Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
Fe O
O grown on Al
grown on Al O
O ; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCD
; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCD野中 洋亮*; 若林 勇希*; 芝田 悟朗; 坂本 祥哉*; 池田 啓祐*; Chi, Z.*; Wan, Y.*; 鈴木 雅弘*; 田中 新*; 田中 雅明*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(4), p.044413_1 - 044413_10, 2023/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study the electronic and magnetic states of as-grown and annealed  Fe
Fe O
O (111)/Al
(111)/Al O3(111) (
O3(111) (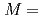 Co, Ni) thin films with various thicknesses grown on Si(111) substrates with the
Co, Ni) thin films with various thicknesses grown on Si(111) substrates with the  -Al
-Al O
O (111)buffer layers by using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), to investigate magnetically dead layers in these films. Although the magnetically dead layers in the as-grown samples are formed near the interface with the Al
(111)buffer layers by using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), to investigate magnetically dead layers in these films. Although the magnetically dead layers in the as-grown samples are formed near the interface with the Al O
O buffer layer, we reveal that ferrimagnetic order is partially recovered by postdeposition annealing at 973 K for 48 hours in air. By analyzing the line shapes of the XAS and XMCD spectra, we conclude that, in the dead layers, there are a significant number of vacancies at the
buffer layer, we reveal that ferrimagnetic order is partially recovered by postdeposition annealing at 973 K for 48 hours in air. By analyzing the line shapes of the XAS and XMCD spectra, we conclude that, in the dead layers, there are a significant number of vacancies at the 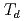 sites of the spinel structure, which may be the microscopic origin of the degraded ferrimagnetic order in the
sites of the spinel structure, which may be the microscopic origin of the degraded ferrimagnetic order in the  Fe
Fe O
O thin films.
thin films.
 Mn
Mn Te studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
Te studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroismVerma, V.*; 坂本 祥哉*; 石川 弘一郎*; Singh, V. R.*; 石上 啓介*; 芝田 悟朗; 門野 利治*; 小出 常晴*; 黒田 真司*; 藤森 淳*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 642, p.414129_1 - 414129_5, 2022/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:53.42(Physics, Condensed Matter)The prototypical diluted magnetic semiconductor Cd Mn
Mn Te is a spin glass (
Te is a spin glass (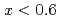 ) or an antiferromagnet (
) or an antiferromagnet (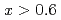 ) but becomes ferromagnetic upon doping with a small amount of Cr atoms. To investigate the origin of the ferromagnetism in Cd
) but becomes ferromagnetic upon doping with a small amount of Cr atoms. To investigate the origin of the ferromagnetism in Cd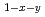 Mn
Mn Cr
Cr Te, we have studied its element specific magnetic properties by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD). Measured XAS and XMCD spectra indicate that both Cr and Mn atoms are divalent and that the magnetic moments of Cr and Mn are aligned parallel. By analyzing the element-specific magnetization curves, we conclude that Cr doping leads to the formation of ferromagnetic or superparamagnetic clusters consisting of several Cr ions surrounded by a much larger number of Mn ions.
Te, we have studied its element specific magnetic properties by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD). Measured XAS and XMCD spectra indicate that both Cr and Mn atoms are divalent and that the magnetic moments of Cr and Mn are aligned parallel. By analyzing the element-specific magnetization curves, we conclude that Cr doping leads to the formation of ferromagnetic or superparamagnetic clusters consisting of several Cr ions surrounded by a much larger number of Mn ions.
 K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering鈴木 博人*; Zhao, G.*; 岡本 淳*; 坂本 祥哉*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; 野中 洋亮*; 芝田 悟朗; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic properties and the electronic excitations of the new diluted magnetic semiconductor Ba K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As have been studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). The sum rule analysis of the XMCD spectra indicates that the Mn atoms are in the high-spin configurations of
have been studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). The sum rule analysis of the XMCD spectra indicates that the Mn atoms are in the high-spin configurations of 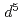 , whereas the presence of competing ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic interactions between the Mn ions reduces the net spin moment. Based on a comparison of the RIXS line shapes with those of Ga
, whereas the presence of competing ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic interactions between the Mn ions reduces the net spin moment. Based on a comparison of the RIXS line shapes with those of Ga Mn
Mn As, it is concluded that the ground state of Mn in Ba
As, it is concluded that the ground state of Mn in Ba K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As consists of both the
consists of both the 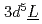 and
and 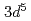 electron configurations.
electron configurations.
 impurity band state as the origin of high Curie temperature in the
impurity band state as the origin of high Curie temperature in the  -type ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb
-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb武田 崇仁*; 坂本 祥哉*; 荒木 恒星*; 藤澤 唯太*; Anh, L. D.*; Tu, N. T.*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; 藤森 淳*; 田中 雅明*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(24), p.245203_1 - 245203_8, 2020/12
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:44.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)(Ga ,Fe
,Fe )Sb is one of the promising ferromagnetic semiconductors for spintronic device applications because its Curie temperature (Tc) is above 300 K when the Fe concentration
)Sb is one of the promising ferromagnetic semiconductors for spintronic device applications because its Curie temperature (Tc) is above 300 K when the Fe concentration  is equal to or higher than 0.20. However, the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb remains to be elucidated. To address this issue, we use resonant photoemission spectroscopy (RPES) and first-principles calculations to investigate the x dependence of the Fe 3
is equal to or higher than 0.20. However, the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb remains to be elucidated. To address this issue, we use resonant photoemission spectroscopy (RPES) and first-principles calculations to investigate the x dependence of the Fe 3 states in (Ga
states in (Ga ,Fe
,Fe )Sb (
)Sb ( = 0.05, 0.15, and 0.25) thin films. The observed Fe 2
= 0.05, 0.15, and 0.25) thin films. The observed Fe 2 -3
-3 RPES spectra reveal that the Fe-3
RPES spectra reveal that the Fe-3 impurity band (IB) crossing the Fermi level becomes broader with increasing
impurity band (IB) crossing the Fermi level becomes broader with increasing  , which is qualitatively consistent with the picture of double-exchange interaction. Comparison between the obtained Fe-3
, which is qualitatively consistent with the picture of double-exchange interaction. Comparison between the obtained Fe-3 partial density of states and the first-principles calculations suggests that the Fe-3
partial density of states and the first-principles calculations suggests that the Fe-3 IB originates from the minority-spin (
IB originates from the minority-spin (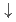 )
) 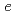 states. The results indicate that enhancement of the double-exchange interaction between
states. The results indicate that enhancement of the double-exchange interaction between 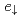 electrons with increasing
electrons with increasing  is the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb.
is the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb.
 ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies
ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies坂本 祥哉*; Tu, N. T.*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; Hai, P. N.*; Anh, L. D.*; 若林 勇希*; 芝田 悟朗*; 堀尾 眞史*; 池田 啓祐*; et al.
Physical Review B, 100(3), p.035204_1 - 035204_8, 2019/07
The electronic structure and the magnetism of the ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb, whose Curie temperature  can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3
can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3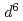 contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3
contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3 electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3
electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3 states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states, presumably consisting of majority-spin
states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states, presumably consisting of majority-spin  -
- hybridized states or minority-spin e states, would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
hybridized states or minority-spin e states, would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
 ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies
ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies坂本 祥哉*; Tu, N. T.*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; Hai, P. N.*; Anh, L. D.*; 若林 勇希*; 芝田 悟朗*; 堀尾 眞史*; 池田 啓祐*; et al.
Physical Review B, 100(3), p.035204_1 - 035204_8, 2019/07
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:66.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The electronic structure and the magnetism of the ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb, whose Curie temperature  can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3
can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3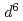 contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3
contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3 electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3
electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3 states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
 VFeAsO
VFeAsO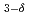 studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism堀尾 眞史*; 竹田 幸治; 並木 宏允*; 片桐 隆雄*; 若林 勇希*; 坂本 祥哉*; 野中 洋亮*; 芝田 悟朗*; 池田 啓祐*; 斎藤 祐児; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(10), p.105001_1 - 105001_2, 2018/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:21.2(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have performed X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) measurements on the iron-based superconductor Sr VFeAsO
VFeAsO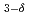 to study the origin of weak ferromagnetism (WFM) reported for this compound. While Fe 3d electrons show a magnetic response similar to the other iron pnictides, signals from V 3d electrons remain finite at zero magnetic field and may be responsible for the WFM.
to study the origin of weak ferromagnetism (WFM) reported for this compound. While Fe 3d electrons show a magnetic response similar to the other iron pnictides, signals from V 3d electrons remain finite at zero magnetic field and may be responsible for the WFM.
 Co
Co )Fe
)Fe O
O (x=0-1) layers on Si(111) studied by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
(x=0-1) layers on Si(111) studied by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism若林 勇希*; 野中 洋亮*; 竹田 幸治; 坂本 祥哉*; 池田 啓祐*; Chi, Z.*; 芝田 悟朗*; 田中 新*; 斎藤 祐児; 山上 浩志; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 2(10), p.104416_1 - 104416_12, 2018/10
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:37.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study the electronic structure and magnetic properties of epitaxial (Ni Co
Co )Fe
)Fe O
O (111) layers with thicknesses
(111) layers with thicknesses  = 1.7 - 5.2 nm grown on Al
= 1.7 - 5.2 nm grown on Al O
O (111)/Si(111) structures. We revealed the crystallographic (octahedral
(111)/Si(111) structures. We revealed the crystallographic (octahedral 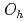 or tetrahedral
or tetrahedral 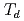 ) sites and the valences of the Fe, Co, and Ni cations using experimental soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism spectra and configuration-interaction cluster-model calculation.
) sites and the valences of the Fe, Co, and Ni cations using experimental soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism spectra and configuration-interaction cluster-model calculation.
坂本 祥哉*; 若林 勇希*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; 鈴木 博人*; 伴 芳祐*; 山上 浩志; 田中 雅明*; 大矢 忍*; 藤森 淳*
Physical Review B, 95(7), p.075203_1 - 075203_5, 2017/02
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:42.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ge Fe
Fe (Ge:Fe) shows ferromagnetic behavior up to a relatively high temperature of 210 K and hence is a promising material for spintronic applications compatible with Si technology. We have studied its underlying electronic structure by soft X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy measurements and first-principles supercell calculation. We observed finite Fe 3
(Ge:Fe) shows ferromagnetic behavior up to a relatively high temperature of 210 K and hence is a promising material for spintronic applications compatible with Si technology. We have studied its underlying electronic structure by soft X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy measurements and first-principles supercell calculation. We observed finite Fe 3 components in the states at the Fermi level (
components in the states at the Fermi level (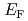 ) in a wide region of momentum space, and the
) in a wide region of momentum space, and the 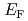 was located
was located  0.35 eV above the valence-band maximum of the host Ge. Our calculation indicates that the
0.35 eV above the valence-band maximum of the host Ge. Our calculation indicates that the 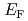 is also within the deep acceptor-level impurity band induced by the strong
is also within the deep acceptor-level impurity band induced by the strong  -
- (
(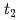 ) hybridization. We conclude that the additional minority-spin
) hybridization. We conclude that the additional minority-spin 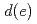 electron characteristic of the Fe
electron characteristic of the Fe state is responsible for the short-range ferromagnetic coupling between Fe atoms.
state is responsible for the short-range ferromagnetic coupling between Fe atoms.
 Mn
Mn granular thin films
granular thin films若林 勇希*; 秋山 了太*; 竹田 幸治; 堀尾 眞史*; 芝田 悟朗*; 坂本 祥哉*; 伴 芳祐*; 斎藤 祐児; 山上 浩志; 藤森 淳*; et al.
Physical Review B, 95(1), p.014417_1 - 014417_6, 2017/01
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:45.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ge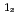 Mn
Mn (GeMn) granular thin films are a unique and promising material for spintronic applications owing to their large positive magnetoresistance (MR). The microscopic origin of the MR has not yet been clarified. Here, we develop a method to separately investigate the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles and the matrix, utilizing the extremely high sensitivity of X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) to the local magnetic state of each atom. We find that the MR ratio is proportional to the product of the magnetizations originating from the nanoparticles and the matrix. This result indicates that the spin-polarized holes in the nanoparticles penetrate into the matrix and that these holes undergo first order magnetic scattering by the paramagnetic Mn atoms in the matrix, which induces the large MR.
(GeMn) granular thin films are a unique and promising material for spintronic applications owing to their large positive magnetoresistance (MR). The microscopic origin of the MR has not yet been clarified. Here, we develop a method to separately investigate the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles and the matrix, utilizing the extremely high sensitivity of X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) to the local magnetic state of each atom. We find that the MR ratio is proportional to the product of the magnetizations originating from the nanoparticles and the matrix. This result indicates that the spin-polarized holes in the nanoparticles penetrate into the matrix and that these holes undergo first order magnetic scattering by the paramagnetic Mn atoms in the matrix, which induces the large MR.
Frandsen, B. A.*; Liu, L.*; Cheung, S. C.*; Guguchia, Z.*; Khasanov, R.*; Morenzoni, E.*; Munsie, T. J. S.*; Hallas, A. M.*; Wilson, M. N.*; Cai, Y.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 7, p.12519_1 - 12519_8, 2016/08
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:77.26(Multidisciplinary Sciences)RENiO (RE = rare-earth element) and V
(RE = rare-earth element) and V O
O are archetypal Mott insulator systems. When tuned by chemical substitution (RENiO
are archetypal Mott insulator systems. When tuned by chemical substitution (RENiO ) or pressure (V
) or pressure (V O
O ), they exhibit a quantum phase transition (QPT) between an antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state and a paramagnetic metallic state. Because novel physics often appears near a Mott QPT, the details of this transition, such as whether it is first or second order, are important. Here, we demonstrate through muon spin relaxation/rotation experiments that the QPT in RENiO
), they exhibit a quantum phase transition (QPT) between an antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state and a paramagnetic metallic state. Because novel physics often appears near a Mott QPT, the details of this transition, such as whether it is first or second order, are important. Here, we demonstrate through muon spin relaxation/rotation experiments that the QPT in RENiO and V
and V O
O is first order: the magnetically ordered volume fraction decreases to zero at the QPT, resulting in a broad region of intrinsic phase separation, while the ordered magnetic moment retains its full value until it is suddenly destroyed at the QPT. These findings bring to light a surprising universality of the pressure-driven Mott transition, revealing the importance of phase separation and calling for further investigation into the nature of quantum fluctuations underlying the transition.
is first order: the magnetically ordered volume fraction decreases to zero at the QPT, resulting in a broad region of intrinsic phase separation, while the ordered magnetic moment retains its full value until it is suddenly destroyed at the QPT. These findings bring to light a surprising universality of the pressure-driven Mott transition, revealing the importance of phase separation and calling for further investigation into the nature of quantum fluctuations underlying the transition.
 Fe
Fe
若林 勇希*; 坂本 祥哉*; 竹田 幸治; 石上 啓介*; 高橋 文雄*; 斎藤 祐児; 山上 浩志; 藤森 淳*; 田中 雅明*; 大矢 忍*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.23295_1 - 23295_9, 2016/03
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:66.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We investigate the local electronic structure and magnetic properties of the group-IV-based ferromagnetic semiconductor, Ge Fe
Fe (GeFe), using soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. Our results show that the doped Fe 3
(GeFe), using soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. Our results show that the doped Fe 3 electrons are strongly hybridized with the Ge 4
electrons are strongly hybridized with the Ge 4 states, and have a large orbital magnetic moment relative to the spin magnetic moment, namely
states, and have a large orbital magnetic moment relative to the spin magnetic moment, namely 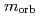 /
/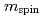
 0.1. We find that nanoscale local ferromagnetic regions, which are formed through ferromagnetic exchange interactions in the high-Fe-content regions of the GeFe films, exist even at room temperature, well above the Curie temperature of 20 - 100K. We observe the intriguing nanoscale expansion of the local ferromagnetic regions with decreasing temperature, followed by a transition of the entire film into a ferromagnetic state at the Curie temperature.
0.1. We find that nanoscale local ferromagnetic regions, which are formed through ferromagnetic exchange interactions in the high-Fe-content regions of the GeFe films, exist even at room temperature, well above the Curie temperature of 20 - 100K. We observe the intriguing nanoscale expansion of the local ferromagnetic regions with decreasing temperature, followed by a transition of the entire film into a ferromagnetic state at the Curie temperature.
 -type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As:Be studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As:Be studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism坂本 祥哉*; Anh, L. D.*; Hai, P. N.*; 芝田 悟朗*; 竹田 幸治; 小林 正起*; 高橋 文雄*; 小出 常晴*; 田中 雅明*; 藤森 淳*
Physical Review B, 93(3), p.035203_1 - 035203_6, 2016/01
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:63.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to investigate the mechanism of ferromagnetic ordering in the new  -type magnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As codoped with Be, we have performed X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) studies. The spectral line shapes suggest that the ferromagnetism is intrinsic, originating from Fe atoms incorporated into the zinc-blende-type InAs lattice. The magnetization curves of Fe measured by XMCD were well reproduced by the superposition of a Langevin function representing superparamagnetic (SPM) behavior of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains and a
-type magnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As codoped with Be, we have performed X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) studies. The spectral line shapes suggest that the ferromagnetism is intrinsic, originating from Fe atoms incorporated into the zinc-blende-type InAs lattice. The magnetization curves of Fe measured by XMCD were well reproduced by the superposition of a Langevin function representing superparamagnetic (SPM) behavior of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains and a  -linear function representing Curie-Weiss paramagnetism even much above the Curie temperatures. The data at 20 K showed a deviation from the Langevin behavior, suggesting a gradual establishment of macroscopic ferromagnetism on lowering temperature. The existence of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains indicated by the SPM behavior suggests spatial fluctuations of Fe concentration on the nanoscale.
-linear function representing Curie-Weiss paramagnetism even much above the Curie temperatures. The data at 20 K showed a deviation from the Langevin behavior, suggesting a gradual establishment of macroscopic ferromagnetism on lowering temperature. The existence of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains indicated by the SPM behavior suggests spatial fluctuations of Fe concentration on the nanoscale.
 -type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As
-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As小林 正起*; Anh, L. D.*; Hai, P. N.*; 竹田 幸治; 坂本 祥哉*; 門野 利治*; 岡根 哲夫; 斎藤 祐児; 山上 浩志; 原田 慈久*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 105(3), p.032403_1 - 032403_4, 2014/07
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:26.85(Physics, Applied)The electronic and magnetic properties of Fe atoms in the ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As codoped with Be have been studied by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) at the Fe 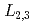 edge. The XAS and XMCD spectra showed simple spectral line shapes similar to Fe metal, but the ratio of the orbital and spin magnetic moments estimated using the XMCD sum rules was significantly larger than that of Fe metal, indicating a significant orbital moment of Fe 3
edge. The XAS and XMCD spectra showed simple spectral line shapes similar to Fe metal, but the ratio of the orbital and spin magnetic moments estimated using the XMCD sum rules was significantly larger than that of Fe metal, indicating a significant orbital moment of Fe 3 electrons in (In,Fe)As:Be. The XMCD intensity as a function of magnetic field indicated hysteretic behavior of the superparamagnetic-like component due to discrete ferromagnetic domains. VC
electrons in (In,Fe)As:Be. The XMCD intensity as a function of magnetic field indicated hysteretic behavior of the superparamagnetic-like component due to discrete ferromagnetic domains. VC