Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Lee, J.; Rossi, F.; 児玉 有; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 佐野 忠史*; 松尾 泰典*; 堀 順一*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.111017_1 - 111017_7, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Silica glass has been used as a base and host material in vitrified radioactive waste and lithium glass scintillator for neutron detection because of its superb transparency, high heat resistance, and excellent chemical inertness. Therefore, an accurate total cross section of the silica glass is important to evaluate the criticality safety for the vitrified wastes and to understand the neutron response for lithium glass scintillators accurately. In the present study, to provide the accurate total cross section in the thermal and epithermal energy range, the neutron transmission measurements were carried out by a pulsed neutron beam with the time-of-flight method at the Kyoto University Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science - Linear Accelerator. We obtained the neutron total cross section of the silica glass in the energy region from 0.002 eV to 25 eV. The obtained results were compared and discussed with the previous results and the evaluated data.
Rodriguez, D.; 赤松 駿介*; Rossi, F.; 鈴木 敏*; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of 65th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/07
Under the MEXT subsidy to promote nuclear security related activities, we will present the preliminary results from the new Fission Signature Assay Instrument that was fabricated and fully installed in November 2023. We will describe the instrument within the context of the JAEA-JRC collaboration development and the experimental activities planned with it in the larger context of finishing off Phase-III development.
Rossi, F.; Lee, J.; 児玉 有; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 堀 順一*; 寺田 和司*; 佐野 忠史*
Proceedings of 65th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07
Various non-destructive assay techniques are being used to verify different nuclear material. However, one of the difficulties of current NDA is the measurement of highly radioactive materials. Since 2015, the JAEA has been working on the development of various active non-destructive assay techniques to address some of the current challenges in nuclear safeguards. Among the various technologies proposed, the Neutron Resonance Analysis system combines signatures from NRTA, NRCA and the newly proposed NRFNA. The combination of those techniques can provide accurate information on the small fissile content in a sample. Neutrons are generated by a pulsed neutron source and slowed down into the moderator. Neutrons are collimated using lead and borated polyethylene to reach the sample, where various neutron-induced reactions occur. n/g PSD plastic scintillators are used to measure the captured gamma rays and fission neutrons at sample location. GS20 is used to collect the transmitted neutrons downstream of the source-sample beamline. A first measurement campaign was performed using natural uranium sample. The possibility of using NRFNA to identify fissile materials within a sample was clearly demonstrated, but the detectors used were not sufficient to achieve a good n/g PSD. New PSD scintillators were introduced. A first measurement campaign was performed in 2023. The acquired data are currently being analyzed, but preliminary results show distinct fission resonance peaks of increasing intensity with varying thicknesses of the same natural uranium samples. Currently, an assembly of multiple scintillators is being investigated to provide a better signal. The new setup will be tested starting in early 2024. In this paper, we will describe in detail the NRA project development and the latest results from experimental campaign. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like"
Rodriguez, D.; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 71(3), p.255 - 268, 2024/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Under the MEXT subsidy to improve nuclear security related capabilities, we are developing the delayed gamma-ray spectroscopic analysis technique. One goal is to develop an inverse Monte Carlo analysis method using spectra from simulations of the interrogation instrument for comparison to the actual measured spectra. This work presents the validity of the Monte Carlo foundation of the analysis compared to experimental results and other simulation codes.
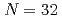
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)理化学研究所RIビームファクトリーにて中性子過剰核 Arビームからの1中性子ノックアウト反応実験を行い、
Arビームからの1中性子ノックアウト反応実験を行い、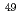 Arのエネルギー準位および分光学的因子を導出した。特に、第一励起状態の
Arのエネルギー準位および分光学的因子を導出した。特に、第一励起状態の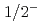 への分光学的因子が大きいことから、始状態の
への分光学的因子が大きいことから、始状態の Arの基底状態において中性子が
Arの基底状態において中性子が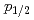 軌道を多く占めていることがわかった。これは、中性子数32がよい魔法数として知られる
軌道を多く占めていることがわかった。これは、中性子数32がよい魔法数として知られる Caとは異なった性質であり、カルシウムからアルゴンへと陽子が2個減ることで閉殻構造が大きく崩れることが明らかになった。
Caとは異なった性質であり、カルシウムからアルゴンへと陽子が2個減ることで閉殻構造が大きく崩れることが明らかになった。
Rodriguez, D.; 赤松 駿介*; Rossi, F.; 鈴木 敏*; 高橋 時音
第44回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2023/11
Under the MEXT subsidy for improving nuclear material security related activities, we present the latest JAEA/ISCN delayed gamma-ray instrument, FSAI; preliminary characterization results; and the experimental and analysis development activities planned using it.
Lee, J.; 児玉 有; Rossi, F.; 弘中 浩太; 小泉 光生; 堀 順一*; 佐野 忠史*
第44回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2023/11
核不拡散・核セキュリティ総合支援センターでは、試料中に含まれる少量の核分裂性物質を特定し定量する能力を向上させるための技術として、中性子飛行時間法を用いた中性子共鳴核分裂中性子分析(Neutron Resonance Fission Neutron Analysis: NRFNA)の技術開発を進めている。本発表会では、核分裂性物質の非破壊分析のために進めているNRFNA技術の紹介及びその基礎実験の結果について報告する。
 O
O近藤 洋介*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; 馬場 秀忠*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
被引用回数:29 パーセンタイル:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)非常に中性子が過剰な原子核 Oは、陽子、中性子ともに魔法数であることから古くからその性質に興味が持たれていたが、酸素の最後の束縛核
Oは、陽子、中性子ともに魔法数であることから古くからその性質に興味が持たれていたが、酸素の最後の束縛核 Oよりも中性子が4個も多いため、これまで観測されてこなかった。この論文では、理化学研究所RIBFにて
Oよりも中性子が4個も多いため、これまで観測されてこなかった。この論文では、理化学研究所RIBFにて Fからの1陽子ノックアウト反応によって
Fからの1陽子ノックアウト反応によって Oを生成し、そこから放出される中性子を測定することによって初めてその観測に成功した。核構造の観点からは、
Oを生成し、そこから放出される中性子を測定することによって初めてその観測に成功した。核構造の観点からは、 Oでは二重閉殻が保たれているか興味が持たれていたが、実験で得られた分光学的因子が殻模型計算で予言されて程度の大きいことから、閉殻構造をもたない可能性が高いことがわかった。
Oでは二重閉殻が保たれているか興味が持たれていたが、実験で得られた分光学的因子が殻模型計算で予言されて程度の大きいことから、閉殻構造をもたない可能性が高いことがわかった。
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; 安田 昌弘*; 近藤 洋介*; 中村 隆司*; Tostevin, J. A.*; 緒方 一介*; 大塚 孝治*; Poves, A.*; 清水 則孝*; 吉田 数貴; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics) Neからの1中性子除去反応を用いて、
Neからの1中性子除去反応を用いて、 Neの詳細な
Neの詳細な 線分光を行った。平行運動量分布の解析に基づき、
線分光を行った。平行運動量分布の解析に基づき、 Neの準位構造とスピンパリティを決定し、初めて負のパリティ状態を同定した。測定された断面積と運動量分布から、N=20とN=28のシェルギャップの消失の証拠となる有意なintruder p-wave強度が明らかになった。束縛状態については、弱いf-waveの可能性のある強度が観測された。いくつかの有効相互作用を用いた大規模殻模型計算では、実験的に観測された大きなp-wave強度と小さなf-wave強度は再現されず、Ne同位体に沿った反転の島への遷移の完全な理論的記述への挑戦が続いていることを示している。
Neの準位構造とスピンパリティを決定し、初めて負のパリティ状態を同定した。測定された断面積と運動量分布から、N=20とN=28のシェルギャップの消失の証拠となる有意なintruder p-wave強度が明らかになった。束縛状態については、弱いf-waveの可能性のある強度が観測された。いくつかの有効相互作用を用いた大規模殻模型計算では、実験的に観測された大きなp-wave強度と小さなf-wave強度は再現されず、Ne同位体に沿った反転の島への遷移の完全な理論的記述への挑戦が続いていることを示している。
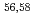 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; 角田 佑介*; 大塚 孝治*; 茶園 亮樹*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:89.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)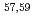 Scからの1陽子ノックアウト反応を用いて、
Scからの1陽子ノックアウト反応を用いて、 Caと
Caと Caのガンマ崩壊を観測した。
Caのガンマ崩壊を観測した。 Caでは1456(12)keVの
Caでは1456(12)keVの 線遷移が、
線遷移が、 Caでは1115(34)keVの遷移が観測された。どちらの遷移も暫定的に
Caでは1115(34)keVの遷移が観測された。どちらの遷移も暫定的に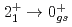 と割り当てられた。有効核子間相互作用をわずかに修正した広い模型空間での殻模型計算では、
と割り当てられた。有効核子間相互作用をわずかに修正した広い模型空間での殻模型計算では、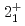 準位エネルギー、2中性子分離エネルギー、反応断面積が実験とよく一致し、N=34閉殻の上に新しい殻が形成されていることを裏付けた。その構成要素である
準位エネルギー、2中性子分離エネルギー、反応断面積が実験とよく一致し、N=34閉殻の上に新しい殻が形成されていることを裏付けた。その構成要素である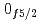 と
と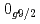 軌道はほぼ縮退しており、これは
軌道はほぼ縮退しており、これは Caが二重魔法核である可能性を排除し、Ca同位体のドリップラインを
Caが二重魔法核である可能性を排除し、Ca同位体のドリップラインを Caあるいはそれ以上にまで広げる可能性がある。
Caあるいはそれ以上にまで広げる可能性がある。
Rodriguez, D.; Rossi, F.
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
Under the MEXT subsidy for the improvement of nuclear security related activities, we will present on the current and future progress of the delayed gamma-ray spectroscopic analysis development. We highlight a paper soon to be released and the plan for finalizing the project goal.
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; Bertolotti, D.*; Bonaldi, C.*; Fontana, C.*; 藤本 正己*; Geerts, W.*; 小泉 光生; Macias, M.*; Nonneman, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/05
Under the MEXT subsidy to improve nuclear security related activities, we present the overview of the JAEA-JRC delayed gamma-ray spectroscopic analysis project. We describe past results, recent joint experiments, and the final goals for this project.
Rossi, F.; 小泉 光生; Rodriguez, D.; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/05
Since 2015, the Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Nonproliferation and Nuclear Security (ISCN) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been working on the development of the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopy non-destructive assay technique for the quantification of fissile-nuclide content in mixed nuclear materials. Thanks to the efforts and lessons learned from past experiments, the ISCN has successfully designed and fabricated a final integrated instrument. The instrument is composed of a moderator and dose shield where different neutron sources, like Cf-252 and neutron generators, can be inserted to irradiate the sample. Within the moderator, a series of neutron detectors are installed for perform prompt neutron analysis and continuous monitoring of the neutron source emission. Thanks to an innovative transfer system, the sample is then moved to the gamma-ray detector in less than 1.5s providing a fast and reliable movement while being safe from possible contamination. In this work, we will describe the design details of this new instrument. This work is supported by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like".
 island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in
island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in  V and
V and  V
VElekes, Z.*; Juh sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; 吉田 数貴; 緒方 一介*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; 馬場 秀忠*; et al.
sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; 吉田 数貴; 緒方 一介*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; 馬場 秀忠*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064321_1 - 064321_10, 2022/12
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:43.00(Physics, Nuclear) Vと
Vと Vの低励起準位構造を初めて探索した。
Vの低励起準位構造を初めて探索した。 Vについては中性子ノックアウト反応と陽子非弾性散乱が、
Vについては中性子ノックアウト反応と陽子非弾性散乱が、 Vについては中性子ノックアウト反応データが得られた。
Vについては中性子ノックアウト反応データが得られた。 Vについては4つ、
Vについては4つ、 Vについては5つの新たな遷移が確認された。Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS)相互作用に基づく殻模型計算との比較によって、それぞれの同位体について確認されたガンマ線のうち3つが、first 11/2
Vについては5つの新たな遷移が確認された。Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS)相互作用に基づく殻模型計算との比較によって、それぞれの同位体について確認されたガンマ線のうち3つが、first 11/2 状態とfirst 9/2
状態とfirst 9/2 状態からの崩壊と決定された。
状態からの崩壊と決定された。 Vについては、(
Vについては、( ,
,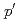 )非弾性散乱断面積は四重極変形と十六重極変形を想定したチャネル結合法により解析されたが、十六重極変形の影響により、明確に反転の島に属するとは決定できなかった。
)非弾性散乱断面積は四重極変形と十六重極変形を想定したチャネル結合法により解析されたが、十六重極変形の影響により、明確に反転の島に属するとは決定できなかった。
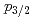 neutron orbital and the
neutron orbital and the 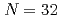 shell closure in
shell closure in  Ca
CaEnciu, M.*; Liu, H. N.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Nowacki, F.*; 緒方 一介*; Poves, A.*; 吉田 数貴; Achouri, N. L.*; 馬場 秀忠*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 129(26), p.262501_1 - 262501_7, 2022/12
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:86.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary) 230MeV/nucleonでの
230MeV/nucleonでの Caからの中性子ノックアウト反応が
Caからの中性子ノックアウト反応が 線分光と行われ、
線分光と行われ、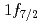 と
と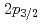 軌道からの中性子ノックアウト反応の運動量分布が測定された。断面積は
軌道からの中性子ノックアウト反応の運動量分布が測定された。断面積は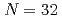 の閉殻と整合し、Ca同位体での
の閉殻と整合し、Ca同位体での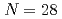 と
と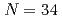 閉殻と同程度に強い閉殻であることが確認された。運動量分布の分析から
閉殻と同程度に強い閉殻であることが確認された。運動量分布の分析から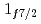 と
と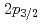 軌道の平均二乗根半径の差は0.61(23)fmと決定され、これはmodified-shell-modelによる予言の0.7fmと整合した。これは、中性子過剰なCa同位体での
軌道の平均二乗根半径の差は0.61(23)fmと決定され、これはmodified-shell-modelによる予言の0.7fmと整合した。これは、中性子過剰なCa同位体での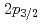 軌道半径が大きいことが、中性子数にしたがって線形的に荷電半径が増える意外な現象の原因であることを示唆している。
軌道半径が大きいことが、中性子数にしたがって線形的に荷電半径が増える意外な現象の原因であることを示唆している。
Rodriguez, D.; 小泉 光生; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference and Room Temperature Semiconductor Detector Conference (2022 IEEE NSS MIC RTSD) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/12
Under the MEXT subsidy to improve nuclear security related activity, we present our latest analytical development of delayed gamma spectroscopic (DGS) analysis for nuclear safeguards. We show the latest results from the ISCN DGS Monte Carlo and comparisons with measured spectra. We highlight differences with other simulation codes, which highlights discrepancies in fission yields from nuclear data and our future direction to improve this for optimal safeguards measurements and reduced uncertainty. We will also summarize how the analysis will be applied with a new instrument designed for small samples for validation of the DGS technique, as well as how this can be applied to full assemblies and alternative fuel cycles.
Rodriguez, D.; 小泉 光生; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音
第43回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2022/11
Under the MEXT subsidy to promote the development of nuclear security related activities, we present our latest delayed gamma-ray spectroscopy analysis and instrument developments. We will highlight important past results, current activities, and future plans.
Rossi, F.; 小泉 光生; Rodriguez, D.; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference and Room Temperature Semiconductor Detector Conference (2022 IEEE NSS MIC RTSD) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2022/11
To address challenges in the safeguard field for the verification of mixed nuclear materials, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency is developing the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopy non-destructive assay technique. Minimally, this technique requires an external source to induce fission in the sample and a gamma-ray detector to collect the high-energy gamma rays emitted from the decay of fission products. In the development of this technique, deuterium-deuterium neutron generators will replace  Cf as the external neutron source. The emitted neutrons are then slowed down in the thermal energy range to enhance the delayed gamma-ray signature coming from the fissile nuclides in the sample. The fission product delayed gamma rays with energy above 3 MeV are then collected with a detector located away from the irradiation position to avoid neutron damage. The collected spectrum is then analyzed, and the peak ratios are used to verify the initial composition of the fissile nuclides. Further, source monitors are required to normalize for the source emission to estimate the fissile mass of the sample. In this work, we will first describe our latest development in designing a delayed gamma-ray spectrometer for small mixed nuclear material samples. We will present latest results obtained from activation experiment and neutron detector characterization. Finally, we will present the usage of a new transfer system designed, fabricated, and tested at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency laboratories. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like". This work was done under the agreement between JAEA and EURATOM in the field of nuclear material safeguards research and development.
Cf as the external neutron source. The emitted neutrons are then slowed down in the thermal energy range to enhance the delayed gamma-ray signature coming from the fissile nuclides in the sample. The fission product delayed gamma rays with energy above 3 MeV are then collected with a detector located away from the irradiation position to avoid neutron damage. The collected spectrum is then analyzed, and the peak ratios are used to verify the initial composition of the fissile nuclides. Further, source monitors are required to normalize for the source emission to estimate the fissile mass of the sample. In this work, we will first describe our latest development in designing a delayed gamma-ray spectrometer for small mixed nuclear material samples. We will present latest results obtained from activation experiment and neutron detector characterization. Finally, we will present the usage of a new transfer system designed, fabricated, and tested at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency laboratories. This work is supported by MEXT under the subsidy for the "promotion for strengthening nuclear security and the like". This work was done under the agreement between JAEA and EURATOM in the field of nuclear material safeguards research and development.
Rodriguez, D.; 小泉 光生; Rossi, F.; 高橋 時音; Abbas, K.*; Nonneman, S.*; Pedersen, B.*; Oberstedt, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Proceedings of International Safeguards; Reflecting on the Past and Anticipating the Future, 7 Pages, 2022/10
Under the MEXT subsidy to develop nuclear security, the ISCN is investigating the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopic analysis technique to evaluate mixed nuclear materials. Primarily we are focusing on developing the analysis for any form of mixed nuclear material, but dominantly used nuclear fuel that is challenging due to the long-lived fission products and minor actinides hiding the U and Pu signatures. We describe the analysis we are developing and the associated instrumentation to interrogate the sample. We show that this can be applied to small samples and assemblies, as well as alternative fuel cycle materials.
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; 小泉 光生; Nonneman, S.*; Oberstedt, S.*; Pedersen, B.*; Rossi, F.; Schillebeeckx, P.*; 高橋 時音
Proceedings of INMM 63rd Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/09
Under the MEXT subsidy to develop nuclear security related technology, we present the overview and ISCN analysis development of the Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopic Analysis project. We summarize the past analysis and instrumentation results and highlight how this affects the evaluation of fissile nuclides in spent nuclear fuel. We further discuss the direction of the third development phase.