Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
雨森 道紘*; 土屋 晴文; Tibet AS Collaboration*; 他93名*
Collaboration*; 他93名*
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(5), p.460 - 464, 2021/05
被引用回数:66 パーセンタイル:98.88(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Cosmic rays (protons and other atomic nuclei) are believed to gain energies of petaelectronvolts (PeV) and beyond at astrophysical particle accelerators called "PeVatrons" inside our Galaxy. Although a characteristic feature of a PeVatron is expected to be a hard gamma-ray energy spectrum that extends beyond 100 teraelectronvolts (TeV) without a cut-off, none of the currently known sources exhibit such a spectrum owing to the low maximum energy of accelerated cosmic rays or owing to insufficient detector sensitivity around 100 TeV. Here, we report the observation of gamma-ray emission from the supernova remnant G106.3+2.7 above 10 TeV. This work provides flux data points up to and above 100 TeV and indicates that the very-high-energy gamma-ray emission above 10 TeV is well correlated with a molecular cloud rather than with the pulsar PSR J2229+6114. Regarding the gamma-ray emission mechanism of G106.3+2.7, this morphological feature appears to favour a hadronic origin via the 
 decay caused by accelerated relativistic protons over a leptonic origin via the inverse Compton scattering by relativistic electrons. Furthermore, we point out that an X-ray flux upper limit on the synchrotron spectrum would provide important information to firmly establish the hadronic scenario as the mechanism of particle acceleration at the source.
decay caused by accelerated relativistic protons over a leptonic origin via the inverse Compton scattering by relativistic electrons. Furthermore, we point out that an X-ray flux upper limit on the synchrotron spectrum would provide important information to firmly establish the hadronic scenario as the mechanism of particle acceleration at the source.
雨森 道紘*; 土屋 晴文; Tibet AS Collaboration*; 他93名*
Collaboration*; 他93名*
Physical Review Letters, 126(14), p.141101_1 - 141101_7, 2021/04
被引用回数:119 パーセンタイル:99.56(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report, for the first time, the long-awaited detection of diffuse gamma rays with energies between 100 TeV and 1 PeV in the Galactic disk. Particularly, all gamma rays above 398 TeV are observed apart from known TeV gamma-ray sources and compatible with expectations from the hadronic emission scenario in which gamma rays originate from the decay of 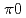 's produced through the interaction of protons with the interstellar medium in the Galaxy. This is strong evidence that cosmic rays are accelerated beyond PeV energies in our Galaxy and spread over the Galactic disk.
's produced through the interaction of protons with the interstellar medium in the Galaxy. This is strong evidence that cosmic rays are accelerated beyond PeV energies in our Galaxy and spread over the Galactic disk.