Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Pikuz, S. A.*; Fortov, V. E.*; 福田 祐仁; 林 由紀雄; Pirozhkov, A. S.; 小瀧 秀行; 下村 拓也; et al.
Laser and Particle Beams, 30(3), p.481 - 488, 2012/09
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:41.90(Physics, Applied)It is shown that various spectroscopic methods based on measurements of X-ray spectra radiated from cluster targets can be used for estimation of the destruction degree of clusters by laser prepulses. These methods allow answering the important issue of preservation of the dense cluster core at the moment of the arrival of the main laser pulse. In addition, they can be used for quantitative estimation of the size of the undestroyed parts of the clusters and also for measuring the temperature and density of the preplasmas produced by the laser prepulses.
Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; Skobelev, I.*; Fortov, V. E.*; Boldarev, A.*; Gasilov, V.*; Chen, L. M.*; Zhang, L.*; Yan, W.*; Yuan, D.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.181 - 201, 2012/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)A study is made of the ultra-short laser pulse irradiation of Ar cluster targets. Experiments have been performed with large cluster sizes and using very high laser contrasts, which have allowed clear and unambiguous observation of exotic inner-shell transitions in near-neutral Ar ions. The interaction of the main laser pulse with the unperturbed target is a necessary requirement for observing these lines. Our measurements are supported by kinetics calculations in which a very detailed atomic model is used. X-ray spectral methods have been proposed to determine the parameters of the appearing plasma at the early stages of its evolution. It has been shown that the spectra of hollow ions are the most informative in the first moments of the heating of a cluster, whereas the diagnostics of the late stages can be performed using the conventional lines of multicharged ions.
石野 雅彦; Faenov, A.*; 田中 桃子; 長谷川 登; 錦野 将元; 保 智己*; Pikuz, S.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Skobelev, I.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.236 - 240, 2012/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:62.21(Physics, Applied)軟X線レーザーによるアブレーション過程の理解を目的として、アルミニウム表面に軟X線レーザーを集光照射した。照射痕を走査型電子顕微鏡で観察したところ、アブレーション構造とは異なる表面改質領域が形成されていることがわかった。この表面改質領域には、ナノメートルオーダーの直径を持つ円錐状構造が多数形成されている。また、円錐状構造が形成されている改質領域は、照射した軟X線レーザーの浸入長に一致する深さであるこことも確認した。軟X線レーザーによるアルミニウム表面に形成される改質構造は、新規のナノ構造形成プロセスとしても興味深い。このX線レーザーとアルミニウム表面との相互作用によって形成される改質領域については、理論計算により提唱されている破砕的モデルで説明することができる。
Inogamov, N. A.*; Anisimov, S. I.*; Petrov, Y. V.*; Khokhlov, V. A.*; Zhakhovskii, V. V.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T.; Fortov, V. E.*; Skobelev, I. Y.*; 加藤 義章*; et al.
Journal of Optical Technology, 78(8), p.473 - 480, 2011/08
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:31.83(Optics)An experimental and theoretical study has been carried out of the ablation of a solid insulator with a wide band gap (LiF) under the action of ultrashort laser pulses of the UV range, obtained in a free-electron laser, and the soft X-ray region, obtained in a silver-plasma laser. A comparison is made of the results obtained on the two laser systems. It is shown that the ablation threshold is about the same for both lasers. A theory is presented that explains the weak growth of the ablation mass with increasing surface energy density of the laser radiation (the fluence) in the case of X-ray lasers as a result of the transition from spallation close to the ablation threshold to evaporative ablation at high fluence values.
Inogamov, N. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Petrov, Y. V.*; Khokhlov, V. A.*; Shepelev, V. V.*; Anisimov, S. I.*; Fortov, V. E.*; et al.
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 51(5), p.419 - 426, 2011/06
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:62.13(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)極短パルス,極端紫外自由電子レーザー(EUV-FEL)パルス(波長:50nm,パルス幅:100fs)をフッ化リチウム(LiF)のような誘電体に照射することで、結晶状態にあるLiFの破砕現象を初めて観測した。低フルーエンスの場合ではLiFの破砕現象が起こり、これがLiFの低いアブレーション閾値の原因となっていることを明らかにした。同様の現象は、ピコ秒パルスの関西光科学研究所X線レーザー装置を用いた実験でも観測されている。この破砕現象は、ナノ秒パルスのX線レーザー装置では観測されておらず、フェムト ピコ秒パルス特有の現象であることをモデル計算から明らかにした。
ピコ秒パルス特有の現象であることをモデル計算から明らかにした。
Starikov, S. V.*; Stegailov, V. V.*; Norman, G. E.*; Fortov, V. E.*; 石野 雅彦; 田中 桃子; 長谷川 登; 錦野 将元; 大場 俊幸*; 海堀 岳史; et al.
JETP Letters, 93(11), p.642 - 647, 2011/04
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:74.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The interaction of radiation of a picosecond X-ray laser (wavelength  = 13.9 nm) with targets made of a thick gold film has been studied theoretically and experimentally. It has been shown experimentally that the action of individual X-ray laser pulses with a fluence of
= 13.9 nm) with targets made of a thick gold film has been studied theoretically and experimentally. It has been shown experimentally that the action of individual X-ray laser pulses with a fluence of 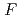
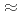 21 mJ/cm
21 mJ/cm initiates the nanostructuring of the gold surface. Explicitly taking into account the electron subsystem, we have proposed an atomistic model of ablation that makes it possible to adequately described the experimental results. The atomistic simulation involves the ion-ion potential depending on the electron temperature
initiates the nanostructuring of the gold surface. Explicitly taking into account the electron subsystem, we have proposed an atomistic model of ablation that makes it possible to adequately described the experimental results. The atomistic simulation involves the ion-ion potential depending on the electron temperature 
 . The use of such a potential makes it possible to take into account an increase in the pressure in the system with increasing
. The use of such a potential makes it possible to take into account an increase in the pressure in the system with increasing 
 and to reveal two laser ablation mechanisms.
and to reveal two laser ablation mechanisms.
石野 雅彦; Faenov, A. Ya.*; 田中 桃子; 長谷川 登; 錦野 将元; 保 智己*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovskii, V. V.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 109(1), p.013504_1 - 013504_6, 2011/01
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:75.63(Physics, Applied)軟X線レーザーによるアブレーション過程の理解を目的として、アルミニウム表面に軟X線レーザーを照射した。照射痕を走査型電子顕微鏡で観察したところ、アブレーション構造とは異なる微細構造(改質領域)が形成されていることを確認した。この領域には70-150nmの直径を持つ円錐状の構造物が多数確認できる。また、円錐構造は平均深さ約40nmの改質領域中に形成されていることもわかった。しかし、軟X線レーザーを複数回照射した領域の円錐構造は、成長することなく破壊されていることがわかった。今回得られた結果は、軟X線レーザーによるアブレーション過程の理解だけでなく、軟X線レーザーの微細加工への応用にも重要な知見を与えると考えられる。
Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Khokhlov, V. A.*; Shepelev, V. V.*; Skobelev, I. Y.*; 加藤 義章*; 田中 桃子; Pikuz, T. A.*; 岸本 牧; et al.
Applied Physics A, 101(1), p.87 - 96, 2010/10
被引用回数:34 パーセンタイル:75.45(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A short laser pulse in wide range of wavelengths, from infrared to X-ray, disturbs electron-ion equilibrium and increases pressure in a heated layer. The case where the pulse duration 
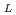 is shorter than acoustic relaxation time
is shorter than acoustic relaxation time 
 is considered. It is shown that this short pulse may cause thermomechanical phenomena such as spallative ablation regardless of wavelength. While the physics of electron-ion relaxation strongly depends on wavelength and various electron spectra of substances. There are spectra with an energy gap in semiconductors and dielectrics opposed to gapless continuous spectra in metals. The paper describes entire sequence of thermomechanical processes from expansion, nucleation, foaming, and nanostructuring to spallation with particular attention to spallation by X-ray pulse.
is considered. It is shown that this short pulse may cause thermomechanical phenomena such as spallative ablation regardless of wavelength. While the physics of electron-ion relaxation strongly depends on wavelength and various electron spectra of substances. There are spectra with an energy gap in semiconductors and dielectrics opposed to gapless continuous spectra in metals. The paper describes entire sequence of thermomechanical processes from expansion, nucleation, foaming, and nanostructuring to spallation with particular attention to spallation by X-ray pulse.
Inogamov, N. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Zhakhovskii, V. V.*; Skobelev, I. Y.*; Khokhlov, V. A.*; 加藤 義章*; 田中 桃子; Pikuz, T. A.*; 岸本 牧; 石野 雅彦; et al.
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 51(4), p.361 - 366, 2010/05
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:60.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Laser-matter interaction is defined by an electric band structure of condensed matter and frequency of electromagnetic radiation. The thermalization processes are different for optical as compared with X-ray quanta and for metals relative to semiconductors and dielectrics, since the light absorption and electron-electron, electron-ion dynamics are sensitive to the electron population in a conduction band and the width of a forbidden gap. Although the thermalization processes are different, the final state is simply a heated matter. Laser heating creates powerful stresses in a target if duration of laser pulse 
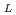 is short in acoustic time scale. Nucleation and material removal take place under such stresses. Such way of removal is called here the spallative ablation. Thus the spallative ablation is an ablation mechanism universally important for qualitatively different materials and quanta.
is short in acoustic time scale. Nucleation and material removal take place under such stresses. Such way of removal is called here the spallative ablation. Thus the spallative ablation is an ablation mechanism universally important for qualitatively different materials and quanta.
Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; 石野 雅彦; Starikov, S. V.*; Stegailov, V. V.*; Norman, G. E.*; Fortov, V.*; Skobelev, I.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Systematic experimental and theoretical studies of the surface modifications resulting from the interactions of both single and multiple SXRL pulses irradiation of metals have been provided. Developed models show that relatively slow electron-ionic relaxation in such metals results in maintaining of the high electron pressure in the near surface region for several picoseconds, that is sufficiently long for the development of the hydrodynamic response that causes the negative pressure region formation and the nanostructuring of a thin surface layer. Obtained results demonstrate that tensile stress created in metals by short X-ray pulse can produce spallative ablation of target even for drastically small X-ray fluencies, which open new opportunities for material nano processing.
Inogamov, N. A.*; Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T.*; Zhakhovski, V.*; Skobelev, I.*; Khokhlov, V.*; Anisimov, S. I.*; Fortov, V. E.*; 福田 祐仁; 加藤 義章*; et al.
no journal, ,
The results of theoretical and experimental studies of ablation of LiF crystal by X-ray laser and FEL beams having photons with 89.3 eV and 20 eV with very short duration of pulse 7 ps and 300 fs are presented. It is found that the crater is formed for fluencies above the threshold Fabl about 10 mJ/cm : Such a small threshold is one order of magnitude less than the one obtained for X-ray ablation by longer (nanoseconds) pulses. The theory explains this dramatic difference as a change-over from more energy consuming evaporative ablation to spallative ablation, when the pulse duration decreases from ns to ps time ranges. We demonstrate that tensile stress created in dielectrics by short X-ray pulse can produce spallative ablation of target even for drastically small X-ray fluencies, which open new opportunities for material nano processing.
: Such a small threshold is one order of magnitude less than the one obtained for X-ray ablation by longer (nanoseconds) pulses. The theory explains this dramatic difference as a change-over from more energy consuming evaporative ablation to spallative ablation, when the pulse duration decreases from ns to ps time ranges. We demonstrate that tensile stress created in dielectrics by short X-ray pulse can produce spallative ablation of target even for drastically small X-ray fluencies, which open new opportunities for material nano processing.
Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovski, V.*; Skobelev, I.*; Khokhlov, V.*; Anisimov, S. I.*; Fortov, V. E.*; 福田 祐仁; 加藤 義章*; et al.
no journal, ,
Theoretical and experimental studies of ablation of LiF crystal by X-ray laser and FEL beams were provided. It was found a very low ablation threshold for both types of irradiation. Such a small threshold is one order of magnitude less than the one obtained for X-ray ablation by longer (nanoseconds) pulses or 2 orders smaller than arradiated by fs visible pulses. The theory explains this dramatic difference as a change-over from more energy consuming evaporative ablation to spallative ablation, when the pulse duration decreases from ns to ps time ranges.
石野 雅彦; Faenov, A. Ya.*; 田中 桃子; Pikuz, T.; 保 智己*; 長谷川 登; 錦野 将元; Starikov, S. V.*; Stegailov, V. V.*; Norman, G. E.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Laser ablation has many technological applications in material micro-meter size processing and fabrication of nano-structures. We show experimentally the possibility of the precise nano-meter size surface structuring of metal aluminum (Al) and gold (Au) surfaces induced by ultra low fluencies of pico-second soft X-ray laser (SXRL) single pulse. The spatially coherent SXRL beam was generated from the silver (Ag) plasma mediums using oscillator-amplifier configuration with Ag double targets. The generated SXRL pulse had the wavelength of 13.9 nm and the duration of 7 ps. On Al surface, the formations of conical structures were observed in the shallow features. On Au surface, the ripple-like structures were observed. The atomistic model of surface modifications is developed that reveals the ultra-low threshold fluency values of this process and suggests it as a splash-melting regime. Our results will open new opportunities for nano-meter size processing for metal surfaces.
河内 哲哉; 石野 雅彦; 錦野 将元; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.; 長谷川 登; Inogamov, N. A.*; Skobelev, I. Y.*; Fortov, V. E.*; Khohlov, V. A.*; et al.
no journal, ,
レーザーアブレーションは材料加工やナノ構造形成などの多くの応用を持つ。レーザーアブレーション時に起こる物質損傷の基礎プロセスも精力的に研究されており、損傷のレーザーパルス幅,光子エネルギー,フルエンス依存性についても徐々に理解されつつある。近年、レーザー駆動の軟X線レーザーや自由電子レーザーなどの新しい軟X線光源が利用可能となり、軟X線による新しいレーザー加工の可能性をわれわれに提示している。軟X線領域のレーザーと物質の相互作用は、光学レーザーのそれとは大きく異なる。軟X線の物質への主な吸収過程は光電離過程であり、光電離による100eV程度の光電子が物質表面の局所的な領域に生成することで瞬時に高温状態が形成される。このような温度の急激な上昇は物質中に応力波を引き起こし、結果として表層部分の破砕や新奇な表面構造を形成する可能性がある。会議においては軟X線レーザーにおけるわれわれが行ったアブレーション実験及び理論計算との比較、そして金属表面のナノ構造形成について報告する。
Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.; 石野 雅彦; Starikov, S. V.*; Stegailov, V. V.*; Norman, G.*; Fortov, V. E.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; 保 智己*; 田中 桃子; et al.
no journal, ,
A systematic experimental study of the surface modifications resulting from the interactions of both single and multiple SXRL pulses in order to confirm the development of the modified structures during multiple shots irradiation. The interactions between single or multiple picosecond soft X-ray laser (SXRL) beam and metal (such as gold (Au), copper (Cu), and aluminum (Al)) surfaces, were investigated. Our results demonstrate that tensile stress created in metals by short X-ray pulse can produce spallative ablation of target even for drastically small X-ray fluencies, which open new opportunities for material nano processing.
Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T. A.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovski, V.*; Khokhlov, V.*; Anisimov, S. I.*; Fortov, V. E.*; 加藤 義章*; 福田 祐仁; 田中 桃子; et al.
no journal, ,
The results of theoretical and experimental studies of ablation of LiF crystal by X-ray beam having photons with 89.3 eV and very short duration of pulse 7 ps are presented. It is found that the crater is formed for fluencies above the threshold 10 mJ/cm . Such a small threshold is one order of magnitude less than the one obtained for X-ray ablation by longer (nanoseconds) pulses. The theory explains this dramatic difference as a change-over from more energy consuming evaporative ablation to spallative ablation, when the pulse duration decreases from ns to ps time ranges.
. Such a small threshold is one order of magnitude less than the one obtained for X-ray ablation by longer (nanoseconds) pulses. The theory explains this dramatic difference as a change-over from more energy consuming evaporative ablation to spallative ablation, when the pulse duration decreases from ns to ps time ranges.