Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, L.*; 宮本 吾郎*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; 諸岡 聡; 及川 勝成*; 友田 陽*; 古原 忠*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation (DT) of austenite ( ) to ferrite (
) to ferrite ( ) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with
) in the hot deformation of various carbon steels was widely investigated. However, the nature of DT remains unclear due to the lack of quantitative analysis of stress partitioning between two phases and the uncertainty of local distribution of substitutional elements at the interface in multi-component carbon steels used in the previous studies. Therefore, in the present study, a binary Fe-Ni alloy with  +
+ duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in
duplex microstructure in equilibrium was prepared and isothermally compressed in  +
+ two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.
two-phase region to achieve quantitative analysis of microstructure evolution, stress partitioning and thermodynamics during DT.  to
to  DT during isothermal compression and
DT during isothermal compression and  to
to  reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between
reverse transformation on isothermal annealing under unloaded condition after deformation were accompanied by Ni partitioning. The lattice strains during thermomechanical processing were obtained via in-situ neutron diffraction measurement, based on which the stress partitioning behavior between  and
and  was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft
was discussed by using the generalized Hooke's law. A thermodynamic framework for the isothermal deformation in solids was established based on the basic laws of thermodynamics, and it was shown that the total Helmholtz free energy change in the deformable material during the isothermal process should be smaller than the work done to the deformable material. Under the present thermodynamic framework, the microstructure evolution in the isothermal compression of Fe-14Ni alloy was well explained by considering the changes in chemical free energy, plastic and elastic energies and the work done to the material. In addition, the stabilization of the soft  phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the
phase in Fe-14Ni alloy by deformation was rationalized since the  to
to  transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
transformation decreased the total Helmholtz free energy by decreasing the elastic and dislocation energies.
 neutron diffraction during cryogenic cooling
neutron diffraction during cryogenic cooling山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.; 藤井 英俊*; 友田 陽*
ISIJ International, 64(2), p.192 - 201, 2024/01
 neutron diffraction measurements were performed on Fe-33Ni-0.004C alloy (33Ni alloy) and Fe-27Ni-0.5C alloy (27Ni-0.5C alloy) during cooling from room temperature to the cryogenic temperature (4 K) to evaluate changes in the lattice constants of austenite and martensite, and changes in the tetragonality of martensite due to thermally induced martensitic transformation. As the martensitic transformation progressed, the lattice constants of austenite in both alloys deviated to smaller values than those predicted considering the thermal shrinkage, accompanied by an increase in the full width at half maximum of austenite. The fresh martensite formed in both alloys had a body-centered tetragonal (BCT) structure, regardless of the carbon content. The tetragonality of martensite decreased with progressive martensitic transformation during cooling in the 33Ni alloy, but was almost constant in the 27Ni-0.5C alloy. This suggests that carbon is necessary to maintain the tetragonality of martensite during cooling. The tetragonality of martensite in the 27Ni-0.5C alloy decreased during room temperature aging because of carbon mobility.
neutron diffraction measurements were performed on Fe-33Ni-0.004C alloy (33Ni alloy) and Fe-27Ni-0.5C alloy (27Ni-0.5C alloy) during cooling from room temperature to the cryogenic temperature (4 K) to evaluate changes in the lattice constants of austenite and martensite, and changes in the tetragonality of martensite due to thermally induced martensitic transformation. As the martensitic transformation progressed, the lattice constants of austenite in both alloys deviated to smaller values than those predicted considering the thermal shrinkage, accompanied by an increase in the full width at half maximum of austenite. The fresh martensite formed in both alloys had a body-centered tetragonal (BCT) structure, regardless of the carbon content. The tetragonality of martensite decreased with progressive martensitic transformation during cooling in the 33Ni alloy, but was almost constant in the 27Ni-0.5C alloy. This suggests that carbon is necessary to maintain the tetragonality of martensite during cooling. The tetragonality of martensite in the 27Ni-0.5C alloy decreased during room temperature aging because of carbon mobility.
徐 平光; Zhang, S.-Y.*; Harjo, S.; Vogel, S. C.*; 友田 陽*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.7_1 - 7_13, 2024/01
Comprehensive information about the  microstructure and crystal structure evolution during the preparation/production processes of various materials is in great demand in order to precisely control the microstructure morphology and the preferred orientation characteristics for the excellent strength-ductility-toughness balance of advanced engineering materials.
microstructure and crystal structure evolution during the preparation/production processes of various materials is in great demand in order to precisely control the microstructure morphology and the preferred orientation characteristics for the excellent strength-ductility-toughness balance of advanced engineering materials.  isothermal annealing experiments of cold rolled 17Ni-0.2C (mass %) martensitic steel sheets were carried out by using the TAKUMI and ENGIN-X time-of-flight neutron diffractometers, respectively. The inverse pole figures based on full-profile refinement were extracted to roughly evaluate the preferred orientation features along three principal sample directions of investigated steel sheets using the General Structure Analysis System (GSAS) software with built-in generalized spherical harmonic functions. The consistent rolling direction (RD) inverse pole figures from TAKUMI and ENGIN-X have confirmed that the time-of-flight neutron diffraction has high repeatability and statistical reliability, revealing that the principal preferred orientation evaluation of steel materials is available through 90
isothermal annealing experiments of cold rolled 17Ni-0.2C (mass %) martensitic steel sheets were carried out by using the TAKUMI and ENGIN-X time-of-flight neutron diffractometers, respectively. The inverse pole figures based on full-profile refinement were extracted to roughly evaluate the preferred orientation features along three principal sample directions of investigated steel sheets using the General Structure Analysis System (GSAS) software with built-in generalized spherical harmonic functions. The consistent rolling direction (RD) inverse pole figures from TAKUMI and ENGIN-X have confirmed that the time-of-flight neutron diffraction has high repeatability and statistical reliability, revealing that the principal preferred orientation evaluation of steel materials is available through 90 TD
TD  ND (transverse direction
ND (transverse direction  normal direction) rotation of the investigated specimen on the sample stage during two neutron diffraction experiments. Moreover, these RD, TD and ND inverse pole figures before and after in situ experiments were compared with the corresponding inverse pole figures recalculated respectively from the MUSASI-L complete pole figure measurement and the HIPPO in situ microstructure evaluation. The similar orientation distribution characteristics suggested that the principal preferred orientation evaluation method can be applied to in situ microstructure evolution of bulk orthorhombic materials and spatially resolved principal preferred orientation mappings of large engineering structure parts.
normal direction) rotation of the investigated specimen on the sample stage during two neutron diffraction experiments. Moreover, these RD, TD and ND inverse pole figures before and after in situ experiments were compared with the corresponding inverse pole figures recalculated respectively from the MUSASI-L complete pole figure measurement and the HIPPO in situ microstructure evaluation. The similar orientation distribution characteristics suggested that the principal preferred orientation evaluation method can be applied to in situ microstructure evolution of bulk orthorhombic materials and spatially resolved principal preferred orientation mappings of large engineering structure parts.
Su, Y. H.; 及川 健一; 篠原 武尚; 甲斐 哲也; 堀野 孝*; 井戸原 修*; 三阪 佳孝*; 友田 陽*
International Journal of Fatigue, 174, p.107729_1 - 107729_12, 2023/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:78.7(Engineering, Mechanical)A novel procedure, double induction quenching (DIQ), effective for improving the fatigue strength of gear products, has been used for producing gears with steep gradients of compressive residual stress generated in the tooth surface. We performed a Bragg edge imaging experiment at a pulsed neutron source to determine the spatial distribution of the {110} lattice spacing (d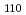 ) and the broadening of the {110} Bragg edge (w
) and the broadening of the {110} Bragg edge (w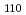 ) on the DIQ gear product after tooth-bending fatigue tests to which different loading cycles were applied. No significant difference occurred in the d
) on the DIQ gear product after tooth-bending fatigue tests to which different loading cycles were applied. No significant difference occurred in the d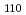 and the w
and the w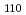 at Hofer 's critical section of the teeth with different loading conditions within the accuracy of data analysis. However, we detected a decrease in the w
at Hofer 's critical section of the teeth with different loading conditions within the accuracy of data analysis. However, we detected a decrease in the w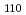 and changes in the residual lattice strain distribution in the axial direction along the tooth root directions at the opposite side of Hofer 's critical section for both teeth after 3
and changes in the residual lattice strain distribution in the axial direction along the tooth root directions at the opposite side of Hofer 's critical section for both teeth after 3 10
10  and 8
and 8 10
10  cycles, relieving the compressive residual stresses during the fatigue process. The residual stress close to the gear tooth surface determined by X-ray diffraction using sequential polishing showed a slight relaxation and redistribution from the tensile side in the hoop direction, complementary to the neutron Bragg edge imaging.
cycles, relieving the compressive residual stresses during the fatigue process. The residual stress close to the gear tooth surface determined by X-ray diffraction using sequential polishing showed a slight relaxation and redistribution from the tensile side in the hoop direction, complementary to the neutron Bragg edge imaging.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionGong, W.; Harjo, S.; 友田 陽*; 諸岡 聡; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 250, p.118860_1 - 118860_16, 2023/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:74.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Martensitic transformation is accompanied by the generation of microscale and macroscale internal stresses during cooling below the martensitic transformation start temperature. These internal stresses have been determined through X-ray or neutron diffraction, but the reported results are not consistent, probably because the measured lattice parameter is influenced not only by the internal stress but also by several factors, including solute elements and crystal defects. Therefore,  neutron diffraction combined with dilatometry measurements during martensitic transformation and subsequent cyclic tempering were performed for an Fe-18Ni alloy. The phase strains calculated by lattice parameter variations show that a hydrostatic compressive strain in austenite and a tensile strain in martensite arose as the martensitic transformation progressed during continuous cooling or isothermal holding. However, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite estimated from these strains failed to hold stress balance law when dense crystal defects involved in the processes. After these crystal defects were removed by appropriate tempering, the stress balance law held well. Meanwhile, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite were changed to opposite, revealing their true identity. Various crystal defects in austenite and martensite, introduced by plastic accommodation, were suggested to affect their lattice parameters and then their phase stresses.
neutron diffraction combined with dilatometry measurements during martensitic transformation and subsequent cyclic tempering were performed for an Fe-18Ni alloy. The phase strains calculated by lattice parameter variations show that a hydrostatic compressive strain in austenite and a tensile strain in martensite arose as the martensitic transformation progressed during continuous cooling or isothermal holding. However, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite estimated from these strains failed to hold stress balance law when dense crystal defects involved in the processes. After these crystal defects were removed by appropriate tempering, the stress balance law held well. Meanwhile, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite were changed to opposite, revealing their true identity. Various crystal defects in austenite and martensite, introduced by plastic accommodation, were suggested to affect their lattice parameters and then their phase stresses.
Wang, Y.*; 友田 陽*; 大村 孝仁*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.
Materialia, 27, p.101685_1 - 101685_9, 2023/03
The evolution of internal stress during displacive transformation is a topic of continuous debate. Neutron diffraction was used to study the isothermal bainite transformation in a 0.4 C low alloyed steel from 773 to 623 K to provide a clearer basis for discussion regarding the change in the austenite lattice parameter. According to diffraction profile analysis, fresh bainite possesses a body-centered tetragonal structure, and its c/a ratio decreases rapidly over time. The austenite lattice parameter increases or decreases depending on whether the transformation temperature is above or below the nose of the Time-Temperature-Transformation (TTT) curve. This isothermal transformation behavior can be divided into two categories: above and below the nose of TTT curve, which correspond to the upper and lower bainites, respectively. The internal stresses caused by the transformation strains are relaxed by dislocation motion and vacancy formation. The yielded dislocations and vacancies not only affect the broadening of both austenite and bainitic ferrite diffraction peaks but also the lattice parameter.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffraction澤口 孝宏*; 友田 陽*; 吉中 奎貴*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118494_1 - 118494_14, 2023/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:45.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fe-Mn-Si-based alloys, show superior resistance to plastic fatigue compared to the conventional steels, which is ascribed to the reversible back-and-forth movement of Shockley partial dislocations associated with a reversible martensitic transformation between the face-centered cubic  -austenite and hexagonal close-packed
-austenite and hexagonal close-packed  -martensite. The purpose of this study was to gather evidence of the reversible martensitic transformation using in situ neutron diffraction under cyclic loading. Three Fe-30Mn-Si-Al alloys with different Gibbs free energy differences at 298 K were studied to unravel the effect of phase stability on the degree of reversibility.
-martensite. The purpose of this study was to gather evidence of the reversible martensitic transformation using in situ neutron diffraction under cyclic loading. Three Fe-30Mn-Si-Al alloys with different Gibbs free energy differences at 298 K were studied to unravel the effect of phase stability on the degree of reversibility.
Su, Y. H.; 及川 健一; 篠原 武尚; 甲斐 哲也; 堀野 孝*; 井戸原 修*; 三阪 佳孝*; 友田 陽*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11, p.4155_1 - 4155_14, 2021/02
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:73.11(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A time-of-flight Bragg-edge neutron transmission imaging was used to investigate the microstructure and strain distributions in a gear hardened by a newly developed two-step induction-heating method: precursor (Sample 1) and final product (Sample 2). The edge- position and edge-broadening were determined and mapped with high spatial resolution, which enabled us to confirm the two-dimensional distributions of the microstructure and residual strain. A deep hardened layer was made for Sample 1 in which martensite was formed on the entire teeth and the outer peripheral portion of the gear body. Sample 2 was subjected to double induction-hardening, where a tempered martensite was formed as the thermal refined microstructure between a fine-grained martensite at the tooth surface and a ferrite-pearlite microstructure at the core. The relationship between edge-broadening and the Vickers hardness described by a linear equation was employed to derive the elastic residual strain. The residual strain map for Sample 2 revealed that a steep compressive strain was introduced into the fine-grained martensite at the tooth surface by the super rapid induction- heating and quenching process. The reversal of tension was speculated to occur below 2 mm from the tooth tip, and the strain was almost zero in the core region.
Wang, Y.*; 友田 陽*; 大村 孝仁*; Gong, W.*; Harjo, S.; 田中 雅彦*
Acta Materialia, 196, p.565 - 575, 2020/09
被引用回数:31 パーセンタイル:90.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The continuous and discontinuous yielding behaviors in ferrite-cementite steels were complementarily investigated via nano- and macroscale deformation examinations. The results obtained by electron microscopy, synchrotron X-ray, and neutron diffractions indicate that the ferrite-cementite interface of the heat-treated specimen is semi-coherent with a high internal stress field, whereas that of the recrystallized one is incoherent with a low internal stress field. Moreover, coherency strain, which depends on the total area of the ferrite-cementite interface, and thermal strain, which is governed by temperature, are the two factors that influence peak broadening. The nanoindentation tests revealed that the critical loads are significantly lower near the semi-coherent interface than those near the incoherent interface and the ferrite grain boundary; this suggests that dislocations are easily emitted from the semi-coherent interface.
細谷 佳弘*; 松村 雄太*; 友田 陽*; 小貫 祐介*; Harjo, S.
ISIJ International, 60(9), p.2097 - 2106, 2020/09
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:31.59(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)In this paper, the microstructure formation during the R&P process and the deformation mechanism that would bring about the excellent strength-ductility balance are discussed based on the results obtained from the in situ neutron diffraction measurement. The results have revealed that the typical Luders-like stress-strain curve of R&P steel is caused by competitive plastic flow between austenite and martensite, and an effective transformation induced plasticity phenomenon.
友田 陽*; 村上 俊夫*; Wang, Y. X.*; 大村 孝仁*; Harjo, S.; Su, Y. H.; 篠原 武尚
Materials Characterization, 163, p.110243_1 - 110243_8, 2020/05
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:32.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, the effects of carbon concentration and magnetic transition on the austenite lattice parameter of Fe-30Mn- C alloys were assessed. A linear relationship was obtained between the carbon content and the lattice parameter determined by neutron diffraction and neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging for austenitic steels bearing 0.007-1.20 mass% C. The results obtained through both methods showed good agreement. In addition, carbon partitioning was evaluated in artificially piled-up discs with different carbon contents in order to develop a new technique for advanced multi-phase steels. The analysis of asymmetry and broadening of the diffraction line profile revealed that the carbon partitioning could be determined. In conclusion, the results presented herein expand the current knowledge on the properties of high Mn austenite.
C alloys were assessed. A linear relationship was obtained between the carbon content and the lattice parameter determined by neutron diffraction and neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging for austenitic steels bearing 0.007-1.20 mass% C. The results obtained through both methods showed good agreement. In addition, carbon partitioning was evaluated in artificially piled-up discs with different carbon contents in order to develop a new technique for advanced multi-phase steels. The analysis of asymmetry and broadening of the diffraction line profile revealed that the carbon partitioning could be determined. In conclusion, the results presented herein expand the current knowledge on the properties of high Mn austenite.
友田 陽*; Wang, Y.*; 大村 孝仁*; 関戸 信彰*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.*; 谷山 明*
鉄と鋼, 106(5), p.262 - 271, 2020/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The phase transformation behavior from austenite upon cooling in a 1.5Mn-1.5Si-0.2C steel was  monitored using dilatometry, X-ray and neutron diffractions. The starting temperature of ferrite transformation was in good agreement between dilatometry and neutron diffraction, whereas much higher in X-ray diffraction. Such a discrepancy in transformation temperature is attributed to the change in chemical composition near the surface of a specimen heated to elevated temperatures in a helium gas atmosphere for X-ray diffraction.
monitored using dilatometry, X-ray and neutron diffractions. The starting temperature of ferrite transformation was in good agreement between dilatometry and neutron diffraction, whereas much higher in X-ray diffraction. Such a discrepancy in transformation temperature is attributed to the change in chemical composition near the surface of a specimen heated to elevated temperatures in a helium gas atmosphere for X-ray diffraction.  neutron diffraction enables us to investigate the changes in lattice constants of ferrite and austenite, which are affected by not only thermal contraction but also transformation strains, thermal misfit strains and carbon enrichment in austenite. Pearlite transformation started after carbon enrichment in austenite reached approximately 0.7 mass% and contributed to diffraction line broadening.
neutron diffraction enables us to investigate the changes in lattice constants of ferrite and austenite, which are affected by not only thermal contraction but also transformation strains, thermal misfit strains and carbon enrichment in austenite. Pearlite transformation started after carbon enrichment in austenite reached approximately 0.7 mass% and contributed to diffraction line broadening.
高橋 治*; 渋井 洋平*; 徐 平光; Harjo, S.; 鈴木 徹也*; 友田 陽*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(1), p.16_1 - 16_15, 2020/03
The characteristics of texture and microstructure of lean duplex stainless steels with low Ni content produced through hot rolling followed by annealing were investigated locally with electron backscatter diffraction and globally with neutron diffraction. Then, the ductile-brittle transition (DBT) behavior was studied by Charpy impact test. It is found that the DBT temperature (DBTT) is strongly affected by the direction of crack propagation, depending on crystallographic texture and microstructural morphology; the DBTT becomes extremely low in the case of fracture accompanying delamination. A high Ni duplex stainless steel examined for comparison, shows a lower DBTT compared with the lean steel in the same crack propagating direction. The obtained results were also discussed through comparing with those of cast duplex stainless steels reported previously (Takahashi et al., Tetsu-to-Hagane, 100(2014), 1150).
細谷 佳弘*; 松村 雄太*; 友田 陽*; 小貫 祐介*; Harjo, S.
鉄と鋼, 106(3), p.154 - 164, 2020/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:12.73(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)By using a steel with standardized chemical composition and conventional manufacturing processes for flat-rolled steel strip, a 1,500 MPa class stainless steel sheet, whose product of yield strength (YS) and total elongation (El) exceeds 30,000 MPa%, was developed and its mass production was established. Besides the excellent YS-El balance, the developed steel sheet has excellent performance for not only an anti-secondary work embrittlement but also high cycle fatigue endurance. The microstructure formation during the R&P process and the deformation mechanism that would bring about the excellent strength-ductility balance are discussed based on the results obtained from the in situ neutron diffraction measurement. The results have revealed that the typical Luders-like stress-strain curve of R&P steel is caused by competitive plastic flow between austenite and martensite, and an effective transformation induced plasticity phenomenon.
Wang, Y.*; 友田 陽*; 大村 孝仁*; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 184, p.30 - 40, 2020/02
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:86.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A high-intensity and high-resolution neutron diffractometer with a thermomechanically controlled processing simulator was employed in-situ to investigate martensite transformation behavior with and without ausforming for a medium-carbon low-alloy steel. Serial neutron diffraction profiles have revealed that the transformation behavior could be successfully monitored during quenching with and without the ausforming process. The lattice parameter and the full width at half maximum of austenite peaks significantly decreases and increases upon martensite transformation, respectively. After ausforming, the data reveal that lattice parameters are larger in austenite whereas smaller in martensite compared with those in the non-ausformed case, which is ascribed to the introduced dislocations. The cutting-edge operant quantitative measurements with neutron diffraction for steel production is demonstrated.
友田 陽*; 小嶋 真由美*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.*; 佐藤 成男*; Ung r, T.*
r, T.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 743, p.32 - 39, 2019/01
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:80.65(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Heterogeneous plastic deformation behavior of 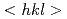 oriented individual grains-family with respect to the tensile direction in austenitic steels was studied using electron back scatter diffraction (EBSD) and neutron diffraction (ND) measurements. The kernel averaged misorientation value determined by EBSD for a plastically deformed specimen was different in grain to grain, suggesting different dislocation densities. Such insights obtained from the surface observations with EBSD were quantitatively evaluated as bulk-averaged data using ND. The convolutional multiple whole profile fitting (CMWP) for ND profiles has revealed different dislocation densities in
oriented individual grains-family with respect to the tensile direction in austenitic steels was studied using electron back scatter diffraction (EBSD) and neutron diffraction (ND) measurements. The kernel averaged misorientation value determined by EBSD for a plastically deformed specimen was different in grain to grain, suggesting different dislocation densities. Such insights obtained from the surface observations with EBSD were quantitatively evaluated as bulk-averaged data using ND. The convolutional multiple whole profile fitting (CMWP) for ND profiles has revealed different dislocation densities in 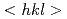 oriented grains-families, showing good coincidence with the EBSD results in trend.
oriented grains-families, showing good coincidence with the EBSD results in trend.
及川 健一; Su, Y. H.; 鬼柳 亮嗣; 川崎 卓郎; 篠原 武尚; 甲斐 哲也; 廣井 孝介; Harjo, S.; Parker, J. D.*; 松本 吉弘*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.436 - 442, 2018/12
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:30.3(Physics, Condensed Matter)We are promoting for practical product observation by the energy-resolved neutron imaging method using high-intensity pulsed neutrons at J-PARC, under the Photon and Quantum Basic Research Coordinated Development Program from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. Bragg edge imaging, one of the energy-resolved neutron imaging methods for visualizing material properties, was applied to feasibility study of the temperature distribution of copper rod, complementary study of the texture and strain distribution of bent steel plates using neutron diffraction and EBSD, and so on. Outline of results obtained by these imaging experiments will be presented.
徐 平光; Harjo, S.; 小島 真由美*; 鈴木 裕士; 伊藤 崇芳*; Gong, W.; Vogel, S. C.*; 井上 純哉*; 友田 陽*; 相澤 一也; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 51(3), p.746 - 760, 2018/06
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:90.58(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Neutron diffraction texture measurements provide bulk textures with excellent grain statistics even for large grained materials, together with the crystallographic parameters and microstructure information such as phase fractions, coherent crystallite size, root mean square microstrain, macroscopic/intergranular stress/strain. The procedure for high stereographic resolution texture and residual stress evaluation was established at the TAKUMI engineering materials diffractometer. The pole figure evaluation of a limestone standard sample with a trigonal crystal structure suggested that the obtained precision for texture measurement is comparable with the oversea well-established neutron beam lines utilized for texture measurements. A high strength martensite-austenite multilayered steel was employed for further verification of the reliability of simultaneous Rietveld analysis of multiphase textures and macro stress tensors. By using a geometric mean micro-mechanical model, the macro stress tensor analysis with a plane stress assumption showed a RD-TD in-plane compressive stress (about -330 MPa) in martensite layers and a RD-TD in-plane tensile stress (about 320 MPa) in austenite layers. The phase stress partitioning was ascribed to the additive effect of volume expansion during martensite transformation and the linear contraction misfit during water quenching.
佐藤 成男*; 黒田 あす美*; 佐藤 こずえ*; 熊谷 正芳*; Harjo, S.; 友田 陽*; 齋藤 洋一*; 轟 秀和*; 小貫 祐介*; 鈴木 茂*
鉄と鋼, 104(4), p.201 - 207, 2018/00
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:44.29(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)To investigate the characteristics of dislocation evolution in ferritic and austenitic stainless steels under tensile deformation, neutron diffraction line-profile analysis was carried out. The austenitic steel exhibited higher work hardening than the ferritic steel. The difference in the work hardening ability between the two steels was explained with the dislocation density estimated by the line-profile analysis. The higher dislocation density of the austenitic steel would originate from its lower stacking fault energy. Dislocation arrangement parameters indicated that the strength of interaction between dislocations in the austenitic steel was stronger than that in the ferritic steel.
友田 陽*; 関戸 信彰*; 徐 平光; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 田中 雅彦*; 篠原 武尚; Su, Y. H.; 谷山 明*
鉄と鋼, 103(10), p.570 - 578, 2017/10
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:50.97(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Various methods were employed to measure the austenite volume fraction in a 1.5Mn-1.5Si-0.2C steel. It has been confirmed that the volume fractions determined by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy/electron back scatter diffraction, X-ray diffraction and neutron diffraction exhibit a general trend to become larger in this order, although the values obtained by X-ray and neutron diffraction are similar in the present steel because austenite is relatively stable. The austenite volume fractions determined by diffraction methods have been found to be affected by the measuring specimen direction, i.e., texture, even by applying the conventional correcting procedure. To avoid this influence, it is recommended to measure both of volume fraction and texture simultaneously using neutron diffraction. Although synchrotron X-ray shows higher angle resolution, its small incident beam size brings poor statistic reliability. The influence of texture cannot be avoided for transmission Bragg edge measurement, either, which must be overcome to realize 2D or 3D volume fraction mapping.