Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ) cross-section measurements at n_TOF EAR2
) cross-section measurements at n_TOF EAR2Alcayne, V.*; 木村 敦; 他134名*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 217, p.111525_1 - 111525_11, 2024/04
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:95.86(Chemistry, Physical)The neutron time-of-flight facility n_TOF at CERN is a spallation source dedicated to measurements of neutron induced reaction cross-sections of interest in nuclear technologies, astrophysics, and other applications. Since 2014, Experimental ARea 2 (EAR2) is operational and delivers a neutron fluence of 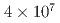 neutrons per nominal proton pulse, which is 50 times higher than the one of the other experimental area. The high neutron flux at EAR2 results in high counting rates in the detectors that challenged the previously existing capture detection systems. For this reason, a Segmented Total Energy Detector (sTED) has been developed to overcome the limitations in the detector's response, by reducing the active volume and by using a photo-multiplier (PMT) optimized for high counting rates. This paper presents the main characteristics of the sTED, including energy and time resolution, response to
neutrons per nominal proton pulse, which is 50 times higher than the one of the other experimental area. The high neutron flux at EAR2 results in high counting rates in the detectors that challenged the previously existing capture detection systems. For this reason, a Segmented Total Energy Detector (sTED) has been developed to overcome the limitations in the detector's response, by reducing the active volume and by using a photo-multiplier (PMT) optimized for high counting rates. This paper presents the main characteristics of the sTED, including energy and time resolution, response to  -rays, and provides details for the Pulse Height Weighting Technique (PHWT). The sTED has been validated to perform neutron-capture cross-section measurements in EAR2 in the neutron energy range from thermal up to at least 400 keV.
-rays, and provides details for the Pulse Height Weighting Technique (PHWT). The sTED has been validated to perform neutron-capture cross-section measurements in EAR2 in the neutron energy range from thermal up to at least 400 keV.
Chiaveri, E.*; Aberle, O.*; Alcayne, V.*; 木村 敦; 他124名*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.17001_1 - 17001_8, 2020/09
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:97.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)Since the start of its operation in 2001, the neutron time of-flight facility of CERN, n_TOF, has become one of the most forefront neutron facilities in the world for wide-energy spectrum neutron cross section measurements. Thanks to the combination of excellent neutron energy resolution and high instantaneous neutron flux available in the two experimental areas, the second of which has been constructed in 2014, n_TOF is providing a wealth of new data on neutron-induced reactions of interest for nuclear astrophysics, advanced nuclear technologies and medical applications. In this document the main characteristics of the n_TOF facility and their relevance for neutron studies in the different areas of research will be outlined. In addition, the future perspectives of the facility will be described including the upgrade of the spallation target, the setup of an imaging installation and the construction of a new irradiation area.
Terranova, N.*; Aberle, O.*; Alcayne, V.*; 木村 敦; 他125名*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.01024_1 - 01024_5, 2020/09
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:96.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The  U(n,f) cross section from 20 MeV up to about 1 GeV has been measured relative to the
U(n,f) cross section from 20 MeV up to about 1 GeV has been measured relative to the 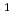 H(n,n)
H(n,n)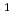 H reaction. The neutron flux impinging on the
H reaction. The neutron flux impinging on the  U sample has been obtained by detecting recoil protons originating from n-p scattering in a C
U sample has been obtained by detecting recoil protons originating from n-p scattering in a C H
H sample. Two Proton Recoil Telescopes (PRT), consisting of several layers of solid-state detectors and fast plastic scintillators, have been set at proton scattering angles of 25.07
sample. Two Proton Recoil Telescopes (PRT), consisting of several layers of solid-state detectors and fast plastic scintillators, have been set at proton scattering angles of 25.07 and 20.32
and 20.32 . Extensive Monte Carlo simulations were performed to characterize proton transport through the PRTs. In this work we compare measured data collected with the PRTs with a full Monte Carlo simulation based on the Geant-4 toolkit.
. Extensive Monte Carlo simulations were performed to characterize proton transport through the PRTs. In this work we compare measured data collected with the PRTs with a full Monte Carlo simulation based on the Geant-4 toolkit.
 U(n, f) cross section relative to n-p scattering up to 1 GeV
U(n, f) cross section relative to n-p scattering up to 1 GeVManna, A.*; Aberle, O.*; Alcayne, V.*; 木村 敦; 他125名*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.01008_1 - 01008_5, 2020/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:92.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)The neutron induced fission of  U is extensively used as a reference for neutron fluence measurements in various applications. However, no data exist on neutron induced fission of
U is extensively used as a reference for neutron fluence measurements in various applications. However, no data exist on neutron induced fission of  U above 200 MeV. The neutron facility n_TOF offers the possibility to improve the situation. The measurement of
U above 200 MeV. The neutron facility n_TOF offers the possibility to improve the situation. The measurement of  U(n,f) relative to the differential n-p scattering cross-section, was carried out with the aim of providing accurate and precise cross section data in the energy range from 10 MeV up to 1 GeV. In this measurements, recoil proton telescopes are used to measure the neutron flux while the fission events are detected and counted with dedicated detectors. In this paper the measurement campaign and the experimental set-up are illustrated.
U(n,f) relative to the differential n-p scattering cross-section, was carried out with the aim of providing accurate and precise cross section data in the energy range from 10 MeV up to 1 GeV. In this measurements, recoil proton telescopes are used to measure the neutron flux while the fission events are detected and counted with dedicated detectors. In this paper the measurement campaign and the experimental set-up are illustrated.