Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
被引用回数:0We study the magnetic properties of the metallic kagome system (Fe Co
Co )Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation (
)Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation ( SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations
SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations  = 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at
= 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at 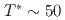 ~K, well beneath the Neel temperature
~K, well beneath the Neel temperature 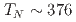 ~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/
~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/ observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)
observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)  SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/
SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/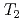 in ZF-
in ZF- SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at
SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at 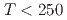 ~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe
~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe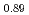 Co
Co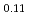 Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe
Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe Co
Co Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature
Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature 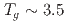 ~K; the ZF and LF-
~K; the ZF and LF- SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of
SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of  at
at 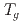 and
and 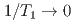 as
as 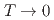 . The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by
. The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by  SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
山田 椋平*; 玉熊 佑紀*; 桑田 遥*; 三枝 裕美*; 渡邊 裕貴; 廣田 誠子*; Jin, Q.*; Cai, Y.*
保健物理(インターネット), 58(3), p.169 - 177, 2023/11
本報告は、2023年6月29日と30日の2日間にわたり開催された第1回日本保健物理学会・日本放射線安全管理学会合同シンポジウム(オンライン)の概要について報告するものである。
 ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; 金子 竜也*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
A pyrite system NiS Se
Se exhibits a bandwidth controlled Mott transition via (S,Se) substitutions in a two-step process: the antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) to antiferromagnetic metal (AFM) transition at
exhibits a bandwidth controlled Mott transition via (S,Se) substitutions in a two-step process: the antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) to antiferromagnetic metal (AFM) transition at 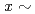 0.45 followed by the AFM to paramagnetic metal (PMM) transition at
0.45 followed by the AFM to paramagnetic metal (PMM) transition at 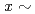 1.0. Among a few other Mott systems which exhibit similar two-step transitions, Ni(S,Se)
1.0. Among a few other Mott systems which exhibit similar two-step transitions, Ni(S,Se) is of particular interest because a large intermediate AFM region in the phase diagram would provide unique opportunities to study the interplay between the spin and charge order. By comparing and combining our muon spin relaxation studies and previous neutron scattering studies, here we propose a picture where the spin order is maintained by the percolation of "nonmetallic" localized and dangling Ni moments surrounded by S, while the charge transition from AFI to AFM is caused by the percolation of the conducting paths generated by the Ni-Se-Ni bonds.
is of particular interest because a large intermediate AFM region in the phase diagram would provide unique opportunities to study the interplay between the spin and charge order. By comparing and combining our muon spin relaxation studies and previous neutron scattering studies, here we propose a picture where the spin order is maintained by the percolation of "nonmetallic" localized and dangling Ni moments surrounded by S, while the charge transition from AFI to AFM is caused by the percolation of the conducting paths generated by the Ni-Se-Ni bonds.
 Cu
Cu N
N O
O as seen via resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
as seen via resonant inelastic X-ray scattering石井 賢司; 筒井 健二; 池内 和彦*; Jarrige, I.; 水木 純一郎; 平賀 晴弘*; 山田 和芳*; 遠山 貴己*; 前川 禎通; 遠藤 康夫*; et al.
Physical Review B, 85(10), p.104509_1 - 104509_5, 2012/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:13.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We perform a resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) study of Ni-substituted La CuO
CuO and Cu-substituted La
and Cu-substituted La NiO
NiO .Resonantly enhanced charge-transfer excitations are successfully observed by tuning the incident photon energy to the
.Resonantly enhanced charge-transfer excitations are successfully observed by tuning the incident photon energy to the  -edge of the substituted element. These excitations display a very weak momentum dependence, evidencing their local character. We find a shift in the energy of the onset edge of these features compared with the non-substituted compounds La
-edge of the substituted element. These excitations display a very weak momentum dependence, evidencing their local character. We find a shift in the energy of the onset edge of these features compared with the non-substituted compounds La CuO
CuO and La
and La NiO
NiO . This shift is quantitatively reproduced by exact diagonalization calculations of the RIXS spectra. RIXS is shown to be a powerful tool to probe the electronic states of substituted elements and to understand their interaction with surrounding atoms.
. This shift is quantitatively reproduced by exact diagonalization calculations of the RIXS spectra. RIXS is shown to be a powerful tool to probe the electronic states of substituted elements and to understand their interaction with surrounding atoms.
 Cu
Cu Ni
Ni O
O
石井 賢司; 池内 和彦*; Jarrige, I.; 水木 純一郎; 平賀 晴弘*; 山田 和芳*; 筒井 健二; 遠山 貴己*; 前川 禎通*; 遠藤 康夫*; et al.
Physica C, 470(Suppl.1), p.S155 - S157, 2010/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)Substitution of a specific element for a component is often used to elucidate its role in the superconductors. For a complete understanding of the substitution effect not only on the superconductivity but also on the electronic states, element-selective experiments are required. In this respect, resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) has proven to be a powerful experimental technique enabling element-selective diagnosis of charge excitations. By tuning the incident photon energy to a given absorption edge of the element, the excitations involving the element are resonantly enhanced. In addition, RIXS has the advantage that momentum dependence can be measured. Using RIXS, we have measured the electronic excitations at the substituting sites in La Cu
Cu Ni
Ni O
O and La
and La Ni
Ni Cu
Cu O
O . Near the absorption edge of the substituting element, namely the Ni
. Near the absorption edge of the substituting element, namely the Ni  -edge for La
-edge for La Cu
Cu Ni
Ni O
O and the Cu
and the Cu  -edge for La
-edge for La Ni
Ni Cu
Cu O
O , charge transfer excitations from the 2
, charge transfer excitations from the 2 level of neighboring oxygen to the upper Hubbard band of the substituted Ni/Cu are observed. Experimental spectra are qualitatively reproduced by a theoretical calculation based on a
level of neighboring oxygen to the upper Hubbard band of the substituted Ni/Cu are observed. Experimental spectra are qualitatively reproduced by a theoretical calculation based on a  -
- model.
model.
Jarrige, I.; Cai, Y. Q.*; 石井 啓文*; 平岡 望*; Bleuzen, A.*
Applied Physics Letters, 93(5), p.054101_1 - 054101_3, 2008/08
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:35.52(Physics, Applied)Charge-transfer excitation is at the source of the photoinduced magnetism observed in several Prussian blue molecule-based magnets. Using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and X-ray absorption spectroscopy, we probe directly the thermally-activated charge transfer in a photomagnetic Fe-Co cyanide, Cs Co
Co [Fe(CN)
[Fe(CN) ]
]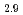 [V]
[V]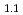 . 16H
. 16H O, where [V] represents [Fe(CN)
O, where [V] represents [Fe(CN) ] vacancies. The temperature dependence of both Co and Fe valence ratios is estimated for the first time in one cooling run, thus yielding a more complete picture of the temperature-induced cooperative electronic modifications. This novel approach, benefiting from relatively short acquisition times, opens the possibility for realtime characterization of the photoinduced magnetism in molecule-based magnets.
] vacancies. The temperature dependence of both Co and Fe valence ratios is estimated for the first time in one cooling run, thus yielding a more complete picture of the temperature-induced cooperative electronic modifications. This novel approach, benefiting from relatively short acquisition times, opens the possibility for realtime characterization of the photoinduced magnetism in molecule-based magnets.
Jarrige, I.; Rueff, J.-P.*; Shieh, S.*; 田口 宗孝*; 大石 泰生*; 松村 武*; 石井 啓文*; 平岡 望*; Cai, Y. Q.*
no journal, ,
Using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and the Anderson impurity model, we estimated the pressure dependence of the Sm and Tm valence and 4 f -5d hybridization in the respectively single and multi-channel Kondo compounds SmTe and TmTe. We observed a usual, continuous Kondo-like f delocalization for SmTe as a function of pressure. On the contrary, our results reveal that the f delocalization in TmTe is discontinuous, characterized by a previously unobserved plateau-like behavior between 4.3 and 6.5 GPa. This is interpreted as an experimental observation of the effect of culminating multi-channel Kondo scattering of d electrons from local moments on the electronic structure. Our study raises the interesting possibility that an NCK effect realized in a compressed mixed-valent f system could impede the concomitant electron delocalization.
石井 賢司; 筒井 健二; 池内 和彦*; Jarrige, I.; 水木 純一郎; 平賀 晴弘*; 山田 和芳*; 遠山 貴己*; 前川 禎通; 石井 啓文*; et al.
no journal, ,
It is widely recognized that inelastic scattering of neutron and X-ray is a powerful tool to investigate dynamical properties of electrons in the energy-momentum space. Especially, inelastic X-ray scattering has become available in the last decade by utilizing brilliant synchrotron radiation X-rays. When the incident X-ray energy is tuned to an absorption edge of a constituent element of materials, resonantly enhanced electronic excitations are observed, which is called resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). An additional characteristic arises from the resonant process, namely, the specific element selectively get involved in the observed excitations. While neutron scattering is predominantly sensitive to spin excitations, one can complementarily measure various excitations of electronic degrees of freedom, charge, spin, and orbital, with the RIXS technique. In our presentation, we show an explicit application of the element selectivity: resonant inelastic X-ray scattering of Ni-substituted La CuO
CuO and Cu-substituted La
and Cu-substituted La NiO
NiO . Resonantly enhanced charge-transfer excitations are successfully observed by tuning the incident photon energy to the K-edge of the substituted element. Combined with theoretical calculations, we will discuss the local electronic states around the substituted element which are affected through the interaction with surrounding atoms.
. Resonantly enhanced charge-transfer excitations are successfully observed by tuning the incident photon energy to the K-edge of the substituted element. Combined with theoretical calculations, we will discuss the local electronic states around the substituted element which are affected through the interaction with surrounding atoms.
Jarrige, I.; Rueff, J.-P.*; Cai, Y. Q.*; Shieh, S.*; 石井 啓文*; 田口 宗孝*
no journal, ,
Among numerous f electron systems which present Kondo properties, intermediate-valent Tm compounds stand out as potential candidates for multichannel Kondo (ncK) effect, since both integer valences Tm2+ and Tm3+ are magnetic. Using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and the Anderson impurity model, we probed the Tm valence and 4f-5d hybridization in the high-pressure intermediate-valent TmTe compound. Our results reveal that the f delocalization is discontinuous, characterized by a previously unobserved plateau-like behavior between the volume collapse transition and the structural transition (4.3 6.5 GPa), with an associated valence (2.55) at odds with the near-trivalency previously reported. This is at odds with the usual, continuous Kondo-like f delocalization, and is interpreted as an experimental observation of the effect of culminating ncK scattering of d electrons from local moments on the electronic structure.
6.5 GPa), with an associated valence (2.55) at odds with the near-trivalency previously reported. This is at odds with the usual, continuous Kondo-like f delocalization, and is interpreted as an experimental observation of the effect of culminating ncK scattering of d electrons from local moments on the electronic structure.
Jarrige, I.; Rueff, J.-P.*; Shieh, S.*; 田口 宗孝*; 石井 啓文*; Cai, Y. Q.*
no journal, ,
Identifying the mechanism of Kondo phenomena is arguably one of the most exciting and widely studied issues in condensed matter physics. Intermediate-valent Tm compounds stand out as potential candidates for multichannel Kondo (ncK) effect, since both integer valences Tm and Tm
and Tm are magnetic. Using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and the Anderson impurity model, we probed the Tm valence and 4f-5d hybridization in the high-pressure intermediate-valent TmTe compound. Our results reveal that the f delocalization is discontinuous, characterized by a previously unobserved plateau-like behavior over the 4.3
are magnetic. Using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and the Anderson impurity model, we probed the Tm valence and 4f-5d hybridization in the high-pressure intermediate-valent TmTe compound. Our results reveal that the f delocalization is discontinuous, characterized by a previously unobserved plateau-like behavior over the 4.3 6.5 GPa range. This is at odds with the usual, continuous Kondo-like f delocalization, and is interpreted as an experimental observation of the effect of culminating ncK scattering of d electrons from local moments on the electronic structure.
6.5 GPa range. This is at odds with the usual, continuous Kondo-like f delocalization, and is interpreted as an experimental observation of the effect of culminating ncK scattering of d electrons from local moments on the electronic structure.