Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sn and spin-orbit splitting in neutron-rich nuclei
Sn and spin-orbit splitting in neutron-rich nucleiOrlandi, R.; Pain, S. D.*; Ahn, S.*; Jungclaus, A.*; Schmitt, K. T.*; Bardayan, D. W.*; Catford, W. N.*; Chapman, R.*; Chipps, K. A.*; Cizewski, J. A.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 785, p.615 - 620, 2018/10
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:57.98(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Low-lying neutron-hole states in  Sn were populated via the
Sn were populated via the  Sn(d,t) reaction at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The triton angular distributions were compared to DWBA calculations and revealed spectroscopic factors compatible with a single-hole nature of the states populated. The data permit to determine the spin-orbit splitting of the strongly bound
Sn(d,t) reaction at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The triton angular distributions were compared to DWBA calculations and revealed spectroscopic factors compatible with a single-hole nature of the states populated. The data permit to determine the spin-orbit splitting of the strongly bound 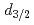 and
and 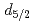 neutron orbits below the shell gap, which was compared to the splitting of the weakly bound 3
neutron orbits below the shell gap, which was compared to the splitting of the weakly bound 3 and 2
and 2 orbits above the gap. The comparison revealed a smaller energy splitting of the 3
orbits above the gap. The comparison revealed a smaller energy splitting of the 3 orbits. All splittings were reproduced using Woods-Saxon calculations, and the lower splitting of the 3
orbits. All splittings were reproduced using Woods-Saxon calculations, and the lower splitting of the 3 orbits was explained to arise from the large radial extent of the wavefunction and small value of the amplitude at the surface. This result is important to understand at a fundamental level the spin-orbit interaction, and its effects on neutron-rich nuclei.
orbits was explained to arise from the large radial extent of the wavefunction and small value of the amplitude at the surface. This result is important to understand at a fundamental level the spin-orbit interaction, and its effects on neutron-rich nuclei.
 Sn studied via the
Sn studied via the  Sn(d,t)
Sn(d,t) Sn reaction
Sn reactionOrlandi, R.; Pain, S. D.*; Bardayan, D. W.*; Gross, C. J.*; Smith, M. S.*; Jungclaus, A.*; Ahn, S.*; Jones, K. L.*; Pittman, S. T.*; Schmitt, K. T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Knowledge of single-particle energies in the vicinity of exotic doubly-magic nuclei is of critical importance to understand evolution of nuclear structure. In the present work, the  Sn(d,t)
Sn(d,t) Sn reaction (Q=-1.055 MeV) was studied in inverse kinematics at HRIBF of Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The
Sn reaction (Q=-1.055 MeV) was studied in inverse kinematics at HRIBF of Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The  Sn ISOL beam was post-accelerated to an energy of 4.39 MeV/u using the ORNL HRIBF accelerator. The beam (average intensity of
Sn ISOL beam was post-accelerated to an energy of 4.39 MeV/u using the ORNL HRIBF accelerator. The beam (average intensity of  1.2e4 pps) impinged on a
1.2e4 pps) impinged on a  250
250  g/cm
g/cm deuterated polyethylene target, for approximately 4 days. Ejected tritons were detected using the Super ORRUBA array of segmented Si telescopes. Low-lying states in
deuterated polyethylene target, for approximately 4 days. Ejected tritons were detected using the Super ORRUBA array of segmented Si telescopes. Low-lying states in  Sn were populated in the experiment. Preliminary results will be shown.
Sn were populated in the experiment. Preliminary results will be shown.
南川 卓也; 小越 友里恵; 桑原 彬; 山田 鉄兵*; Zanella, M.*; Jansat, S.*; Manning, T.*; Rosseinsky, M.*
no journal, ,
液体廃棄物中から、放射性セシウム(Cs)とストロンチウム(Sr)を取り除く材料としては、ゼオライトなど細孔性の材料が知られているが、これらの細孔は非常に安定であるため、細孔中からこれらの元素を取り出し、回収することや、細孔のサイズを自由に変化させることは困難である。一方、最近研究が進んできた配位高分子(MOF)は、配位子と金属を選択することで細孔をデザインできるため、細孔の大きさを自由に変化させることができる。また、この材料の細孔は、溶液の変化に敏感なため、一度取り込んだゲスト分子も溶液条件を変化させれば容易に取り出すことができる。本研究では、新規なMOFである(NH )[Ln(C
)[Ln(C O
O )
) (H
(H O)] (Ln=Y, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu)を合成し、MOFの細孔サイズをこれまでにない方法で制御し、調整することで、溶液中からCsやSrを選択的に分離した。また、一度取り込んだCsやSrをMOFから回収する実験を行い、放射性廃棄物から有用な放射性金属元素を回収できる可能性を示した。
O)] (Ln=Y, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu)を合成し、MOFの細孔サイズをこれまでにない方法で制御し、調整することで、溶液中からCsやSrを選択的に分離した。また、一度取り込んだCsやSrをMOFから回収する実験を行い、放射性廃棄物から有用な放射性金属元素を回収できる可能性を示した。