Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Micheau, C.; 上田 祐生; 元川 竜平; Bauduin, P.*; Girard, L.*; Diat, O.*
Langmuir, 39(31), p.10965 - 10977, 2023/07
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:71.78(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Understanding clay flotation mechanisms has become a major concern because of the increasing level of environmental contamination of soil and ground water by heavy metals and radionuclides. Clays are often used as sorbents for extracting metals in indirect flotation processes but can function simultaneously as defoamers. However, how foam generation and stability depend on the molecular interactions between the clays and surfactant is still controversial. In the present study, an amine polyethoxylated surfactant was used as a bifunctional surfactant that collected clay particles and acted as a foaming agent in the flotation process. The pH conditions strongly affected the surfactant physicochemical properties, allowing the clay extraction efficiency to be tuned. The interfacial recovery factor of the clays almost reached 100 percent under acidic (pH lower than 6) and neutral (pH 6-10) conditions, whereas it was negative under alkaline conditions (pH higher than 10), contrary to expectations. To elucidate the mechanisms involved in the particle flotation process for each of the pH conditions, the bulk and foam phases were analyzed. The effects of electrostatic interactions between the solutes and multiscale structure on the clay extraction behavior were investigated by electrophoretic measurements, dynamic light scattering, small-angle neutron scattering, and image analysis. Based on these results, three flotation processes were found depending on pH range: surfactant foam fractionation at pH higher than 10; clay particle foam flotation at pH 6-10; and particle froth flotation at pH lower than 6.
Villard, L.*; Bottino, A.*; Brunner, S.*; Casati, A.*; Chowdhury, J.*; Dannert, T.*; Ganesh, R.*; Garbet, X.*; G rler, T.*; Grandgirard, V.*; et al.
rler, T.*; Grandgirard, V.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 52(12), p.124038_1 - 124038_18, 2010/11
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:60.19(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper presents some of the main recent advances in gyrokinetic theory and computing of turbulence. A past controversy regarding the finite size (finite 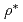 ) effect in ITG turbulence has now been resolved. Now, both Eulerian and Lagrangian global codes are shown to agree and to converge to the flux-tube result in the
) effect in ITG turbulence has now been resolved. Now, both Eulerian and Lagrangian global codes are shown to agree and to converge to the flux-tube result in the 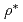
 0 limit. It is found, however, that an appropriate treatment of geometrical terms is necessary. Turbulent processes are characterized by a chaotic behavior, often accompanied by bursts and avalanches. Performing ensemble averages of statistically independent simulations, starting from different initial conditions, is presented as a way to assess the intrinsic variability of turbulent fluxes and obtain reliable estimates of the standard deviation.
0 limit. It is found, however, that an appropriate treatment of geometrical terms is necessary. Turbulent processes are characterized by a chaotic behavior, often accompanied by bursts and avalanches. Performing ensemble averages of statistically independent simulations, starting from different initial conditions, is presented as a way to assess the intrinsic variability of turbulent fluxes and obtain reliable estimates of the standard deviation.
Micheau, C.; 元川 竜平; 上田 祐生; Bauduin, P.*; Diat, O.*; Girard, L.*
no journal, ,
Flotation process takes the advantage of foam to extract and concentrate solutes (ions, molecules, colloids and particles) without using organic solvent. Among all of the potential applications, particle flotation has proven its efficiency for paper deinking, ore and mineral extraction. In addition, the interest in the flotation of clay particles has increased over the past few decades because of the environmental contamination of soil and ground water by heavy metals and radionuclides. In this study, we used Ethomeen C/25, a polyethoxylated tallow amine, for the extraction of Laponite RD, a synthetic clay. This pH-sensitive surfactant plays the role of foaming agent and collector. The objective was to determine how the foam microscopic structure depends on the molecular interaction between the clay and the surfactant and to correlate these results to the extraction efficiency. For this purpose, clay extraction experiments were performed as function of pH. High extraction yield was obtained for pH  10, whereas an unexpected negative recovery factor is observed for higher pHs meaning that clays are repelled from the foam interfaces. To determine the mechanisms involved in the flotation process for each pH condition, bulk and foam were investigated using electrophoretic analysis, dynamic light scattering, small-angle neutron scattering, and image analysis (see Figure 1). From these results, we described the impact of clay on foam structure and stability, and established three different flotation regimes: (i) froth flotation of gel-like clay particles at pH
10, whereas an unexpected negative recovery factor is observed for higher pHs meaning that clays are repelled from the foam interfaces. To determine the mechanisms involved in the flotation process for each pH condition, bulk and foam were investigated using electrophoretic analysis, dynamic light scattering, small-angle neutron scattering, and image analysis (see Figure 1). From these results, we described the impact of clay on foam structure and stability, and established three different flotation regimes: (i) froth flotation of gel-like clay particles at pH  6, (ii) foam flotation of clay aggregates at 6
6, (ii) foam flotation of clay aggregates at 6  pH
pH  10, and (iii) foam fractionation with the depletion of clays at pH
10, and (iii) foam fractionation with the depletion of clays at pH  10. A continuous process for soil remediation is designed by alternating regimes (ii) and (iii) adjusting the pH.
10. A continuous process for soil remediation is designed by alternating regimes (ii) and (iii) adjusting the pH.