Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 他3名*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
The need for lightweight materials with mechanical integrity at ultralow temperatures drives the development of advanced alloys for cryogenic use. Additive manufacturing via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) offers a scalable way to create alloys with tailored properties. Here, we show that LPBF-processed Al10SiMg exhibits a high ultimate tensile strength (395 MPa) and uniform elongation (25%) at 15 K. These enhancements stem from grain refinement, increased geometrically necessary dislocations, and stress partitioning between the Al matrix and the stiffer Si phase, aiding strain accommodation.  neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
neutron diffraction reveals that the Si phase, with its higher yield strength, bears most of the load, while the Al matrix undergoes continuous strain hardening, extending deformation capacity. These results highlight Al10SiMg's promise for cryogenic applications such as hydrogen storage, aerospace, and quantum computing hardware.
Naeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tian, J.*; Kong, H.*; Romero-Resendiz, L.*; Fan, Z.*; Jiang, F.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 924, p.147819_1 - 147819_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Face-centered cubic (fcc) medium-/high-entropy alloys (M/HEAs) typically enhance strength and ductility at cryogenic temperatures via stacking faults, twinning, or martensitic transformation. However, in-situ neutron diffraction on VCoNi MEA at 15 K reveals that strain hardening is driven solely by rapid dislocation accumulation, without these mechanisms. This results in increased yield strength, strain hardening, and fracture strain. The behavior, explained by the Orowan equation, challenges conventional views on cryogenic strengthening in fcc M/HEAs and highlights the role of dislocation-mediated plasticity at low temperatures.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionNaeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Knowles, A. J.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wang, X.-L.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; 他6名*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 916, p.147374_1 - 147374_8, 2024/11
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:57.76(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Heterostructured materials (HSMs) improve the strength-ductility trade-off of alloys, but their cryogenic performance under real-time deformation is unclear. We studied heterostructured CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy via  neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Sun, X.*; Qi, J.*; Liu, P.*; Harjo, S.; 中島 健次; Li, B.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 133(12), p.126701_1 - 126701_6, 2024/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:43.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)It has long been suspected that magnetism could play a vital role in the phase stability of multi- component high-entropy alloys. However, the nature of the magnetic order, if any, has remained elusive. Here, by using elastic and inelastic neutron scattering, we demonstrate evidence of antiferromagnetic order below  80 K and strong spin fluctuations persisting to room temperature in a single-phase face-centered cubic (fcc) CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Despite the chemical complexity, the magnetic structure in CrMnFeCoNi can be described as
80 K and strong spin fluctuations persisting to room temperature in a single-phase face-centered cubic (fcc) CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Despite the chemical complexity, the magnetic structure in CrMnFeCoNi can be described as  -Mn-like, with the magnetic moments confined in alternating (001) planes and pointing toward the
-Mn-like, with the magnetic moments confined in alternating (001) planes and pointing toward the 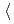 111
111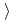 direction. Combined with first-principles calculation results, it is shown that the antiferromagnetic order and spin fluctuations help stabilized the fcc phase in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy.
direction. Combined with first-principles calculation results, it is shown that the antiferromagnetic order and spin fluctuations help stabilized the fcc phase in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy.
Ma, Y.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Sun, X.*; Yang, Z.*; He, F.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 270, p.119822_1 - 119822_13, 2024/05
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:94.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report an in situ neutron diffraction study of 316 L that reveals an extraordinary work-hardening rate (WHR) of  7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite (
7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite ( -to-
-to- ') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the
') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the  '-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the
'-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the  -to-
-to- ' phase transformation was mediated by the
' phase transformation was mediated by the  -martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the
-martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the  phase with the
phase with the  phase.
phase.
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q. H.*; Fang, X.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Ma, Y.*; 舘 幸男
Sedimentary Geology, 465, p.106633_1 - 106633_14, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Geology)Archie's cementation factor, m, is a critical parameter for petrophysical studies, and the value is influenced by several factors such as the shape, type, and size of grains, degrees of diagenesis, and associated pore structure. Using integrated experimental and theoretical approaches, the goal of this study is to obtain the cementation factor of rocks (both reservoir rock and caprock) and assess the impact of diagenesis processes on the values of the cementation factor. Thirteen samples of geologically diverse rocks (six mudstones, four fossiliferous limestones, two marbles, and one sandstone) were selected to achieve these research objectives. Two approaches, the diffusion of gas tracers and the Bosanquet formula calculation using pore-throat sizes from mercury intrusion porosimetry analyses, were used to derive the cementation factors of these rock samples. These rocks were categorized into two groups based on the correlation between average pore-throat diameter and diffusivity, and an exponential-law relationship between the cementation factor and porosity was determined for these sample groups. In addition, thin-section petrography and field emission-scanning electron microscopy observations were utilized to investigate diagenetic processes, with four diagenetic patterns being established: (1) strong compaction, strong cementation, and weak dissolution-diagenesis pattern; (2) weak compaction, medium cementation, and weak dissolution-diagenesis pattern; (3) weak compaction, medium cementation, and strong dissolution-diagenesis pattern; and (4) fracture-matrix pattern. The results indicated that diagenetic processes and microfractures contribute to the variability in the cementation factors in these rock samples.
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; 古府 麻衣子; 中島 健次; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:89.71(Physics, Applied)The desire for intrinsically low lattice thermal conductivity (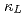 ) in thermoelectrics motivates numerous efforts on understanding the microscopic mechanisms of heat transport in solids. Here, based on theoretical calculations, we demonstrate that
) in thermoelectrics motivates numerous efforts on understanding the microscopic mechanisms of heat transport in solids. Here, based on theoretical calculations, we demonstrate that  -MgAgSb hosts low-energy localized phonon bands and avoided crossing of the rattler modes, which coincides with the inelastic neutron scattering result. Using the two-channel lattice dynamical approach, we find, besides the conventional contribution (
-MgAgSb hosts low-energy localized phonon bands and avoided crossing of the rattler modes, which coincides with the inelastic neutron scattering result. Using the two-channel lattice dynamical approach, we find, besides the conventional contribution ( 70% at 300 K) from particlelike phonons propagating, the coherence contribution dominated by the wavelike tunneling of phonons accounts for
70% at 300 K) from particlelike phonons propagating, the coherence contribution dominated by the wavelike tunneling of phonons accounts for  30% of total
30% of total 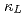 at 300 K. By considering dual contributions, our calculated room-temperature
at 300 K. By considering dual contributions, our calculated room-temperature 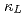 of 0.64 Wm
of 0.64 Wm K
K well agrees with the experimental value of 0.63 Wm
well agrees with the experimental value of 0.63 Wm K
K . More importantly, our computations give a nonstandard
. More importantly, our computations give a nonstandard 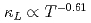 dependence, perfectly explaining the abnormal temperature-trend of
dependence, perfectly explaining the abnormal temperature-trend of 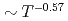 in experiment for
in experiment for  -MgAgSb. By molecular dynamics simulation, we reveal that the structure simultaneously has soft crystalline sublattices with the metavalent bonding and fluctuating liquid-like sublattices with thermally induced large amplitude vibrations. These diverse forms of chemical bonding arouse mixed part-crystal part-liquid state, scatter strongly heat-carrying phonons, and finally produce extremely low
-MgAgSb. By molecular dynamics simulation, we reveal that the structure simultaneously has soft crystalline sublattices with the metavalent bonding and fluctuating liquid-like sublattices with thermally induced large amplitude vibrations. These diverse forms of chemical bonding arouse mixed part-crystal part-liquid state, scatter strongly heat-carrying phonons, and finally produce extremely low 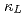 . The fundamental research from this study will accelerate the design of ultralow-
. The fundamental research from this study will accelerate the design of ultralow-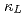 materials for energy-conversion applications.
materials for energy-conversion applications.
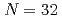
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)理化学研究所RIビームファクトリーにて中性子過剰核 Arビームからの1中性子ノックアウト反応実験を行い、
Arビームからの1中性子ノックアウト反応実験を行い、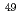 Arのエネルギー準位および分光学的因子を導出した。特に、第一励起状態の
Arのエネルギー準位および分光学的因子を導出した。特に、第一励起状態の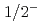 への分光学的因子が大きいことから、始状態の
への分光学的因子が大きいことから、始状態の Arの基底状態において中性子が
Arの基底状態において中性子が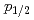 軌道を多く占めていることがわかった。これは、中性子数32がよい魔法数として知られる
軌道を多く占めていることがわかった。これは、中性子数32がよい魔法数として知られる Caとは異なった性質であり、カルシウムからアルゴンへと陽子が2個減ることで閉殻構造が大きく崩れることが明らかになった。
Caとは異なった性質であり、カルシウムからアルゴンへと陽子が2個減ることで閉殻構造が大きく崩れることが明らかになった。
 Sn
Sn
Huang, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Ye, H.*; Bao, S.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Liao, J.*; Cao, S.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; Deng, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(1), p.014434_1 - 014434_9, 2024/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:57.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)TbMn Sn
Sn is a correlated topological magnet with a Mn-based kagome lattice, in which a Chern gap opens at the Dirac point at low temperatures. The magnetic moment direction of the ferrimagnetic order changes from in the kagome plane to the out-of-plane upon cooling, which is essential for generating the Chern gap, but the underlying mechanism for the spin reorientation remains elusive. Here, we investigate the spin-reorientation transition in TbMn
is a correlated topological magnet with a Mn-based kagome lattice, in which a Chern gap opens at the Dirac point at low temperatures. The magnetic moment direction of the ferrimagnetic order changes from in the kagome plane to the out-of-plane upon cooling, which is essential for generating the Chern gap, but the underlying mechanism for the spin reorientation remains elusive. Here, we investigate the spin-reorientation transition in TbMn Sn
Sn using neutron scattering. We provide direct evidence for the spin-reorientation transition and unveil the coexistence of two Tb modes at 200 K. To account for these results, we put forward a model based on SU(N) spin-wave theory, in which there is a temperature evolution of the ground state Tb
using neutron scattering. We provide direct evidence for the spin-reorientation transition and unveil the coexistence of two Tb modes at 200 K. To account for these results, we put forward a model based on SU(N) spin-wave theory, in which there is a temperature evolution of the ground state Tb 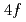 orbitals, driven by the crystalline electric field, single-ion anisotropy, and exchange interactions between Tb and Mn ions. Our findings shed light on the complex magnetism of TbMn
orbitals, driven by the crystalline electric field, single-ion anisotropy, and exchange interactions between Tb and Mn ions. Our findings shed light on the complex magnetism of TbMn Sn
Sn , despite its relatively simple ground state magnetic structure, and provide insights into the mechanisms for tuning magnetic topological materials.
, despite its relatively simple ground state magnetic structure, and provide insights into the mechanisms for tuning magnetic topological materials.
Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Zhang, T.*; Zhao, C.*; Iltaf, K. H.*; Liu, S. Q.*; 深津 勇太
Energy Reports (Internet), 9, p.3661 - 3682, 2023/12
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:64.37(Energy & Fuels)This study evaluates petrophysical properties of representative geological rocks in the context of injectivity, storage space, and caprock integrity for effective utilization and long-term storage of carbon dioxide. A total of 10 geological rocks were selected as representative storage media for consideration as saline aquifers & depleted oil and gas reservoirs, basalts, and cap rocks, as well as utilization in organic-rich shale and coal seams. An integrated suite of laboratory tests, including liquid immersion porosimetry, gas expansion porosimetry, grain size distribution, mercury intrusion porosimetry, and gas diffusion, were performed on these various rock samples. The results exhibit a disparity of petrophysical properties among two broad groups of rocks: rocks selected for possible storage of CO have porosities of
have porosities of  10-25%, permeabilities of
10-25%, permeabilities of  10
10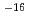 -10
-10 m
m ,
,  m-sized pore-throat size distribution, and mostly good pore connectivity; in contrast, the potential caprocks have porosities of
m-sized pore-throat size distribution, and mostly good pore connectivity; in contrast, the potential caprocks have porosities of  0.5-5%, permeabilities of
0.5-5%, permeabilities of  10
10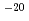 -10
-10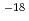 m
m , pore throat sizes of
, pore throat sizes of  50 nm, and probably poorly connected pore networks. An understanding of the measured facets of pore structure and contribution of fractures is also critical in the context of different testing principles and data interpretation of petrophysical analyses, as well as observational scales in the laboratory and field, and therefore reliable confidence of CO
50 nm, and probably poorly connected pore networks. An understanding of the measured facets of pore structure and contribution of fractures is also critical in the context of different testing principles and data interpretation of petrophysical analyses, as well as observational scales in the laboratory and field, and therefore reliable confidence of CO storage and utilization performance. Our work further illustrates the controlling influence of grain size distribution and geological processes on pore size distribution and pore connectivity for a wide range of rock types and lithologies, and particularly presents the extent and behavior of CO
storage and utilization performance. Our work further illustrates the controlling influence of grain size distribution and geological processes on pore size distribution and pore connectivity for a wide range of rock types and lithologies, and particularly presents the extent and behavior of CO gas diffusion with a custom-designed apparatus for a holistic understanding of various petrophysical attributes of widely different geological rocks.
gas diffusion with a custom-designed apparatus for a holistic understanding of various petrophysical attributes of widely different geological rocks.
Ratliff, H.; McGirl, N. A.*; Beach, M. R.*; Castellanos, L. A.*; Clowdsley, M. S.*; Heilbronn, L. H.*; LaTessa, C.*; Norbury, J. W.*; Rusek, A.*; Sivertz, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 544, p.165121_1 - 165121_15, 2023/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Experiments emulating the deep-space radiation environment within an enclosed spacecraft were conducted at the NASA Space Radiation Laboratory; this was achieved by bombarding various combinations of two consecutive thick targets with Galactic Cosmic Ray-like particle beams. While all secondary particles generated in the first of these two targets could be characterized using time-of-flight techniques, characterization of the neutrons produced in the second target, emulating the "back wall" of a spacecraft, required the development and implementation of deconvolution techniques. This work covers this methodology, its validation, and the systematic results present within this benchmark dataset of neutron yields from the secondary target.
 Be ground-state molecular structure using
Be ground-state molecular structure using  Be(
Be(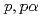 )
) He triple differential reaction cross-section measurements
He triple differential reaction cross-section measurementsLi, P. J.*; Beaumel, D.*; Lee, J.*; Assi , M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; 延与 佳子*; et al.
, M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; 延与 佳子*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(21), p.212501_1 - 212501_7, 2023/11
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Beのクラスター構造を(
Beのクラスター構造を(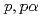 )反応を用いて調査した。三重微分断面積が実験的に測定され、Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R
)反応を用いて調査した。三重微分断面積が実験的に測定され、Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R pke波動関数の方法や反対称化分子動力学を用いた歪曲波インパルス近似計算と比較した。実験データと理論計算の顕著な一致が確認され、
pke波動関数の方法や反対称化分子動力学を用いた歪曲波インパルス近似計算と比較した。実験データと理論計算の顕著な一致が確認され、 Beの比較的コンパクトな分子状態を確認した。
Beの比較的コンパクトな分子状態を確認した。
民井 淳*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; 稲倉 恒法*; Khan, E.*; 木戸 英治*; 木村 真明*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; 稲倉 恒法*; Khan, E.*; 木戸 英治*; 木村 真明*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:83.85(Physics, Nuclear)光核反応は原子核構造の観点からも応用の観点からも重要であるにも関わらず、その反応断面積は未だに不定性が大きい。近年、超高エネルギー宇宙線の起源を探るために、鉄よりも軽い原子核の光核反応断面積を正確に知る必要が指摘されている。この状況を打破するため、原子核物理の実験、理論、宇宙物理の共同研究となるPANDORAプロジェクトが始まった。本論文はその計画の概要をまとめたものである。原子核実験ではRCNP、iThembaによる仮想光子実験とELI-NPによる実光子実験などが計画されている。原子核理論では、乱雑位相近似計算、相対論的平均場理論、反対称化分子動力学、大規模殻模型計算などが計画されている。これらで得られた信頼性の高い光核反応データベースと宇宙線伝搬コードを組み合わせ、超高エネルギー宇宙線の起源の解明に挑む。
Ratliff, H.; McGirl, N. A.*; Beach, M. R.*; Castellanos, L. A.*; Clowdsley, M. S.*; Heilbronn, L. H.*; LaTessa, C.*; Norbury, J. W.*; Rusek, A.*; Sivertz, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 542, p.87 - 94, 2023/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:25.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)Experiments at the NASA Space Radiation Laboratory were performed to develop a benchmark dataset relevant to space radiation shielding scenarios by bombarding aluminum and polyethylene targets with galactic cosmic ray-like ion beams. Unique to this experiment, a dual-target configuration was used to emulate an enclosed environment in space in which the radiation environment must be characterized. Neutrons produced by interactions in both thick targets were detected and characterized; this paper discusses the neutrons produced in the most upstream of the two thick targets, detailing the role of source ion and target configuration on neutron yield.
 O
O近藤 洋介*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; 馬場 秀忠*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
被引用回数:29 パーセンタイル:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)非常に中性子が過剰な原子核 Oは、陽子、中性子ともに魔法数であることから古くからその性質に興味が持たれていたが、酸素の最後の束縛核
Oは、陽子、中性子ともに魔法数であることから古くからその性質に興味が持たれていたが、酸素の最後の束縛核 Oよりも中性子が4個も多いため、これまで観測されてこなかった。この論文では、理化学研究所RIBFにて
Oよりも中性子が4個も多いため、これまで観測されてこなかった。この論文では、理化学研究所RIBFにて Fからの1陽子ノックアウト反応によって
Fからの1陽子ノックアウト反応によって Oを生成し、そこから放出される中性子を測定することによって初めてその観測に成功した。核構造の観点からは、
Oを生成し、そこから放出される中性子を測定することによって初めてその観測に成功した。核構造の観点からは、 Oでは二重閉殻が保たれているか興味が持たれていたが、実験で得られた分光学的因子が殻模型計算で予言されて程度の大きいことから、閉殻構造をもたない可能性が高いことがわかった。
Oでは二重閉殻が保たれているか興味が持たれていたが、実験で得られた分光学的因子が殻模型計算で予言されて程度の大きいことから、閉殻構造をもたない可能性が高いことがわかった。
 SnSe
SnSe
Ren, Q.*; Gupta, M. K.*; Jin, M.*; Ding, J.*; Wu, J.*; Chen, Z.*; Lin, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Rodriguez-Velamazan, J. A.*; 古府 麻衣子; et al.
Nature Materials, 22(8), p.999 - 1006, 2023/08
被引用回数:78 パーセンタイル:99.19(Chemistry, Physical)Ultralow thermal conductivity and fast ionic diffusion endow superionic materials with excellent performance both as thermoelectric converters and as solid-state electrolytes. Yet the correlation and interdependence between these two features remain unclear owing to a limited understanding of their complex atomic dynamics. Here we investigate ionic diffusion and lattice dynamics in argyrodite Ag SnSe
SnSe using synchrotron X-ray and neutron scattering techniques along with machine-learned molecular dynamics. We identify a critical interplay of the vibrational dynamics of mobile Ag and a host framework that controls the overdamping of low-energy Ag-dominated phonons into a quasi-elastic response, enabling superionicity. Concomitantly, the persistence of long-wavelength transverse acoustic phonons across the superionic transition challenges a proposed 'liquid-like thermal conduction' picture. Rather, a striking thermal broadening of low-energy phonons, starting even below 50 K, reveals extreme phonon anharmonicity and weak bonding as underlying features of the potential energy surface responsible for the ultralow thermal conductivity (
using synchrotron X-ray and neutron scattering techniques along with machine-learned molecular dynamics. We identify a critical interplay of the vibrational dynamics of mobile Ag and a host framework that controls the overdamping of low-energy Ag-dominated phonons into a quasi-elastic response, enabling superionicity. Concomitantly, the persistence of long-wavelength transverse acoustic phonons across the superionic transition challenges a proposed 'liquid-like thermal conduction' picture. Rather, a striking thermal broadening of low-energy phonons, starting even below 50 K, reveals extreme phonon anharmonicity and weak bonding as underlying features of the potential energy surface responsible for the ultralow thermal conductivity ( 0.5 Wm
0.5 Wm K
K ) and fast diffusion. Our results provide fundamental insights into the complex atomic dynamics in superionic materials for energy conversion and storage.
) and fast diffusion. Our results provide fundamental insights into the complex atomic dynamics in superionic materials for energy conversion and storage.
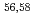 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; 角田 佑介*; 大塚 孝治*; 茶園 亮樹*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:89.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)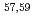 Scからの1陽子ノックアウト反応を用いて、
Scからの1陽子ノックアウト反応を用いて、 Caと
Caと Caのガンマ崩壊を観測した。
Caのガンマ崩壊を観測した。 Caでは1456(12)keVの
Caでは1456(12)keVの 線遷移が、
線遷移が、 Caでは1115(34)keVの遷移が観測された。どちらの遷移も暫定的に
Caでは1115(34)keVの遷移が観測された。どちらの遷移も暫定的に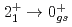 と割り当てられた。有効核子間相互作用をわずかに修正した広い模型空間での殻模型計算では、
と割り当てられた。有効核子間相互作用をわずかに修正した広い模型空間での殻模型計算では、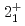 準位エネルギー、2中性子分離エネルギー、反応断面積が実験とよく一致し、N=34閉殻の上に新しい殻が形成されていることを裏付けた。その構成要素である
準位エネルギー、2中性子分離エネルギー、反応断面積が実験とよく一致し、N=34閉殻の上に新しい殻が形成されていることを裏付けた。その構成要素である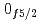 と
と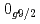 軌道はほぼ縮退しており、これは
軌道はほぼ縮退しており、これは Caが二重魔法核である可能性を排除し、Ca同位体のドリップラインを
Caが二重魔法核である可能性を排除し、Ca同位体のドリップラインを Caあるいはそれ以上にまで広げる可能性がある。
Caあるいはそれ以上にまで広げる可能性がある。
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; 安田 昌弘*; 近藤 洋介*; 中村 隆司*; Tostevin, J. A.*; 緒方 一介*; 大塚 孝治*; Poves, A.*; 清水 則孝*; 吉田 数貴; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics) Neからの1中性子除去反応を用いて、
Neからの1中性子除去反応を用いて、 Neの詳細な
Neの詳細な 線分光を行った。平行運動量分布の解析に基づき、
線分光を行った。平行運動量分布の解析に基づき、 Neの準位構造とスピンパリティを決定し、初めて負のパリティ状態を同定した。測定された断面積と運動量分布から、N=20とN=28のシェルギャップの消失の証拠となる有意なintruder p-wave強度が明らかになった。束縛状態については、弱いf-waveの可能性のある強度が観測された。いくつかの有効相互作用を用いた大規模殻模型計算では、実験的に観測された大きなp-wave強度と小さなf-wave強度は再現されず、Ne同位体に沿った反転の島への遷移の完全な理論的記述への挑戦が続いていることを示している。
Neの準位構造とスピンパリティを決定し、初めて負のパリティ状態を同定した。測定された断面積と運動量分布から、N=20とN=28のシェルギャップの消失の証拠となる有意なintruder p-wave強度が明らかになった。束縛状態については、弱いf-waveの可能性のある強度が観測された。いくつかの有効相互作用を用いた大規模殻模型計算では、実験的に観測された大きなp-wave強度と小さなf-wave強度は再現されず、Ne同位体に沿った反転の島への遷移の完全な理論的記述への挑戦が続いていることを示している。
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, K.*; 内堀 昭寛; 岡野 靖; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; 高田 孝*; 岡本 孝司*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 13(13), p.7705_1 - 7705_29, 2023/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:36.16(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)For a sodium-cooled fast reactor, the capability for stable cooling and avoiding re-criticality on the debris bed is essential for achieving in-vessel retention when severe accidents occur. However, an unexploited uncertainty still existed regarding the compound effect of the heterogeneous configuration and dynamic particle redistribution for the debris bed's criticality and cooling safety assessment. Therefore, this research aims to develop a numerical tool for investigating the effects of the different transformations of the heterogeneous configurations on the debris bed's criticality/cooling assessment. Based on the newly proposed methodology in this research, via integrating the Discrete Element Method (DEM) with Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and Monte-Carlo-based Neutronics (MCN), the coupled CFD-DEM-MCN solver was constructed with the originally created interface to integrate two existing codes. The effects of the different bed configurations' transformations on the bed safety assessments were also quantitively confirmed, indicating that the effect of the particle-centralized fissile material had the dominant negative effect on the safety margin of avoiding re-criticality and particle re-melting accidents and had a more evident impact than the net bed-centralized effect. This coupled solver can serve to further assess the debris bed's safety via a multi-physics simulation approach, leading to safer SFR design concepts.
Kwon, H.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; Gangaraju, M. K.*; Zargaran, A.*; Wang, J.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Lee, B.-J.*; Kim, H. S.*
Acta Materialia, 248, p.118810_1 - 118810_12, 2023/04
被引用回数:54 パーセンタイル:99.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Maraging steels, known for ultrahigh strength and good fracture toughness, derive their superior properties from lath martensite structure with high-density nanoprecipitates. In this work, we designed a novel Fe-based medium-entropy alloy with a chemical composition of Fe Co
Co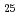 Ni
Ni Mo
Mo in atomic% by utilizing the characteristics of the maraging steels. By a single-step aging of only 10 min at 650
in atomic% by utilizing the characteristics of the maraging steels. By a single-step aging of only 10 min at 650  C, the alloy showed microstructures consisting of a very high number density of (Fe, Co, Ni)
C, the alloy showed microstructures consisting of a very high number density of (Fe, Co, Ni) Mo
Mo -type nanoprecipitates in lath martensite structure and reverted FCC phase, which led to ultrahigh yield strength higher than 2 GPa. This work demonstrates a novel direction to produce strong and ductile materials by expanding the horizons of material design with the aid of high-entropy concept and overcoming the limits of conventional materials.
-type nanoprecipitates in lath martensite structure and reverted FCC phase, which led to ultrahigh yield strength higher than 2 GPa. This work demonstrates a novel direction to produce strong and ductile materials by expanding the horizons of material design with the aid of high-entropy concept and overcoming the limits of conventional materials.