Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹; 瓜谷 章*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1062, p.169227_1 - 169227_6, 2024/05
We have developed a new position-sensitive optical fiber radiation sensor that achieves single-end readout and high dose rate application. The sensor determines the incident position of radiation on the optical fiber by using the wavelength dependency of light attenuation within the fiber. Through the analysis of the output wavelength spectrum from the fiber end, the incident position of radiation on the optical fiber can be inversely estimated using the spectrum unfolding procedure. Using this optical fiber sensor, we conducted a measurement of radiation distribution inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). The actual trend of incident position of radiation was successfully reproduced in a high dose rate area, with a maximum dose rate exceeding 100 mSv/h. This validates the effectiveness of our new position-sensitive optical fiber radiation sensor.
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.1013 - 1026, 2023/08
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:98.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) suffered a meltdown in the aftermath of the large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake that occurred on 11 March 2011. A massive amount of radioactive substance was spread over a wide area both inside and outside the FDNPS site. In this study, we present an approach for visualizing a radioactive hotspot on a standby gas-treatment system filter train, a highly contaminated piece of equipment in the air-conditioning room of the Unit 2 reactor building of FDNPS, using radiation imaging based on a Compton camera. In addition to fixed-point measurements using only the Compton camera, data acquisition while moving using an integrated Radiation Imaging System (iRIS), which combines a Compton camera with a simultaneous localization and mapping device and a survey meter, enabled the three-dimensional visualization of the hotspot location on the filter train. In addition, we visualized the hotspot and quantitatively evaluated its radioactivity. Notably, the visualized hotspot location and estimated radioactivity value are consistent with the accident investigation report of the FDNPS. Finally, the extent to which the radioactivity increased the ambient dose equivalent rate in the surrounding environment was explored.
 Sn nanodot
Sn nanodot佐藤 佑磨*; 竹内 祐太郎*; 山根 結太*; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 大野 英男*; 深見 俊輔*
Applied Physics Letters, 122(12), p.122404_1 - 122404_5, 2023/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:54.89(Physics, Applied)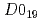 -Mn
-Mn Sn, an antiferromagnet having a non-collinear spin structure in a kagome lattice, has attracted great attention owing to various intriguing properties such as large anomalous Hall effect. Stability of magnetic state against thermal fluctuation, characterized in general by the thermal stability factor
Sn, an antiferromagnet having a non-collinear spin structure in a kagome lattice, has attracted great attention owing to various intriguing properties such as large anomalous Hall effect. Stability of magnetic state against thermal fluctuation, characterized in general by the thermal stability factor  , has been well studied in ferromagnetic systems but not for antiferromagnets. Here we study
, has been well studied in ferromagnetic systems but not for antiferromagnets. Here we study  of the antiferromagnetic Mn
of the antiferromagnetic Mn Sn nanodots as a function of their diameter
Sn nanodots as a function of their diameter  . To obtain
. To obtain  , we measure the switching probability as a function of pulse-field amplitude and analyze the results based on a model developed by accounting for two and six-fold magnetic anisotropies in the kagome plane. We observe no significant change in
, we measure the switching probability as a function of pulse-field amplitude and analyze the results based on a model developed by accounting for two and six-fold magnetic anisotropies in the kagome plane. We observe no significant change in  down to
down to 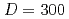 nm below which it decreases with
nm below which it decreases with  . The obtained
. The obtained  dependence is well explained by a single-domain and nucleation-mediated reversal models. These findings provide a basis to understand the thermal fluctuation and reversal mechanism of antiferromagnets for device application.
dependence is well explained by a single-domain and nucleation-mediated reversal models. These findings provide a basis to understand the thermal fluctuation and reversal mechanism of antiferromagnets for device application.
塩田 祐揮; 矢部 孝則; 村上 牧生; 磯部 祐太; 佐藤 方実; 浜野 知治; 高木 剛彦; 長沖 吉弘
JAEA-Technology 2022-001, 117 Pages, 2022/07
もんじゅ廃止措置計画の第一段階では「燃料体取出し作業」を行う。「燃料体取出し作業」では、炉外燃料貯蔵槽に貯蔵中の燃料体を洗浄・缶詰し燃料池に貯蔵する「燃料体の処理」、炉心にある燃料体を模擬体等と交換し炉外燃料貯蔵槽に貯蔵する「燃料体の取出し」を交互に行い、炉心にある370体と炉外燃料貯蔵槽にある160体の燃料体を全て燃料池に貯蔵する。「燃料体の処理作業」に用いる燃料取扱設備の自動化運転は約10年ぶりの作業であった。このため、2017年度から作業開始までに設備の点検を行い、作業に先立ち使用済み制御棒等を用いて総合試験、模擬訓練を行った。そのうえで、最初の「燃料体の処理作業」として、2018年度に炉外燃料貯蔵槽にあった86体の燃料体を洗浄・缶詰し燃料池に貯蔵した。あわせて、「燃料体の取出し」に向けて76体の模擬体を炉外燃料貯蔵槽の空ポット内に貯蔵した。その間、86種類、232件の警報・不具合等が発生したが、何れも燃料体や設備の安全に直ちに影響を及ぼした事象ではなく、燃料体落下等の安全上重要な事象及び移送機器の機構部分のスティック等の長期停止可能性のある事象は発生していない。機器故障は、燃料出入機本体Bグリッパの爪開閉クラッチ破損の1件であるが補修して作業を再開できた。複数回発生したナトリウム化合物の固着や機器の連続使用が直接要因となった機器の動作・性能の状態異常は、直接要因の除去あるいは特別採用した上で作業を継続した。その他、動作のタイムアウト等の系統制御に係る不具合等も多く発生したものの、安全を確保したうえで作業を継続することができた。もんじゅの燃料取扱設備はナトリウム冷却高速炉固有の機能を持つものであり、実燃料体を対象とした連続・継続的な運転は途に就いたばかりである。このため、原理的に完全な発生防止が難しい事象、使用実績が少ないことに起因する事象、システムの最適化が十分でないことに起因する事象を「対策を施したとしても発生する事象」と想定し、その発生頻度を出来る限り抑える対策と工程影響を最小化する復旧策を施すこととした。
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(6), p.677 - 687, 2022/06
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:95.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) went into meltdown after being hit by a large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011. Measuring and understanding the distribution of radioactive contamination inside the FDNPS is essential for decommissioning work, reducing exposure to workers, and ensuring decontamination. This paper reports the visualization tests of radioactive contamination in the Unit 1/2 exhaust stack of the FDNPS using a compact Compton camera. Fixed-point measurements were conducted using only a Compton camera and moving measurements using an integrated radiation imaging system (iRIS) that combines a Compton camera with a simultaneous localization and mapping device. For the moving measurements, an operator carrying the iRIS acquires data continuously while walking in a passage near the stack. With both types of measurements, high-intensity contamination was detected at the base of the stack, and detailed three-dimensional (3D) visualization of the contamination was obtained from the moving measurement. The fixed-point measurements estimated the source intensity of the contamination from the reconstructed contamination image acquired by the Compton camera. Furthermore, workers can experience the work environment before actual work by importing a 3D structure model into a virtual reality system displaying the contamination image.
 Sn thin films by magneto-optical Kerr effect
Sn thin films by magneto-optical Kerr effect内村 友宏*; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 佐藤 佑磨*; 竹内 祐太郎*; 金井 駿*; 武智 涼太*; 岸 桂輔*; 山根 結太*; DuttaGupta, S.*; 家田 淳一; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 120(17), p.172405_1 - 172405_5, 2022/04
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:83.82(Physics, Applied)We perform a hysteresis-loop measurement and domain imaging for 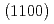 -oriented
-oriented 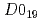 -Mn
-Mn Sn
Sn
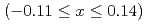 thin films using magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) and compare it with the anomalous Hall effect (AHE) measurement. We obtain a large Kerr rotation angle of 10 mdeg., comparable with bulk single-crystal Mn
thin films using magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) and compare it with the anomalous Hall effect (AHE) measurement. We obtain a large Kerr rotation angle of 10 mdeg., comparable with bulk single-crystal Mn Sn. The composition
Sn. The composition  dependence of AHE and MOKE shows a similar trend, suggesting the same origin, i.e., the non-vanishing Berry curvature in the momentum space. Magnetic domain observation at the saturated state shows that x dependence of AHE and MOKE is explained by an amount of reversible area that crucially depends on the crystalline structure of the film. Furthermore, in-depth observation of the reversal process reveals that the reversal starts with nucleation of sub-micrometer-scale domains dispersed in the film, followed by a domain expansion, where the domain wall preferentially propagates along the
dependence of AHE and MOKE shows a similar trend, suggesting the same origin, i.e., the non-vanishing Berry curvature in the momentum space. Magnetic domain observation at the saturated state shows that x dependence of AHE and MOKE is explained by an amount of reversible area that crucially depends on the crystalline structure of the film. Furthermore, in-depth observation of the reversal process reveals that the reversal starts with nucleation of sub-micrometer-scale domains dispersed in the film, followed by a domain expansion, where the domain wall preferentially propagates along the ![$$[11bar{2}0]$$](/search/images/ERNTCMK2MJQXE4ZSPUYF0JA.gif) direction. Our study provides a basic understanding of the spatial evolution of the reversal of chiral-spin structure in non-collinear antiferromagnetic thin films.
direction. Our study provides a basic understanding of the spatial evolution of the reversal of chiral-spin structure in non-collinear antiferromagnetic thin films.
持丸 貴則*; 小泉 光生; 高橋 時音; 弘中 浩太; 木村 祥紀; 佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 山西 弘城*; 若林 源一郎*
第42回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2021/11
日本原子力研究開発機構では、文部科学省核セキュリティ強化等補助事業の下、大規模公共イベント等において、核・放射性物質を用いたテロ行為等を未然に防ぐため、イベント会場にそれらが持ち込まれた場合に迅速に検知するための技術・装置の開発を目的とし、広域における放射性物質検知技術開発を4年計画で進めている。本講演では、プロジェクトの概要を説明するとともに、技術開発の進捗状況を一部紹介する。
北山 佳治; 寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 7(4), p.042006_1 - 042006_7, 2021/10
Gamma-ray imaging is a technique to visualize the spatial distribution of radioactive materials. Recently, gamma-ray imaging has been applied to research on decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident and environmental restoration, and active research has been conducted. This study is the elemental technology study of the new gamma-ray imager GISAS (Gamma-ray Imager using Small-Angle Scattering), which is assumed to be applied to the decommissioning site of FDNPS. GISAS consists of a set of directional gamma-ray detectors that do not require a shield. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of the shield free directional gamma-ray detector by simulation. The simulation result suggests that by measuring several keV of scattered electron energy by scatterer detector, gamma rays with ultra-small angle scattering could be selected. By using Compton scattering kinematics, a shield-free detector with directivity of about 10 could be feasible. By arranging the directional gamma-ray detectors in an array, it is expected to realize the GISAS, which is small, light, and capable of quantitative measurement.
could be feasible. By arranging the directional gamma-ray detectors in an array, it is expected to realize the GISAS, which is small, light, and capable of quantitative measurement.
寺阪 祐太; 渡辺 賢一*; 瓜谷 章*; 山崎 淳*; 佐藤 優樹; 鳥居 建男; 若井田 育夫
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 7(4), p.042002_1 - 042002_7, 2021/10
福島第一原子力発電所原子炉建物内の高線量率環境での線源分布測定への応用を目指し、波長スペクトルのアンフォールディング処理に基づく光ファイバーを用いた新しい一次元放射線分布測定法を開発した。開発した手法は光ファイバー内を伝搬する光の減衰量が波長依存であることを利用して、光ファイバー端から出力された波長スペクトルをアンフォールディングすることにより、光ファイバーへの放射線の入射位置を逆推定するというものである。この手法は光強度の積分値を利用するため、パルスカウンティングを行う放射線検出器を使用した場合に高線量率環境下で発生する計数損失や信号パイルアップの問題を回避することができる。本研究では紫外光源と Sr/
Sr/ Y放射線源を用いた基礎実験を行い、線源位置検出の基本特性を確認した。
Y放射線源を用いた基礎実験を行い、線源位置検出の基本特性を確認した。
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 鳥居 建男
日本原子力学会誌ATOMO , 62(11), p.645 - 649, 2020/11
, 62(11), p.645 - 649, 2020/11
東京電力ホールディングス福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉作業を円滑に進めるにあたり、作業環境に飛散・沈着した放射性物質の分布を「見える化」して把握することは、作業者の被ばく線量の低減や詳細な作業計画の立案を行う上で重要である。ここではわれわれが福島第一原子力発電所やその周辺で行なってきた放射線イメージング技術の開発及び現場における実証例を紹介する。
佐藤 優樹; 小澤 慎吾*; 寺阪 祐太; 峯本 浩二郎*; 田村 智志*; 新宮 一駿*; 根本 誠*; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(6), p.734 - 744, 2020/06
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:93.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., suffered a meltdown as a result of a large tsunami triggered by the Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011. To proceed with the environmental recovery by decontamination, drawing a radiation distribution map that can indicate the distribution of radioactive substances is extremely important to establish detailed decontamination plans. We developed a remote radiation imaging system consisting of a lightweight Compton camera and a multi-copter drone to remotely measure the distribution of the radioactive substances. This system can perform radiation imaging using a Compton camera while flying and moving. In addition, it is also possible to draw the distribution of radioactive substances three-dimensionally by projecting the radiation image measured with the Compton camera on a three-dimensional topography model separately acquired by a 3D-LiDAR. We conducted a survey of radioactive hotspots in difficult-to-return zone in the coastal area of Fukushima, Japan. The drone system succeeded in three-dimensional visualization of several hotspots deposited on the ground. Such remote technology would be useful not only for monitoring the difficult-to-return zone, but also for monitoring distribution of radioactive substances inside the site of the FDNPS where decommissioning work is ongoing.
寺阪 祐太; 渡辺 賢一*; 瓜谷 章*; 山崎 淳*; 佐藤 優樹; 鳥居 建男; 若井田 育夫
Proceedings of International Youth Nuclear Congress 2020 (IYNC 2020) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/05
For the application in the measurement of the high dose rate hot spots inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station buildings, we propose a wavelength-resolved type one-dimensional radiation distribution sensing method using plastic scintillating fiber (PSF). The proposing method estimates the incident position of radiation to the PSF by the unfolding of the wavelength spectrum output from the fiber edge using the fact that the attenuation length of scintillating light depends on the wavelength. By measuring the response function in advance, which defined as the wavelength spectrum measured at the fiber edge by the spectrometer with every transmission distance, the spectrum which can obtain when measured a certain radiation distribution can be expressed as the convolution of the response function. This method can avoid the problem of chance coincidence effect and signal pile-up, which occurs in the radiation detector with pulse counting mode under high dose rate field because this method measures the integrated light intensity. Through basic experiment using the ultraviolet irradiation source and  Sr point source, basic properties of inverse estimation of irradiated position were confirmed, which showed that source position was reasonably estimated using the response function which obtained by the ultraviolet irradiation source in advance.
Sr point source, basic properties of inverse estimation of irradiated position were confirmed, which showed that source position was reasonably estimated using the response function which obtained by the ultraviolet irradiation source in advance.
北山 佳治; 寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹; 鳥居 建男
Proceedings of International Youth Nuclear Congress 2020 (IYNC 2020) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/05
At the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), various works are under-way for decommissioning. Depending on work places, there are radioactive hotspot. Therefore measuring the position of the hotspot in advance is important for safety of the worker. The system that can easily measure the dose rate distribution in work place has been demanded. There are two methods for imaging a dose rate distribution: a pinhole camera and a Compton camera. A pinhole camera can determine direction of radiation source in one event, but the weight becomes heavy because a shield is required. On the other hand, since the Compton camera does not require a shield, it can be reduced in the size and weight. However, Compton imaging method generate many ghosts of cone traces, which reduce the signal-to-noise ratio. We propose a new gamma-ray imager that works like a pinhole camera without a shield. This is achieved by arranging directional gamma ray detectors that does not require a shield. In this work, we have performed principle verification of a directional gamma-ray detector that is a basic component of the new gamma-ray imager by using Geant4 Monte Carlo simulation.
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 宇津木 弥*; 菊地 弘幸*; 清岡 英男*; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.801 - 808, 2019/09
被引用回数:54 パーセンタイル:99.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., went into meltdown in the aftermath of a large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake of 11 March 2011. Measurement of radiation distribution inside the FDNPS buildings is indispensable to execute decommissioning tasks in the reactor buildings. We conducted a radiation imaging experiment inside the reactor building of Unit 1 of FDNPS by using a compact Compton camera mounted on a crawler robot and remotely visualized gamma-rays streaming from deep inside the reactor building. Moreover, we drew a radiation image obtained using the Compton camera onto the three-dimensional (3-D) structural model of the experimental environment created using photogrammetry. In addition, the 3-D model of the real working environment, including the radiation image, was imported into the virtual space of the virtual reality system. These visualization techniques help workers recognize radioactive contamination easily and decrease their own exposure to radiation because the contamination cannot be observed with the naked eye.
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 宮村 浩子; 冠城 雅晃; 谷藤 祐太; 川端 邦明; 鳥居 建男
Reactor Dosimetry; 16th International Symposium on Reactor Dosimetry (ISRD-16) (ASTM STP 1608), p.428 - 436, 2018/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)We developed a lightweight compact Compton camera to measure the distribution of radioactive contamination inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. We conducted performance evaluation tests in the coastal area of Fukushima, Japan, using the camera, which employs a cerium (Ce)-doped GAGG (Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O ) scintillator coupled with a multipixel photon counter. The camera can clearly visualize spreading of radioactivity along the ground surface. In addition, we performed three-dimensional image reconstruction of the distribution of radioactive contamination using the multi-angle data obtained with the Compton camera. We succeeded in obtaining a three-dimensional image of radioactive contamination in the outdoor area.
) scintillator coupled with a multipixel photon counter. The camera can clearly visualize spreading of radioactivity along the ground surface. In addition, we performed three-dimensional image reconstruction of the distribution of radioactive contamination using the multi-angle data obtained with the Compton camera. We succeeded in obtaining a three-dimensional image of radioactive contamination in the outdoor area.
佐藤 優樹; 谷藤 祐太; 寺阪 祐太; 宇佐美 博士; 冠城 雅晃; 川端 邦明; 宇津木 弥*; 菊地 弘幸*; 高平 史郎*; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(9), p.965 - 970, 2018/09
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:96.7(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., went into meltdown after the occurrence of a large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake of March 11, 2011. The radiation distribution measurements inside the FDNPS buildings are indispensable to execute decommissioning tasks in the reactor buildings. We conducted the radiation imaging experiment inside the turbine building of Unit 3 of the FDNPS using a compact Compton camera, and succeeded in visualizing the high-dose contamination (up to 3.5 mSv/h). We also drew a three-dimensional radiation distribution map inside the turbine building by integrating the radiation image resulting from the Compton camera into the point cloud data of the experimental environment acquired using the scanning laser range finder. The radiation distribution map shows the position of these contaminations on the real space image of the turbine building. The radiation distribution map helps workers to easily recognize the radioactive contamination and to decrease the radiation exposure; the contamination cannot be observed with the naked eye, naturally.
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 小澤 慎吾*; 谷藤 祐太; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 13(8), p.T08011_1 - T08011_10, 2018/08
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:31.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., suffered a meltdown after a large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011. The measurement of radiation distribution inside FDNPS buildings is indispensable for executing appropriate decommissioning tasks in the reactor's buildings. In addition, it is extremely important to accurately predict the location of radioactive contamination beforehand because the working time is limited owing to radiation exposure to workers. In this paper, a simple virtual reality (VR) system that can detect radioactive substances in virtual space has been developed to simulate real working environments. A three-dimensional (3D) photo-based model of the real working environment, including an image of the radioactive substance, was imported into the virtual space of the VR system. The developed VR system can be accessed using a smartphone and a cardboard goggle. The VR system is expected to be useful for preliminary training of workers and for recognizing radioactive hotspots during decommissioning of the work environment.
佐藤 優樹; 小澤 慎吾*; 谷藤 祐太; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 13(3), p.P03001_1 - P03001_8, 2018/03
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:35.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., went into meltdown after the large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake of March 11, 2011. Radiation distribution measurements inside FDNPS buildings are indispensable to execute decommissioning tasks in the reactor buildings. We have developed a method of three-dimensional (3-D) image reconstruction for radioactive substances using a compact Compton camera. We also succeeded in visually recognize the position of the radioactive substances on the real space by integration of the 3D radiation image and the 3D photo-model created by photogrammetry.
 -ray imager mounted on a multicopter drone
-ray imager mounted on a multicopter drone佐藤 優樹; 小澤 慎吾*; 寺阪 祐太; 冠城 雅晃; 谷藤 祐太; 川端 邦明; 宮村 浩子; 和泉 良*; 鈴木 敏和*; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(1), p.90 - 96, 2018/01
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:98.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)A remote radiation imaging system comprising a lightweight Compton camera and a multicopter drone was developed to remotely and quickly measure radioactive contamination inside the buildings of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). The drone system is used for measuring detailed radiation distributions in narrow areas, which have been difficult to gauge with conventional aircraft monitoring using helicopters. A measurement of radiation distributions in outdoor environments in the coastal areas of Fukushima, Japan, was performed. The drone system with the Compton camera succeeded in remote observations of dense hotspots from the sky over a contaminated area near the FDNPS. The time required for image reconstruction is approximately 550 s in the case of a 9-m flight altitude for the hotspots with a surface dose rate of several tens of  Sv/h. This drone system will be used inside the buildings of the FDNPS for remote measurement of radioactive contamination.
Sv/h. This drone system will be used inside the buildings of the FDNPS for remote measurement of radioactive contamination.
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 小澤 慎吾*; 宮村 浩子; 冠城 雅晃; 谷藤 祐太; 川端 邦明; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(11), p.C11007_1 - C11007_8, 2017/11
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:65.26(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., went into meltdown after the large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake of March 11, 2011. Very large amounts of radionuclides were released from the damaged plant. Radiation distribution measurements inside the building of FDNPS are indispensable to execute the decommission tasks in the reactor buildings. We have developed a light-weight compact Compton camera to three-dimensionally measure the distribution of radioactive contamination inside FDNPS. The total weight of the Compton camera is lower than 1.0 kg. The  -ray sensor of the Compton camera employs the Ce-doped GAGG scintillators coupled with a multi-pixel photon counter (MPPC: Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.,). We performed the 3D image reconstruction of the
-ray sensor of the Compton camera employs the Ce-doped GAGG scintillators coupled with a multi-pixel photon counter (MPPC: Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.,). We performed the 3D image reconstruction of the  Cs-radioactive sources as shown in Fig. 1; the 3D radiation image is reconstructed using the multi-angle data measured with the Compton camera. Here, we introduce the development status of the 3D radiation imaging system consisting of the Compton camera. Moreover, we present the results of a performance evaluation test for 3D image reconstruction of radioactive contaminations in details.
Cs-radioactive sources as shown in Fig. 1; the 3D radiation image is reconstructed using the multi-angle data measured with the Compton camera. Here, we introduce the development status of the 3D radiation imaging system consisting of the Compton camera. Moreover, we present the results of a performance evaluation test for 3D image reconstruction of radioactive contaminations in details.