Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sn
SnBenito, J.*; Fraile, L. M.*; Korgul, A.*; Piersa, M.*; Adamska, E.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 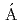 lvarez-Rodr
lvarez-Rodr guez, R.*; 他81名*
guez, R.*; 他81名*
Physical Review C, 102(1), p.014328_1 - 014328_18, 2020/07
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:76.51(Physics, Nuclear)The structure of the doubly magic 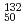 Sn
Sn has been investigated at the ISOLDE facility at CERN, populated both by the
has been investigated at the ISOLDE facility at CERN, populated both by the  -decay of
-decay of  In and
In and  -delayed neutron emission of
-delayed neutron emission of  In. The level scheme of
In. The level scheme of  Sn is greatly expanded with the addition of 68
Sn is greatly expanded with the addition of 68  -ray transitions and 17 levels. The identification of particle-hole multiplets both for protons and neutrons and the transition rates connecting different particle-hole configurations may provide input on the two-body matrix elements and single-particle states for state-of-the-art calculations.
-ray transitions and 17 levels. The identification of particle-hole multiplets both for protons and neutrons and the transition rates connecting different particle-hole configurations may provide input on the two-body matrix elements and single-particle states for state-of-the-art calculations.
 decay of
decay of  In;
In;  emission from neutron-unbound states in
emission from neutron-unbound states in  Sn
SnPiersa, M.*; Korgul, A.*; Benito, J.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 他75名*
Physical Review C, 99(2), p.024304_1 - 024304_10, 2019/02
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:75.77(Physics, Nuclear)Excited states in  Sn were investigated through the
Sn were investigated through the  decay of
decay of  In at the ISOLDE facility. The ISOLDE Resonance Ionization Laser Ion Source (RILIS) provided isomer-selective ionization for
In at the ISOLDE facility. The ISOLDE Resonance Ionization Laser Ion Source (RILIS) provided isomer-selective ionization for  In, allowing us to study separately, and in detail, the
In, allowing us to study separately, and in detail, the  -decay branch of
-decay branch of  In
In 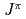 = (9/2
= (9/2 ) ground state and its
) ground state and its 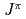 = (1/2
= (1/2 ) isomer. Thanks to the large spin difference of the two
) isomer. Thanks to the large spin difference of the two  -decaying states of
-decaying states of  In, it is possible to investigate separately the lower and higher spin states in the daughter,
In, it is possible to investigate separately the lower and higher spin states in the daughter,  Sn, and thus to probe independently different single-particle and single-hole levels. We report here new
Sn, and thus to probe independently different single-particle and single-hole levels. We report here new  transitions observed in the decay of
transitions observed in the decay of  In, including those assigned to the deexcitation of the neutron-unbound states.
In, including those assigned to the deexcitation of the neutron-unbound states.
 -spectroscopy at an intense cold neutron beam facility
-spectroscopy at an intense cold neutron beam facilityJentschel, M.*; Blanc, A.*; de France, G.*; K ster, U.*; Leoni, S.*; Mutti, P.*; Simpson, G.*; Soldner, T.*; Ur, C.*; Urban, W.*; et al.
ster, U.*; Leoni, S.*; Mutti, P.*; Simpson, G.*; Soldner, T.*; Ur, C.*; Urban, W.*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(11), p.P11003_1 - P11003_33, 2017/11
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:85.20(Instruments & Instrumentation)A highly efficient array of high-purity germanium (HPGe) detectors was developed and operated at the cold neutron beam facility PF1B of the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL) to carry out nuclear structure studies, via measurements of  -rays following neutron-induced capture and fission reactions. The setup consisted of a collimation system producing a pencil beam with a thermal capture equivalent flux of about 10
-rays following neutron-induced capture and fission reactions. The setup consisted of a collimation system producing a pencil beam with a thermal capture equivalent flux of about 10 ns
ns cm
cm at the target position and negligible neutron halo. The target was surrounded by an array of eight to ten anti-Compton shielded EXOGAM Clover detectors, four to six anti-Compton shielded large coaxial GASP detectors and two standard Clover detectors. For a part of the campaign the array was combined with 16 LaBr
at the target position and negligible neutron halo. The target was surrounded by an array of eight to ten anti-Compton shielded EXOGAM Clover detectors, four to six anti-Compton shielded large coaxial GASP detectors and two standard Clover detectors. For a part of the campaign the array was combined with 16 LaBr :(Ce) detectors from the FATIMA collaboration.
:(Ce) detectors from the FATIMA collaboration.
 -forbidden 1/2
-forbidden 1/2
 3/2
3/2
 transition in
transition in  Sn
SnLic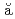 , R.*; Mach, H.*; Fraile, L. M.*; Gargano, A.*; Borge, M. J. G.*; M
, R.*; Mach, H.*; Fraile, L. M.*; Gargano, A.*; Borge, M. J. G.*; M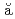 rginean, N.*; Sotty, C. O.*; Vedia, V.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Benzoni, G.*; et al.
rginean, N.*; Sotty, C. O.*; Vedia, V.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Benzoni, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 93(4), p.044303_1 - 044303_7, 2016/04
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:54.19(Physics, Nuclear)The levels in  Sn populated from the
Sn populated from the 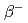 decay of
decay of  In isomers were investigated at the ISOLDE facility of CERN using the newly commissioned ISOLDE Decay Station. The lowest 1/2
In isomers were investigated at the ISOLDE facility of CERN using the newly commissioned ISOLDE Decay Station. The lowest 1/2 state and the 3/2
state and the 3/2 ground state in
ground state in  Sn are expected to have configurations dominated by the neutron
Sn are expected to have configurations dominated by the neutron 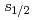 (
( =0) and
=0) and 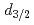 (
( =2) single-particle states, respectively. Consequently, these states should be connected by a somewhat slow
=2) single-particle states, respectively. Consequently, these states should be connected by a somewhat slow  -forbidden
-forbidden  transition. Using fast-timing spectroscopy we have measured the half-life of the 1/2
transition. Using fast-timing spectroscopy we have measured the half-life of the 1/2 315.3-keV state,
315.3-keV state, 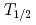 = 19(10) ps, which corresponds to a moderately fast
= 19(10) ps, which corresponds to a moderately fast  transition. Shell-model calculations using the CD-Bonn effective interaction, with standard effective charges and
transition. Shell-model calculations using the CD-Bonn effective interaction, with standard effective charges and 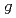 factors, predict a 4-ns half-life for this level. We can reconcile the shell-model calculations to the measured
factors, predict a 4-ns half-life for this level. We can reconcile the shell-model calculations to the measured 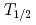 value by the renormalization of the
value by the renormalization of the  effective operator for neutron holes.
effective operator for neutron holes.