Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
山口 充孝; 鳥飼 幸太*; 河地 有木; 島田 博文*; 佐藤 隆博; 長尾 悠人; 藤巻 秀; 国分 紀秀*; 渡辺 伸*; 高橋 忠幸*; et al.
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 61(9), p.3638 - 3644, 2016/05
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:100(Engineering, Biomedical)2012年にPhys. Med. Biol.誌にアクセプトされた原著論文("Beam range estimation by measuring bremsstrahlung", Phys. Med. Biol. 57 (2012) 2843)について、計算コードPHITSを用いた水中での炭素イオンの飛程に関して再計算したところ、飛程の値に間違いが見つかった。今後、制動輻射を用いたビームモニタリングに関する研究を行う上で無視することができない差異であるため、関連する記述内容も含め、訂正した原稿を投稿する。
山口 充孝; 長尾 悠人; 河地 有木; 佐藤 隆博; 藤巻 秀; 神谷 富裕; 鳥飼 幸太*; 島田 博文*; 菅井 裕之*; 酒井 真理*; et al.
International Journal of PIXE, 26(1&2), p.61 - 72, 2016/00
炭素線治療中にその軌道上の生体組織内で発生する局所的密度減少は、ブラッグピーク位置のシフトを引き起こし、誤照射の原因となる。この密度減少を炭素線照射中に確認できれば、誤照射を軽減する対策が立てられる。そこで、重粒子線治療で発生する二次電子による制動輻射のうち、発生量が多く効率的測定が可能な低エネルギー光子(63-68keV)による生体内の局所的密度減少の検出方法を開発している。今回、空気間隙による密度減少の存在の検出が可能かどうかをPHITSコードを用いたモンテカルロシミュレーションにより次のように評価した。ビーム軸方向の長さが50mm、奥行き200mm、高さ200mmのアクリルブロック2個を、ビーム軸方向に10mmの間隙を設けて設置した。また、検出器として、幅2.4mmのスリットを持つ鉛製コリメータとテルル化カドミウム製の検出素子を組み合わせた。炭素線を照射した際にビーム軸に対して垂直方向に放出される63-68keVの光子を検出したところ、その検出量に明らかな増減が確認できた。この結果は、間隙の存在を十分検出することが可能であることを示す。
吉田 由香里*; 溝端 健亮*; 松村 彰彦*; 磯野 真由*; 八高 知子*; 中野 隆史*; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦; 金井 達明*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 81, 2015/03
日本の炭素線治療において臨床線量を決定するために用いられているclinical RBE (cRBE)はexperimental RBE (eRBE)にscaling factorをかけたものである。eRBEはhuman salivary gland(HSG)細胞を用いたコロニー形成法によりlinear-quadratic(LQ)モデルで得られた 値および
値および 値から求められた各LETにおけるRBEが採用されており、これが全ての患者(すなわちすべての細胞および組織)における炭素線治療計画に反映されている。しかしながら、RBEは線量,線量率,細胞や組織の種類、エンドポイント、酸素化の程度などにより異なる。そこで、群馬大学重粒子線照射施設(GHMC)のLET 13
値から求められた各LETにおけるRBEが採用されており、これが全ての患者(すなわちすべての細胞および組織)における炭素線治療計画に反映されている。しかしながら、RBEは線量,線量率,細胞や組織の種類、エンドポイント、酸素化の程度などにより異なる。そこで、群馬大学重粒子線照射施設(GHMC)のLET 13 80keV/
80keV/ m、および原子力機構TIARAのLET 108
m、および原子力機構TIARAのLET 108 158keV/
158keV/ mの炭素線を用い、その線量分布を評価すると共に、ヒト正常皮膚細胞への照射を行い、得られたRBE値について過去のHSG細胞の結果と比較・解析した。
mの炭素線を用い、その線量分布を評価すると共に、ヒト正常皮膚細胞への照射を行い、得られたRBE値について過去のHSG細胞の結果と比較・解析した。
高橋 昭久*; 久保 誠*; 五十嵐 千恵*; 吉田 由香里*; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦; 中野 隆史*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 82, 2015/03
放射線によるDNA二本鎖切断(DSB)は致命的であるが、相同組換え(HR)および非相同末端結合(NHEJ)によって修復される。そこで、我々は殺細胞効果におよぼすDNA二本鎖切断修復のLET依存性を明らかにすることを目的に、DNA二本鎖切断修復の異なる細胞における高LET放射線感受性をコロニー形成法で評価した。その結果、NHEJがはたらく野生型細胞とHR欠損細胞は108keV/ mの炭素線で高いRBE値を示した。SER値はHR修復欠損ではLETの違いによらず約2と一定だったのに対して、NHEJ修復欠損ではX線に比べて、HR修復欠損よりも高い値を示した。
mの炭素線で高いRBE値を示した。SER値はHR修復欠損ではLETの違いによらず約2と一定だったのに対して、NHEJ修復欠損ではX線に比べて、HR修復欠損よりも高い値を示した。
高橋 昭久*; 久保 誠*; Ma, H.*; 中川 彰子*; 吉田 由香里*; 磯野 真由*; 金井 達明*; 大野 達也*; 古澤 佳也*; 舟山 知夫; et al.
Radiation Research, 182(3), p.338 - 344, 2014/09
被引用回数:57 パーセンタイル:90.66(Biology)DNA二本鎖切断(DSB)は相同組換え(HR)と非相同末端結合(NHEJ)により修復される。重粒子線治療における放射線増感剤の標的候補を明らかにすることを目的とした。がん抑制遺伝子p53欠損マウス胚線維芽細胞由来の野生型細胞, HR修復欠損細胞, NHEJ修復欠損細胞,二重修復欠損細胞を用いた。各細胞にX線,炭素線,鉄線,ネオン線,アルゴン線を照射し、コロニー形成法で生存率を調べた。10%生存率線量値(D10値)を用いて、増感比は(野生型細胞のD10値)/(修復欠損細胞のD10値)の式で算出した。D10値はいずれの線質においても、野生型細胞 HR修復欠損細胞
HR修復欠損細胞 NHEJ修復欠損細胞
NHEJ修復欠損細胞 二重修復欠損細胞の順に低くなった。HR修復欠損による増感比はLET無関係に一定で約2であった。一方、NHEJ修復欠損の増感比はLETが高くなるに従い減少するものの、HR修復欠損よりも高い増感効果を示した。高LET放射線の高RBEの要因はNHEJ修復の抑制と誤修復であり、炭素線における増感剤の主要な標的候補はNHEJ修復であることが示唆された。
二重修復欠損細胞の順に低くなった。HR修復欠損による増感比はLET無関係に一定で約2であった。一方、NHEJ修復欠損の増感比はLETが高くなるに従い減少するものの、HR修復欠損よりも高い増感効果を示した。高LET放射線の高RBEの要因はNHEJ修復の抑制と誤修復であり、炭素線における増感剤の主要な標的候補はNHEJ修復であることが示唆された。
村田 和俊*; 野田 真永*; 尾池 貴洋*; 高橋 昭久*; 吉田 由香里*; 鈴木 義行*; 大野 達也*; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦; 高橋 健夫*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 55(4), p.658 - 664, 2014/07
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:55.86(Biology)ヒト肺がん細胞A549株のRhoシグナル伝達経路を介した遊走能に対し、炭素線照射が及ぼす影響を解析した。照射48時間経過後、炭素線照射したA549細胞の遊走能は大きくなり、遊走突起の形成も増加した。この遊走能の炭素線照射による増加は、X線照射後のそれと類似していた。ウェスタンブロット解析の結果は、照射した細胞がP-MLC2-S19タンパク質発現を増加させている一方で、MLC2タンパク質ファミリー全体の発現量に変化がないことを示した。ROCKタンパク質阻害剤であるY-27632の細胞への投与は、このP-MLC2-S19タンパク質の発現増加を抑制し、遊走能を低下させた。これらの結果より、ヒト肺がん細胞A549細胞への炭素線照射は、細胞遊走能をRhoシグナル伝達経路経由で増加させており、それはROCKタンパク質阻害剤で抑制されることが明らかとなった。
 -ray simultaneous imaging by using a Si/CdTe Compton camera
-ray simultaneous imaging by using a Si/CdTe Compton camera鈴木 義行*; 山口 充孝; 小高 裕和*; 島田 博文*; 吉田 由香里*; 鳥飼 幸太*; 佐藤 隆博; 荒川 和夫*; 河地 有木; 渡辺 茂樹; et al.
Radiology, 267(3), p.941 - 947, 2013/06
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:65.03(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Capabillity tests of 3D imaging for medical applications were performed by using a new Compton camera.  F,
F,  I and
I and  Ga separately compacted into micro tubes were injected subcutaneously into a Wister rat and imaged after sacrifice of the rat (ex-vivo model). In a separate experiment
Ga separately compacted into micro tubes were injected subcutaneously into a Wister rat and imaged after sacrifice of the rat (ex-vivo model). In a separate experiment  In-chloride and
In-chloride and  I-Methylnorcholestenol were injected into a rat intravenously and
I-Methylnorcholestenol were injected into a rat intravenously and  Cu was injected into the stomach orally just before imaging (more physiological model). The Compton camera demonstrated its 3D multinuclear imaging capability by separating out the three nuclear distributions clearly in ex-vivo model. In the more physiological model, the distributions of
Cu was injected into the stomach orally just before imaging (more physiological model). The Compton camera demonstrated its 3D multinuclear imaging capability by separating out the three nuclear distributions clearly in ex-vivo model. In the more physiological model, the distributions of  I and
I and  Cu were clearly imaged although
Cu were clearly imaged although  In was difficult to visualize due to blurring at low energy region of
In was difficult to visualize due to blurring at low energy region of  -ray. In conclusion, our new Compton camera successfully demonstrated highly resolved multiplanar and multinuclear
-ray. In conclusion, our new Compton camera successfully demonstrated highly resolved multiplanar and multinuclear  -ray simultaneous imaging.
-ray simultaneous imaging.
山口 充孝; 長尾 悠人; 河地 有木; 藤巻 秀; 神谷 富裕; 小高 裕和*; 国分 紀秀*; 武田 伸一郎*; 渡辺 伸*; 高橋 忠幸*; et al.
Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Record (NSS/MIC), 3 Pages, 2013/00
A Monte Carlo simulation system was developed to estimate the response of Compton camera against  -ray emissions from RI spots in a PET-standard human-body phantom. The quality of the three-dimensional imaging program for the Si/CdTe Compton camera to reconstruct the image of the RI spots in a phantom was evaluated by the system, when the phantom has three hot sphere-regions with the same known RI density and different diameters, in other words, different known intensities. The density values of the hot regions reconstructed by the three-dimensional imaging program for the Compton camera were consistent to the known intensities of the RI. It demonstrates sufficient quality of the program for Si/CdTe Compton camera to image RI spots in the phantom.
-ray emissions from RI spots in a PET-standard human-body phantom. The quality of the three-dimensional imaging program for the Si/CdTe Compton camera to reconstruct the image of the RI spots in a phantom was evaluated by the system, when the phantom has three hot sphere-regions with the same known RI density and different diameters, in other words, different known intensities. The density values of the hot regions reconstructed by the three-dimensional imaging program for the Compton camera were consistent to the known intensities of the RI. It demonstrates sufficient quality of the program for Si/CdTe Compton camera to image RI spots in the phantom.
山口 充孝; 鳥飼 幸太*; 河地 有木; 島田 博文*; 佐藤 隆博; 長尾 悠人; 藤巻 秀; 国分 紀秀*; 渡辺 伸*; 高橋 忠幸*; et al.
Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Record (NSS/MIC), 2 Pages, 2013/00
We studied a new method to monitor a beam range in heavy-ion radiation therapy on the basis of measurement of low energy photons emitted from a track of the ion beam. A 290 MeV/u carbon beam was injected into a cylindrical water phantom. A CdTe semiconductor detector with a lead slit having a width of 2 mm was placed at a side of the phantom. In order to measure the position dependence of the low energy photon count, the beam range was varied by changing the energy of injected ions using a binary energy degrader placed about 100 cm upstream of the beam focal point. The measured photon count decreased when the detector got closer to the end point of the beam range and the derivative of the photon count values sharply changed within a depth variation of a few mm in front of the range position. This was explained by our theoretical study assuming secondary electron bremsstrahlung. These results indicate that this new method could be useful to estimate the range position from the observation of bremsstrahlung with an accuracy of a few mm.
 -ray camera
-ray camera武田 伸一郎*; 一戸 悠人*; 萩野 浩一*; 小高 裕和*; 湯浅 孝行*; 石川 真之介*; 福山 太郎*; 齋藤 新也*; 佐藤 有*; 佐藤 悟朗*; et al.
Physics Procedia, 37, p.859 - 866, 2012/10
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:98.43(Physics, Applied)ASTRO-Hミッションのために開発されたSi/CdTe半導体両面ストリップ検出器(DSD)を利用したコンプトンカメラを用い、放射線ホットスポットのモニタリングの実行可能性チェックを目的とした複数放射線源の画像化実験を行った。本装置は半導体検出器によって与えられた良好なエネルギー分解能により、既に商業的な画像処理システムが提供するホットスポットの画像可能力に加え、複数の放射性同位元素を同定する能力を有する。今回の実験では、 Ba(356keV),
Ba(356keV),  Na(511keV)及び
Na(511keV)及び Cs(662keV)の三放射性同位元素を同時に測定し、これらの画像化に成功した。5つの検出器モジュール(有効面積: 1.7
Cs(662keV)の三放射性同位元素を同時に測定し、これらの画像化に成功した。5つの検出器モジュール(有効面積: 1.7 10
10 cm
cm )を積み重ねることによって、662keVの
)を積み重ねることによって、662keVの 線に対し、検出効率1.68
線に対し、検出効率1.68 10
10 、及び、3.8度の角度分解能を確認した。本装置は、より多くの検出器モジュールをスタックすることにより、さらに大きな検出効率を達成することが可能である。
、及び、3.8度の角度分解能を確認した。本装置は、より多くの検出器モジュールをスタックすることにより、さらに大きな検出効率を達成することが可能である。
武者 篤*; 吉田 由香里*; 高橋 健夫*; 安藤 興一*; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦; 根岸 明秀*; 横尾 聡*; 中野 隆史*
Journal of Radiation Research, 53(4), p.545 - 550, 2012/07
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:45.05(Biology)The purpose of this study is to clarify the effect of a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG), in combination with X-rays or carbon-ion beams on cell killing in human oral squamous cell carcinoma LMF4 cells. Cell survival was measured by colony formation assay. Cell cycle distribution was analyzed by flow cytometry. Expression of DNA repair-related proteins was investigated by western blotting. The results showed 17-AAG having synergistic effects on cell lethality with X-rays, but not with carbon-ion beams. The 17-AAG decreased G /M arrest induced by X-rays, but not by carbon-ion beams. Both X-ray and carbon-ion irradiation up-regulated expression of non-homologous end-joining- associated proteins, Ku70 and Ku80, but 17-AAG inhibited only X-ray-induced up-regulation of Ku70 and Ku80. These results show that 17-AAG with X-rays releases G
/M arrest induced by X-rays, but not by carbon-ion beams. Both X-ray and carbon-ion irradiation up-regulated expression of non-homologous end-joining- associated proteins, Ku70 and Ku80, but 17-AAG inhibited only X-ray-induced up-regulation of Ku70 and Ku80. These results show that 17-AAG with X-rays releases G /M phase arrest and then cells carrying misrepaired DNA damage move to G
/M phase arrest and then cells carrying misrepaired DNA damage move to G phase. We demonstrate, for the first time, that the radiosensitization effect of 17-AAG is not seen for carbon-ion beams because 17-AAG does not affect these changes.
phase. We demonstrate, for the first time, that the radiosensitization effect of 17-AAG is not seen for carbon-ion beams because 17-AAG does not affect these changes.
山口 充孝; 鳥飼 幸太*; 河地 有木; 島田 博文*; 佐藤 隆博; 長尾 悠人; 藤巻 秀; 国分 紀秀*; 渡辺 伸*; 高橋 忠幸*; et al.
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 57(10), p.2843 - 2856, 2012/05
被引用回数:41 パーセンタイル:79.35(Engineering, Biomedical)We describe a new method for estimating the beam range in heavy-ion radiation therapy by measuring the ion beam bremsstrahlung. We experimentally confirm that the secondary electron bremsstrahlung process provides the dominant bremsstrahlung contribution. A Monte Carlo simulation shows that the number of background photons from annihilation  rays is about 1% of the bremsstrahlung strength in the low-energy region used in our estimation (63-68 keV). Agreement between the experimental results and the theoretical prediction for the characteristic shape of the bremsstrahlung spectrum validates the effectiveness of our new method in estimating the ion beam range.
rays is about 1% of the bremsstrahlung strength in the low-energy region used in our estimation (63-68 keV). Agreement between the experimental results and the theoretical prediction for the characteristic shape of the bremsstrahlung spectrum validates the effectiveness of our new method in estimating the ion beam range.
吉田 由香里*; 鈴木 義行*; Al-Jahdari, W. S.*; 浜田 信行*; 舟山 知夫; 白井 克幸*; 加藤 弘之*; 坂下 哲哉; 小林 泰彦; 中野 隆史*
Journal of Radiation Research, 53(1), p.87 - 92, 2012/02
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:41.9(Biology)To clarify the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values of carbon ion (C) beams in normal brain tissues, a rat organotypic slice culture system was used. The cerebellum was dissected from 10-day-old Wistar rats, cut parasagittally into approximately 600- m-thick slices and cultivated using a membrane-based culture system with a liquid-air interface. Slices were irradiated with 140 kV X-rays and 18.3 MeV/amu C-beams (linear energy transfer = 108 keV/
m-thick slices and cultivated using a membrane-based culture system with a liquid-air interface. Slices were irradiated with 140 kV X-rays and 18.3 MeV/amu C-beams (linear energy transfer = 108 keV/ m). After irradiation, the slices were evaluated histopathologically using hematoxylin and eosin staining, and apoptosis was quantified using the TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Disorganization of the external granule cell layer (EGL) and apoptosis of the external granule cells (EGCs) were induced within 24 h after exposure to doses of more than 5 Gy from C-beams and X-rays. In the early postnatal cerebellum, morphological changes following exposure to C-beams were similar to those following exposure to X-rays. The RBEs values of C-beams using the EGL disorganization and the EGC TUNEL index endpoints ranged from 1.4 to 1.5. This system represents a useful model for assaying the biological effects of radiation on the brain, especially physiological and time-dependent phenomena.
m). After irradiation, the slices were evaluated histopathologically using hematoxylin and eosin staining, and apoptosis was quantified using the TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Disorganization of the external granule cell layer (EGL) and apoptosis of the external granule cells (EGCs) were induced within 24 h after exposure to doses of more than 5 Gy from C-beams and X-rays. In the early postnatal cerebellum, morphological changes following exposure to C-beams were similar to those following exposure to X-rays. The RBEs values of C-beams using the EGL disorganization and the EGC TUNEL index endpoints ranged from 1.4 to 1.5. This system represents a useful model for assaying the biological effects of radiation on the brain, especially physiological and time-dependent phenomena.
山口 充孝; 河地 有木; 神谷 富裕; 佐藤 隆博; 鈴井 伸郎; 藤巻 秀; 小高 裕和*; 石川 真之介*; 国分 紀秀*; 渡辺 伸*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 145, 2012/01
現在、三次元撮像が可能な医学用コンプトンカメラとしてマルチヘッドコンプトンカメラシステムの開発を行っている。今回、システムの構成要素であるヘッドモジュールプロトタイプ機の製作を行い、Ba133点線源を用い性能試験を行った。測定結果は線源の位置を正確に反映し、点線源の撮像が問題なく可能であることを確認できた。測定データから見積もった装置の空間分解能は、シミュレーションスタディで得られている結果とよく一致した。装置近傍領域においては、検出器面に対して垂直方向の分解能も有することが、実験結果及びシミュレーション結果の両面から実証された。
山口 充孝; 河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 藤巻 秀; 神谷 富裕; 小高 裕和*; 石川 真之介*; 国分 紀秀*; 渡辺 伸*; 高橋 忠幸*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 648(Suppl.1), p.S2 - S7, 2011/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:19.86(Instruments & Instrumentation)現在Si/CdTeコンプトンカメラを用いた、3次元撮像が可能な医学・生物学用のイメージングシステムの構築を進めている。このシステムは、数十keVから数MeVの広いエネルギー範囲において、高いエネルギー分解能及び空間分解能を有し、複数核種同時イメージングが可能であるという特徴を有する。これまでにカメラの近接領域においては、単一のカメラヘッドのみで、奥行き方向の情報を取得可能であることを、シミュレーションスタディを通して示してきたが、今回、実際に実機を用いて測定を行い、奥行き方向も含めた3次元情報が一台のヘッドのみで取得可能であることを確認した。また、得られた位置分解能が、シミュレーションスタディの結果とよく一致していることも確認できた。
 1 pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells; Comparison between X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation
1 pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells; Comparison between X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation清原 浩樹*; 石崎 泰樹*; 鈴木 義行*; 加藤 弘之*; 浜田 信行*; 大野 達也*; 高橋 健夫*; 小林 泰彦; 中野 隆史*
Journal of Radiation Research, 52(3), p.287 - 292, 2011/03
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:51.48(Biology)Radiation-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression on endothelial cells was investigated with the use of an inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF- 1) receptor kinase (SB431542) and the effects of X-ray and carbon-ion beam were compared. Expression of ICAM-1 was increased by X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation and decreased significantly with SB431542 after both irradiations. The expression of ICAM-1 by 2 Gy of carbon-ion beam irradiation was 6.7 fold higher than that of non-irradiated cells, while 5 Gy of X-ray irradiation increased the expression of ICAM-1 by 2.5 fold. According to ICAM-1 expression, the effect of carbon-ion beam irradiation was about 2.2, 4.4 and 5.0 times greater than that of the same doses of X-ray irradiation (1, 2 and 5 Gy, respectively). The present results suggested that radiation-induced ICAM-1 expression on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVE cells) was, at least partially, regulated by TGF-
1) receptor kinase (SB431542) and the effects of X-ray and carbon-ion beam were compared. Expression of ICAM-1 was increased by X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation and decreased significantly with SB431542 after both irradiations. The expression of ICAM-1 by 2 Gy of carbon-ion beam irradiation was 6.7 fold higher than that of non-irradiated cells, while 5 Gy of X-ray irradiation increased the expression of ICAM-1 by 2.5 fold. According to ICAM-1 expression, the effect of carbon-ion beam irradiation was about 2.2, 4.4 and 5.0 times greater than that of the same doses of X-ray irradiation (1, 2 and 5 Gy, respectively). The present results suggested that radiation-induced ICAM-1 expression on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVE cells) was, at least partially, regulated by TGF- 1. Carbon-ion beam induced significantly higher ICAM-1 expression than X-ray.
1. Carbon-ion beam induced significantly higher ICAM-1 expression than X-ray.
神沼 拓也*; 鈴木 義行*; 白井 克幸*; 水井 利幸*; 野田 真永*; 吉田 由香里*; 舟山 知夫; 高橋 健夫*; 小林 泰彦; 白尾 智明*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 51(6), p.627 - 631, 2010/11
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:33.86(Biology)The direct biological effects of radiation, particularly accelerated heavy particle ions, on neurons are not fully known. Hence, the direct effect of carbon-ion beams on immature neurons was investigated by comparing to the effect of X-rays  using primary hippocampal neurons. Primary neurons were prepared from hippocampi of fetal rats at embryonic day 18 from timed pregnant Wistar rats and cultured with Banker's methods. At 7 Days
using primary hippocampal neurons. Primary neurons were prepared from hippocampi of fetal rats at embryonic day 18 from timed pregnant Wistar rats and cultured with Banker's methods. At 7 Days 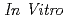 (DIV), the cells were irradiated with 140 kV X-ray and 18.3 MeV/amu carbon-ion beams (LET = 108 keV/
(DIV), the cells were irradiated with 140 kV X-ray and 18.3 MeV/amu carbon-ion beams (LET = 108 keV/ m). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 12 hours after irradiation. Then, the cells were treated with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and DAPI staining for measuring the percentage of apoptosis (apoptotic index: AI). AI in sham-irradiated hippocampal neurons was 18%. The value of AI (AIs) of the cells irradiated with X-rays at 10 or 30 Gy were 15% or 23%, respectively. AI in cells irradiated with carbon-ion beams at 1 Gy, 3 Gy, 5 Gy and 10 Gy were 22%, 23%, 24% and 33%, respectively. AI was significantly increased by carbon-ion beams at 10 Gy (p
m). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 12 hours after irradiation. Then, the cells were treated with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and DAPI staining for measuring the percentage of apoptosis (apoptotic index: AI). AI in sham-irradiated hippocampal neurons was 18%. The value of AI (AIs) of the cells irradiated with X-rays at 10 or 30 Gy were 15% or 23%, respectively. AI in cells irradiated with carbon-ion beams at 1 Gy, 3 Gy, 5 Gy and 10 Gy were 22%, 23%, 24% and 33%, respectively. AI was significantly increased by carbon-ion beams at 10 Gy (p  0.001). The apoptosis of hippocampal neurons increased in a dose-dependent manner following both X-ray and carbon-ion beams irradiation. Carbon-ion beams were about 10-fold more effective than X-rays for apoptosis induction in immature hippocampal neurons.
0.001). The apoptosis of hippocampal neurons increased in a dose-dependent manner following both X-ray and carbon-ion beams irradiation. Carbon-ion beams were about 10-fold more effective than X-rays for apoptosis induction in immature hippocampal neurons.
山口 充孝; 河地 有木; 神谷 富裕; 鈴井 伸郎; 藤巻 秀; 小高 裕和*; 石川 真之介*; 国分 紀秀*; 渡辺 伸*; 高橋 忠幸*; et al.
2010 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record (CD-ROM), p.2004 - 2007, 2010/10
In recent developed radionuclide-based imaging technologies utilized for biological and medical studies, wide dynamic range of radiation intensity with a good quantitative linearity is one of the most important factors. However, the linearity of a detector or a sensor generally breaks due to the dead-time increasing in high counting rate. Therefore, in case of an imaging camera, which is a large set of detectors, it is essential to measure the sensitivity profile of it varying with the radiation source intensity for correction of nonlinearity of each detector. Si/CdTe Compton camera is comprised of two layered double-sided Si strip detectors and two layered double-sided CdTe strip detectors with a four-layer laminated structure. For imaging, the source positions of  -rays are identified by analysing the deposited energies and the scattering angles from counted events in those of detectors. In this work, the Compton camera that was newly developed for biological and medical applications was investigated on the counting rate performance, and the sensitivity profile of this highly complicated imaging system was measured using a
-rays are identified by analysing the deposited energies and the scattering angles from counted events in those of detectors. In this work, the Compton camera that was newly developed for biological and medical applications was investigated on the counting rate performance, and the sensitivity profile of this highly complicated imaging system was measured using a  F point
F point  -ray source. The intense source of 20 MBq was used to measure the sensitivity profiles for a wide range of counting rate in a short period. The result was compared with a calculation using a model considering the dead time of the detection system.
-ray source. The intense source of 20 MBq was used to measure the sensitivity profiles for a wide range of counting rate in a short period. The result was compared with a calculation using a model considering the dead time of the detection system.
原田 耕作*; 野中 哲生*; 浜田 信行*; 桜井 英幸*; 長谷川 正俊*; 舟山 知夫; 柿崎 竹彦*; 小林 泰彦; 中野 隆史*
Cancer Science, 100(4), p.684 - 688, 2009/04
被引用回数:56 パーセンタイル:75.67(Oncology)The aim of the present study was to clarify the mechanisms of cell death induced by heavy-ion irradiation focusing on the bystander effect in human lung cancer A549 cells. In microbeam irradiation, each of 1, 5 and 25 cells under confluent cell conditions was irradiated with 1, 5 or 10 particles of energetic carbon ions, and then the surviving fraction of the population was measured by a clonogenic assay in order to investigate the bystander effect of heavy-ions. In this experiment, the limited number of cells (0.0001-0.002%, 5-25 cells) under confluent cell conditions irradiated with 5 or 10 carbon ions resulted in an exaggerated 8-14% increase in cell death by clonogenic assay. However, these overshooting responses were not observed under exponentially growing cell conditions. Furthermore, these responses were inhibited in cells treated with an inhibitor of gap junctional intercellular communication (GJIC), whereas these were markedly enhanced by the addition of a stimulator of GJIC. The present results suggest that bystander cell killing by heavy-ions was induced mainly by direct cell-to-cell communication, such as GJIC, which might play important roles in the bystander responses.
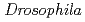 Schneider cells
Schneider cells河村 英将*; 立井 一明*; 野中 哲生*; 大日方 英*; 服部 友保*; 小川 愛*; 風間 秀子*; 浜田 信行*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(2), p.161 - 169, 2009/03
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:26.99(Biology)Cells exposed to genotoxic stress, such as ionizing radiation and DNA damaging reagents, either arrest the cell cycle to repair the genome, or undergo apoptosis, depending on the extent of the DNA damage. DNA damage also has been implicated in various differentiation processes. It has been reported that  -ray exposure or treatment with DNA-damaging agents could induce myogenic differentiation in
-ray exposure or treatment with DNA-damaging agents could induce myogenic differentiation in 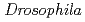 Schneider cells. However, the mechanism underlying this process has been poorly understood. In this study, exposure of Schneider cells to X-rays or energetic carbon ion beams caused increase of TUNEL-positive cells and conversion of round-shaped cells to elongated cells. Both upregulation of genes related to myogenesis and increase of myosin indicate that the radiation-induced morphological changes of Schneider cells were accompanied with myogenic differentiation. Because the intracellular ceramide was increased in Schneider cells after exposure to X-ray, we examined whether exogenous ceramide could mimic radiation-induced myogenic differentiation. Addition of membrane-permeable C
Schneider cells. However, the mechanism underlying this process has been poorly understood. In this study, exposure of Schneider cells to X-rays or energetic carbon ion beams caused increase of TUNEL-positive cells and conversion of round-shaped cells to elongated cells. Both upregulation of genes related to myogenesis and increase of myosin indicate that the radiation-induced morphological changes of Schneider cells were accompanied with myogenic differentiation. Because the intracellular ceramide was increased in Schneider cells after exposure to X-ray, we examined whether exogenous ceramide could mimic radiation-induced myogenic differentiation. Addition of membrane-permeable C -ceramide to Schneider cells increased apoptosis and expression of myogenic genes. These results suggest that ceramide plays important roles in both apoptosis and the radiation-induced myogenic differentiation process.
-ceramide to Schneider cells increased apoptosis and expression of myogenic genes. These results suggest that ceramide plays important roles in both apoptosis and the radiation-induced myogenic differentiation process.