Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 伊藤 小百合; 石岡 典子; 菊地 郁*; 塚本 崇志*; 草川 知行*; 藤巻 秀
Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2009 NSS/MIC) (CD-ROM), p.1257 - 1258, 2009/10
In recent years, radionuclide-based imaging technologies have been providing researchers with exciting new opportunities to study biology. The positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS), which has a planar PET scanner, is one of the most powerful techniques used for conducting plant researches in order to study the distribution and translocation of water, sugar, nutrients, and environmental pollutants. In the sink-source relationship in the plant body, source abilities of a leaf imaged using a compartmental model analysis with PETIS data. In this case, to clarify the mechanism of the growth and development of the agricultural produces, we performed imaging experiments of sugar translocation to sink organ of fruits. A near leaf of the target fruits (Eggplant and Tomato) inhaled carbon-11 labeled carbon dioxide (100 MBq), and the translocation of carbon-11 labeled photoassimilate into fruits was imaged by PETIS for two hours. As a result, serial images of graduate increasing  C activity and its ununiformly distribution in the fruit were acquired successfully. And also velocities of photoassimilate translocation and changes in the contributing rate with time of translocation from the leaf were estimated by analysis of PETIS data.
C activity and its ununiformly distribution in the fruit were acquired successfully. And also velocities of photoassimilate translocation and changes in the contributing rate with time of translocation from the leaf were estimated by analysis of PETIS data.
 Fe translocation in barley as monitored by a Positron-Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS); Evidence for the direct translocation of Fe from roots to young leaves via phloem
Fe translocation in barley as monitored by a Positron-Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS); Evidence for the direct translocation of Fe from roots to young leaves via phloem塚本 崇志*; 中西 啓仁*; 内田 博*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 森 敏*; 西澤 直子*
Plant & Cell Physiology, 50(1), p.48 - 57, 2009/01
被引用回数:88 パーセンタイル:90.06(Plant Sciences)The real-time translocation of iron (Fe) in barley ( L. cv. Ehimehadaka no.1) was visualized using the positron-emitting tracer
L. cv. Ehimehadaka no.1) was visualized using the positron-emitting tracer  Fe and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). PETIS allowed us to monitor Fe translocation in barley non-destructively under various conditions. In all cases,
Fe and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). PETIS allowed us to monitor Fe translocation in barley non-destructively under various conditions. In all cases,  Fe first accumulated at the basal part of the shoot. Fe-deficient barley showed greater translocation of
Fe first accumulated at the basal part of the shoot. Fe-deficient barley showed greater translocation of  Fe from roots to shoots than did Fe-sufficient barley. In the dark, translocation of
Fe from roots to shoots than did Fe-sufficient barley. In the dark, translocation of  Fe to the youngest leaf was equivalent to or higher than that under the light condition, while the translocation of
Fe to the youngest leaf was equivalent to or higher than that under the light condition, while the translocation of  Fe to the older leaves was decreased, in both Fe-deficient and Fe-sufficient barley. This suggests the possibility that the mechanism and/or pathway of Fe translocation to the youngest leaf may be different from that to the older leaves. When phloem transport in the leaf was blocked by steam treatment,
Fe to the older leaves was decreased, in both Fe-deficient and Fe-sufficient barley. This suggests the possibility that the mechanism and/or pathway of Fe translocation to the youngest leaf may be different from that to the older leaves. When phloem transport in the leaf was blocked by steam treatment,  Fe translocation from the roots to older leaves was not affected, while
Fe translocation from the roots to older leaves was not affected, while  Fe translocation to the youngest leaf was reduced. We propose a novel model in which root-absorbed Fe is translocated from the basal part of the shoots and/or roots to the youngest leaf via phloem in graminaceous plants.
Fe translocation to the youngest leaf was reduced. We propose a novel model in which root-absorbed Fe is translocated from the basal part of the shoots and/or roots to the youngest leaf via phloem in graminaceous plants.
鈴木 基史*; 塚本 崇志*; 井上 晴彦*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 高橋 美智子*; 中西 啓仁*; 森 敏*; 西澤 直子*
Plant Molecular Biology, 66(6), p.609 - 617, 2008/04
被引用回数:138 パーセンタイル:95.26(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Rice secretes Deoxymugineic acid (DMA) in response to Fe deficiency to take up Fe in the form of Fe(III)-DMS complex. In contrast with barley, the roots of which secrete DMS in response to Zn deficiency, the amount of DMA secreted by rice roots was slightly decreased under conditions of low Zn supply. There was a concomitant increase in endogenous DMA in rice shoots, suggesting that DMA plays a role in the translocation of Zn within Zn-deficient rice plants. The expression of 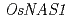 and
and 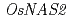 was not increased in Zn-deficient roots but that of
was not increased in Zn-deficient roots but that of 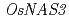 was increased in Zn-deficient roots and shoots. The expression of
was increased in Zn-deficient roots and shoots. The expression of 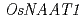 was also increased in Zn-deficient roots and dramatically increased in shoots; correspondingly, HPLC analysis was unable to detect nicotianamine in Zn-deficient shoots. The expression of
was also increased in Zn-deficient roots and dramatically increased in shoots; correspondingly, HPLC analysis was unable to detect nicotianamine in Zn-deficient shoots. The expression of 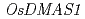 was increased in Zn-deficient shoots. Analyses using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) showed that Zn-deficient rice roots absorbed less
was increased in Zn-deficient shoots. Analyses using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) showed that Zn-deficient rice roots absorbed less  Zn-DMA than
Zn-DMA than  Zn
Zn . Importantly, supply of
. Importantly, supply of  Zn-DMA rather than
Zn-DMA rather than  Zn
Zn increased the translocation of
increased the translocation of  Zn into the leaves of Zn-deficient plants. This was especially evident in the discrimination center (DC). These results suggest that DMA in Zn-deficient rice plants has an important role in the distribution of Zn within the plant rather than in the absorption of Zn from the soil.
Zn into the leaves of Zn-deficient plants. This was especially evident in the discrimination center (DC). These results suggest that DMA in Zn-deficient rice plants has an important role in the distribution of Zn within the plant rather than in the absorption of Zn from the soil.
石丸 泰寛*; Kim, S.*; 塚本 崇志*; 大木 宏之*; 小林 高範*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 高橋 美智子*; 中西 啓仁*; 森 敏*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(18), p.7373 - 7378, 2007/05
被引用回数:130 パーセンタイル:93.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Fe deficiency is a worldwide agricultural problem on calcareous soils. Rice plants use a well documented phytosiderophore-based system to take up Fe from the soil. Rice plants are extremely susceptible to low-Fe supply, however, because of low phytosiderophore secretion and low Fe reduction activity. A yeast Fe
reduction activity. A yeast Fe chelate-reductase gene
chelate-reductase gene 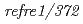 , selected for better performance at high pH, was fused to the promoter of the Fe-regulated transporter,
, selected for better performance at high pH, was fused to the promoter of the Fe-regulated transporter, 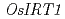 , and introduced into rice plants. The transgene was expressed in response to a low-Fe nutritional status in roots of transformants. Transgenic rice plants expressing the
, and introduced into rice plants. The transgene was expressed in response to a low-Fe nutritional status in roots of transformants. Transgenic rice plants expressing the 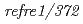 gene showed higher Fe
gene showed higher Fe chelate-reductase activity and a higher Fe-uptake rate than vector controls under Fe-deficient conditions. Consequently, transgenic rice plants exhibited an enhanced tolerance to low-Fe availability and 7.9x the grain yield of nontransformed plants in calcareous soils.
chelate-reductase activity and a higher Fe-uptake rate than vector controls under Fe-deficient conditions. Consequently, transgenic rice plants exhibited an enhanced tolerance to low-Fe availability and 7.9x the grain yield of nontransformed plants in calcareous soils.
塚本 崇志*; 中西 啓仁*; 長谷 純宏; 田中 淳; 西澤 直子*; 森 敏*
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 93, 2007/02
カドミウムは毒性の高い土壌汚染金属であり、根やシュートの生長を阻害し、植物の栄養吸収やホメオスタシスに悪影響を及ぼす。また、穀物への蓄積により、ヒトや家畜の健康に害を及ぼす。本研究では、イオンビーム育種技術によるカドミウム吸収特性変異イネの選抜を行い、従来法では得られていないカドミウム吸収又は移行特性変異株の獲得を目指している。一次選抜として、250又は500ppmのカドミウム濃度に調整した培養土を用いて、イオンビーム変異処理した「日本晴」M1種子から得たM2種子約2500粒を人工気象室内で栽培し、生存した個体を選抜した。その結果、500ppm区で顕著な生育阻害効果が認められた。また、ほかの個体よりも生育の良い変異体を51個体得た。現在、これらの変異体からM3種子を収穫中である。
 Fe translocation from the roots to the ear of rice using a Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS)
Fe translocation from the roots to the ear of rice using a Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS)塚本 崇志*; 中西 啓仁*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 西澤 直子*; 森 敏*
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 124, 2007/02
鉄は植物に必須な元素であるが、イネ中での移行、特に根で吸収された鉄の穂への移行については不明な点が多い。そこで、イネの穂への鉄の移行経路を明らかにするために、 Feを用いたポジトロンイメージング計測を試みた。開花から3週間の登熟期のイネの根から
Feを用いたポジトロンイメージング計測を試みた。開花から3週間の登熟期のイネの根から Feを吸収させ、植物内における動態をPETISにより計測したところ、
Feを吸収させ、植物内における動態をPETISにより計測したところ、 Fe投与後3.5時間で穂と止め葉に
Fe投与後3.5時間で穂と止め葉に Feが到達したことが明らかとなった。また、移行経路上にある節に
Feが到達したことが明らかとなった。また、移行経路上にある節に Feが集積していることがわかった。これらの結果から、鉄は導管から節において篩管へ移行した後、止め葉を経由せずに直接穂に輸送されることが示唆された。
Feが集積していることがわかった。これらの結果から、鉄は導管から節において篩管へ移行した後、止め葉を経由せずに直接穂に輸送されることが示唆された。
 N-nitrate in transgenic rice plant over-expressing nitrate transporter
N-nitrate in transgenic rice plant over-expressing nitrate transporter佐藤 大祐*; 森 真理*; 片山 寿人*; 北村 治滋*; 河合 敏彦*; 藤巻 秀; 鈴井 伸郎; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 松橋 信平; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 128, 2007/02
窒素は作物生産で最も重要な元素であるが、水環境への汚染負荷原因物質として農地からの流出が問題となっており、農地への投入窒素量を低減しても高い生産性が維持できるイネの開発が急務となっている。この課題を解決するために、イネの硝酸吸収にかかわる硝酸イオントランスポーターを高発現させた形質転換イネを作出し、ポジトロン放出核種を用いた計測によりその特性の解析を行った。根で吸収された硝酸イオンを地上部へ輸送する能力について、野生株と硝酸イオントランスポーター高発現株とで比較したところ、硝酸イオントランスポーター高発現株では、単位時間あたり・単位根乾重量あたりの硝酸吸収量が野生株の1.6倍であることがわかった。また、PETISによる根から地上部への Nの移行計測でも同様の傾向が確認されていることから、硝酸イオントランスポーター高発現イネは野生株のイネに比べ、根を介した地上部への高い硝酸輸送能を持つことが明らかになった。
Nの移行計測でも同様の傾向が確認されていることから、硝酸イオントランスポーター高発現イネは野生株のイネに比べ、根を介した地上部への高い硝酸輸送能を持つことが明らかになった。
大山 卓爾*; 末吉 邦*; 大竹 憲邦*; 伊藤 小百合*; 石橋 弘規*; Hara, T.*; Kimura, T.*; 松橋 信平; 藤巻 秀; 鈴井 伸郎; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 122, 2007/02
As nodulated leguminous crops grow, they assimilate both gaseous nitrogen and combined nitrogen. Combined N especially the NO
 form inhibits all phases of nodulation and N
form inhibits all phases of nodulation and N fixation process, although the mechanism have not been fully elucidated. Tungstate is a non-essential element for plant growth, which exerts harmaful effects on plants. When tungstate is applied to the plant medium, it competes with molybdate and inhibits some enzymes, which have a Mo cofactor in the active site such as nitrate reductase and nitrogenase. Application WO
fixation process, although the mechanism have not been fully elucidated. Tungstate is a non-essential element for plant growth, which exerts harmaful effects on plants. When tungstate is applied to the plant medium, it competes with molybdate and inhibits some enzymes, which have a Mo cofactor in the active site such as nitrate reductase and nitrogenase. Application WO
 to the culuture medium diturbed nitrate transport to the shoot. In this report, WO
to the culuture medium diturbed nitrate transport to the shoot. In this report, WO
 was introduced into cut end of petiole of primary leaf and investigated that
was introduced into cut end of petiole of primary leaf and investigated that  NO
NO
 transport from root to shoot was inhibited or not.
transport from root to shoot was inhibited or not.
 Mn translocation in barley monitored using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system
Mn translocation in barley monitored using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system塚本 崇志*; 中西 啓仁*; 清宮 正一郎*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 西澤 直子*; 森 敏*
Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 52(6), p.717 - 725, 2006/12
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:63.02(Plant Sciences)Until now, the real-time uptake and movement of Mn, has not been documented in plants. In this study, the real-time translocation of Mn in barley was visualized using  Mn and PETIS. In all cases,
Mn and PETIS. In all cases,  Mn first accumulated in the discrimination center (DC), suggesting that this region may play an important role in Mn distribution in graminaceous plants. Mn deficient barley showed greater translocation of
Mn first accumulated in the discrimination center (DC), suggesting that this region may play an important role in Mn distribution in graminaceous plants. Mn deficient barley showed greater translocation of  Mn from roots to shoots than did Mn-sufficient barley. In contrast, the translocation of
Mn from roots to shoots than did Mn-sufficient barley. In contrast, the translocation of  Mn from roots to shoots was suppressed in Mn-excess barley. In Mn-sufficient barley, the dark treatment did not suppress the translocation of
Mn from roots to shoots was suppressed in Mn-excess barley. In Mn-sufficient barley, the dark treatment did not suppress the translocation of  Mn to the youngest leaf, suggesting that the translocation of Mn to the youngest leaf is independent of the transpiration stream. Our results show that the translocation of Mn from the roots to the DC depends passively on water flow, but actively on the Mn transporter(s).
Mn to the youngest leaf, suggesting that the translocation of Mn to the youngest leaf is independent of the transpiration stream. Our results show that the translocation of Mn from the roots to the DC depends passively on water flow, but actively on the Mn transporter(s).
鈴木 基史*; 高橋 美智子*; 塚本 崇志*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 矢崎 潤史*; 岸本 直己*; 菊池 尚志*; 中西 啓仁*; 森 敏*; et al.
Plant Journal, 48(1), p.85 - 97, 2006/10
被引用回数:172 パーセンタイル:95.77(Plant Sciences)Mugineic acid family phytosiderophores (MAs) are metal chelators that are produced in graminaceous plants in response to Fe deficiency, but current evidence regarding secretion of MAs during Zn deficiency is contradictory. HPLC analysis showed that Zn deficiency induces the synthesis and secretion of MAs in barley plants. Studies of the genes involved in the methionine cycle using microarray analysis showed that the transcripts of these genes were increased in both Zn-deficient and Fe-deficient barley roots. Analysis using the PETIS confirmed that more  Zn(II)-MAs than
Zn(II)-MAs than  Zn
Zn were absorbed by the roots of Zn-deficient barley plants. These data suggest that the increased biosynthesis and secretion of MAs arising from a shortage of Zn are not due to an induced Fe deficiency, and that secreted MAs are effective in absorbing Zn from the soil.
were absorbed by the roots of Zn-deficient barley plants. These data suggest that the increased biosynthesis and secretion of MAs arising from a shortage of Zn are not due to an induced Fe deficiency, and that secreted MAs are effective in absorbing Zn from the soil.
 -phytosiderophore and as Fe
-phytosiderophore and as Fe
石丸 泰寛*; 鈴木 基史*; 塚本 崇志*; 鈴木 一正*; 中園 幹生*; 小林 高範*; 和田 泰明*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 高橋 美智子*; et al.
Plant Journal, 45(3), p.335 - 346, 2006/02
被引用回数:545 パーセンタイル:99.64(Plant Sciences)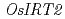 gean was isolated from rice, which is highly homologous to
gean was isolated from rice, which is highly homologous to 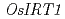 . Real-time PCR analysis revealed that
. Real-time PCR analysis revealed that 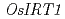 and
and 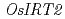 are expressed predominantly in roots, and these transporters are induced by low-Fe condition. Analysis using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system showed that rice plants are able to take up both an Fe
are expressed predominantly in roots, and these transporters are induced by low-Fe condition. Analysis using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system showed that rice plants are able to take up both an Fe -phytosiderophore and Fe
-phytosiderophore and Fe . This result indicates that, in addition to absorbing an Fe
. This result indicates that, in addition to absorbing an Fe -phytosiderophore, rice possesses a novel Fe-uptake system that directly absorbs the Fe
-phytosiderophore, rice possesses a novel Fe-uptake system that directly absorbs the Fe , a strategy that is advantageous for growth in submerged conditions.
, a strategy that is advantageous for growth in submerged conditions.
河地 有木; 藤巻 秀; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 塚本 崇志; 石岡 典子; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平
no journal, ,
植物が養分として必須としている元素の動態が示す生理機能は未だに解明されていない部分が多い。また一方、植物体内の有害元素であるカドミウムなどは土壌及び食料の汚染が社会問題となっており、植物体内における動態と輸送の分子機構の解明が急がれている。日本原子力研究開発機構量子ビーム応用研究部門では農学など植物を対象とした研究への応用を目指し、植物体内での栄養成分の吸収・輸送・蓄積の過程を可視化するためのポジトロンイメージング装置(PETIS:Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System)の開発を行ってきた。これまでに、高崎量子応用研究所のAVFサイクロトロンを利用して、多様なポジトロン放出核種標識化合物の製造技術を開発し、植物栄養学や植物生理学の研究に用いている。
塚本 崇志*; 中西 啓仁*; 西澤 直子*; 森 敏*; 長谷 純宏; 田中 淳
no journal, ,
本研究では、イオンビーム育種技術によるカドミウム吸収特性変異イネの選抜を行い、従来法では得られていないカドミウム吸収又は移行特性変異株の獲得を目指している。一次選抜として、250又は500ppmのカドミウム濃度に調整した培養土を用いて、イオンビーム変異処理したM1種子から得たM2種子約2500粒を人工気象室内で栽培し、生存した個体を選抜した。その結果、500ppm区で顕著な生育阻害効果が認められた。また、ほかの個体よりも生育の良い変異体を幾つか得た。
中西 啓仁*; 塚本 崇志*; 西澤 直子*; 森 敏*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平
no journal, ,
鉄と亜鉛は植物に必須な元素であるが、これらの植物体内における動態には未解明な部分が多く、特に、登熟期のイネにおける金属元素の移行を直接計測した報告はない。本研究では、PETISを用いたポジトロン放出金属元素の登熟期のイネ生体内における移行を計測し、新たな知見を得ることを目的とした。開花後3週間のイネに Fe
Fe -デオキシムギネ酸又は
-デオキシムギネ酸又は Zn
Zn を経根吸収させ、それぞれの移行をPETISにより計測した。その結果、
を経根吸収させ、それぞれの移行をPETISにより計測した。その結果、 Fe,
Fe,  Znのいずれについても複数存在する節への蓄積が観察された。それぞれの節における
Znのいずれについても複数存在する節への蓄積が観察された。それぞれの節における Fe及び
Fe及び Zn移行量の解析から、先端に近い上位の節ほど単位重量あたりの蓄積量が多いことがわかり、何らかの生理的な制御により上位の節に優先的に金属元素を蓄積する仕組みの存在が示唆された。
Zn移行量の解析から、先端に近い上位の節ほど単位重量あたりの蓄積量が多いことがわかり、何らかの生理的な制御により上位の節に優先的に金属元素を蓄積する仕組みの存在が示唆された。
 C]光合成産物転流量の測定
C]光合成産物転流量の測定草川 知行*; 塚本 崇志*; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 伊藤 小百合; 鈴井 伸郎; 藤巻 秀; 石岡 典子; 堀内 尚美*; 荻原 勲*
no journal, ,
トマトでは、各果房直下の側枝を利用して1果房あたりの葉数を増加させると果実糖度が向上すると報告されている。そこで側枝利用による果実糖度向上の要因を明らかにするために、非破壊的に植物生体内の物質の動態を観察することのできるPositron-Emitting Tracer Imaging System(PETIS)を用いて、トマトの葉から果実への光合成産物の移行を可視化し、同一個体で果房直下葉と側枝葉からのトマト果実への光合成産物の転流量を比較した。結果、果実への光合成産物の転流量は直下葉より側枝葉のほうが多く、果実の糖度向上には側枝葉から光合成産物の転流量が大きく貢献していると考えられた。
河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 伊藤 小百合; 石岡 典子; 菊地 郁*; 塚本 崇志*; 草川 知行*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
さまざまな放射線計測技術を駆使して、植物生体内の元素動態を可視化し、その生理機能の解明を目的とした、計装及び測定技術の開発を行ってきた。これまでに、放射性炭素( C)とポジトロンイメージング技術(PETIS)を用いたソース器官(葉)における光合成機能の可視化に成功しているが、さらに、計測視野をシンク器官(果実)に移し、同様の実験手法を適用することで、光合成産物の果実への定量的かつ非侵襲的な転流動態の可視化を可能にした。測定環境や
C)とポジトロンイメージング技術(PETIS)を用いたソース器官(葉)における光合成機能の可視化に成功しているが、さらに、計測視野をシンク器官(果実)に移し、同様の実験手法を適用することで、光合成産物の果実への定量的かつ非侵襲的な転流動態の可視化を可能にした。測定環境や C標識二酸化炭素(
C標識二酸化炭素( CO
CO )投与量の最適化といった本手法の確立は、果実成長・肥大メカニズムといったシンク器官における生理機能の解明に貢献すると期待される。
)投与量の最適化といった本手法の確立は、果実成長・肥大メカニズムといったシンク器官における生理機能の解明に貢献すると期待される。