Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
志賀 基之; Thomsen, B.; 君塚 肇*
Physical Review B, 109(5), p.054303_1 - 054303_12, 2024/02
パラジウム中の水素の中性子非弾性散乱スペクトルを有限温度での核量子効果を考慮して計算した。経路積分に基づく半古典分子動力学と機械学習ポテンシャルを組合せた計算手法を用いた。計算されたスペクトルは、水素原子の振動励起の基本波と第一高調波に対応するピークの位置と強度に関して、実験スペクトルとよく一致した。古典分子動力学法との比較から、中性子非弾性散乱スペクトルにおいて核量子効果が本質的な役割を果たしていることが示された。
志賀 基之; Thomsen, B.; 永井 佑紀
アンサンブル, 25(4), p.303 - 310, 2023/10
並列分子シミュレーションソフトウェア「PIMD」を紹介する。第一原理経路積分分子動力学による水の構造、リングポリマー分子動力学による金属中水素の量子拡散、超伝導体の機械学習ポテンシャル作成とフォノン物性、メタダイナミクスによる多価アルコール脱水反応などの具体例を通じて、その使用法を解説する。
君塚 肇*; Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
Journal of Physics; Energy (Internet), 4(3), p.034004_1 - 034004_13, 2022/07
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:75.5(Energy & Fuels)パラジウム-水素系の人工ニューラルネットワークに基づく原子間ポテンシャルを開発するとともに、パラジウム結晶中の水素同位体の量子拡散について、経路積分分子動力学計算を行った。50-1500Kの広い温度範囲で軽水素と重水素の拡散係数を計算し、低温と高温における拡散機構の違いを明らかにした。
 path integral simulations
path integral simulationsThomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 24(18), p.10851 - 10859, 2022/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:16.81(Chemistry, Physical)The heavy hydrogen isotopes D and T are found in trace amounts in water, and they can when their concentration rises play an intricate role in modulating the physical properties of the liquid. We present an analysis of the microscopic structures of ambient light water (H O(l)), heavy water(D
O(l)), heavy water(D O(l)), T
O(l)), T O(l), HDO(aq) and HTO(aq) studied by
O(l), HDO(aq) and HTO(aq) studied by  path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD). Unlike previous
path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD). Unlike previous  PIMD investigations of H
PIMD investigations of H O(l) and D
O(l) and D O(l) [Chen et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2003, 91, 215503] [Machida et al., J. Chem. Phys., 2017, 148, 102324] we do find that D
O(l) [Chen et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2003, 91, 215503] [Machida et al., J. Chem. Phys., 2017, 148, 102324] we do find that D O(l) is more structured than H
O(l) is more structured than H O(l), as is predicted by experiment. The agreement between experiment and our simulation for H
O(l), as is predicted by experiment. The agreement between experiment and our simulation for H O(l) and D
O(l) and D O(l) allows us to accurately predict intra- and intermolecular structures of T
O(l) allows us to accurately predict intra- and intermolecular structures of T O(l) HDO(aq) and HTO(aq). T
O(l) HDO(aq) and HTO(aq). T O(l) is found to have a similar intermolecular structure to that of D
O(l) is found to have a similar intermolecular structure to that of D O(l), while the intramolecular structure is more compact, giving rise to a smaller dipole moment that that if H
O(l), while the intramolecular structure is more compact, giving rise to a smaller dipole moment that that if H O(l) and D
O(l) and D O(l). For the mixed isotope species, HDO(aq) and HTO(aq), we find smaller dipole moments and less hydrogen bonds when compared with the pure species H
O(l). For the mixed isotope species, HDO(aq) and HTO(aq), we find smaller dipole moments and less hydrogen bonds when compared with the pure species H O and D
O and D O. We can attribute this effect to the relative compactness of the mixed isotope species, which results in a lower dipole moment when compared to that of the pure species.
O. We can attribute this effect to the relative compactness of the mixed isotope species, which results in a lower dipole moment when compared to that of the pure species.
 study of nuclear quantum effects on sub- and supercritical water
study of nuclear quantum effects on sub- and supercritical waterThomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
Journal of Chemical Physics, 155(19), p.194107_1 - 194107_11, 2021/11
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:52.59(Chemistry, Physical)The structures of water in the ambient, sub-, and supercritical conditions at various densities were studied systematically by  path integral molecular dynamics simulations. It was found that the nuclear quantum effects (NQEs) have significant impact on the structure of hydrogen bonds in close contact, not only in the ambient condition but also in the sub-, and supercritical conditions. The NQEs on the structure beyond the hydrogen bond contact are important in ambient water, but not much for water in the sub-, and supercritical conditions. The NQEs are furthermore important for determining the number of hydrogen bonds in the ambient conditions, this role is however diminished in the sub- and supercritical conditions. The NQEs does nevertheless show their importance in determining the intramolecular structure of water and the close contact structures of the hydrogen bonds, even at sub- and supercritical conditions. Using the RPBE-D3 functional, the computed radial distribution functions for the ambient water are in excellent agreement with experimental data, upgrading our previous results using the BLYP-D2 functional [Machida, et al., J. Chem. Phys. 148, 102324 (2018)]. The computed radial distribution functions for water in the sub- and supercritical conditions were carefully compared with experiment. In particular, we found that the first peak in hydrogen pair distribution functions matches only when the NQEs are taken into account.
path integral molecular dynamics simulations. It was found that the nuclear quantum effects (NQEs) have significant impact on the structure of hydrogen bonds in close contact, not only in the ambient condition but also in the sub-, and supercritical conditions. The NQEs on the structure beyond the hydrogen bond contact are important in ambient water, but not much for water in the sub-, and supercritical conditions. The NQEs are furthermore important for determining the number of hydrogen bonds in the ambient conditions, this role is however diminished in the sub- and supercritical conditions. The NQEs does nevertheless show their importance in determining the intramolecular structure of water and the close contact structures of the hydrogen bonds, even at sub- and supercritical conditions. Using the RPBE-D3 functional, the computed radial distribution functions for the ambient water are in excellent agreement with experimental data, upgrading our previous results using the BLYP-D2 functional [Machida, et al., J. Chem. Phys. 148, 102324 (2018)]. The computed radial distribution functions for water in the sub- and supercritical conditions were carefully compared with experiment. In particular, we found that the first peak in hydrogen pair distribution functions matches only when the NQEs are taken into account.
 path integral molecular dynamics
path integral molecular dynamicsThomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
Journal of Chemical Physics, 154(8), p.084117_1 - 084117_10, 2021/02
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:64.31(Chemistry, Physical)第一原理経路積分分子動力学シミュレーションにより、室温条件での水の同位体置換体の酸性度定数に対する核量子効果を計算した。この手法は、実験的に測定された液体D Oの酸性度定数を再現するだけでなく、希少性のために不明な液体T
Oの酸性度定数を再現するだけでなく、希少性のために不明な液体T Oや、HDOおよびHTO水溶液の酸性度定数の理論的予測も可能にする。計算結果は、核量子効果が酸性度定数の絶対的評価において不可欠な役割を果たすことを示している。
Oや、HDOおよびHTO水溶液の酸性度定数の理論的予測も可能にする。計算結果は、核量子効果が酸性度定数の絶対的評価において不可欠な役割を果たすことを示している。
Thomsen, B.
no journal, ,
We present a method for using general fit basis functions for fitting molecular Potential energy surfaces (PES), the method allows for both linear and non-linear optimization of the functional form. It was found that by using Morse oscillators for fitting the PES of Imidazole (C N
N H
H ) significantly fewer electronic structure calculations were needed for an accurate description of the PES. The method thus both allows for increased flexibility and computational savings when calculating the PES.
) significantly fewer electronic structure calculations were needed for an accurate description of the PES. The method thus both allows for increased flexibility and computational savings when calculating the PES.
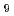 O
O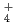 Infra-Red spectrum through clustering of path integral molecular dynamics trajectories
Infra-Red spectrum through clustering of path integral molecular dynamics trajectoriesThomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
We present the IR spectrum of the protonated water cluster H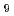 O
O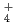 calculated by using the Weight Averaged Approach (WAA), where the weights are found by clustering the structures found in a path integral molecular dynamics simulation. The WAA method was used to model the motions of nine low lying cluster relaxation modes in the protonated water cluster, which we were not able to include in a previous calculation of the spectrum of this cluster. It is expected that this procedure will result in a better reproduction of the broadening of the IR spectrum and might reveal the nature of one of the missing vibrational bands in the previous calculation.
calculated by using the Weight Averaged Approach (WAA), where the weights are found by clustering the structures found in a path integral molecular dynamics simulation. The WAA method was used to model the motions of nine low lying cluster relaxation modes in the protonated water cluster, which we were not able to include in a previous calculation of the spectrum of this cluster. It is expected that this procedure will result in a better reproduction of the broadening of the IR spectrum and might reveal the nature of one of the missing vibrational bands in the previous calculation.
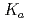 (H
(H O) and p
O) and p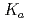 (D
(D O) using path integral molecular dynamics
O) using path integral molecular dynamicsThomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
We present the p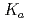 of water and phenol in bulk and water solution respectively calculated using path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) and ab-initio molecular dynamics (AIMD). The PIMD method offers the advantage of modeling the quantum effect of the protons, thereby offering a larger accuracy over the AIMD. Furthermore we study the results of isotope exchange from hydrogen to deuterium in the two systems, and effect not captured by AIMD.
of water and phenol in bulk and water solution respectively calculated using path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) and ab-initio molecular dynamics (AIMD). The PIMD method offers the advantage of modeling the quantum effect of the protons, thereby offering a larger accuracy over the AIMD. Furthermore we study the results of isotope exchange from hydrogen to deuterium in the two systems, and effect not captured by AIMD.
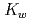 of subcritical and critical H
of subcritical and critical H O and D
O and D O
OThomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
In this study we seek to calculate the p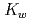 of Sub- and Critical water using Path Integral Molecular Dynamics (PIMD). Using this method, we are able to capture both the dynamical effect of solvent relaxation and the isotope substitution effect. This makes the method ideal for studying the large change in p
of Sub- and Critical water using Path Integral Molecular Dynamics (PIMD). Using this method, we are able to capture both the dynamical effect of solvent relaxation and the isotope substitution effect. This makes the method ideal for studying the large change in p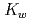 water undergoes as the temperature and pressure is increased towards supercritical levels, and the isotope effect on these changes.
water undergoes as the temperature and pressure is increased towards supercritical levels, and the isotope effect on these changes.
Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
The autoionization constant (pKw) of water is the most fundamental part of conventional acid-base chemistry and it has been the subject of countless studies, the nuclear quantum effects (NQEs) on this fundamental property have however not previously been studied. In this study we use coordination number (CN) constrained molecule dynamics (MD) and path integral MD (PIMD) to calculate the pKw of water and its isotopologs. The potential energy of water was here described by either an empirical forcefield (OSS2), semi-empirical tight binding density functional theory (DFTB) or ab-initio density functional theory (DFT).
Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
In a recently published paper we explore the NQEs on the autoionization constant (pK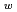 ) of water. We do this by using coordination number restrained path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD), which allows for molecular dynamics (MD) including NQEs in an ab-initio fashion. We employ two different methods for calculating the pK
) of water. We do this by using coordination number restrained path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD), which allows for molecular dynamics (MD) including NQEs in an ab-initio fashion. We employ two different methods for calculating the pK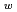 of water using the calculated free energy curve of proton dissociation from a water molecule. The first is a two- state model which enables the calculation of the quantitative pK
of water using the calculated free energy curve of proton dissociation from a water molecule. The first is a two- state model which enables the calculation of the quantitative pK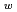 of water. The second, based on the work of M. Sprik, presents a method for calculate the pK
of water. The second, based on the work of M. Sprik, presents a method for calculate the pK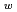 of the water isotopologs relative to that of water. The electronic potential is in our calculations described by an empirical force field (OSS2), the semi-empirical Density Functional based Tight Binding (DFTB), and ab-initio density functional theory (DFT). Our ongoing research focuses on the NQEs in water at standard, sub critical, and super critical conditions. This builds on a previous study, which found that at room temperature the NQEs in the hydrogen bonds enabled a population of hydrogen in the predissociation region of the O-H radial distribution function (RDF). The current calculations of the O-H RDF using PIMD shown in Figure 1 display an excellent agreement with experimental data as well as highlighting the density only present in the simulations including the NQEs. Our initial results indicate that the NQEs remain the sole source of predissociative density in the O-H RDF even at sub and super critical conditions, underlining the necessity of modelling NQEs in a calculation targeting the quantitative value of waters pK
of the water isotopologs relative to that of water. The electronic potential is in our calculations described by an empirical force field (OSS2), the semi-empirical Density Functional based Tight Binding (DFTB), and ab-initio density functional theory (DFT). Our ongoing research focuses on the NQEs in water at standard, sub critical, and super critical conditions. This builds on a previous study, which found that at room temperature the NQEs in the hydrogen bonds enabled a population of hydrogen in the predissociation region of the O-H radial distribution function (RDF). The current calculations of the O-H RDF using PIMD shown in Figure 1 display an excellent agreement with experimental data as well as highlighting the density only present in the simulations including the NQEs. Our initial results indicate that the NQEs remain the sole source of predissociative density in the O-H RDF even at sub and super critical conditions, underlining the necessity of modelling NQEs in a calculation targeting the quantitative value of waters pK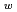 . The size of the NQEs does also vary according to temperature, which may explain the part of the strong temperature/pressure dependence of the pK
. The size of the NQEs does also vary according to temperature, which may explain the part of the strong temperature/pressure dependence of the pK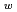 of water.
of water.
Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
We report the latest reports from our theoretical investigation of nuclear quantum effects (NQEs) in water, including the effects found in sub- and supercritical water. Classical molecular dynamics (MD) does not take these effects into account, and we therefore employ path integral MD (PIMD) and ab initio force fields to create a highly accurate model of the equilibrium properties of water. One example of the NQEs would be the changes in structure observed when protium (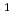 H) is substituted for deuterium (D) or tritium (T).
H) is substituted for deuterium (D) or tritium (T).
 study of nuclear quantum effects in water
study of nuclear quantum effects in waterThomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
We present our recent findings on nuclear quantum effects in water from  path integral molecular dynamics simulations. This includes both the temperature/state dependence when going from ambient to sub- and supercritical water, and the isotope substitution effect in going from H
path integral molecular dynamics simulations. This includes both the temperature/state dependence when going from ambient to sub- and supercritical water, and the isotope substitution effect in going from H O to D
O to D O, T
O, T O and HDO(aq) and HTO(aq).
O and HDO(aq) and HTO(aq).
Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
We report the results of our recent studies of ambient water and its isotopologues using ab initio path integral molecular dynamics simulations. These types of simulations allow us to describe the nuclear quantum effects (NQEs) with high accuracy which naturally manifests as the differences in properties and structure of H O, D
O, D O and other isotopologues of water. Here the inclusion of NQEs causes the liquid to be less structured that results from classical molecular dynamics simulations. With increasing isotope mass, going from H
O and other isotopologues of water. Here the inclusion of NQEs causes the liquid to be less structured that results from classical molecular dynamics simulations. With increasing isotope mass, going from H O to D
O to D O, we find in agreement with experimental observation that the liquid becomes more structured. For water molecules with mixed isotopologue composition, HDO and HTO, in H
O, we find in agreement with experimental observation that the liquid becomes more structured. For water molecules with mixed isotopologue composition, HDO and HTO, in H O we however find that the molecules and their surroundings are less structured. As water is heated up and reaches sub- and supercritical conditions the long-range modulation of the structure due to NQEs disappears. The short-range effects on especially the hydrogen bounded structures remain even at high temperatures. We will also briefly discuss our ongoing efforts to describe the dynamics of the ambient liquid, where both an explicit dependence of the mass of the particles and NQEs are important.
O we however find that the molecules and their surroundings are less structured. As water is heated up and reaches sub- and supercritical conditions the long-range modulation of the structure due to NQEs disappears. The short-range effects on especially the hydrogen bounded structures remain even at high temperatures. We will also briefly discuss our ongoing efforts to describe the dynamics of the ambient liquid, where both an explicit dependence of the mass of the particles and NQEs are important.
Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
We report the structure and dynamics of ambient water and its isotopologues including nuclear quantum effects (NQEs) using ab initio path integral methods. For the pure isotopologues, light (H O(l)) and heavy (D
O(l)) and heavy (D O(l)) water, and T
O(l)) water, and T O(l), we find that the heavier isotopologues are more ordered due to more hydrogen bonds being formed in the heavier isotopologues liquid phases. The mixed isotope species, HDO(aq) and HTO(aq), have less structured hydration shells and form fewer hydrogen bonds than H
O(l), we find that the heavier isotopologues are more ordered due to more hydrogen bonds being formed in the heavier isotopologues liquid phases. The mixed isotope species, HDO(aq) and HTO(aq), have less structured hydration shells and form fewer hydrogen bonds than H O(l). This can be attributed to the relative compactness and asymmetry of the mixed isotope species, which results in a lower dipole moment when compared to that of the pure species. The translational and rotational dynamics of H
O(l). This can be attributed to the relative compactness and asymmetry of the mixed isotope species, which results in a lower dipole moment when compared to that of the pure species. The translational and rotational dynamics of H O(l) and D
O(l) and D O(l) are slowed down by the inclusion of NQEs in the simulations, which is correlated with an extension of hydrogen bond lifetimes in simulations including NQEs.
O(l) are slowed down by the inclusion of NQEs in the simulations, which is correlated with an extension of hydrogen bond lifetimes in simulations including NQEs.
Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
Nuclear quantum effects (NQEs) are important for the description of the hydrogen bonds in water, and their inclusion in molecular dynamics simulations of the liquid state is therefore essential for the accurate modeling of the structure. This remains true even under the sub- and supercritical conditions, i.e. water in the liquid or fluid state at high temperature and under high pressure. The exchange of the protium to deuterium or tritium has a large effect on the size of the NQEs, as it is found that light water (H O) forms a more disordered liquid phase than that of heavy water (D
O) forms a more disordered liquid phase than that of heavy water (D O). For the mixed isotopologue species, HDO and HTO, dissolved in water we find a less structured hydration shells and fewer hydrogen bonds than in light water. The translational and rotational dynamics of heavy water are slowed down compared to light water, which is correlated with the extension of hydrogen bond lifetimes as protium is exchanged for deuterium.
O). For the mixed isotopologue species, HDO and HTO, dissolved in water we find a less structured hydration shells and fewer hydrogen bonds than in light water. The translational and rotational dynamics of heavy water are slowed down compared to light water, which is correlated with the extension of hydrogen bond lifetimes as protium is exchanged for deuterium.
Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
量子力学のファインマン経路定式化に基づく経路積分分子動力学(PIMD)とその関連手法は、バルク相物質における核量子効果を直接モデリングする方法を提供する。しかし、これらの手法の各タイムステップでは、第一原理レベルで複数の電子構造エネルギー、勾配、応力ベクトルを評価する必要がある。そのため、第一原理レベルで追求するには、非常に計算コストがかかる。最近、機械学習ポテンシャル(MLP)が、PIMD法のコストを下げ、長時間のダイナミクスを第一原理精度で研究できる方法として提案されている。本発表では、パラジウム金属中の水素拡散を複数の温度にわたって研究した結果を紹介する。また、MLPを水とその同位体のPIMD研究に適用するための現在進行中の取り組みについても説明する。
Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
核量子効果(NQEs)が水の構造とダイナミクスの性質にどのような影響を与えるかを調べるための我々の進行中の取り組みについて報告する。NQEをモデル化するために、我々は経路積分分子動力学法(PIMD)を採用しているが、この方法ではNQEをモデル化するために各タイムステップで数回の第一原理計算を行う必要がある。シミュレーションをより計算コストのかからないものにするため、現在、機械学習ポテンシャル(MLP)を用いて系を記述することに取り組んでいる。このMLPは、水の同位体間の移行が可能であり、水の相図全体にわたって機能するはずである。ここでは、水のMLP記述を改良するための進行中の作業と、このMLPを使ったPIMDシミュレーションの結果について最新情報を提供する。
Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
no journal, ,
水は核量子効果(NQE)の影響を強く受ける液体であり、その構造や性質は、軽水(H O)と重水(D
O)と重水(D O)の間で観察される違いからも明らかである。これらの違いは、いわゆる経路積分分子動力学(PIMD)シミュレーションを行うことによって理論的に明らかになる。過去には、このような研究を行うために第一原理DFTベースのポテンシャルを使用してきたが、これは大きな計算コストを伴う。ここでは、DFTの代わりに機械学習ポテンシャル(MLP)を使用することで、計算コストを削減し、軽水と重水のシミュレーションをより長く、より収束させることを目指す。
O)の間で観察される違いからも明らかである。これらの違いは、いわゆる経路積分分子動力学(PIMD)シミュレーションを行うことによって理論的に明らかになる。過去には、このような研究を行うために第一原理DFTベースのポテンシャルを使用してきたが、これは大きな計算コストを伴う。ここでは、DFTの代わりに機械学習ポテンシャル(MLP)を使用することで、計算コストを削減し、軽水と重水のシミュレーションをより長く、より収束させることを目指す。