄物を中性子照射ガンマ線スペクトル測定(NIGS)により仕分ける手法の開発を進めている。回収物中の核燃料物質量を評価する際、ジルコニウムやホウ素等の非核燃料物質量が核燃料物質量評価に影響する。そこで、これらの非核燃料物質に対するNIGSの応答を原子力機構・プルトニウム燃料技術開発センターで測定した。その結果、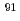 Zrの中性子捕獲反応による即発ガンマ線ピーク(6295keV)、及び
Zrの中性子捕獲反応による即発ガンマ線ピーク(6295keV)、及び Bの非弾性散乱反応(第一励起準位)からの脱励起ガンマ線ピーク(2124.5keV)を利用できる可能性が示された。
Bの非弾性散乱反応(第一励起準位)からの脱励起ガンマ線ピーク(2124.5keV)を利用できる可能性が示された。
三星 夏海; 長谷 竹晃; 小菅 義広*; 岡田 豊史
no journal, ,
本報告は、福島第一原子力発電所における燃料デブリの性状把握や仕分けのための非破壊計測に対する候補技術の特性評価の一環として実施したパッシブ中性子法の適用性評価結果を示すものである。今回、燃料デブリ中の中性子吸収材や減速材による中性子計数率への影響をシミュレーション及び実測にて評価し、中性子吸収材や減速材による影響を明らかにした。また、燃料デブリ中のPu量の定量について、主な中性子放出核種であるCm-244(短半減期核種)とPu核種(長半減期核種)の半減期の違いに着目して重量を評価する手法について、シミュレーション及び実測により有効性を評価した。
能見 貴佳; 長谷 竹晃; 小菅 義広*; 白茂 英雄; 浅野 隆
no journal, ,
本報告では、福島第一原子力発電所における燃料デブリ中の核燃料物質定量技術へのパッシブ中性子法の適用性評価の内、燃料デブリ中の核燃料物質定量のためのパッシブ中性子法に対する特性研究のフェーズ1の評価結果について報告する。本手法は、Differential Die-away Self-Interrogation (DDSI)法により中性子増倍及び吸収効果を補正するとともに、これを用い補正した中性子同時計数値によりCm-244実効質量を定量し、 線計測または計算コードより得られる燃料組成情報から核燃料物質を定量するものである。本件では、乾式貯蔵及び湿式貯蔵の共通モデル(フェーズ1)について、シミュレーションにより「燃料デブリ組成の変動に起因する不確かさ」を求めた。その結果、中性子増倍吸収効果に起因する不確かさは補正により大幅に低減されることが確認された。このことから、DDSI法は燃料デブリに対して有効と考えられる。また、湿式貯蔵は乾式貯蔵に比べて不確かさが大きくなることが確認された。これは、収納容器内に存在する水が、中性子を熱化することにより、不確かさの要因となる中性子増倍吸収効果の増加及び検出効率の変動に寄与しているためと考えられる。これらのことから本手法の適用にあたっては、収納容器内の水分の有無及び水分含有率の変動の範囲について、留意する必要がある。
線計測または計算コードより得られる燃料組成情報から核燃料物質を定量するものである。本件では、乾式貯蔵及び湿式貯蔵の共通モデル(フェーズ1)について、シミュレーションにより「燃料デブリ組成の変動に起因する不確かさ」を求めた。その結果、中性子増倍吸収効果に起因する不確かさは補正により大幅に低減されることが確認された。このことから、DDSI法は燃料デブリに対して有効と考えられる。また、湿式貯蔵は乾式貯蔵に比べて不確かさが大きくなることが確認された。これは、収納容器内に存在する水が、中性子を熱化することにより、不確かさの要因となる中性子増倍吸収効果の増加及び検出効率の変動に寄与しているためと考えられる。これらのことから本手法の適用にあたっては、収納容器内の水分の有無及び水分含有率の変動の範囲について、留意する必要がある。