Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 , isolated from freshwater fish in Japan
, isolated from freshwater fish in Japan佐藤 勝也; 小野寺 威文*; 面曽 宏太*; 武田-矢野 喜代子*; 片山 豪*; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 4(1), p.e01631-15_1 - e01631-15_2, 2016/01
 was isolated as a gram-negative, red-pigmented, radioresistant, rod-shaped bacterium from freshwater fish. The draft genome sequence of
was isolated as a gram-negative, red-pigmented, radioresistant, rod-shaped bacterium from freshwater fish. The draft genome sequence of  ATCC 43672 was 4,092,497 bp, with an average G+C content of 67.5% and comprised of 4 circular contigs and 3 linear contigs that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BCMS00000000. The draft genome sequence indicates that
ATCC 43672 was 4,092,497 bp, with an average G+C content of 67.5% and comprised of 4 circular contigs and 3 linear contigs that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BCMS00000000. The draft genome sequence indicates that  possesses a DNA damage response regulator (encoded by
possesses a DNA damage response regulator (encoded by  homolog) and radiation-desiccation response regulons (
homolog) and radiation-desiccation response regulons ( ,
, 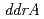 ,
, 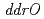 ,
,  and
and 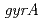 homologs etc.), which are involved in the unique radiation-desiccation response system in
homologs etc.), which are involved in the unique radiation-desiccation response system in  . As it is for
. As it is for  ,
, 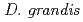 seems to employ the same radioresistant mechanisms. In future, the draft genome sequence of
seems to employ the same radioresistant mechanisms. In future, the draft genome sequence of 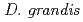 will be useful for elucidating the common principles of the radioresistance based on the extremely efficient DNA repair mechanisms in Deinococcus species by the comparative analysis of genomic sequences.
will be useful for elucidating the common principles of the radioresistance based on the extremely efficient DNA repair mechanisms in Deinococcus species by the comparative analysis of genomic sequences.
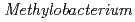 sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with
sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with 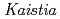 sp. 32K
sp. 32K藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子*; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 清水 哲*; 若林 佑*; 鳴海 一成*; 中村 顕*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 3(5), p.e01005-15_1 - e01005-15_2, 2015/09
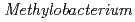 sp. ME121 was isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with
sp. ME121 was isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with 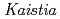 sp. 32K during our screening of L-glucose-utilizing microorganisms, and its growth was enhanced by coculture. It was expected that genomic analysis of this bacterium would provide novel information on coculture-dependent growth enhancement. The genomic information of symbiotic bacteria could be of use for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying microbial symbiosis. The draft genome sequence of
sp. 32K during our screening of L-glucose-utilizing microorganisms, and its growth was enhanced by coculture. It was expected that genomic analysis of this bacterium would provide novel information on coculture-dependent growth enhancement. The genomic information of symbiotic bacteria could be of use for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying microbial symbiosis. The draft genome sequence of 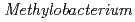 sp. ME121 is 7,096,979 bp in total length and comprises 197 large contigs (
sp. ME121 is 7,096,979 bp in total length and comprises 197 large contigs ( 500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BBUX00000000. The draft genome sequence shows that
500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BBUX00000000. The draft genome sequence shows that 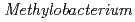 sp. ME121 has some genes that encode putative methanol/ethanol family PQQ-dependent dehydrogenases involved in methylotrophy. Some unknown factor provided by the coculture may contribute to increase the growth of
sp. ME121 has some genes that encode putative methanol/ethanol family PQQ-dependent dehydrogenases involved in methylotrophy. Some unknown factor provided by the coculture may contribute to increase the growth of 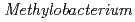 sp. ME121.
sp. ME121.
 sp. strain TCA20, isolated from a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions
sp. strain TCA20, isolated from a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子*; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 佐野 元彦*; 高橋 優嘉*; 鳴海 一成*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 2(5), p.e00866-14_1 - e00866-14_2, 2014/09
Calcium-dependent  sp. strain TCA20 was isolated from a water sample of a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may be the basis for the research of calcium ion homeostasis. The draft genome sequence of
sp. strain TCA20 was isolated from a water sample of a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may be the basis for the research of calcium ion homeostasis. The draft genome sequence of  sp. strain TCA20 totals 5,631,463 bp in length and is composed of 33 large contigs (
sp. strain TCA20 totals 5,631,463 bp in length and is composed of 33 large contigs ( 500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession no. BBIW00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence shows that
500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession no. BBIW00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence shows that  sp. strain TCA20 has a calcium-specific calcium/proton antiporter, ChaA, and a P-type calcium-transporting ATPase, YloB, was identified as calcium transporters. These transporters may also be important for the growth of
sp. strain TCA20 has a calcium-specific calcium/proton antiporter, ChaA, and a P-type calcium-transporting ATPase, YloB, was identified as calcium transporters. These transporters may also be important for the growth of  sp. strain TCA20 under the high concentration of calcium ions.
sp. strain TCA20 under the high concentration of calcium ions.
 sp. strain TS-2, isolated from a jumping spider
sp. strain TS-2, isolated from a jumping spider藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子*; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 佐野 元彦*; 鳴海 一成*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 2(3), p.e00458-14_1 - e00458-14_2, 2014/05
The potassium-dependent alkaliphilic  sp. strain TS-2 was isolated from the mashed extract of a jumping spider, and its draft genome sequence was obtained. Comparative genomic analysis with a previously sequenced sodium-dependent alkaliphilic
sp. strain TS-2 was isolated from the mashed extract of a jumping spider, and its draft genome sequence was obtained. Comparative genomic analysis with a previously sequenced sodium-dependent alkaliphilic  species may reveal potassium-dependent alkaline adaptation mechanisms. The draft genome sequence of
species may reveal potassium-dependent alkaline adaptation mechanisms. The draft genome sequence of 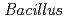 sp. strain TS-2 was 4,360,646 bp in total length, comprised 58 large contigs (
sp. strain TS-2 was 4,360,646 bp in total length, comprised 58 large contigs ( 500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BAWL00000000. In the draft genome sequence of
500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BAWL00000000. In the draft genome sequence of 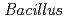 sp. strain TS-2, two sets of
sp. strain TS-2, two sets of 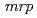 genes, which encode multisubunit secondary cation/proton antiporter-3 family proteins, were annotated. The Mrp complex acts as an Na
genes, which encode multisubunit secondary cation/proton antiporter-3 family proteins, were annotated. The Mrp complex acts as an Na /H
/H antiporter in typical alkaliphilic
antiporter in typical alkaliphilic 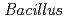 species and plays a critical role in the sodium-dependent alkaline adaptation mechanism.
species and plays a critical role in the sodium-dependent alkaline adaptation mechanism.

佐藤 勝也; 小野寺 威文*; 武田 喜代子; 鳴海 一成*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 110, 2014/03
In this study, we investigated mutant frequencies of two different antibiotic-resistant mutants for carbon ion beams in  and identified the mutation sites in the streptomycin-resistant (Sm
and identified the mutation sites in the streptomycin-resistant (Sm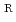 ) mutants. The Sm
) mutants. The Sm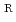 mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. It seems that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purpose. Four kinds of mutation sites at the
mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. It seems that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purpose. Four kinds of mutation sites at the 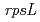 locus were determined from 8 Sm
locus were determined from 8 Sm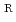 mutants. These mutations cause amino acid substitutions at position 43 (Lys to Thr or Arg) and 88 (Lys to Glu or Arg) in the S12 protein, respectively. The two hot spots at Lys43 and Lys88 in the S12 protein might be a binding target of streptomycin or adjacent to the center of streptomycin interaction with the ribosome.
mutants. These mutations cause amino acid substitutions at position 43 (Lys to Thr or Arg) and 88 (Lys to Glu or Arg) in the S12 protein, respectively. The two hot spots at Lys43 and Lys88 in the S12 protein might be a binding target of streptomycin or adjacent to the center of streptomycin interaction with the ribosome.
 and
and 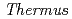
小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 太田 敏博*; 鳴海 一成*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 111, 2014/03
The 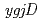 and
and 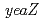 orthologs are highly conserved in eubacteria, and the former is also widely found in the genomes of archaea and eukaryotes. However, their functions are still poorly understood.
orthologs are highly conserved in eubacteria, and the former is also widely found in the genomes of archaea and eukaryotes. However, their functions are still poorly understood.  and
and 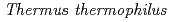 possess the both orthologs hereafter
possess the both orthologs hereafter 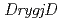 ,
,  ,
, 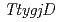 and
and 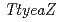 , respectively. We have reported that the
, respectively. We have reported that the 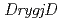 and
and  disruptants show extreme sensitivity to mitomycin C (MMC), which causes interstrand DNA cross-links. In this study, we constructed
disruptants show extreme sensitivity to mitomycin C (MMC), which causes interstrand DNA cross-links. In this study, we constructed 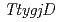 and
and 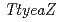 gene expression plasmids and the resultant plasmids were introduced into the
gene expression plasmids and the resultant plasmids were introduced into the 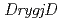 and
and  disruptant strains. To investigate whether
disruptant strains. To investigate whether 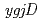 and
and 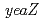 orthologs share the common function in
orthologs share the common function in  and
and 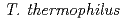 , these generated strains were challenged by MMC.
, these generated strains were challenged by MMC.

布柴 達男*; 坂田 弥生*; 山内 理子*; 佐藤 勝也; 小野寺 威文*; 鳴海 一成*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 118, 2014/03
The LOH (loss of heterozygosity) induction by various ion beam radiations was investigated in diploid  . The ion beams
. The ion beams  C
C ,
,  C
C ,
,  He
He and
and  Ar
Ar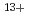 at the lowest dose (75, 75, 200 and 150 Gy, respectively), which had 30
at the lowest dose (75, 75, 200 and 150 Gy, respectively), which had 30 50% lethality, induced LOH with 10-fold higher frequency. The LOH induction was predominantly (
50% lethality, induced LOH with 10-fold higher frequency. The LOH induction was predominantly ( 90%) resulted from homologous recombination. Pol
90%) resulted from homologous recombination. Pol may be involved in the induction of LOH by ion beam radiations, because in the strain lacking Rev3, only slight induction of LOH was observed. In addition, the effects of 14 herbal extracts were examined on iron-beam radiation induced LOH, and ethanol extract of
may be involved in the induction of LOH by ion beam radiations, because in the strain lacking Rev3, only slight induction of LOH was observed. In addition, the effects of 14 herbal extracts were examined on iron-beam radiation induced LOH, and ethanol extract of 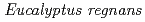 possessed inhibitory effect on LOH induced by
possessed inhibitory effect on LOH induced by  C
C ion-beam radiation with the manner dependent on doses of extract.
ion-beam radiation with the manner dependent on doses of extract.
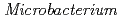 sp. strain TS-1
sp. strain TS-1藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 佐野 元彦*; 鳴海 一成*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 1(6), P. e01043-13, 2013/12
Alkaliphilic 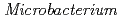 sp. strain TS-1, newly isolated from the jumping spider, showed Na
sp. strain TS-1, newly isolated from the jumping spider, showed Na -independent growth and motility. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may provide beneficial information for Na
-independent growth and motility. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may provide beneficial information for Na -independent alkaline adaptation mechanisms. The draft genome sequence of
-independent alkaline adaptation mechanisms. The draft genome sequence of 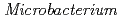 sp. strain TS-1 was 3,396,165 bp in total length and comprised 3 large contigs (2,699,404 bp, 691,278 bp, and 5,483 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/ EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BASQ00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence indicated that this bacterium has 3 sets of
sp. strain TS-1 was 3,396,165 bp in total length and comprised 3 large contigs (2,699,404 bp, 691,278 bp, and 5,483 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/ EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BASQ00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence indicated that this bacterium has 3 sets of 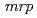 genes, which encode multisubunit secondary cation/proton antiporter-3 family proteins for pH homeostasis. The annotation also indicated that this bacterium has genes involved in chemotaxis/flagellar components, including one set of
genes, which encode multisubunit secondary cation/proton antiporter-3 family proteins for pH homeostasis. The annotation also indicated that this bacterium has genes involved in chemotaxis/flagellar components, including one set of 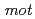 genes.
genes.
 YgjD and YeaZ are involved in the repair of DNA cross-links
YgjD and YeaZ are involved in the repair of DNA cross-links小野寺 威文; 佐藤 勝也; 太田 敏博*; 鳴海 一成
Extremophiles, 17(1), p.171 - 179, 2013/01
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:26.85(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Orthologs of 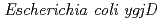 and
and 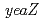 genes are highly conserved in various organisms. The genome of the radioresistant bacterium
genes are highly conserved in various organisms. The genome of the radioresistant bacterium  possesses single orthologs of
possesses single orthologs of 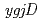 (DR_0382) and
(DR_0382) and 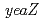 (DR_0756). Complete loss of either one or both genes did not result in any significant changes in cell growth efficiency, indicating that both genes are not essential for cell viability in
(DR_0756). Complete loss of either one or both genes did not result in any significant changes in cell growth efficiency, indicating that both genes are not essential for cell viability in  , unlike the case with other species such as
, unlike the case with other species such as  ,
, 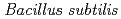 and
and  . Survival rates following DNA damage induced by hydrogen peroxide,
. Survival rates following DNA damage induced by hydrogen peroxide,  -methyl-
-methyl-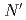 -nitro-
-nitro- -nitrosoguanidine, ultra violet radiation,
-nitrosoguanidine, ultra violet radiation,  -rays, cisplatin and mitomycin C (MMC) were compared among the wild-type strain and
-rays, cisplatin and mitomycin C (MMC) were compared among the wild-type strain and 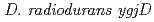 /
/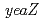 null mutants. Interestingly, the null mutants exhibited high sensitivity to MMC, which mainly causes interstrand DNA cross-links. The sensitivity of the null mutants to MMC was restored to that of the wild-type by transformation with plasmids expressing these genes. These results suggest that
null mutants. Interestingly, the null mutants exhibited high sensitivity to MMC, which mainly causes interstrand DNA cross-links. The sensitivity of the null mutants to MMC was restored to that of the wild-type by transformation with plasmids expressing these genes. These results suggest that 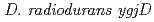 and
and 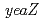 genes are involved in DNA repair and play a role in the repair of DNA cross-links in
genes are involved in DNA repair and play a role in the repair of DNA cross-links in  .
.

佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平*; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 103, 2013/01
 exhibits extraordinary resistance to the lethal effects of ionizing radiations. This resistance has been attributed to its highly proficient DNA repair capacity. In this study, we investigated antibiotics-resistant mutant frequencies for different LET radiations in
exhibits extraordinary resistance to the lethal effects of ionizing radiations. This resistance has been attributed to its highly proficient DNA repair capacity. In this study, we investigated antibiotics-resistant mutant frequencies for different LET radiations in  . Rifampicin is one of the antibiotics that inhibit RNA synthesis by directly interacting with the RNA polymerase beta subunit protein encoded by
. Rifampicin is one of the antibiotics that inhibit RNA synthesis by directly interacting with the RNA polymerase beta subunit protein encoded by 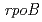 gene. By genetically altering the
gene. By genetically altering the 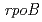 gene in genome, Rif
gene in genome, Rif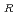 mutant can be generated. The Rif
mutant can be generated. The Rif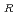 mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. The highest Rif
mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. The highest Rif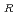 mutant frequencies were observed at a dose range that give 10
mutant frequencies were observed at a dose range that give 10 to 10
to 10 of surviving fraction. There is the possibility that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purposes.
of surviving fraction. There is the possibility that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purposes.
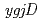 and
and 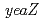 orthologs, in DNA repair of
orthologs, in DNA repair of 
小野寺 威文; 佐藤 勝也; 太田 敏博*; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 104, 2013/01
The 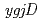 and
and 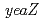 orthologs are highly conserved in eubacteria, and the former is also widely found in the genomes of archaea and eukaryotes.
orthologs are highly conserved in eubacteria, and the former is also widely found in the genomes of archaea and eukaryotes.  , well known as a radioresistant bacterium, possesses the both orthologs, hereafter
, well known as a radioresistant bacterium, possesses the both orthologs, hereafter 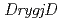 and
and  . In this study, we successfully constructed
. In this study, we successfully constructed 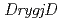 disruptant,
disruptant,  disruptant and
disruptant and 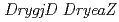 double-disruptant strains. This result clearly indicated that neither
double-disruptant strains. This result clearly indicated that neither 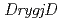 nor
nor  genes is essential for cell viability in
genes is essential for cell viability in  . These gene disruptant strains exhibited extreme sensitivity to mitomycin-C compare to the wild-type strain. The deficiency of
. These gene disruptant strains exhibited extreme sensitivity to mitomycin-C compare to the wild-type strain. The deficiency of 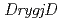 and
and  genes was complemented to restore the wild-type phenotype by introducing plasmids that express these genes.
genes was complemented to restore the wild-type phenotype by introducing plasmids that express these genes.
布柴 達男*; 平澤 佑啓*; 山内 理子*; 佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平*; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 111, 2013/01
The LOH (loss of heterozygosity) induction by various ion beam radiations was investigated in diploid  . The ion beams
. The ion beams  C
C ,
,  C
C ,
,  He
He and
and  Ar
Ar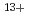 at the lowest dose (75, 75, 200 and 150 Gy, respectively), which had 30-50% lethality, induced LOH with 10-fold higher frequency. The LOH induction was predominantly (
at the lowest dose (75, 75, 200 and 150 Gy, respectively), which had 30-50% lethality, induced LOH with 10-fold higher frequency. The LOH induction was predominantly ( 90%) resulted from gene conversion or crossover through homologous recombination, and followed by chromosome loss through chromosome mis-segregation. Induction of LOH by
90%) resulted from gene conversion or crossover through homologous recombination, and followed by chromosome loss through chromosome mis-segregation. Induction of LOH by  C
C was also examined in
was also examined in  deficient in AP endonuclease (Apn1), translesion DNA polymerases Pol
deficient in AP endonuclease (Apn1), translesion DNA polymerases Pol encoded by Rad30 and Pol
encoded by Rad30 and Pol encoded by Rev3 and Rev7. Pol
encoded by Rev3 and Rev7. Pol may be involved in the induction of LOH, because a slight induction of LOH by
may be involved in the induction of LOH, because a slight induction of LOH by  C
C was observed in the Rev3-deficient strain.
was observed in the Rev3-deficient strain.
 RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination
RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination佐藤 勝也; 菊地 正博; Ishaque, A. M.*; 大庭 寛史*; 山田 貢; 手島 光平; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
DNA Repair, 11(4), p.410 - 418, 2012/04
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:59.83(Genetics & Heredity)放射線抵抗性細菌の相同組換え機構におけるRecFORタンパク質の役割を明らかにするために、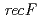 ,
, 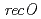 及び
及び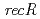 遺伝子破壊株を作製し、分子遺伝学及び分子生物学的解析を行った。
遺伝子破壊株を作製し、分子遺伝学及び分子生物学的解析を行った。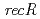 遺伝子破壊株では、形質転換効率の著しい低下が見られたことから、RecRタンパク質は、細胞内に取り込んだ外来DNAの安定性に関与していることがわかった。また、
遺伝子破壊株では、形質転換効率の著しい低下が見られたことから、RecRタンパク質は、細胞内に取り込んだ外来DNAの安定性に関与していることがわかった。また、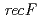 遺伝子破壊株は、他の遺伝子破壊株に比べて、
遺伝子破壊株は、他の遺伝子破壊株に比べて、 線,紫外線及びマイトマイシンCに非常に感受性を示した。これらの高い感受性は、RecFタンパク質が、組換え修復タンパク質RecAの活性化に重要な役割を担っていることに起因していることがわかった。以上のことから、放射線抵抗性細菌の効率的なDNA鎖切断修復を担うextended synthesis-dependent strand annealing(伸長合成依存的DNA鎖対合)経路の初期段階として、RecF及びRecRタンパク質は、RecAタンパク質の活性化とDNAの安定性にそれぞれ関与していることを明らかにした。
線,紫外線及びマイトマイシンCに非常に感受性を示した。これらの高い感受性は、RecFタンパク質が、組換え修復タンパク質RecAの活性化に重要な役割を担っていることに起因していることがわかった。以上のことから、放射線抵抗性細菌の効率的なDNA鎖切断修復を担うextended synthesis-dependent strand annealing(伸長合成依存的DNA鎖対合)経路の初期段階として、RecF及びRecRタンパク質は、RecAタンパク質の活性化とDNAの安定性にそれぞれ関与していることを明らかにした。

佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 106, 2012/01
In this study, we investigated lethal effects of different LET radiations in  and
and  gene disruptant strains and determined the relationship between LET and RBE. In both gene disruptant strains, radiosensitivities to four kinds of ion beams (
gene disruptant strains and determined the relationship between LET and RBE. In both gene disruptant strains, radiosensitivities to four kinds of ion beams ( He
He ,
,  C
C ,
,  C
C and
and  Ne
Ne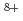 ) were almost equal to that of the
) were almost equal to that of the  rays. Both gene disruptant strains did not exhibit the dependence of LET on RBE at range of LET from about 0.2 to 441 keV/
rays. Both gene disruptant strains did not exhibit the dependence of LET on RBE at range of LET from about 0.2 to 441 keV/ m. These results indicate that RecA-mediated HR and PprA-mediated NHEJ mechanisms in
m. These results indicate that RecA-mediated HR and PprA-mediated NHEJ mechanisms in  play important roles in repairing the ion beams-induced clustered damage as well as the
play important roles in repairing the ion beams-induced clustered damage as well as the  ray-induced damage.
ray-induced damage.
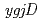 and
and 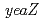 orthologs, in DNA repair of
orthologs, in DNA repair of 
小野寺 威文; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 太田 敏博*
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 107, 2012/01
In this study, we generated 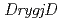 and
and  disruptant strains and investigated the disruption effect to DNA damaging agents in an effort to gain insight into the role of DrygjD and DryeaZ proteins in
disruptant strains and investigated the disruption effect to DNA damaging agents in an effort to gain insight into the role of DrygjD and DryeaZ proteins in  . We successfully constructed
. We successfully constructed 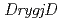 disruptant,
disruptant,  disruptant and
disruptant and 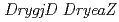 double-disruptant strains. All the disruptant strains did not exhibit the delayed growth compared to the wild-type strain, clearly indicating that neither DrygjD nor DryeaZ protein is essential for cell viability. These gene disruptant strains exhibited extremely sensitivity to mitomycin C (MMC), which causes inter- and intrastrand DNA crosslinking, suggesting that DrygjD and DryeaZ proteins are involved in the DNA repair mechanism and especially play a critical role in MMC-induced DNA damage in
double-disruptant strains. All the disruptant strains did not exhibit the delayed growth compared to the wild-type strain, clearly indicating that neither DrygjD nor DryeaZ protein is essential for cell viability. These gene disruptant strains exhibited extremely sensitivity to mitomycin C (MMC), which causes inter- and intrastrand DNA crosslinking, suggesting that DrygjD and DryeaZ proteins are involved in the DNA repair mechanism and especially play a critical role in MMC-induced DNA damage in  .
.
小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
日本微生物生態学会誌, 26(2), p.75 - 77, 2011/09
イオンビーム変異誘発研究グループでは、放射線抵抗性細菌の代表選手である の著しく高い放射線耐性の原因を解明する研究に携わってきた。2011年3月の東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故により放出された放射性物質が表層土壌に降下した。表層土や汚泥に含まれる主たる放射性核種はセシウムである。セシウムは土壌に強く吸着しているので、今後の放射性物質の除染の必要性を考えた場合、表層土や汚泥からセシウムを選択的に取り出す技術の確立が急務とされている。このような土の除染対策に微生物を直接利用することは現実的ではないにせよ、大量の放射性廃棄物を別途保管しなければならないことを考えると、土からセシウムを回収する何らかの技術が確立された後、二次的にセシウムを濃縮・回収し、保管する放射性廃棄物の量をなるべく減らすことが必要となってくる。この二次的なセシウム濃縮に微生物を利用することを、さまざまな方法の中の選択肢のひとつとして考えることは可能であろう。二次濃縮ともなれば、被曝量は微生物の致死線量には至らずとも、突然変異を高頻度に誘発することになる。濃縮効率,低コスト,安全性などを勘案すると、放射線抵抗性細菌は、二次的な放射性セシウム濃縮のための宿主として有望かも知れないと考えている。
の著しく高い放射線耐性の原因を解明する研究に携わってきた。2011年3月の東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故により放出された放射性物質が表層土壌に降下した。表層土や汚泥に含まれる主たる放射性核種はセシウムである。セシウムは土壌に強く吸着しているので、今後の放射性物質の除染の必要性を考えた場合、表層土や汚泥からセシウムを選択的に取り出す技術の確立が急務とされている。このような土の除染対策に微生物を直接利用することは現実的ではないにせよ、大量の放射性廃棄物を別途保管しなければならないことを考えると、土からセシウムを回収する何らかの技術が確立された後、二次的にセシウムを濃縮・回収し、保管する放射性廃棄物の量をなるべく減らすことが必要となってくる。この二次的なセシウム濃縮に微生物を利用することを、さまざまな方法の中の選択肢のひとつとして考えることは可能であろう。二次濃縮ともなれば、被曝量は微生物の致死線量には至らずとも、突然変異を高頻度に誘発することになる。濃縮効率,低コスト,安全性などを勘案すると、放射線抵抗性細菌は、二次的な放射性セシウム濃縮のための宿主として有望かも知れないと考えている。
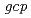 の遺伝学的解析
の遺伝学的解析北原 一正*; 小野寺 威文; 星野 貴行*; 鳴海 一成; 中村 顕*
no journal, ,
O-sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase(Gcp)は、糖タンパク質を特異的に分解する分泌型プロテアーゼとして、最初に動物病原菌で発見された。Gcpのオルソログは、真核生物・古細菌・バクテリアを問わず、ゲノム配列が決定されたほとんどすべての生物で高度に保存されている。さらに興味深いことに、同遺伝子は大腸菌や枯草菌,酵母といったモデル微生物では生育に必須であることが明らかになっている。われわれは高度好熱菌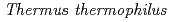 HB27株のGcpオルソログをコードするTTC0888(
HB27株のGcpオルソログをコードするTTC0888(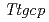 )遺伝子破壊株と、放射線抵抗性細菌
)遺伝子破壊株と、放射線抵抗性細菌 R1株のGcpオルソログをコードするDR0382(
R1株のGcpオルソログをコードするDR0382(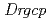 )の取得に成功した。
)の取得に成功した。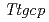 遺伝子破壊株は、過酸化水素とDNAアルキル化剤であるニトロソグアニジンに対して感受性を示した。一方、
遺伝子破壊株は、過酸化水素とDNAアルキル化剤であるニトロソグアニジンに対して感受性を示した。一方、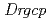 遺伝子破壊株はUVやDNAに架橋を形成するマイトマイシンCに対して感受性を示した。
遺伝子破壊株はUVやDNAに架橋を形成するマイトマイシンCに対して感受性を示した。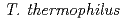 と
と はいずれもGcpオルソログを破壊でき、その表現型は異なる部分があるが、いずれもDNA修復系との関与が示唆された。今後は、各酵素の活性や相互作用について詳細な解析を行っていく予定である。
はいずれもGcpオルソログを破壊でき、その表現型は異なる部分があるが、いずれもDNA修復系との関与が示唆された。今後は、各酵素の活性や相互作用について詳細な解析を行っていく予定である。
 の遺伝学的解析
の遺伝学的解析中村 顕*; 北原 一正*; 小野寺 威文; 星野 貴行*; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
O-sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase(Gcp)とアノテートされている遺伝子は、そのオルソログが真核生物・古細菌・バクテリアを問わず、ゲノム配列が決定されたほとんどすべての生物で見いだされ、高い相同性を示す。この遺伝子は大腸菌や枯草菌などのモデルバクテリア、並びにモデル真核生物の酵母で必須遺伝子に分類されており、Gcpは重要な生命現象を担っていることが考えられる。大腸菌のGcpオルソログが別の必須タンパク質(YeaZ)と複合体を形成するという報告もなされている。今回、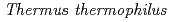 (
(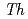 )及び
)及び (
(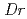 )を用いて、Gcpオルソログ及びYeaZオルソログの遺伝子破壊株の示す表現型について検討したところ、
)を用いて、Gcpオルソログ及びYeaZオルソログの遺伝子破壊株の示す表現型について検討したところ、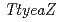 破壊株は
破壊株は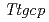 破壊株と同様に高塩濃度に対して感受性を示したが、
破壊株と同様に高塩濃度に対して感受性を示したが、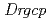 破壊株は
破壊株は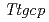 破壊株とは異なり、高塩濃度感受性を示さなかった。また、
破壊株とは異なり、高塩濃度感受性を示さなかった。また、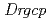 破壊株,
破壊株, 破壊株ともに、DNA損傷剤であるmitomycin Cに対して強い感受性を示したが、
破壊株ともに、DNA損傷剤であるmitomycin Cに対して強い感受性を示したが、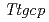 破壊株は示さなかった。一方、
破壊株は示さなかった。一方、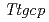 破壊株は酸化剤であるH
破壊株は酸化剤であるH O
O に対して顕著な感受性を示した。
に対して顕著な感受性を示した。
佐藤 勝也; 菊地 正博; 大庭 寛史*; 山田 貢; 手島 光平; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
放射線抵抗性細菌の相同組換え機構におけるRecFORタンパク質の役割を明らかにするために、RecF, RecO及びRecR欠損株を作製し、分子遺伝学及び分子生物学的解析を行った。欠損株の 線,紫外線及びマイトマイシンCの各変異原に対する耐性は、いずれもRecF欠損株
線,紫外線及びマイトマイシンCの各変異原に対する耐性は、いずれもRecF欠損株 RecO欠損株
RecO欠損株 RecR欠損株の順であった。このことは、各変異原によって誘発されるDNA損傷の修復には、RecFORの中でRecFタンパク質の機能が最重要であることを示している。また、欠損株における遺伝子交換反応の頻度は、RecF欠損株
RecR欠損株の順であった。このことは、各変異原によって誘発されるDNA損傷の修復には、RecFORの中でRecFタンパク質の機能が最重要であることを示している。また、欠損株における遺伝子交換反応の頻度は、RecF欠損株 RecO欠損株
RecO欠損株 RecR欠損株の順であった。このことから、遺伝子交換反応には、RecFORの中でRecRタンパク質の機能が最重要であることがわかった。以上の結果から、DNAに損傷がある場合の相同組換えとDNAに損傷がない場合の相同組換えではRecFタンパク質とRecRタンパク質の重要度が逆転しており、それぞれの反応で相同組換えのメカニズムが異なるということを明らかにした。
RecR欠損株の順であった。このことから、遺伝子交換反応には、RecFORの中でRecRタンパク質の機能が最重要であることがわかった。以上の結果から、DNAに損傷がある場合の相同組換えとDNAに損傷がない場合の相同組換えではRecFタンパク質とRecRタンパク質の重要度が逆転しており、それぞれの反応で相同組換えのメカニズムが異なるということを明らかにした。
小野寺 威文; 北原 一正*; 中村 顕*; 佐藤 勝也; 太田 敏博*; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
 -sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase (Gcp)とアノテートされている遺伝子は、大腸菌や出芽酵母などでは必須遺伝子に分類され、
-sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase (Gcp)とアノテートされている遺伝子は、大腸菌や出芽酵母などでは必須遺伝子に分類され、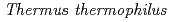 や
や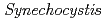 sp. PCC6803では、必須遺伝子ではないことが明らかとなっている。その機能として、出芽酵母ではミトコンドリアの
sp. PCC6803では、必須遺伝子ではないことが明らかとなっている。その機能として、出芽酵母ではミトコンドリアの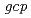 オルソログ(
オルソログ(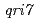 )変異株は、ゲノムDNAが消失することや
)変異株は、ゲノムDNAが消失することや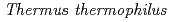 においては、その遺伝子破壊株は高塩濃度下では生育が抑制されることが報告されており、現在のところ、生物間における
においては、その遺伝子破壊株は高塩濃度下では生育が抑制されることが報告されており、現在のところ、生物間における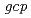 オルソログの役割について相互の関連性は見いだされていない。そこでわれわれは、放射線抵抗性細菌
オルソログの役割について相互の関連性は見いだされていない。そこでわれわれは、放射線抵抗性細菌 を用いてGcpオルソログをコードする遺伝子(
を用いてGcpオルソログをコードする遺伝子(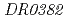 ,以下、
,以下、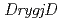 ), YeaZオルソログをコードする遺伝子(
), YeaZオルソログをコードする遺伝子(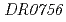 ,以下、
,以下、 )と、
)と、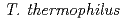 のGcpオルソログをコードする遺伝子(
のGcpオルソログをコードする遺伝子(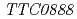 ,以下、
,以下、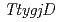 ), YeaZオルソログをコードする遺伝子(
), YeaZオルソログをコードする遺伝子(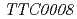 ,以下、
,以下、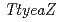 )の機能的役割について遺伝学的解析を行った。
)の機能的役割について遺伝学的解析を行った。