Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Cao, T.*; Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 他10名*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 940, p.148534_1 - 148534_16, 2025/09
The thermal stability of microstructure and mechanical performance is crucial for the industrial application of laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) superalloy components in gas turbines and jet engines. This work investigated the microstructural evolution and strengthening mechanism of LPBF Mar-M509 cobalt-based superalloy before and after thermal exposure at 1200  C using multi-scale microstructural characterization and in situ neutron diffraction tensile testing. The as-built Mar-M509 superalloy exhibited a heterogeneous microstructural features with coarse columnar and fine equiaxed grains, both containing dendritic and cellular substructures enriched with nanoscale carbides and high-density dislocations. The ultra high strength of the as-built sample was primarily attributed to dislocation-precipitation synergistic strengthening. After thermal exposure at 1200
C using multi-scale microstructural characterization and in situ neutron diffraction tensile testing. The as-built Mar-M509 superalloy exhibited a heterogeneous microstructural features with coarse columnar and fine equiaxed grains, both containing dendritic and cellular substructures enriched with nanoscale carbides and high-density dislocations. The ultra high strength of the as-built sample was primarily attributed to dislocation-precipitation synergistic strengthening. After thermal exposure at 1200  C for 4 h, the dendritic and cellular substructures disappeared and the dislocation density decreased significantly. This study reveals the microstructural evolution and instability of LPBF Mar-M509 superalloy under high-temperature exposure and the impacts on mechanical properties, which provides critical support for the development of cobalt-based superalloys in high-temperature application fields.
C for 4 h, the dendritic and cellular substructures disappeared and the dislocation density decreased significantly. This study reveals the microstructural evolution and instability of LPBF Mar-M509 superalloy under high-temperature exposure and the impacts on mechanical properties, which provides critical support for the development of cobalt-based superalloys in high-temperature application fields.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study山下 享介*; 古賀 紀光*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 藤井 英俊*; 梅澤 修*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
Ferrite-austenite duplex stainless steels offer excellent strength and ductility, making them suitable for extreme environments. In this study,  neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
Zheng, R.*; Gong, W.; 他6名*
Acta Materialia, 293, p.121098_1 - 121098_12, 2025/07
Hall-Petch law fails when grains smaller than a critical size, due to grain boundary (GB) kinetics-dominated plasticity. To enhance strength, improving GB stability is a consideration. However, this often requires a significant amount of alloying elements, posing resource challenges. Additionally, practical fabrication of extremely fine grains is still an issue. In our study, we firstly demonstrate a remarkable hardening-by-annealing phenomenon in magnesium (Mg) with relatively large grain sizes of 0.2-0.5  m, even with ultra-low yttrium (Y) addition. We reveal that annealing induces GB segregation/relaxation, effectively limiting the GB kinetics and promoting dislocation-dominated plasticity. Furthermore, the accompanying dislocation annihilation hinders deformation due to dislocation scarcity. As a result, we discovered extraordinary hardening in bulk ultrafine grained Mg-Y ultra-dilute alloy. This work offers a promising avenue for developing energy- and resource-efficient sustainable Mg alloys with superior mechanical properties.
m, even with ultra-low yttrium (Y) addition. We reveal that annealing induces GB segregation/relaxation, effectively limiting the GB kinetics and promoting dislocation-dominated plasticity. Furthermore, the accompanying dislocation annihilation hinders deformation due to dislocation scarcity. As a result, we discovered extraordinary hardening in bulk ultrafine grained Mg-Y ultra-dilute alloy. This work offers a promising avenue for developing energy- and resource-efficient sustainable Mg alloys with superior mechanical properties.
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 他4名*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Face-centered cubic (FCC) equi-atomic multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs) exhibit excellent mechanical properties from cryogenic to room temperatures. At room temperature, deformation is dominated by dislocation slip, while at cryogenic temperatures (CTs), reduced stacking fault energy enhances strain hardening with twinning. This study uses in-situ neutron diffraction to analyze the temperature-dependent deformation behavior of Al (CoNiV)
(CoNiV)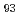 , a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
, a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*; 伊東 達矢; 山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
被引用回数:0An ultrafine-grained 304 austenitic stainless steel exhibited pronounced serrated Luders deformation at 20 K, with stress and temperature oscillations reaching 200 MPa and 20 K.  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
友田 陽*; Harjo, S.; 徐 平光; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.; Wang, Y.*
Metals, 15(6), p.610_1 - 610_19, 2025/05
Lattice parameters of product and matrix phases in steels have been measured using in situ X-ray and neutron diffraction during forward and reverse transformations. These parameters are influenced by temperature, transformation-induced internal stresses, alloying element partitioning, crystal defects, and magnetic strains. Disentangling these contributions is essential for understanding lattice behavior. This review explores internal strain (stress) associated with ferrite, pearlite, bainite, martensite, and reverse austenite transformations, emphasizing the distinction between diffusional and displacive mechanisms. It also examines how plastic deformation of austenite affects subsequent bainite or martensite formation. The roles of dislocations and vacancies are identified as critical areas for further research.
Wang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 他7名*
Acta Materialia, 288, p.120840_1 - 120840_14, 2025/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Low yield strength and the presence of Luders bands constitute principal impediments to the extensive applications of conventional medium Mn steels with a duplex microstructure of ferrite and austenite. Flash heating and the concept of chemical heterogeneity have been combined to engineer a duplex austenite-martensite microstructure in medium Mn steels, which has proven effective in augmenting the yield strength and mitigating the occurrence of Luders bands. However, the underlying mechanisms remain ambiguous. In the present work, the effect of austenite stability on yielding behavior was systematically investigated in an austenite-martensite duplex medium Mn steel. Austenite stability was identified as the critical factor governing yield strength, where reduced stability promotes early stage deformation induced martensite transformation, thereby decreasing yield strength. Diminished austenite stability may as well induce enhanced work hardening, thereby result in the inclination and eventual elimination of yield plateau, concomitant with the disappearance of Luders bands. These observations expand our current understanding of the yielding behavior in medium Mn steels and offer insights for the design of other advanced high strength steels.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Incorporating solute hydrogen into Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic stainless steels enhances both strength and ductility, providing a promising solution to hydrogen embrittlement by causing solid-solution strengthening and assisting deformation twinning. However, its impacts on the relevant lattice defects evolution ( , dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using
, dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using  neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 他3名*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
The need for lightweight materials with mechanical integrity at ultralow temperatures drives the development of advanced alloys for cryogenic use. Additive manufacturing via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) offers a scalable way to create alloys with tailored properties. Here, we show that LPBF-processed Al10SiMg exhibits a high ultimate tensile strength (395 MPa) and uniform elongation (25%) at 15 K. These enhancements stem from grain refinement, increased geometrically necessary dislocations, and stress partitioning between the Al matrix and the stiffer Si phase, aiding strain accommodation.  neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
Go, J.*; Park, M.-H.*; Gao, S.*; 松宮 久*; Gong, W.; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1014, p.178749_1 - 178749_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:89.83(Chemistry, Physical)In Mg alloys, basal dislocation slip is the preferential slip system that is activated at room temperature, while non-basal slips are typically difficult to activate owing to their high critical resolved shear stress. Until now, minimal focus has been directed towards the influence of loading direction on slip behavior in pre-twinned AZ31 alloys. This study employed transmission electron microscopy to demonstrate that non-basal slips, specifically prismatic and pyramidal I slips, are activated under deformation conditions where de-twinning is difficult in a pre-twinned AZ31 Mg alloy. When the tensile loading direction is parallel to the precompression direction, de-twinning and basal slip are the primary deformation modes. Conversely, when the tensile loading direction is perpendicular to the precompression direction, where de-twinning is challenging to activate, both basal and non-basal slips, such as prismatic and pyramidal I slips, emerge as the primary deformation modes. These results indicate that the pre-twinned AZ31 Mg alloy cannot deform solely through basal slips, and the activation of either de-twinning or non-basal slips is necessary to satisfy the von Mises criterion. Our findings in this study demonstrate the impact of non-basal slip activity on macroscopic yield stress and overall deformation, hence enhancing the understanding of magnesium alloy deformation mechanisms.
Naeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tian, J.*; Kong, H.*; Romero-Resendiz, L.*; Fan, Z.*; Jiang, F.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 924, p.147819_1 - 147819_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Face-centered cubic (fcc) medium-/high-entropy alloys (M/HEAs) typically enhance strength and ductility at cryogenic temperatures via stacking faults, twinning, or martensitic transformation. However, in-situ neutron diffraction on VCoNi MEA at 15 K reveals that strain hardening is driven solely by rapid dislocation accumulation, without these mechanisms. This results in increased yield strength, strain hardening, and fracture strain. The behavior, explained by the Orowan equation, challenges conventional views on cryogenic strengthening in fcc M/HEAs and highlights the role of dislocation-mediated plasticity at low temperatures.
Song, Y.*; Xu, S.*; 佐藤 駿介*; Lee, I.*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 長迫 実*; 川崎 卓郎; 鬼柳 亮嗣; Harjo, S.; et al.
Nature, 638, p.965 - 971, 2025/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:88.78(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In advanced applications like aerospace and space exploration, materials must balance lightness, functionality, and extreme thermal fluctuation resistance. Shape-memory alloys show promise with strength, toughness, and substantial strain recovery due to superelasticity, but maintaining low mass and effective operation at cryogenic temperatures is challenging. We hereby introduce a novel shape-memory alloy that adheres to these stringent criteria. Predominantly composed of Ti and Al with a chemical composition of Ti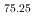 Al
Al Cr
Cr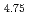 , this alloy 25 is characterized by a low density (4.36
, this alloy 25 is characterized by a low density (4.36 10
10 kg/m
kg/m ) and a high specific strength (185
) and a high specific strength (185 10
10 Pa
Pa m
m /kg) at room temperature, while exhibiting excellent superelasticity. The superelasticity, owing to a reversible stress-induced phase transformation from an ordered body-centered cubic parent phase to an ordered orthorhombic martensite, allows for a recoverable strain exceeding 7%. Remarkably, this functionality persists across a broad range of temperatures, from deep cryogenic 4.2 K to above room temperature, arising from an unconventional temperature dependence of transformation stresses. Below a certain threshold during cooling, the critical transformation stress inversely correlates with temperature. We interpret this behavior from the perspective of a temperature-dependent anomalous lattice instability of the parent phase. This alloy holds potential in everyday appliances requiring flexible strain accommodations, as well as components designed for extreme environmental conditions such as deep space and liquefied gases.
/kg) at room temperature, while exhibiting excellent superelasticity. The superelasticity, owing to a reversible stress-induced phase transformation from an ordered body-centered cubic parent phase to an ordered orthorhombic martensite, allows for a recoverable strain exceeding 7%. Remarkably, this functionality persists across a broad range of temperatures, from deep cryogenic 4.2 K to above room temperature, arising from an unconventional temperature dependence of transformation stresses. Below a certain threshold during cooling, the critical transformation stress inversely correlates with temperature. We interpret this behavior from the perspective of a temperature-dependent anomalous lattice instability of the parent phase. This alloy holds potential in everyday appliances requiring flexible strain accommodations, as well as components designed for extreme environmental conditions such as deep space and liquefied gases.
吉田 周平*; Gong, W.; 他9名*
Acta Materialia, 283, p.120498_1 - 120498_15, 2025/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:63.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Face-centered cubic (FCC) high/medium entropy alloys (HEAs/MEAs), novel multi-principal element alloys, are known to exhibit exceptional mechanical properties at room temperature; however, the origin is still elusive. Here, we report the deformation microstructure evolutions in a tensile-deformed Co Cr
Cr Ni
Ni representative MEA and Co
representative MEA and Co Ni
Ni alloy, a conventional binary alloy for comparison. These FCC alloys have high/low friction stresses, and share similar other material properties. The Co
alloy, a conventional binary alloy for comparison. These FCC alloys have high/low friction stresses, and share similar other material properties. The Co Cr
Cr Ni
Ni MEA exhibited higher yield strength and work-hardening ability than in the Co
MEA exhibited higher yield strength and work-hardening ability than in the Co Ni
Ni alloy. Deformation microstructures in the Co
alloy. Deformation microstructures in the Co Cr
Cr Ni
Ni alloy were marked by the presence of coarse dislocation cells (DCs) regardless of grain orientation and a few deformation twins (DTs) in grains with the tensile axis (TA) near
alloy were marked by the presence of coarse dislocation cells (DCs) regardless of grain orientation and a few deformation twins (DTs) in grains with the tensile axis (TA) near  1 1 1
1 1 1 . In contrast, the MEA developed three distinct deformation microstructures depending on grain orientations: fine DCs in grains with the TA near
. In contrast, the MEA developed three distinct deformation microstructures depending on grain orientations: fine DCs in grains with the TA near  1 0 0
1 0 0 , planar dislocation structure (PDS) in grains with other orientations, and a high density of DTs along with PDS in grains oriented
, planar dislocation structure (PDS) in grains with other orientations, and a high density of DTs along with PDS in grains oriented  1 1 1
1 1 1 . These findings demonstrate that FCC HEAs/MEAs with high friction stresses naturally develop unique deformation microstructures which is beneficial for realizing superior mechanical properties compared to conventional materials.
. These findings demonstrate that FCC HEAs/MEAs with high friction stresses naturally develop unique deformation microstructures which is beneficial for realizing superior mechanical properties compared to conventional materials.
 neutron diffraction measurement during tensile deformation
neutron diffraction measurement during tensile deformation山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 北條 智彦*; 興津 貴隆*; 藤井 英俊*
ISIJ International, 64(14), p.2051 - 2060, 2024/12
An Fe-0.15C-5Mn-0.5Si-0.05Nb steel annealed at 660 C and 685
C and 685 C showed L
C showed L ders deformation followed by high work hardening, with variations in L
ders deformation followed by high work hardening, with variations in L ders strain and hardening behavior.
ders strain and hardening behavior.  neutron diffraction during tensile tests analyzed phase stresses, strength contributions, and austenite orientation. Deformation-induced martensite contributed
neutron diffraction during tensile tests analyzed phase stresses, strength contributions, and austenite orientation. Deformation-induced martensite contributed  1000 MPa to strength near tensile failure, while austenite mainly enhanced ductility via transformation-induced plasticity. Austenite transformed to martensite during L
1000 MPa to strength near tensile failure, while austenite mainly enhanced ductility via transformation-induced plasticity. Austenite transformed to martensite during L ders deformation regardless of orientation, though 311-oriented grains tended to remain along the tensile direction.
ders deformation regardless of orientation, though 311-oriented grains tended to remain along the tensile direction.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionNaeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Knowles, A. J.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wang, X.-L.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; 他6名*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 916, p.147374_1 - 147374_8, 2024/11
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:63.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Heterostructured materials (HSMs) improve the strength-ductility trade-off of alloys, but their cryogenic performance under real-time deformation is unclear. We studied heterostructured CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy via  neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
Harjo, S.; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.205 - 208, 2024/11
This study aimed to elucidate the effect of grain size on the deformation behavior of TRIP steel. We prepared metastable austenitic Fe-24Ni-0.3C steel samples with average grain sizes of 35 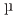 m (coarse grain: CG) and 0.5
m (coarse grain: CG) and 0.5 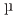 m (ultrafine-grain: UFG) for in situ neutron diffraction studies during tensile deformation at room temperature. Our observations revealed increases in dislocation density in both samples prior to DIMT, indicating that plastic deformation precedes DIMT regardless of grain size. In the UFG sample, a significant rise in dislocation density occurred just around the yielding point with minimal increases in macroscopic plastic strain. Additionally, the dislocations exhibited strong dipole arrangements.
m (ultrafine-grain: UFG) for in situ neutron diffraction studies during tensile deformation at room temperature. Our observations revealed increases in dislocation density in both samples prior to DIMT, indicating that plastic deformation precedes DIMT regardless of grain size. In the UFG sample, a significant rise in dislocation density occurred just around the yielding point with minimal increases in macroscopic plastic strain. Additionally, the dislocations exhibited strong dipole arrangements.
 neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Hydrogen embrittlement has long been an obstacle to the development of safe infrastructure. However, in contrast to hydrogen's embrittling effect, recent research has revealed that the addition of hydrogen improves both the strength and uniform elongation of AISI Type 310S austenitic stainless steel. A detailed understanding of how hydrogen affects the deformation mechanism of this steel could pave the way for the development of more advanced materials with superior properties. In the present study,  neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:87.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using a hybrid method of in situ neutron diffraction and digital image correlation, we found that ultrafine-grained 304 stainless steel exhibits Luders deformation after yielding, in which the deformation behavior changes from a cooperation mechanism involving dislocation slip and martensitic transformation to one primarily governed by martensitic transformation, as the temperature decreases from 295 K to 77 K. Such martensitic transformation-governed Luders deformation delays the activation of plastic deformation in both the austenite parent and martensite product, resulting in delayed strain hardening. This preserves the strain-hardening capability for the later stage of deformation, thereby maintaining a remarkable elongation of 29% while achieving a high tensile strength of 1.87 GPa at 77 K.
Wang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Su, Y. H.; Li, B.*
Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 60(8), p.1001 - 1016, 2024/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:41.92(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The correlation between the atomic structure, microstructure, and macroscopic properties of structural materials remains a core issue in materials research. In recent years, substantial progress has been achieved in constructing accelerator-based neutron sources and related experimental techniques, offering a robust platform for an in-depth understanding of the aforementioned correlation under real-time and in situ conditions. This article reviews the latest advancements in the application of major neutron characterization techniques, including neutron diffraction, Bragg-edge imaging, small-angle neutron scattering, pair distribution function analysis, and quasi-elastic/inelastic neutron scattering, in structural materials. Furthermore, it particularly highlights the origins and evolution of internal stresses during the phase transformations of steels, deformation mechanisms in light metals such as magnesium alloys, and microstructure and residual stress analyses using Bragg-edge imaging. Finally, a brief outlook on future development trends is provided.
 Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement
Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement中本 美緒*; 菅野 未知央*; 荻津 透*; 杉本 昌弘*; 谷口 諒*; 廣瀬 清慈*; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 淡路 智*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 34(5), p.8400806_1 - 8400806_6, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)For an accelerator magnet, a certain mechanical strength is required to sustain against a transverse compression stress due to Lorentz force. A bronze-route Nb Sn wire with Cu-Nb reinforcement was developed by Tohoku University and Furukawa Electric to enhance the strength against axial tension. The Cu-Nb reinforcement wire also exhibited some indication of strength improvement against transverse compression; however, the details of a reinforcement mechanism for the transverse compression stress have not been clarified. In this study, the internal strains of Nb
Sn wire with Cu-Nb reinforcement was developed by Tohoku University and Furukawa Electric to enhance the strength against axial tension. The Cu-Nb reinforcement wire also exhibited some indication of strength improvement against transverse compression; however, the details of a reinforcement mechanism for the transverse compression stress have not been clarified. In this study, the internal strains of Nb Sn bronze-route wires with and without the Cu-Nb reinforcement under transverse compression stress were evaluated by neutron diffraction at BL19 (TAKUMI) in J-PARC. The samples were attached to jig with solder only at the ends and compression was applied at the center of the samples with 30-mm anvil with 5-mm wide and 8- to 15-mm high beam. Since a critical current, Ic of a superconducting wire depends on the three-dimensional strain, internal strain of Nb
Sn bronze-route wires with and without the Cu-Nb reinforcement under transverse compression stress were evaluated by neutron diffraction at BL19 (TAKUMI) in J-PARC. The samples were attached to jig with solder only at the ends and compression was applied at the center of the samples with 30-mm anvil with 5-mm wide and 8- to 15-mm high beam. Since a critical current, Ic of a superconducting wire depends on the three-dimensional strain, internal strain of Nb Sn along the axial and two orthogonal radial directions were evaluated at room temperature (RT). In the different setup, Ic measurements of the wires under transverse compression stresses were also performed at 4.2 K and 14.5 T. Using 3-mm wide anvil, the transverse compression was applied at 4.2 K or RT. The neutron diffraction results indicated no significant differences in the internal strains of Nb
Sn along the axial and two orthogonal radial directions were evaluated at room temperature (RT). In the different setup, Ic measurements of the wires under transverse compression stresses were also performed at 4.2 K and 14.5 T. Using 3-mm wide anvil, the transverse compression was applied at 4.2 K or RT. The neutron diffraction results indicated no significant differences in the internal strains of Nb Sn under transverse compression between the samples with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement, while the Ic measurements showed potential increase in the irreversible stress (
Sn under transverse compression between the samples with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement, while the Ic measurements showed potential increase in the irreversible stress (
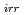 ) for Cu-Nb reinforced wires. The reason for this discrepancy was discussed based on the difference in the experimental setups for each measurement.
) for Cu-Nb reinforced wires. The reason for this discrepancy was discussed based on the difference in the experimental setups for each measurement.