Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wang, Z.; 松本 俊慶; 柴本 泰照; Duan, G.*
Journal of Computational Physics, 537, p.114072_1 - 114072_29, 2025/09
被引用回数:0In this study, we develop a novel sharp surface tension (SST) model for multiphase particle methods. Our approach integrates surface tension directly into pressure computation, enabling precise representation of pressure discontinuities across interfaces and effectively mitigating parasitic currents. In addition, to improve curvature accuracy, particularly in scenarios involving topological changes, a co-directional scheme is proposed to faithfully consider interfacial normal vectors. Furthermore, we reconstruct the interfacial particle shifting scheme to separately address tangential, normal, and repulsive components, effectively suppressing the common problem of interface particle mixing in multiphase particle methods. The effectiveness and reliability are rigorously validated through a series of numerical tests, including the Rayleigh-Taylor instability, curvature verification, droplet deformation and coalescence, as well as bubble rising and coalescence. The results demonstrate the superior accuracy and robustness of the proposed method, marking a significant advancement in simulations of multiphase flow with surface tension.
Wang, Z.; 松本 俊慶; Duan, G.*; 松永 拓也*
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 414, p.116168_1 - 116168_49, 2023/09
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:89.36(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Recently, consistent meshfree particle methods have been intensively studied. It has been pointed out that numerical inaccuracy or instability could easily occur with incomplete or biased neighbor support. This study proposes a new meshfree particle method called the compact moving particle semi-implicit (CMPS) method to decrease the condition number. In the proposed CMPS, the first-order and second-order derivatives are discretized separately, enhancing the numerical stability significantly. By adopting a small dilation parameter of the compact support, the CMPS can remarkably improve accuracy and reduce computational costs. Formulations for zeroth-order, first-order, and second-order derivatives are derived, and various boundary conditions, e.g., Dirichlet and Neumann, are discussed. In order to better deal with complex free-surface flows using the CMPS, some new numerical techniques, i.e., optimized regularization and reconstructed particle shifting schemes, are also developed. Furthermore, the surface fitting method is extended to address the surface tension. A convergence study is conducted in complex geometry to verify the stability, accuracy, and efficiency of the CMPS. Then, second-order accuracy is confirmed using the Taylor-Green vortex problem. After that, numerical examples concerning various free-surface flows, including square patch, hydrostatic pressure, dam break, droplet oscillation, and droplet coalescence, are calculated to demonstrate the potential of the CMPS.
Li, G.*; Duan, G.*; Liu, X.*; Wang, Z.
Moving Particle Semi-implicit Method; Recent Developments and Applications, 266 Pages, 2023/00
Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method has experienced decades of research and development since it was firstly proposed in 1996. The advanced numerical models have been developed. As the MPS method is becoming mature and stable, more and more researchers are engaging in its development and applying it to the simulations of complex multicomponent and multiphase flow in engineering. This book provides a comprehensive overview of the advanced numerical models of MPS method, including the improved discretization scheme, stabilization method, boundary condition, multiphase flow and fluid-structure interaction. The applications in the fields of nuclear engineering and ocean engineering are summarized as well. It promotes a deep understanding of the current challenges and the future development directions of the MPS method. This book is a valuable reference resource for the researchers, engineers and postgraduates with an interest in computational fluid dynamics and meshless particle methods.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; 西尾 勝久; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; 牧井 宏之; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; 廣瀬 健太郎; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:33.27(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The long-lived  Fe (with a half-life of 2.62 Myr) is a crucial diagnostic of active nucleosynthesis in the Milky Way galaxy and in supernovae near the solar system. The neutron-capture reaction
Fe (with a half-life of 2.62 Myr) is a crucial diagnostic of active nucleosynthesis in the Milky Way galaxy and in supernovae near the solar system. The neutron-capture reaction  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe on
Fe on  Fe (half-life=44.5 days) is the key reaction for the production of
Fe (half-life=44.5 days) is the key reaction for the production of  Fe in massive stars. This reaction cross section has been previously constrained by the Coulomb dissociation experiment, which offered partial constraint on the E1
Fe in massive stars. This reaction cross section has been previously constrained by the Coulomb dissociation experiment, which offered partial constraint on the E1  -ray strength function but a negligible constraint on the M1 and E2 components. In this work, for the first time, we use the surrogate ratio method to experimentally determine the
-ray strength function but a negligible constraint on the M1 and E2 components. In this work, for the first time, we use the surrogate ratio method to experimentally determine the  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross sections in which all the components are included. We derived a Maxwellian-averaged cross section of 27.5
Fe cross sections in which all the components are included. We derived a Maxwellian-averaged cross section of 27.5 3.5 mb at
3.5 mb at 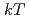 = 30 keV and 13.4
= 30 keV and 13.4 1.7 mb at
1.7 mb at 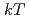 = 90 keV, roughly 10%-20% higher than previous estimates. We analyzed the impact of our new reaction rates in nucleosynthesis models of massive stars and found that uncertainties in the production of
= 90 keV, roughly 10%-20% higher than previous estimates. We analyzed the impact of our new reaction rates in nucleosynthesis models of massive stars and found that uncertainties in the production of  Fe from the
Fe from the  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe rate are at most 25
Fe rate are at most 25 . We conclude that stellar physics uncertainties now play a major role in the accurate evaluation of the stellar production of
. We conclude that stellar physics uncertainties now play a major role in the accurate evaluation of the stellar production of  Fe.
Fe.
Wang, Z.; Duan, G.*; 越塚 誠一*; 山路 哲史*
Nuclear Power Plant Design and Analysis Codes, p.439 - 461, 2021/00
The Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method is one kind of particles methods which are based on Lagrangian approach. It has been developed to analyze complex thermal-hydraulic problems, including those in nuclear engineering. Since meshes are no longer used, large deformation of free surfaces or interfaces can be simulated without the problems of mesh distortion. This approach is effective in solving multiphase fluid dynamics which is subject to complex motion of free surfaces or interfaces. Since its development, MPS method has been extensively utilized for wide range of applications in nuclear engineering. In this chapter, the basic theory of the MPS method is firstly explained. Then, some examples of its application in nuclear engineering, including bubble dynamic, vapor explosion, jet breakup, multiphase flow instability, in-vessel phenomenon, molten spreading, molten core concrete interaction (MCCI) and flooding, are presented.
Wang, Z.; Duan, G.*; 松永 拓也*; 杉山 智之
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 157, p.119919_1 - 119919_20, 2020/08
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:78.69(Thermodynamics)Enforcing accurate and consistent boundary conditions is a difficult issue for particle methods, due to the lack of information outside boundaries. Recently, consistent Neumann boundary condition enforcement is developed for the least squares moving particle semi-implicit method (LSMPS). However, the Robin boundary cannot be straightforwardly considered by that method because no computational variables are defined on the wall boundary. In this paper, a consistent Robin boundary enforcement for heat transfer problem is proposed. Based on the Taylor series expansion, the Robin boundary condition for temperature is converted to the fitting function of internal rather than boundary particles and incorporated into least squares approach for discretization schemes. Arbitrary geometries can be easily treated due to the use of polygons for wall boundary. A convergence study was firstly carried out to verify the consistency. Then, numerical tests of 1-D and 2-D heat conduction problems subjected to mixed boundary conditions were performed for verification, and good agreements with theoretical solutions were observed. Natural convection problems with different boundary conditions in an annulus were carried out for further validations of heat-fluid coupling. Excellent agreements between the present and literature results were demonstrated.
Li, X.; 佐藤 一憲; 山路 哲史*; Duan, G.*
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/07
溶融コリウム・コンクリート相互作用(MCCI)は軽水炉の仮想的シビアアクシデント時の後期フェーズにおいて炉容器外で生じる可能性のある重要事象である。本研究では、MPS法を用いてKITによって実施された模擬物質による成層化溶融プールの実験COMET-L3に対する3次元解析を行った。コリウム/クラスト/コンクリート間の伝熱は粒子間の熱伝導モデルで模擬した。さらに、ケイ酸系コンクリートではケイ酸系析出物の効果によって軸方向と径方向の浸食が異なる可能性が既往研究から示唆されていることから、2つの異なる解析ケースを実施した。解析の結果、MCCIにおいて金属コリウムは酸化物コリウムと全く異なるコンクリート浸食パターンを示しており、アクシデントマネジメントにおける格納系境界の溶融貫通時間の評価に考慮する必要があることが分かった。
菊池 満; Fasoli, A.*; 滝塚 知典*; Diamond, P.*; Medvedev, S.*; Duan, X.*; 図子 秀樹*; 古川 勝*; 岸本 泰明*; Wu, Y.*; et al.
no journal, ,
トカマクにおける標準的なD型Hモードプラズマシナリオは熱粒子制御の観点からは課題を含んでいる。革新的なトカマク配位として負三角度の可能性が菊池等によって議論されている。CRPP-EPFLによる負三角度プラズマの実験と理論研究で閉じ込め改善が報告されており、負三角度配位はSOL流速の低減が示唆される。近年のタイプII ELMやグラッシーELMの理論研究によると第2安定化領域へのアクセスを閉じることと運動論的効果が小ELMの達成に重要であることがわかってきた。Medvedevによると負三角度では第2安定化領域への窓が閉じることが分かっている。講演では、これらを含む最近の理解進展をまとめる。
Li, X.*; 山路 哲史*; Duan, G.*; 古谷 正祐*; 深井 尋史*; 佐藤 一憲; 間所 寛; 大石 佑治*
no journal, ,
The Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method is being developed for simulation of multi-component liquid/solid relocation with solid-liquid phase changes. Main model developments and validation of the developed code against the simulated spreading and ablation experiments are summarized in the current paper.
竹見 哲也*; 吉田 敏哉; Duan, G.*
no journal, ,
近畿地方に上陸した2018年21号台風は、甚大な強風災害を大阪市内で引き起こした。都市域の人工構造物群は局所的な突風の強度に大きく影響する。そのため、都市構造物群による潜在的な風災害リスクを理解することが求められている。本研究では、2018年21号台風が上陸した期間を対象に、大阪市の都市構造物群が及ぼす突風への影響を、領域気象モデルとLarge Eddy Simulationを用いて評価した。解析結果から、大阪市の地表最大風速は推定60-70m/sであり、この風速値は300m上空の風速値に匹敵することが分かった。さらに、瞬間的な突風と建物密度の関係性を解析し、適度な建物密度を有する場所で最も突風の強度が高いことが分かった。