Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Xu, Z.*; Litzinger, A.*; 佐久間 一幸; Arora, B.*; Hazenberg, P.*; Wang, L.*; Gonzalez Raymat, H.*; Fabricatore, E.*; Wainwright, Haruko*; Eddy-Dilek, C.*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2024/03
We leverage the Advanced Terrestrial Simulator (ATS), a comprehensive model encompassing overland flow, groundwater processes, canopy and ground evapotranspiration effects. ATS is integrated with reactive transport models, including PFLOTRAN and CrunchFlow, to capture the intricate dynamics of key nuclear-related geochemical species. The Advanced Long-term Environmental Monitoring Systems (ALTEMIS) project extends its efforts across multiple scales: 1) Watershed Scale ATS Model: At the Savannah River Site, we employ a watershed-scale ATS model to quantify the water budget and estimate evapotranspiration fluxes.; 2) Integrated Hydrology Model for Floodplains: Our integrated hydrology model zooms in on the floodplain of Fourmiles Creek, enabling quantification of upwelling groundwater fluxes into wetlands and surface ponds. It also used to assess contaminant migration into Fourmiles Creek; 3) Fully Integrated Reactive Transport Model: Focused on the F-Area seepage basin, one of the largest nuclear waste processing facilities, we develop both 2D transect and 3D basin models. These models estimate the behavior of radioactive elements such as uranium and tritium, as well as non-reactive geochemical species.; 4) Sr-90 Sorption Model: Informed by extensive Sr-90 sorption experiments on minerals and core samples, we parameterize both electrostatic and non-electrostatic sorption models for Sr-90. These models are integrated into multiple reactive transport frameworks, significantly enhancing our ability to accurately predict Sr-90 migration under varying pH conditions.
 experiments on the flow and freezing of metal fuel and cladding melts, 1; Test conditions and overview of the results
experiments on the flow and freezing of metal fuel and cladding melts, 1; Test conditions and overview of the results深野 義隆; 川田 賢一; 佐藤 一憲; Wright, A. E.*; Kilsdonk, D. J.*; Aeschlimann, R. W.*; Bauer, T. H.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles (FR 2009) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2012/00
For metal fueled fast reactors, assessment of the core disruptive accident (CDA) is necessary for both design and licensing. The objectives of the Core Alloy Flow and Erosion (CAF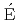 ) experiments are to investigate the fundamental flow, metallurgical interaction, and freezing behavior of uranium-iron-type melts within iron-based trough-shaped flow channels and provide information that can support the development of mathematical models that describe the movements of molten fuel-bearing core materials during CDAs. In the CAFE experiments, melt produced in yttria-coated crucible by induction heating flowed down within approximately 660 mm long inclined trough and was received by the catch cup located below the bottom of the trough. Flow was observed and recorded by three video cameras and many thermocouples. Four UT series tests were conducted using molten uranium whose melting point is 1400 K. Two E1T series tests were performed using U-Fe eutectic mixture whose melting point is 1000 K. In each test, 1 to 1.65 kg of melt was introduced into an inclined trough. These test results provide understandings on fundamental flow and freezing behavior of melts including metallurgical interaction in the steel flow channels with a variety of melt and flow channel conditions and also offer useful information for developing analytical models to describe such behavior.
) experiments are to investigate the fundamental flow, metallurgical interaction, and freezing behavior of uranium-iron-type melts within iron-based trough-shaped flow channels and provide information that can support the development of mathematical models that describe the movements of molten fuel-bearing core materials during CDAs. In the CAFE experiments, melt produced in yttria-coated crucible by induction heating flowed down within approximately 660 mm long inclined trough and was received by the catch cup located below the bottom of the trough. Flow was observed and recorded by three video cameras and many thermocouples. Four UT series tests were conducted using molten uranium whose melting point is 1400 K. Two E1T series tests were performed using U-Fe eutectic mixture whose melting point is 1000 K. In each test, 1 to 1.65 kg of melt was introduced into an inclined trough. These test results provide understandings on fundamental flow and freezing behavior of melts including metallurgical interaction in the steel flow channels with a variety of melt and flow channel conditions and also offer useful information for developing analytical models to describe such behavior.
 experiments on the flow and freezing of metal fuel and cladding melts, 2; Results, analysis, and applications
experiments on the flow and freezing of metal fuel and cladding melts, 2; Results, analysis, and applicationsWright, A. E.*; Bauer, T. H.*; Kilsdonk, D. J.*; Aeschlimann, R. W.*; 深野 義隆; 川田 賢一; 佐藤 一憲
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles (FR 2009) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2012/00
The Core Alloy Flow and Erosion (CAF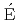 ) experiments have measured fundamental flow, metallurgical interaction, and freezing behavior of uranium and uranium-iron melts within iron-based trough-shaped flow channels relevant to phenomena that might occur in a hypothetical severe accident in a metal fueled fast reactor. CAF
) experiments have measured fundamental flow, metallurgical interaction, and freezing behavior of uranium and uranium-iron melts within iron-based trough-shaped flow channels relevant to phenomena that might occur in a hypothetical severe accident in a metal fueled fast reactor. CAF simulations conducted so far have engineered interactions of fuel and structural materials over a prototypic range of accident-related melt compositions and temperatures. Real-time measurements included flow-channel temperatures and video recording of the flowing melt. Post-test evaluations compare and contrast flow behaviors, trough damage, and debris distribution and indicate that thermo-chemical interactions play a central role in the interaction of molten fuel debris flowing on cold structure and may inhibit bulk freezing of the debris on the structure.
simulations conducted so far have engineered interactions of fuel and structural materials over a prototypic range of accident-related melt compositions and temperatures. Real-time measurements included flow-channel temperatures and video recording of the flowing melt. Post-test evaluations compare and contrast flow behaviors, trough damage, and debris distribution and indicate that thermo-chemical interactions play a central role in the interaction of molten fuel debris flowing on cold structure and may inhibit bulk freezing of the debris on the structure.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; 秋葉 康之*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; 青木 和也*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:49.6(Physics, Nuclear)重いフレーバーのメソンの崩壊からの電子の測定は、このメソンの収量が金金衝突では陽子陽子に比べて抑制されていることを示している。われわれはこの研究をさらに進めて二つの粒子の相関、つまり重いフレーバーメソンの崩壊からの電子と、もう一つの重いフレーバーメソンあるいはジェットの破片からの荷電ハドロン、の相関を調べた。この測定は重いクォークとクォークグルオン物質の相互作用についてのより詳しい情報を与えるものである。われわれは特に金金衝突では陽子陽子に比べて反対側のジェットの形と収量が変化していることを見いだした。
Bonoli, P. T.*; Harvey, R. W.*; Kessel, C. E.*; Imbeaux, F.*; 及川 聡洋; Schneider, M.*; Barbato, E.*; Decker, J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Forest, C. B.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
ITER定常運転プラズマを対象として、複数の低域混成波(LH)電流駆動計算コードを比較した。LH計算コードには2次元速度空間で定義されたFokker-Planck方程式をもとにしたコード及び1次元Fokker-Planck方程式をもとにしたコードがあり、2次元Fokker-Planckコードは最も適切な取り扱いをしていると考えられる。2次元コードは1次元コードに比べて40%程度大きいLH駆動電流を与えた。また、捕捉粒子効果の考慮も重要であることもわかった。さらに、バウンス平均したオペレータの導入が必要であり、バウンス平均していないオペレータを使った場合30%程度計算結果が異なる。また、核融合生成物である3.5MeVのアルファ粒子によるLH波の吸収を評価した。アルファ粒子の異常輸送によりLH波吸収領域でのアルファ粒子密度が増加する場合でも、LH波周波数3.7GHzにおいてアルファ粒子により吸収されるLHパワーは7.7%と小さく、LH機器の設計値である5GHzに対して周波数選択の余地があることを示した。