Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ramadhan, R. S.*; Glaser, D.*; 祖山 均*; Kockelmann, W.*; 篠原 武尚; Pirling, T.*; Fitzpatrick, M. E.*; Tremsin, A. S.*
Acta Materialia, 239, p.118259_1 - 118259_12, 2022/10
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:65.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mechanical surface treatment technologies such as laser peening and cavitation peening require detailed characterization, including residual stress analysis, to optimize their processing parameters. Recent developments at neutron facilities allow non-destructive 2-dimensional residual strain mapping through Bragg edge imaging. The present work highlights the application of Bragg edge neutron imaging for the study of mechanical surface treatments, through determination of lattice spacing distributions by energy-resolved radiography. Through three different examples, the unique capabilities of the method are demonstrated, particularly for providing near surface residual strain maps within samples with complex geometries with relatively high spatial resolution. By providing a comparison with X-ray diffraction and neutron diffraction results, the present work emphasizes the potential of Bragg edge neutron imaging as a tool for surface treatment research.
Tremsin, A. S.*; Gao, Y.*; Makinde, A.*; Bilheux, H. Z.*; Bilheux, J. C.*; An, K.*; 篠原 武尚; 及川 健一
Additive Manufacturing, 46, p.102130_1 - 102130_20, 2021/10
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:60.07(Engineering, Manufacturing)Microstructures produced by Additive Manufacturing (AM) techniques determine many characteristics of components where these materials are used. Residual stress and texture are among those characteristics, which need to be optimized. In this study, we employ energy-resolved neutron imaging to investigate, non-destructively, the uniformity of texture and to map the distribution of strain due to residual stress in Inconel 625 samples. The samples used in this study were printed by a direct metal laser melting additive manufacturing technique. Strain and texture variation are measured at room temperature as well as their changes during annealing at 700 C and 875
C and 875 C in a vacuum furnace. The uniformity of crystalline plane distribution, from which texture can be inferred, is imaged with sub-mm spatial resolution for the entire sample area.
C in a vacuum furnace. The uniformity of crystalline plane distribution, from which texture can be inferred, is imaged with sub-mm spatial resolution for the entire sample area.
Tremsin, A. S.*; Bilheux, H. Z.*; Bilheux, J. C.*; 篠原 武尚; 及川 健一; Gao, Y.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1009, p.165493_1 - 165493_12, 2021/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:43.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)The investigation of microstructure of crystalline materials is one of the possible and frequently used applications of energy-resolved neutron imaging. The position of Bragg edges is defined by sharp changes in neutron transmission and can thus be determined by the measurement of the transmission spectra as a function of neutron wavelength. The accuracy of this measurement depends on both the data analysis technique and the quality of the measured spectra. While the optimization of reconstruction methods was addressed in several previous studies, here we introduce an important prerequisite when aiming for high resolution Bragg edge strain imaging - a well calibrated flight path across the entire field of view (FOV). Compared to e.g. powder diffraction, imaging often uses slightly different geometries and hence requires a calibration for each particular setup. We herein show the importance of this calibration across the entire FOV in order to determine the instrumental error correction for pulsed neutron beamlines.
Busi, M.*; Kalentics, N.*; Morgano, M.*; Griffiths, S.*; Tremsin, A. S.*; 篠原 武尚; Log , R.*; Leinenbach, C.*; Strobl, M.*
, R.*; Leinenbach, C.*; Strobl, M.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11, p.14919_1 - 14919_9, 2021/07
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:33.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Laser powder bed fusion is an additive manufacturing technique extensively used for the production of metallic components. Despite this process has reached a status at which parts are produced with mechanical properties comparable to those from conventional production, it is still prone to introduce detrimental tensile residual stresses towards the surfaces along the building direction, implying negative consequences on fatigue life and resistance to crack formations. Laser shock peening (LSP) is a promising method adopted to compensate tensile residual stresses and to introduce beneficial compressive residual stress on the treated surfaces. Using neutron Bragg edge imaging, we perform a parametric study of LSP applied to 316L steel samples produced by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing.
Busi, M.*; Kalentics, N.*; Morgano, M.*; Griffiths, S.*; Tremsin, A. S.*; 篠原 武尚; Log , R.*; Leinenbach, C.*; Strobl, M.*
, R.*; Leinenbach, C.*; Strobl, M.*
Additive Manufacturing, 39, p.101848_1 - 101848_9, 2021/03
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:69.98(Engineering, Manufacturing)Laser powder bed fusion is an efficient technique for additive manufacturing of metallic materials. The quality of the material produced depends on the optimization of a large range of build parameters and the complex thermo- mechanical build process is prone to inducing detrimental material features such as porosity and residual stresses negatively affecting fatigue resistance and lifetime. Here we apply neutron Bragg edge radiography in a para- metric study on printing 316L steel. The parameters concerned are the laser scanning speed and strategy as well as the optional use of support structures. Analyses of the full field single shot wavelength-resolved Bragg edge radiography data enables to characterize local density inhomogeneities, as well as cracks, based on the long wavelength tail of the spectrum and variations of the stress field but also textural features based on the Bragg edge pattern. It is found that in the performed study not only respective differences in the residual stresses due to parameter variation are manifesting but also systematic irregularities due to machine imperfections (e.g. issues with the powder coater) are observed in the printed samples. The study supports the use of the parallel scanning strategy without supports and with the lower utilized scanning speed.
 observation and analysis of solid-state diffusion and liquid migration in a crystal growth system; A Segregation-driven diffusion couple
observation and analysis of solid-state diffusion and liquid migration in a crystal growth system; A Segregation-driven diffusion coupleTremsin, A. S.*; Perrodin, D.*; Losko, A. S.*; Vogel, S. C.*; 篠原 武尚; 及川 健一; Bizarri, G. A.*; Bourret, E. D.*; Peterson, J. H.*; Wang, K. P.*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 186, p.434 - 442, 2020/03
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:32.05(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Energy-resolved neutron imaging is employed for  measurements of dopant transport in a simple experiment performed before the crystal growth of the scintillator BaBrCl:5%Eu via a vertical gradient freeze technique. During a stabilization period preceding growth, we observed the diffusion of Eu from the solid phase into the melt over a period of approximately 4 h. Comparing the measured centerline concentration profile with a mathematical model for the system, we estimate the solid-state diffusivity of Eu in BaBrCl as
measurements of dopant transport in a simple experiment performed before the crystal growth of the scintillator BaBrCl:5%Eu via a vertical gradient freeze technique. During a stabilization period preceding growth, we observed the diffusion of Eu from the solid phase into the melt over a period of approximately 4 h. Comparing the measured centerline concentration profile with a mathematical model for the system, we estimate the solid-state diffusivity of Eu in BaBrCl as 
 = 1.9
= 1.9  10
10 m
m /s and an upper limit for the liquid-phase diffusivity of Eu in the melt as
/s and an upper limit for the liquid-phase diffusivity of Eu in the melt as 
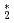 = 2.5
= 2.5  10
10 m
m /s, at temperatures near the melting point. We compare this experiment, where diffusion is driven by a concentration discontinuity arising from segregation, to the classical diffusion couple technique.
/s, at temperatures near the melting point. We compare this experiment, where diffusion is driven by a concentration discontinuity arising from segregation, to the classical diffusion couple technique.
Hendriks, J. N.*; Gregg, A. W. T.*; Jackson, R. R.*; Wensrich, C. M.*; Wills, A.*; Tremsin, A. S.*; 篠原 武尚; Luzin, V.*; Kirstein, O.*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 3(11), p.113803_1 - 113803_11, 2019/11
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:46.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper presents a proof-of-concept demonstration of triaxial strain tomography from Bragg-edge neutron imaging within a three-dimensional sample. Bragg-edge neutron transmission can provide high-resolution images of the average through thickness strain within a polycrystalline material. This poses an associated rich tomography problem which seeks to reconstruct the full triaxial strain field from these images. The presented demonstration is an important step toward solving this problem, and toward a technique capable of studying the residual strain and stress within engineering components. A Gaussian process based approach is used that ensures the reconstruction satisfies equilibrium and known boundary conditions.
Sales, M.*; 篠原 武尚; S rensen, M. K.*; Knudsen, E. B.*; Tremsin, A.*; Strobl, M.*; Schmidt, S.*
rensen, M. K.*; Knudsen, E. B.*; Tremsin, A.*; Strobl, M.*; Schmidt, S.*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 52(20), p.205001_1 - 205001_6, 2019/05
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:42.34(Physics, Applied)Three dimensional polarimetric neutron tomography is an emerging method for nondestructive investigation of magnetic field strength and direction distribution in three dimensions. It utilises the Larmor precession of the neutron spin in the presence of an external magnetic field and has so far been restricted to the measurement of magnetic fields weak enough to keep the neutron precession below the phase-wrapping limit at 180 degree. Through the use of polychromatic time-of-flight information in combination with an iterative forward model reconstruction algorithm we have gone beyond this limit, thereby vastly broadening the potential of the technique. We present the reconstructed magnetic field of a measured current carrying solenoid as a proof-of-principle for this novel method, as well as successfully applying the method to a simulated data set of a sample consisting of multiple magnetic domains.
Tremsin, A. S.*; 篠原 武尚; 及川 健一; Li, J.*; Monteiro, P. J. M.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 927, p.174 - 183, 2019/05
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:66.26(Instruments & Instrumentation)In this study we compare the accuracy of water thickness reconstruction from two types of neutron imaging experiments: neutron radiography with a white beam spectrum and energy-resolved neutron imaging. The results of present study indicate that the accuracy of water mapping appeared to be comparable within the 2% - 4% error in our experiments dominated by non-optimized calibration of background signal. The accuracy of water thickness reconstruction was verified with a calibration step wedge sample for both imaging modalities. We also demonstrate the applicability of this technique for the studies of water absorptivity and porosity of ancient Roman concrete samples extracted from Cosa and Portus Traiani sites. These reconstruction methods are not only limited to quantification of water or hydrogencontaining substances, but can be implemented to any other material with relatively high neutron attenuation.
Tremsin, A. S.*; Ganguly, S.*; Meco, S. M.*; Pardal, G.*; 篠原 武尚; Bruce Feller, W.*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(4), p.1130 - 1140, 2016/08
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:72.31(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)A nondestructive study of the internal structure and compositional gradient of dissimilar metal-alloy welds through energy-resolved neutron imaging is described in this paper. The presence of Bragg edges in the measured neutron transmission spectra can be used to characterize the internal residual strain within the samples and some microstructural features, while neutron resonance absorption provides the possibility to map the degree of uniformity in mixing of the participating alloys and intermetallic formation within the welds. This paper demonstrates the potential of neutron energy-resolved imaging to measure all these characteristics simultaneously in a single experiment with sub-mm spatial resolution.
Tremsin, A. S.*; Gao, Y.*; Dial, L. C.*; Grazzi, F.*; 篠原 武尚
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 17(1), p.324 - 336, 2016/07
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:53.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Non-destructive testing techniques based on neutron imaging and diffraction can provide information on the internal structure of relatively thick metal samples (up to several cm), which are opaque to other conventional non-destructive methods. Spatially resolved neutron transmission spectroscopy is an extension of traditional neutron radiography, where multiple images are acquired simultaneously, each corresponding to a narrow range of energy. The analysis of transmission spectra enables studies of bulk microstructures at the spatial resolution comparable to the detector pixel. In this study we demonstrate the possibility of imaging (with about 100  m resolution) distribution of some microstructure properties, such as residual strain, texture, voids and impurities in Inconel 625 samples manufactured with an additive manufacturing method called direct metal laser melting (DMLM).
m resolution) distribution of some microstructure properties, such as residual strain, texture, voids and impurities in Inconel 625 samples manufactured with an additive manufacturing method called direct metal laser melting (DMLM).