Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発
MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発伊東 達矢; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
物性研だより, 63(3), p.8 - 10, 2023/10
メタ磁性形状記憶合金は磁場により駆動することが出来る形状記憶合金であり、センサーやアクチュエーター等での応用が期待されている。しかし、これまでに開発されてきた合金系ではマルテンサイト変態に伴うエネルギーロスが大きいという問題点があった。近年、我々の研究グループではPd MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
近年、水素添加によりSUS310Sの強度と延性が共に向上することが報告された。本研究では、「匠」を利用した引張試験中その場中性子回折実験を行い、転位密度や積層欠陥密度など、個々の因子に対する水素の影響を定量的に解明することを試みた。
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Mao, W.; 伊東 達矢
no journal, ,
J-PARCのMLFに設置されたTAKUMIは、材料工学や機械工学に関わる材料研究のための飛行時間型中性子回折装置である。中性子回折パターンに表れるBragg反射の位置・強度・プロファイルを詳細に解析することで、材料の内部応力・相比・転位・集合組織など、新材料の設計や構造物の信頼性評価に役立つ様々な情報を得ることができる。中性子回折法はこれらの情報の、ex-situ及びin-situ観察に適しており、工学材料研究のための強力な手段である。本発表では、2022年に公開されたTAKUMIを用いた研究成果からハイライトなものを抜粋して紹介・議論する。
今富 大介*; 石川 遼典*; 仲田 玲*; 伊東 達矢; Han, K.*; 長迫 実*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
no journal, ,
高Mn鋼への亜鉛めっき処理において界面反応の理解のためにFe-Mn-Zn状態図の決定が必要不可欠である。そこで本研究ではまず基本となるMn-Zn二元系状態図について決定した。
清水 来紀*; Xu, X.*; 伊東 達矢; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
no journal, ,
Co-Cr-Al-Si合金は約15%程度の超弾性回復ひずみを有するが、応力誘起マルテンサイト変態開始時の過剰な応力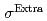 が超弾性疲労特性を劣化させる可能性がある。本研究では中性子回折により
が超弾性疲労特性を劣化させる可能性がある。本研究では中性子回折により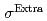 の起源を調査する。
の起源を調査する。
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
従来のオーステナイト系ステンレス鋼(ASS)の降伏強度は、面心立方晶の結晶構造のため、極低温では比較的低いままである。最近の研究で、304 ASSの超微細粒(UFG)化は、冷間圧延とその後の焼鈍によって容易に達成できることが明らかになった。粗大結晶粒を有する従来の304 ASSと比較して、室温で、UFG 304 ASSは、良好な延性を維持しながら、結晶粒微細化強化のために著しく高い降伏強度を有する。しかしながら、UFG 304 ASSの低温機械的特性は未だ不明である。本研究では、77 295Kの異なる温度範囲におけるUFG 304 ASSの引張変形挙動を系統的に調査した。その結果、最適な機械的特性は77Kで達成され、極めて高い降伏強さと極限引張強さ、および比較的良好な伸びが得られた。UFG304ASSの低温変形メカニズムについては、その場中性子回折と組織観察を踏まえて議論した。
295Kの異なる温度範囲におけるUFG 304 ASSの引張変形挙動を系統的に調査した。その結果、最適な機械的特性は77Kで達成され、極めて高い降伏強さと極限引張強さ、および比較的良好な伸びが得られた。UFG304ASSの低温変形メカニズムについては、その場中性子回折と組織観察を踏まえて議論した。
Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Mao, W.; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction, as a powerful microstructure probe, is reliable for tracking globally averaged crystallographic information associated with microstructure evolution and deformation behavior in structural materials. TAKUMI, is a neutron diffractometer for engineering materials studies at MLF, J-PARC, covering a wide d-range with a good balance between high neutron flux and high resolution. Additionally, a variety of specific sample environments at TAKUMI enable the in situ studies under extreme conditions, such as cryogenic deformation (10K ), thermomechanical controlled processes (
), thermomechanical controlled processes ( 1473K), fatigue, etc. Crystallographic information including phase fraction, lattice strain (stress), texture, dislocation density, stacking fault probability, etc., obtained by neutron diffraction can uniquely provide insights into microstructure evolution and deformation mechanisms in bulky materials. Various in situ studies on various metallic materials, as well as ex situ measurements, such as residual stress mapping and microstructure characterization for specific purposes, have been conducted. In the presentation, the specifications of the diffractometer TAKUMI and several recent studies on deformation mechanisms in metallic materials using in situ neutron diffraction will be introduced.
1473K), fatigue, etc. Crystallographic information including phase fraction, lattice strain (stress), texture, dislocation density, stacking fault probability, etc., obtained by neutron diffraction can uniquely provide insights into microstructure evolution and deformation mechanisms in bulky materials. Various in situ studies on various metallic materials, as well as ex situ measurements, such as residual stress mapping and microstructure characterization for specific purposes, have been conducted. In the presentation, the specifications of the diffractometer TAKUMI and several recent studies on deformation mechanisms in metallic materials using in situ neutron diffraction will be introduced.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
カーボンニュートラルの実現のため、水素は化石燃料を代替するエネルギーキャリアとして注目を集めている。歴史的に水素は鉄鋼材料の脆化を引き起こすとされてきたが、小川らはSUS310Sに水素を添加することで強度と延性が共に向上することを報告した。これらは水素による固溶強化と双晶変形の促進によると定性的に説明されているが、変形中の転位や積層欠陥の発達に対して、水素がどのような影響を与えるかその詳細は明らかとなっていない。本研究は、その場中性子回折により、これらの欠陥に対する水素の影響を明らかにすることを目的とする。
Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Mao, W.; 伊東 達矢; 相澤 一也; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Mechanical properties, as the principal properties of structural metallic materials, are governed by the microstructures. To track the structure-property relationship associated with various solid-solid reactions such as phase transformation and plastic deformation, is crucial for the development of structural metallic materials. TAKUMI [1], an engineering materials neutron diffractometer at MLF, J-PARC, covering a large d-range with a good balance between high neutron flux and high resolution is reliable to investigate various dynamic phenomena associated with microstructure evolution and deformation behavior. In addition, a variety of specifical sample environments at TAKUMI allow the in-situ studies under extreme environments such as cryogenic deformation (10K~), thermomechanical controlled process (~1473K), fatigue, etc. Crystallographic information including phase fraction, lattice strain (stress), texture, dislocation density, etc. as obtained by neutron diffraction can uniquely provide insights into microstructure evolution and deformation mechanisms in bulky materials. In the presentation, several recent studies on microstructure evolution and deformation mechanisms in metallic materials including steels, high-entropy alloys, magnesium alloys using in-situ neutron diffraction via TAKUMI will be introduced.
Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Mao, W.; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Neutrons are used to investigate stresses and crystallographic microstructures inside engineering materials, taking advantage of their large penetrating power and the ability to see the arrangement of atoms by diffraction methods. A pulsed neutron diffractometer has been developed in J-PARC and operated for more a decade. The present status of the diffractometer and some highlights will be introduced.
伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
近年、高圧ガス環境中で均一に水素を固溶させたオーステナイト系ステンレス鋼SUS310Sにおいて、強度・延性が共に向上することが報告された。これは水素による固溶強化と双晶変形の促進によると説明されているが、転位密度や積層欠陥など、個々の因子に対する水素の影響の詳細は明らかとなっていない。本研究では、J-PARCの工学材料回折装置「匠」での引張試験中その場中性子回折により、変形メカニズムを明らかにすることを試みた。得られた中性子回折パターンから、水素による体積変化や固溶強化の存在を確認した。更に、転位密度、積層欠陥密度、双晶変形開始ひずみ・応力を評価した。これらの解析により、水素が変形メカニズムに与える影響を明らかにした。