Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
根本 美穂*; 海老根 典也; 岡本 明子; 保坂 泰久*; 都築 克紀; 寺田 宏明; 早川 剛; 外川 織彦
JAEA-Technology 2021-013, 41 Pages, 2021/08
北朝鮮が地下核実験を実施した際には、原子力緊急時支援・研修センター(支援・研修センター)は、原子力規制庁からの要請に基づき、国による対応への支援活動として、原子力基礎工学研究センター(基礎工センター)の協力を得て、WSPEEDI-IIを用いて放射性物質の大気拡散予測計算を実施し、予測結果を原子力規制庁に提出する。本報告書は、北朝鮮地下核実験対応に特化するために基礎工センターで開発され、平成25年(2013年)2月から平成29年(2017年)9月までに実施された3回の地下核実験対応に使用されたWSPEEDI-II自動計算システムの支援・研修センターへの移管と整備について記述する。また、移管・整備した自動計算システムに関するその後の保守と運用について説明するとともに、北朝鮮地下核実験対応における今後の課題について記述する。
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*; et al.
Proceedings of 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '14) (Internet), p.28 - 33, 2014/07
Three-dimensional (3D) cooling of 40-keV  Mg
Mg ion beams with Doppler laser cooling and the coupling resonance has been demonstrated in the storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University toward the production of ultralow-emittance beams, in other words, ultracold beams and so-called crystalline beams. So far, the transverse temperatures of 6 K and 2 K have been experimentally attained in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, at a low beam intensity of about
ion beams with Doppler laser cooling and the coupling resonance has been demonstrated in the storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University toward the production of ultralow-emittance beams, in other words, ultracold beams and so-called crystalline beams. So far, the transverse temperatures of 6 K and 2 K have been experimentally attained in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, at a low beam intensity of about 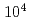 ions in the ring. These temperatures are the lowest ever attained by laser cooling of ion beams. Systematic molecular dynamics simulations predict the realization of further lower temperatures,
ions in the ring. These temperatures are the lowest ever attained by laser cooling of ion beams. Systematic molecular dynamics simulations predict the realization of further lower temperatures,  1 mK and
1 mK and  0.1 K in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, if the laser spot size and detuning are properly adjusted even with such a low laser power (
0.1 K in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, if the laser spot size and detuning are properly adjusted even with such a low laser power ( 10 mW) as utilized in the experiments at S-LSR. A 3D ordered state of the beam with 3D laser cooling is also predicted. Recent experimental achievements and latest simulation results are presented.
10 mW) as utilized in the experiments at S-LSR. A 3D ordered state of the beam with 3D laser cooling is also predicted. Recent experimental achievements and latest simulation results are presented.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.143 - 145, 2014/06
We have experimentally demonstrated transverse indirect laser cooling utilizing synchro-betatron resonance coupling in the ion accumulation cooler ring S-LSR. However, its efficiency was rather poor for relatively high beam intensity of 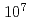 ions in the ring due to beam heating by intra-beam scattering and its cooling time was as long as 100 s. By application of beam scraping and optimization of laser detuning together with equilibrium deceleration with the use of an induction accelerator, we could reach the lowest transverse temperatures ever attained by laser cooling as 7.0 K and 2.1 K for the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. The prospect of generating an ultra-low-temperature beam and realizing beam crystallization will be discussed on the basis of the present result.
ions in the ring due to beam heating by intra-beam scattering and its cooling time was as long as 100 s. By application of beam scraping and optimization of laser detuning together with equilibrium deceleration with the use of an induction accelerator, we could reach the lowest transverse temperatures ever attained by laser cooling as 7.0 K and 2.1 K for the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. The prospect of generating an ultra-low-temperature beam and realizing beam crystallization will be discussed on the basis of the present result.
 )
) (SrMnO
(SrMnO )
) superlattice revealed by resonant soft X-ray scattering
superlattice revealed by resonant soft X-ray scattering久保田 正人; 山田 浩之*; 中尾 裕則*; 岡本 淳*; 山崎 裕一*; 澤 彰仁*; 村上 洋一*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 53(5S1), p.05FH07_1 - 05FH07_5, 2014/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:8.84(Physics, Applied)We have investigated the magnetic and electronic properties of (LaMnO )
) (SrMnO
(SrMnO )
) superlattice fabricated on a lattice-matched La
superlattice fabricated on a lattice-matched La Sr
Sr Al
Al Ta
Ta O
O substrate by resonant soft X-ray scattering. The temperature- and
substrate by resonant soft X-ray scattering. The temperature- and  -dependences of the energy spectra were measured around the Mn
-dependences of the energy spectra were measured around the Mn 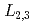 -absorption edges. We successfully observed not only a signal that reflects the valence modulation of Mn ion, but also a magnetic signal reflecting ferromagnetism. Compared with the calculated models, we concluded that the ferromagnetism mainly originates from the magnetic moments at the Mn sites sandwiched by LaO layers.
-absorption edges. We successfully observed not only a signal that reflects the valence modulation of Mn ion, but also a magnetic signal reflecting ferromagnetism. Compared with the calculated models, we concluded that the ferromagnetism mainly originates from the magnetic moments at the Mn sites sandwiched by LaO layers.
 high-spin state with a large orbital angular momentum in La
high-spin state with a large orbital angular momentum in La Ca
Ca CoO
CoO
岡本 淳*; 中尾 裕則*; 山崎 裕一*; 和達 大樹*; 田中 新*; 久保田 正人; 堀金 和正*; 村上 洋一*; 山田 和芳*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(4), p.044705_1 - 044705_6, 2014/04
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:55.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The antiferromagnetic insulator La Ca
Ca CoO
CoO has been investigated by Co L
has been investigated by Co L -edge and O K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) measurements and Co L
-edge and O K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) measurements and Co L -edge resonant soft X-ray magnetic scattering (RXMS)measurement to determine the Co electronic structures associated with magnetic ordering. Co L
-edge resonant soft X-ray magnetic scattering (RXMS)measurement to determine the Co electronic structures associated with magnetic ordering. Co L -edge linear-dichroic XAS shows that Co
-edge linear-dichroic XAS shows that Co takes a high-spin (HS) state and Co
takes a high-spin (HS) state and Co takes a low-spin (LS) state. Using Co L
takes a low-spin (LS) state. Using Co L -edge RXMS, we directly determined that an antiferromagnetic order is formed with a HS state of Co
-edge RXMS, we directly determined that an antiferromagnetic order is formed with a HS state of Co ions. Moreover, the spin and orbital angular momenta of the Co
ions. Moreover, the spin and orbital angular momenta of the Co HS state are quantitatively estimated to be 1.1
HS state are quantitatively estimated to be 1.1 0.1 and 1.0
0.1 and 1.0 0.1, respectively, and to align parallel in the ab plane by utilizing the cluster model calculation. The large orbital angular momentum of the Co
0.1, respectively, and to align parallel in the ab plane by utilizing the cluster model calculation. The large orbital angular momentum of the Co HS state originates from the small
HS state originates from the small 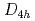 -symmetry crystal field splitting of
-symmetry crystal field splitting of 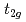 levels, which is comparable with the spin-orbit coupling constant of the Co 3
levels, which is comparable with the spin-orbit coupling constant of the Co 3 orbital.
orbital.
百合 庸介; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; He, Z.*; 想田 光*; 野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '13) (Internet), p.162 - 165, 2013/11
Efficient transverse laser cooling of a low-intensity heavy-ion beam has been recently accomplished experimentally by means of the resonant coupling method at the cooler storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University. In parallel with the experimental effort, multi-dimensional laser cooling of the ion beam has been studied also numerically with the molecular dynamics (MD) simulation code in which the stochastic interaction between ions and laser photons is incorporated in order to search optimum laser-cooling conditions and verify the results of the experiment. The present MD result demonstrates that, in spite of the limited experimental conditions of the cooling laser such as low power, fixed frequency, and short cooling section, a three-dimensionally low-temperature beam of 40-keV  Mg
Mg can be obtained through resonant coupling at a low intensity of
can be obtained through resonant coupling at a low intensity of 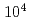 ions in the ring, which is consistent with the experimental result.
ions in the ring, which is consistent with the experimental result.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '13) (Internet), p.157 - 161, 2013/11
We have tried to approach to the lowest attainable beam temperature with laser cooling of a 40-keV  Mg
Mg ion beam at a cooler storage ring S-LSR, which has a superperiodicity of six and is designed to be tough against resonant perturbation to the circulating beam. The capability of active indirect transverse laser cooling has been experimentally demonstrated with the use of the theoretically-proposed synchro-betatron resonance coupling scheme. For the reduction of beam heating due to intrabeam scattering, an additional scheme has been established to control the intensity of the circulating beam down to
ion beam at a cooler storage ring S-LSR, which has a superperiodicity of six and is designed to be tough against resonant perturbation to the circulating beam. The capability of active indirect transverse laser cooling has been experimentally demonstrated with the use of the theoretically-proposed synchro-betatron resonance coupling scheme. For the reduction of beam heating due to intrabeam scattering, an additional scheme has been established to control the intensity of the circulating beam down to 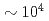 ions by scraping the outskirt of the beam with the use of a horizontally-moving scraper, which could cool the horizontal and vertical beam temperature down to
ions by scraping the outskirt of the beam with the use of a horizontally-moving scraper, which could cool the horizontal and vertical beam temperature down to 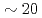 K and
K and 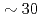 K, respectively, at an operation tune without horizontal-vertical (H-V) coupling. In the present paper, we would like to also present our recent results with H-V coupling in addition to longitudinal-horizontal coupling toward further reduction of the transverse beam temperature.
K, respectively, at an operation tune without horizontal-vertical (H-V) coupling. In the present paper, we would like to also present our recent results with H-V coupling in addition to longitudinal-horizontal coupling toward further reduction of the transverse beam temperature.
He, Z.*; Wei, J.*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*
Proceedings of 25th North American Particle Accelerator Conference (NA-PAC '13) (Internet), p.1298 - 1300, 2013/09
The power of the cooling laser currently available in a compact ion cooler ring S-LSR, Kyoto University, is quite limited for generating ultralow-temperature ion beams. Therefore, parameters of laser cooling should be carefully determined in order to approach the lowest possible temperature in the experiment. This paper mainly concerns optimization of laser-cooling parameters and prediction of a possible lower limit of beam temperature in S-LSR, based on systematic molecular dynamics simulations. The adiabatic capture process of the ion beam was introduced to prevent the emittance from blowing up during bunching. The spot size of the laser was optimized with the total laser power limited. An optimum solenoid field strength was obtained for three-dimensional cooling. The lowest beam temperature achievable in S-LSR was predicted by choosing the parameters optimized.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; He, Z.*; Grieser, M.*; 野田 章*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(3), p.030202_1 - 030202_4, 2013/03
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:22.83(Physics, Applied)The efficiency of indirect transverse laser cooling of a heavy-ion beam using synchro-betatron resonant coupling (SBRC) was improved by the reduction of the beam intensity through scraping the tail part of the beam. In order to measure the beam size at low beam intensity, a new scheme was established where the beam profile was determined from the beam survival ratio by changing the insertion position of a beam scraper. At a beam intensity of 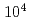 particles in the ring, the transverse cooling time of the beam was reduced to 1.2 s, and horizontal and vertical minimum beam sizes were 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm, corresponding to the beam temperatures of 20 K and 29 K, respectively. The cooling time was much improved compared with that of our previous experiment, 100 s at
particles in the ring, the transverse cooling time of the beam was reduced to 1.2 s, and horizontal and vertical minimum beam sizes were 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm, corresponding to the beam temperatures of 20 K and 29 K, respectively. The cooling time was much improved compared with that of our previous experiment, 100 s at 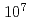 particles (Nakao et al.). The transverse temperature was comparable to that in other work (Madsen et al.), in spite of the limitation in the experimental conditions such as low laser power and short laser-cooling section. This suggests that the present SBRC scheme has a potential capacity for attaining a lower-temperature beam or even Coulomb crystallization.
particles (Nakao et al.). The transverse temperature was comparable to that in other work (Madsen et al.), in spite of the limitation in the experimental conditions such as low laser power and short laser-cooling section. This suggests that the present SBRC scheme has a potential capacity for attaining a lower-temperature beam or even Coulomb crystallization.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; Meshkov, I.*; Smirnov, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd Russian Particle Accelerator Conference (RuPAC 2012) (Internet), p.48 - 52, 2012/09
Various approaches to attaining low-temperature beams have been continued in the cooler storage ring S-LSR at Kyoto University. One-dimensional ordering of electron-cooled 7-MeV protons was realized with an abrupt longitudinal temperature jump from 2 K to 0.3 K at a particle number of around 2000. Laser cooling has been applied to 40-keV  Mg
Mg beams toward the realization of crystalline beams. For a coasting beam, the lowest longitudinal temperature of 3.6 K was attained at
beams toward the realization of crystalline beams. For a coasting beam, the lowest longitudinal temperature of 3.6 K was attained at 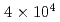 ions. The temperature was limited due to intra-beam scattering (IBS). On the other hand, the transverse temperature of the beam indirectly cooled through IBS was saturated at 500 K for
ions. The temperature was limited due to intra-beam scattering (IBS). On the other hand, the transverse temperature of the beam indirectly cooled through IBS was saturated at 500 K for 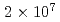 ions. In order to cool the transverse direction further, synchro-betatron resonance coupling has been applied to a bunched Mg beam. The transverse temperature has been reduced to the order of
ions. In order to cool the transverse direction further, synchro-betatron resonance coupling has been applied to a bunched Mg beam. The transverse temperature has been reduced to the order of 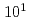 K at the beam intensity of
K at the beam intensity of 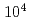 ions by the reduction of the beam intensity using a scraper.
ions by the reduction of the beam intensity using a scraper.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 野田 章*; 神保 光一*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.388 - 390, 2012/08
京都大学化学研究所のイオン蓄積・冷却リングS-LSRでは、シンクロ・ベータトロン共鳴によって重イオンビームの運動の進行方向と水平方向の振動を結合させ、レーザー冷却によって横方向を間接的に冷却する実験を進めている。冷却の過程において、粒子数が多い場合Intra-beam散乱による自己加熱作用によって冷却が阻害されるため、スクレイパーによってビーム外縁部の粒子を除去することによって冷却効率を高めている。このとき、2枚のスクレイパーを用い、1枚目のスクレイパーで粒子数を減らした後、2枚目のスクレイパーの挿入距離を変えてビームの残存率を測定することで、ビーム中心からの距離とその内側にある粒子の割合が得られ、この関係から冷却後のビームサイズを測定した。その結果、40keV  Mg
Mg ビームについて、水平・鉛直ベータトロンチューン、及びシンクロトロンチューンがそれぞれ(2.074, 1.120, 0.072)、1枚目のスクレイパーをビーム中心から0.3mmまで挿入して粒子数を1
ビームについて、水平・鉛直ベータトロンチューン、及びシンクロトロンチューンがそれぞれ(2.074, 1.120, 0.072)、1枚目のスクレイパーをビーム中心から0.3mmまで挿入して粒子数を1 10
10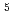 まで減少させた条件で、水平方向ビームサイズが0.3mm、温度に換算して52Kまで冷却されていることを観測した。この時、ビームサイズが1/eになるまでの冷却時間は1.25秒であった。
まで減少させた条件で、水平方向ビームサイズが0.3mm、温度に換算して52Kまで冷却されていることを観測した。この時、ビームサイズが1/eになるまでの冷却時間は1.25秒であった。
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.72 - 74, 2012/08
Laser cooling of 40-keV Mg ion has been performed at S-LSR. Indirect transverse laser cooling of a bunched beam with the use of synchro-betatron resonance coupling (SBRC) has been experimentally indicated. However, it is not so efficient due to heating by intra-beam scattering for the ion number of 10 . For attaining very low-temperature beam, it is inevitable to reduce the beam intensity without deterioration of beam detection signal. For this purpose, we have applied controlled scraping of a laser-cooled beam. After beam injection, the beam tail is cut off by a scraper moving in the horizontal direction and laser-cooled both in the longitudinal and horizontal directions with SBRC. Then, the horizontal beam size was measured with another scraper moving also in the horizontal direction. With this scheme, the beam intensity could be reduced from 10
. For attaining very low-temperature beam, it is inevitable to reduce the beam intensity without deterioration of beam detection signal. For this purpose, we have applied controlled scraping of a laser-cooled beam. After beam injection, the beam tail is cut off by a scraper moving in the horizontal direction and laser-cooled both in the longitudinal and horizontal directions with SBRC. Then, the horizontal beam size was measured with another scraper moving also in the horizontal direction. With this scheme, the beam intensity could be reduced from 10 to 10
to 10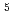 , which resulted in rather efficient indirect transverse laser cooling with the cooling time of about 1 sec.
, which resulted in rather efficient indirect transverse laser cooling with the cooling time of about 1 sec.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 野田 章*; 頓宮 拓*; 伊藤 清一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.397 - 399, 2012/05
The longitudinal temperature of 40 keV  Mg
Mg beams was measured through bunch length measurement during laser cooling at S-LSR. The bunch length was measured as time-domain signals from a pair of parallel-plate electrostatic pickups. Injected non-cooled beams gave a bunch length of 2.5 m and cooled beams had two components of broad and sharp distributions. The broad distribution had a longitudinal length of 2.2 m, which is close to that of the initial beam. The length of the sharp distribution shrunk to 0.25 m and is expected as a cooled part. The capture efficiency of cooling, which represents the ratio of particle numbers of the cooled part and the total particle number, varied with laser detuning. With a scanning range of 2 GHz, it was improved from 66% to 92%, while the bunch became longer by 10% with scanning. A new scheme for improving the capture efficiency will be applied to attain a strong signal from a low-current low-temperature beam.
beams was measured through bunch length measurement during laser cooling at S-LSR. The bunch length was measured as time-domain signals from a pair of parallel-plate electrostatic pickups. Injected non-cooled beams gave a bunch length of 2.5 m and cooled beams had two components of broad and sharp distributions. The broad distribution had a longitudinal length of 2.2 m, which is close to that of the initial beam. The length of the sharp distribution shrunk to 0.25 m and is expected as a cooled part. The capture efficiency of cooling, which represents the ratio of particle numbers of the cooled part and the total particle number, varied with laser detuning. With a scanning range of 2 GHz, it was improved from 66% to 92%, while the bunch became longer by 10% with scanning. A new scheme for improving the capture efficiency will be applied to attain a strong signal from a low-current low-temperature beam.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 伊藤 清一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.394 - 396, 2012/05
Mg ion beams have been successfully laser-cooled both in longitudinal and transverse directions at S-LSR in ICR, Kyoto University. The cooling rate, however, is not strong enough to realize a crystalline beam due to heating from intra-beam scattering (IBS). Reduction of the beam intensity is inevitable to suppress this IBS effect, which, however, had resulted in poor S/N ratio for observation of the transverse beam size. We, therefore, describe a new beam-scraping scheme: The scheme selects out ions in the distribution tail of the transverse phase space, keeping the beam density in the core part by simultaneous application of multi-dimensional laser cooling and beam scraping. The strategy to realize the scheme effectively has been searched by combination of the beam experiments and computer simulations.
小嶋 健介; 奥村 啓介; 浅井 志保; 半澤 有希子; 岡本 力; 利光 正章; 伊奈川 潤; 木村 貴海; 金子 悟*; 鈴木 健介*
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2011/12
高レベル放射性廃棄物の品質管理及び長期安全性評価において、使用済燃料中の長寿命核分裂生成物(LLFP)の正確なインベントリ評価が重要である。日本では、実用軽水炉の使用済燃料の組成を評価する際に燃焼計算コードORGEN2が広く使われているが、同コードに組み込まれているライブラリは古く、また、分析が困難なために測定データが不足している Se,
Se,  Tc,
Tc,  Sn及び
Sn及び Cs等のLLFPに対する評価が不十分である。使用済燃料組成等のインベントリ評価の精度向上を図るため、最新核データライブラリであるJENDL-4.0の中性子断面積や核分裂収率等を用いて、新たなORIGEN2用ライブラリを作成した。Cooper, Calvert-Cliffs-1, H. B. Robinson-2, 大飯原発1号機の実機使用済燃料サンプルに対する照射後試験解析に新ライブラリを用いた結果、新ライブラリは、LLFPのインベントリ評価に対し、良い適用性を示すことがわかった。
Cs等のLLFPに対する評価が不十分である。使用済燃料組成等のインベントリ評価の精度向上を図るため、最新核データライブラリであるJENDL-4.0の中性子断面積や核分裂収率等を用いて、新たなORIGEN2用ライブラリを作成した。Cooper, Calvert-Cliffs-1, H. B. Robinson-2, 大飯原発1号機の実機使用済燃料サンプルに対する照射後試験解析に新ライブラリを用いた結果、新ライブラリは、LLFPのインベントリ評価に対し、良い適用性を示すことがわかった。
 Se,
Se,  Tc,
Tc,  Sn and
Sn and  Cs
Cs奥村 啓介; 浅井 志保; 半澤 有希子; 鈴木 英哉; 利光 正章; 伊奈川 潤; 岡本 力; 篠原 伸夫; 金子 悟*; 鈴木 健介*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.369 - 374, 2011/10
軽水炉使用済燃料中の長寿命核分裂生成物の正確なインベントリ評価のために、JENDL-4.0等の最新核データを採用した新しい燃焼チェーンモデルと崩壊データを開発した。この最新核データとMVP-BURNを、 Se,
Se,  Tc,
Tc,  Sn,
Sn,  Csのインベントリ測定を含む幾つかの照射後試験解析に適用した。それらの1つは、原子力機構が実施した新しい測定である。これらの解析の結果、原子力機構による新しい測定値は、異なる研究機関で異なる技術により測定された他の照射後試験データとよく整合していることが確認できた。また、本計算による結果は、
Csのインベントリ測定を含む幾つかの照射後試験解析に適用した。それらの1つは、原子力機構が実施した新しい測定である。これらの解析の結果、原子力機構による新しい測定値は、異なる研究機関で異なる技術により測定された他の照射後試験データとよく整合していることが確認できた。また、本計算による結果は、 Seと
Seと Csの生成量に対して、10%以内で実験値とよく一致することがわかった。一方、
Csの生成量に対して、10%以内で実験値とよく一致することがわかった。一方、 Tcと
Tcと Snについては、およそ50%までの過大評価がみられた。これらの差異は、試料を溶解する際の不溶解残渣の影響、又は、解析における核分裂収率の誤差に起因するものと考えられる。
Snについては、およそ50%までの過大評価がみられた。これらの差異は、試料を溶解する際の不溶解残渣の影響、又は、解析における核分裂収率の誤差に起因するものと考えられる。
奥村 啓介; 浅井 志保; 半澤 有希子; 岡本 力; 鈴木 英哉; 利光 正章; 伊奈川 潤; 木村 貴海; 鈴木 健介*; 金子 悟*
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.1443 - 1450, 2011/09
軽水炉使用済燃料からの高レベル放射性廃棄物に存在する長寿命核分裂生成物のインベントリ評価手法は、長期間に渡る廃棄物処理処分の安全性評価に重要である。Se-79, Tc-99, Sn-126, Cs-135といった難分析長寿命核分裂生成物のインベントリ評価手法を開発するため、最新の燃焼計算コードとデータを使用して、燃料仕様や燃焼条件をパラメータとするサーベイ計算を行った。その中で、燃料集合体タイプ(PWR/BWR),U-235初期濃縮度,減速材温度,ボイド率,出力密度などを考えられる範囲で変動させた。その結果、前述の長寿命核分裂生成物の燃焼特性と生成の範囲が明らかとなった。これらの結果から、高レベル放射性廃棄物に存在する難分析長寿命核分裂生成物のインベントリを、測定が容易な核種(キー核種)の分析値との相関から決定するスケーリングファクタ法とそのキー核種を提案する。
 Sr
Sr RuO
RuO across the ferromagnetic quantum phase transition
across the ferromagnetic quantum phase transition岡本 淳*; 岡根 哲夫; 斎藤 祐児; 寺井 恒太*; 藤森 伸一; 村松 康司*; 吉井 賢資; 間宮 一敏*; 小出 常晴*; 藤森 淳; et al.
Physical Review B, 76(18), p.184441_1 - 184441_5, 2007/11
被引用回数:34 パーセンタイル:76.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sr濃度xが0.3以上で強磁性に転移するCa Sr
Sr RuO
RuO の磁性と電子構造の関係をRu 3
の磁性と電子構造の関係をRu 3 及びO 1
及びO 1 内殻吸収分光の磁気円二色性(XMCD)を用いて研究した。XMCD構造はxが0.3付近で現れ、強磁性相ではxとともに単調に増大した。XMCD強度がxとともに単調に増大することはStoner型の遍歴強磁性に見られるものであるが、Ru 3
内殻吸収分光の磁気円二色性(XMCD)を用いて研究した。XMCD構造はxが0.3付近で現れ、強磁性相ではxとともに単調に増大した。XMCD強度がxとともに単調に増大することはStoner型の遍歴強磁性に見られるものであるが、Ru 3 , O 1
, O 1 ともにXMCDスペクトル形状に変化が見られなかったことはCa
ともにXMCDスペクトル形状に変化が見られなかったことはCa Sr
Sr RuO
RuO の遍歴強磁性が強い電子相関に影響されていることを示している。
の遍歴強磁性が強い電子相関に影響されていることを示している。
 Mn
Mn N
NHwang, J. I.*; 石田 行章*; 小林 正起*; 平田 玄*; 田久保 耕*; 溝川 貴司*; 藤森 淳; 岡本 淳; 間宮 一敏*; 斎藤 祐児; et al.
Physical Review B, 72(8), p.085216_1 - 085216_6, 2005/08
被引用回数:64 パーセンタイル:87.86(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)常磁性Ga Mn
Mn Nの電子構造について光電子分光(PES),X線吸収分光(XAS)によって調べた。XAS実験スペクトルを理論計算と比較することによって、GaN中Mnは正四面体配位結晶場中の2価で説明できることがわかった。この結果に従い、Mn2p及びMn3d光電子スペクトルを配置間相互作用クラスターモデルで解析した。これにより見積もられた電子構造パラメータから計算したp-d交換相互作用定数の大きさはGa
Nの電子構造について光電子分光(PES),X線吸収分光(XAS)によって調べた。XAS実験スペクトルを理論計算と比較することによって、GaN中Mnは正四面体配位結晶場中の2価で説明できることがわかった。この結果に従い、Mn2p及びMn3d光電子スペクトルを配置間相互作用クラスターモデルで解析した。これにより見積もられた電子構造パラメータから計算したp-d交換相互作用定数の大きさはGa Mn
Mn Asの1.6倍であることが判明した。また、内殻PESからはMn濃度の上昇に伴ってフェルミレベルが降下する様子とバンドギャップ中に新たな状態が生成され増大する様子が観測された。以上のことから、Ga
Asの1.6倍であることが判明した。また、内殻PESからはMn濃度の上昇に伴ってフェルミレベルが降下する様子とバンドギャップ中に新たな状態が生成され増大する様子が観測された。以上のことから、Ga Mn
Mn Nにおいて十分な正孔濃度を実現することで高い転移点を持つ強磁性が発現する可能性が実験的に示された。
Nにおいて十分な正孔濃度を実現することで高い転移点を持つ強磁性が発現する可能性が実験的に示された。
長沼 毅*; 岩月 輝希; 村上 由記; 濱 克宏; 岡本 拓士*; 谷本 大輔*; 藤田 夕佳*; 渡辺 史子*; 足立 奈保美*; 佐藤 誠*
JNC TY7400 2003-001, 116 Pages, 2003/05
本報告書は、核燃料サイクル開発機構東濃地科学センターと広島大学生物生産学部間で行われた先行基礎工学共同研究「深部地質環境に対する微生物の影響に関する研究-地下微生物群集の種組成と代謝の多様性に関する研究」の成果を取りまとめるものである。概要を以下に示す。岐阜県東濃地域において、地下深部の微生物の存在量と多様性に関する研究を行った。蛍光染色法による全菌数の計測、呼吸活性やエステラーゼ活性等に基づいて、生菌数を調査したところ、全菌数の約0.001%-100%と求められた。これらの微生物の存在量は、環境要因(岩盤中の割れ目本数、地下水の水理・地球化学条件等)に依存していた。ウラン鉱床を含む堆積岩深部においては、地下水中の酸化還元化学種、微生物生息数、硫酸イオンの硫黄同位体比から、硫酸還元菌による硫酸還元反応が主要な酸化還元反応であることが明らかになった。また、硫酸イオンと塩酸イオンが良い相関を示しながら震度とともに増加しており、硫酸イオンの期限は堆積岩上部の海成層であると考えられた。このような地下水-鉱物-微生物システムにおける酸化還元プロセスは、海成層が陸地化してからも、硫酸還元菌が海成層から供給される硫酸イオンを堆積岩下部に豊富に存在する有機物で還元することで長期間続いてきたと推察される。硫酸イオンの供給速度と岩層中の硫酸態硫黄の含有量から、現在の水理条件が続く場合、硫酸還元菌による硫酸還元反応は今後数十万年間以上にわたって継続し、ウランを保持する還元環境が維持されると推察される。一方、花崗岩中の地下水においては、鉄関連細菌が鉄による酸化還元状態の形成に重要な役割を果たしていると考えられる。特に、花崗岩上部では鉄酸化菌が鉄コロイドの沈没に関与していると推察される。