Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
佐藤 哲也*; 加藤 岳生*; 大上 能悟*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 107(8), p.L180406_1 - L180406_6, 2023/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:54.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We examine the mechanical rotation of a levitated magnetic particle that is induced by ferromagnetic resonance under microwave irradiation. We show that two stable solutions appear in a certain range of parameters by bifurcation when the rotation frequency is comparable to the microwave frequency. This phenomenon originates from the coexistence of the Barnett and the Einstein-de Haas effects. We also reveal that this measurement is sensitive to the strength of the spin-rotation coupling. Our work provides a platform for accessing a microscopic relaxation process from spin to macroscopic rotation.
大上 能悟*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review A, 106(4), p.L041501_1 - L041501_7, 2022/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:42.78(Optics)Mechanical rotation and oscillation have far lower frequencies than light does; thus they are not coupled to each other conventionally. In this Letter, we show that the torsional mechanical oscillation of an optical cavity can be coupled to the optical modes by introducing birefringence, which produces nondegenerate modes in the cavity: ordinary and extraordinary rays. Twisting the cavity mixes them and modulates the electromagnetic energy. We find the torsional optomechanical Hamiltonian by quantizing the total energy and reveal that the torsional oscillation can be resonantly driven by light.
田島 裕之*; 大上 能悟*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review A, 106(3), p.033310_1 - 033310_8, 2022/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:23.32(Optics)We elucidate the multiparticle transport of pair tunneling and spin tunneling in strongly correlated interfaces. Not only usual single-particle tunneling but also interaction-induced multiparticle tunneling processes naturally arise from a conventional microscopic model without any empirical parameters, through the overlap of the many-body wave functions around the interface. We demonstrate how anomalous tunneling currents occur in a strongly interacting system due to the pair-tunneling process which we derived microscopically. Our formulation is useful for junction systems in various disciplines, including atomtronics, spintronics, and nuclear reactions.
大湊 友也*; 大上 能悟*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 105(19), p.195409_1 - 195409_9, 2022/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:17.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Angular momentum conversion between mechanical rotation and the valley degree of freedom in 2D Dirac materials is investigated theoretically. Coupling between the valley and vorticity of dynamic lattice distortions is derived by applying the 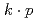 method to 2D Dirac materials with an inertial effect. Lattice strain effects are also incorporated. Valley transfer and valley-dependent carrier localization are predicted using the dynamic lattice distortions. The transport properties are found to be controllable, allowing the system to be insulating and to generate pulsed charge current. Our formalism offers a route toward mechanical manipulation of valley dynamics in 2D Dirac materials.
method to 2D Dirac materials with an inertial effect. Lattice strain effects are also incorporated. Valley transfer and valley-dependent carrier localization are predicted using the dynamic lattice distortions. The transport properties are found to be controllable, allowing the system to be insulating and to generate pulsed charge current. Our formalism offers a route toward mechanical manipulation of valley dynamics in 2D Dirac materials.
大上 能悟*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 105(2), p.L020302_1 - L020302_5, 2022/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:17.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We propose a spin transport induced by inertial motion. Our system is composed of two host media and a narrow vacuum gap in between. One of the hosts is sliding at a constant speed relative to the other. This mechanical motion causes the Doppler effect, which shifts the density of states and the nonequilibrium distribution function in the moving medium. Those shifts induce the difference in the distribution function between the two media, and they result in tunneling spin current. The spin current is calculated from the Schwinger-Keldysh formalism with a spin tunneling Hamiltonian. This scheme does not require temperature difference, voltage, or chemical potential.
大上 能悟*; 松尾 衛
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 22(3), p.033040_1 - 033040_7, 2020/03
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:70.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We propose and analyze surface-plasmon-driven electron spin currents in a thin metallic film. The electron gas in the metal follows the transversely rotating electric fields of the surface plasmons (SPs), which leads to a static magnetization gradient. We consider herein SPs in a thin-film insulator-metal-insulator structure and solve the spin diffusion equation in the presence of a magnetization gradient. The results reveal that the SPs at the metal interfaces generate spin currents in the metallic film. For thinner film, the SPs become strongly hybridized, which increases the magnetization gradient and enhances the spin current. We also discuss how the spin current depends on SP wavelength and the spin-diffusion length of the metal. The polarization of the spin current can be controlled by tuning the wavelength of the SPs and/or the spin diffusion length.