Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*; et al.
Proceedings of 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '14) (Internet), p.28 - 33, 2014/07
Three-dimensional (3D) cooling of 40-keV  Mg
Mg ion beams with Doppler laser cooling and the coupling resonance has been demonstrated in the storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University toward the production of ultralow-emittance beams, in other words, ultracold beams and so-called crystalline beams. So far, the transverse temperatures of 6 K and 2 K have been experimentally attained in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, at a low beam intensity of about
ion beams with Doppler laser cooling and the coupling resonance has been demonstrated in the storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University toward the production of ultralow-emittance beams, in other words, ultracold beams and so-called crystalline beams. So far, the transverse temperatures of 6 K and 2 K have been experimentally attained in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, at a low beam intensity of about 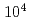 ions in the ring. These temperatures are the lowest ever attained by laser cooling of ion beams. Systematic molecular dynamics simulations predict the realization of further lower temperatures,
ions in the ring. These temperatures are the lowest ever attained by laser cooling of ion beams. Systematic molecular dynamics simulations predict the realization of further lower temperatures,  1 mK and
1 mK and  0.1 K in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, if the laser spot size and detuning are properly adjusted even with such a low laser power (
0.1 K in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, if the laser spot size and detuning are properly adjusted even with such a low laser power ( 10 mW) as utilized in the experiments at S-LSR. A 3D ordered state of the beam with 3D laser cooling is also predicted. Recent experimental achievements and latest simulation results are presented.
10 mW) as utilized in the experiments at S-LSR. A 3D ordered state of the beam with 3D laser cooling is also predicted. Recent experimental achievements and latest simulation results are presented.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.143 - 145, 2014/06
We have experimentally demonstrated transverse indirect laser cooling utilizing synchro-betatron resonance coupling in the ion accumulation cooler ring S-LSR. However, its efficiency was rather poor for relatively high beam intensity of 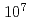 ions in the ring due to beam heating by intra-beam scattering and its cooling time was as long as 100 s. By application of beam scraping and optimization of laser detuning together with equilibrium deceleration with the use of an induction accelerator, we could reach the lowest transverse temperatures ever attained by laser cooling as 7.0 K and 2.1 K for the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. The prospect of generating an ultra-low-temperature beam and realizing beam crystallization will be discussed on the basis of the present result.
ions in the ring due to beam heating by intra-beam scattering and its cooling time was as long as 100 s. By application of beam scraping and optimization of laser detuning together with equilibrium deceleration with the use of an induction accelerator, we could reach the lowest transverse temperatures ever attained by laser cooling as 7.0 K and 2.1 K for the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. The prospect of generating an ultra-low-temperature beam and realizing beam crystallization will be discussed on the basis of the present result.
百合 庸介; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; He, Z.*; 想田 光*; 野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '13) (Internet), p.162 - 165, 2013/11
Efficient transverse laser cooling of a low-intensity heavy-ion beam has been recently accomplished experimentally by means of the resonant coupling method at the cooler storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University. In parallel with the experimental effort, multi-dimensional laser cooling of the ion beam has been studied also numerically with the molecular dynamics (MD) simulation code in which the stochastic interaction between ions and laser photons is incorporated in order to search optimum laser-cooling conditions and verify the results of the experiment. The present MD result demonstrates that, in spite of the limited experimental conditions of the cooling laser such as low power, fixed frequency, and short cooling section, a three-dimensionally low-temperature beam of 40-keV  Mg
Mg can be obtained through resonant coupling at a low intensity of
can be obtained through resonant coupling at a low intensity of 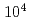 ions in the ring, which is consistent with the experimental result.
ions in the ring, which is consistent with the experimental result.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '13) (Internet), p.157 - 161, 2013/11
We have tried to approach to the lowest attainable beam temperature with laser cooling of a 40-keV  Mg
Mg ion beam at a cooler storage ring S-LSR, which has a superperiodicity of six and is designed to be tough against resonant perturbation to the circulating beam. The capability of active indirect transverse laser cooling has been experimentally demonstrated with the use of the theoretically-proposed synchro-betatron resonance coupling scheme. For the reduction of beam heating due to intrabeam scattering, an additional scheme has been established to control the intensity of the circulating beam down to
ion beam at a cooler storage ring S-LSR, which has a superperiodicity of six and is designed to be tough against resonant perturbation to the circulating beam. The capability of active indirect transverse laser cooling has been experimentally demonstrated with the use of the theoretically-proposed synchro-betatron resonance coupling scheme. For the reduction of beam heating due to intrabeam scattering, an additional scheme has been established to control the intensity of the circulating beam down to 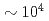 ions by scraping the outskirt of the beam with the use of a horizontally-moving scraper, which could cool the horizontal and vertical beam temperature down to
ions by scraping the outskirt of the beam with the use of a horizontally-moving scraper, which could cool the horizontal and vertical beam temperature down to 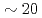 K and
K and 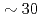 K, respectively, at an operation tune without horizontal-vertical (H-V) coupling. In the present paper, we would like to also present our recent results with H-V coupling in addition to longitudinal-horizontal coupling toward further reduction of the transverse beam temperature.
K, respectively, at an operation tune without horizontal-vertical (H-V) coupling. In the present paper, we would like to also present our recent results with H-V coupling in addition to longitudinal-horizontal coupling toward further reduction of the transverse beam temperature.
He, Z.*; Wei, J.*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*
Proceedings of 25th North American Particle Accelerator Conference (NA-PAC '13) (Internet), p.1298 - 1300, 2013/09
The power of the cooling laser currently available in a compact ion cooler ring S-LSR, Kyoto University, is quite limited for generating ultralow-temperature ion beams. Therefore, parameters of laser cooling should be carefully determined in order to approach the lowest possible temperature in the experiment. This paper mainly concerns optimization of laser-cooling parameters and prediction of a possible lower limit of beam temperature in S-LSR, based on systematic molecular dynamics simulations. The adiabatic capture process of the ion beam was introduced to prevent the emittance from blowing up during bunching. The spot size of the laser was optimized with the total laser power limited. An optimum solenoid field strength was obtained for three-dimensional cooling. The lowest beam temperature achievable in S-LSR was predicted by choosing the parameters optimized.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; He, Z.*; Grieser, M.*; 野田 章*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(3), p.030202_1 - 030202_4, 2013/03
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:22.83(Physics, Applied)The efficiency of indirect transverse laser cooling of a heavy-ion beam using synchro-betatron resonant coupling (SBRC) was improved by the reduction of the beam intensity through scraping the tail part of the beam. In order to measure the beam size at low beam intensity, a new scheme was established where the beam profile was determined from the beam survival ratio by changing the insertion position of a beam scraper. At a beam intensity of 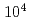 particles in the ring, the transverse cooling time of the beam was reduced to 1.2 s, and horizontal and vertical minimum beam sizes were 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm, corresponding to the beam temperatures of 20 K and 29 K, respectively. The cooling time was much improved compared with that of our previous experiment, 100 s at
particles in the ring, the transverse cooling time of the beam was reduced to 1.2 s, and horizontal and vertical minimum beam sizes were 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm, corresponding to the beam temperatures of 20 K and 29 K, respectively. The cooling time was much improved compared with that of our previous experiment, 100 s at 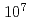 particles (Nakao et al.). The transverse temperature was comparable to that in other work (Madsen et al.), in spite of the limitation in the experimental conditions such as low laser power and short laser-cooling section. This suggests that the present SBRC scheme has a potential capacity for attaining a lower-temperature beam or even Coulomb crystallization.
particles (Nakao et al.). The transverse temperature was comparable to that in other work (Madsen et al.), in spite of the limitation in the experimental conditions such as low laser power and short laser-cooling section. This suggests that the present SBRC scheme has a potential capacity for attaining a lower-temperature beam or even Coulomb crystallization.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; Meshkov, I.*; Smirnov, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd Russian Particle Accelerator Conference (RuPAC 2012) (Internet), p.48 - 52, 2012/09
Various approaches to attaining low-temperature beams have been continued in the cooler storage ring S-LSR at Kyoto University. One-dimensional ordering of electron-cooled 7-MeV protons was realized with an abrupt longitudinal temperature jump from 2 K to 0.3 K at a particle number of around 2000. Laser cooling has been applied to 40-keV  Mg
Mg beams toward the realization of crystalline beams. For a coasting beam, the lowest longitudinal temperature of 3.6 K was attained at
beams toward the realization of crystalline beams. For a coasting beam, the lowest longitudinal temperature of 3.6 K was attained at 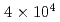 ions. The temperature was limited due to intra-beam scattering (IBS). On the other hand, the transverse temperature of the beam indirectly cooled through IBS was saturated at 500 K for
ions. The temperature was limited due to intra-beam scattering (IBS). On the other hand, the transverse temperature of the beam indirectly cooled through IBS was saturated at 500 K for 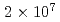 ions. In order to cool the transverse direction further, synchro-betatron resonance coupling has been applied to a bunched Mg beam. The transverse temperature has been reduced to the order of
ions. In order to cool the transverse direction further, synchro-betatron resonance coupling has been applied to a bunched Mg beam. The transverse temperature has been reduced to the order of 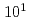 K at the beam intensity of
K at the beam intensity of 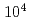 ions by the reduction of the beam intensity using a scraper.
ions by the reduction of the beam intensity using a scraper.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 野田 章*; 神保 光一*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.388 - 390, 2012/08
京都大学化学研究所のイオン蓄積・冷却リングS-LSRでは、シンクロ・ベータトロン共鳴によって重イオンビームの運動の進行方向と水平方向の振動を結合させ、レーザー冷却によって横方向を間接的に冷却する実験を進めている。冷却の過程において、粒子数が多い場合Intra-beam散乱による自己加熱作用によって冷却が阻害されるため、スクレイパーによってビーム外縁部の粒子を除去することによって冷却効率を高めている。このとき、2枚のスクレイパーを用い、1枚目のスクレイパーで粒子数を減らした後、2枚目のスクレイパーの挿入距離を変えてビームの残存率を測定することで、ビーム中心からの距離とその内側にある粒子の割合が得られ、この関係から冷却後のビームサイズを測定した。その結果、40keV  Mg
Mg ビームについて、水平・鉛直ベータトロンチューン、及びシンクロトロンチューンがそれぞれ(2.074, 1.120, 0.072)、1枚目のスクレイパーをビーム中心から0.3mmまで挿入して粒子数を1
ビームについて、水平・鉛直ベータトロンチューン、及びシンクロトロンチューンがそれぞれ(2.074, 1.120, 0.072)、1枚目のスクレイパーをビーム中心から0.3mmまで挿入して粒子数を1 10
10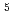 まで減少させた条件で、水平方向ビームサイズが0.3mm、温度に換算して52Kまで冷却されていることを観測した。この時、ビームサイズが1/eになるまでの冷却時間は1.25秒であった。
まで減少させた条件で、水平方向ビームサイズが0.3mm、温度に換算して52Kまで冷却されていることを観測した。この時、ビームサイズが1/eになるまでの冷却時間は1.25秒であった。
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.72 - 74, 2012/08
Laser cooling of 40-keV Mg ion has been performed at S-LSR. Indirect transverse laser cooling of a bunched beam with the use of synchro-betatron resonance coupling (SBRC) has been experimentally indicated. However, it is not so efficient due to heating by intra-beam scattering for the ion number of 10 . For attaining very low-temperature beam, it is inevitable to reduce the beam intensity without deterioration of beam detection signal. For this purpose, we have applied controlled scraping of a laser-cooled beam. After beam injection, the beam tail is cut off by a scraper moving in the horizontal direction and laser-cooled both in the longitudinal and horizontal directions with SBRC. Then, the horizontal beam size was measured with another scraper moving also in the horizontal direction. With this scheme, the beam intensity could be reduced from 10
. For attaining very low-temperature beam, it is inevitable to reduce the beam intensity without deterioration of beam detection signal. For this purpose, we have applied controlled scraping of a laser-cooled beam. After beam injection, the beam tail is cut off by a scraper moving in the horizontal direction and laser-cooled both in the longitudinal and horizontal directions with SBRC. Then, the horizontal beam size was measured with another scraper moving also in the horizontal direction. With this scheme, the beam intensity could be reduced from 10 to 10
to 10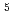 , which resulted in rather efficient indirect transverse laser cooling with the cooling time of about 1 sec.
, which resulted in rather efficient indirect transverse laser cooling with the cooling time of about 1 sec.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 野田 章*; 頓宮 拓*; 伊藤 清一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.397 - 399, 2012/05
The longitudinal temperature of 40 keV  Mg
Mg beams was measured through bunch length measurement during laser cooling at S-LSR. The bunch length was measured as time-domain signals from a pair of parallel-plate electrostatic pickups. Injected non-cooled beams gave a bunch length of 2.5 m and cooled beams had two components of broad and sharp distributions. The broad distribution had a longitudinal length of 2.2 m, which is close to that of the initial beam. The length of the sharp distribution shrunk to 0.25 m and is expected as a cooled part. The capture efficiency of cooling, which represents the ratio of particle numbers of the cooled part and the total particle number, varied with laser detuning. With a scanning range of 2 GHz, it was improved from 66% to 92%, while the bunch became longer by 10% with scanning. A new scheme for improving the capture efficiency will be applied to attain a strong signal from a low-current low-temperature beam.
beams was measured through bunch length measurement during laser cooling at S-LSR. The bunch length was measured as time-domain signals from a pair of parallel-plate electrostatic pickups. Injected non-cooled beams gave a bunch length of 2.5 m and cooled beams had two components of broad and sharp distributions. The broad distribution had a longitudinal length of 2.2 m, which is close to that of the initial beam. The length of the sharp distribution shrunk to 0.25 m and is expected as a cooled part. The capture efficiency of cooling, which represents the ratio of particle numbers of the cooled part and the total particle number, varied with laser detuning. With a scanning range of 2 GHz, it was improved from 66% to 92%, while the bunch became longer by 10% with scanning. A new scheme for improving the capture efficiency will be applied to attain a strong signal from a low-current low-temperature beam.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 伊藤 清一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.394 - 396, 2012/05
Mg ion beams have been successfully laser-cooled both in longitudinal and transverse directions at S-LSR in ICR, Kyoto University. The cooling rate, however, is not strong enough to realize a crystalline beam due to heating from intra-beam scattering (IBS). Reduction of the beam intensity is inevitable to suppress this IBS effect, which, however, had resulted in poor S/N ratio for observation of the transverse beam size. We, therefore, describe a new beam-scraping scheme: The scheme selects out ions in the distribution tail of the transverse phase space, keeping the beam density in the core part by simultaneous application of multi-dimensional laser cooling and beam scraping. The strategy to realize the scheme effectively has been searched by combination of the beam experiments and computer simulations.
Yu, P.*; He, Z.*; Wei, J.*; Sessler, A. M.*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.1943 - 1945, 2010/05
In the process of beam cooling, the main heating source is intra-beam scattering (IBS), in which Coulomb collisions among particles lead to a growth of the beam's 6D phase-space volume. The results of molecular dynamics simulations have shown an increase of heating rate as the temperature increases from absolute zero, then a peak in the heating rate, and subsequent decrease with increasing temperature. On the other hand, in the traditional IBS theory, heating rate increases monotonically as the temperature becomes lower and lower. In this paper, we attempt to extend the traditional IBS theory valid at high temperatures to relatively low temperature range, by including some many-body effects in the traditional IBS theory. In particular, we take into account the static and dynamic effect of the self-electromagnetic field of the beam. We shall show how these effects modify the traditional theory, and present the evaluation of IBS heating rate of an ion beam in the low temperature range.
Wei, J.*; Yu, P.*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; Li, X.-P.*; Sessler, A. M.*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '09) (Internet), p.86 - 90, 2010/00
During the past several decades, beam crystallization has been studied both theoretically and experimentally. Theoretical investigations have been numerical, mainly using computer modeling based on the method of molecular dynamics, and analytical, based on phonon theory. Experimental investigations involve both ion storage rings and ion traps using both electron and laser beam cooling. Topics of interests include crystal stability in various accelerator lattices and under different beam conditions, crystalline beam formation in shear-free ring lattices with both magnets and electrodes, experimental simulation of alternating-gradient conditions with an ion trap, etc. In this paper, we first review theoretical approaches and major conclusions pertaining to beam crystallization. Then, we analyze conditions and methods of the various major experiments. Finally, we discuss, both theoretically and experimentally, some improvements, open questions, and challenges in beam crystallization.
百合 庸介; 岡本 宏巳*; 杉本 寛*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(12), p.124501_1 - 124501_10, 2009/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:10.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The collisional heating process of highly space-charge-dominated coasting ion beams in a storage ring was systematically investigated using the molecular dynamics simulation technique. To evaluate the heating rate over the whole temperature range, the simulation was started from an ultra-low-emittance state where the beam is Coulomb crystallized. When the ring is properly designed, the heating rate is quite low at ultralow temperature because random Coulomb collisions are suppressed. It gradually increases during the melting process of a Coulomb crystal and eventually comes to a peak at relatively low temperature where the beam is in a liquid phase. The dependence of the heating behavior is explored on various machine and beam parameters, such as the line density, betatron tune, kinetic energy, and mass number of ions. An approximate formula is given to estimate the magnitude of emittance at which the collisional heating is maximized.
岡本 宏巳*; 杉本 寛*; 百合 庸介
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.8, p.950 - 954, 2009/09
We study the heating of space-charge-dominated coasting beams circulating in a storage ring. A number of molecular dynamics simulations are performed systematically to figure out the parameter-dependence of the heating rate due to interparticle Coulomb collisions. We introduce a new definition of the Coulomb coupling constant  that characterizes the phase of one-component plasmas. The new
that characterizes the phase of one-component plasmas. The new  is based on observable quantities and can be applied to dispersive situations. It is confirmed that the heating rate comes to a peak when the beam is in a liquid phase; the peak is always located at
is based on observable quantities and can be applied to dispersive situations. It is confirmed that the heating rate comes to a peak when the beam is in a liquid phase; the peak is always located at 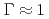 regardless of particle species, beam energy, the strength of external confinement forces, and line density.
regardless of particle species, beam energy, the strength of external confinement forces, and line density.
岡本 宏巳*; 杉本 寛*; 百合 庸介; 池上 将弘*; Wei, J.*
Proceedings of 10th International Computational Accelerator Physics Conference (ICAP 2009) (Internet), p.151 - 156, 2009/08
An ultimate goal in accelerator physics is to produce a "zero-emittance" beam, which is equivalent to making the beam temperature the absolute zero in the center-of-mass frame. At this limit, if somehow reached, the beam is Coulomb crystallized. Schiffer and co-workers first applied the molecular dynamics (MD) technique to study the fundamental features of various Coulomb crystals. Their pioneering work was later generalized by Wei et al. who explicitly incorporated discrete alternating-gradient lattice structures into MD simulations. This talk summarizes recent numerical efforts made to clarify the dynamic behavior of ultra-cold and crystalline ion beams. The MD modeling of beam crystallization in a storage ring is outlined, including how one can approach the ultra-low emittance limit. Several possible methods are described of cooling an ion beam with radiation pressure (the Doppler laser cooling).
百合 庸介; 岡本 宏巳*
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.3080 - 3082, 2008/06
We investigate the heating process of highly space-charge-dominated ion beams in a storage ring, using the molecular dynamics simulation technique. To evaluate the heating rate over the whole temperature range, we start from an ultra-low-emittance state where the beam is Coulomb crystallized, apply perturbation to it, and follow the emittance evolution. When the ring lattice is properly designed, the heating rate is quite low at ultralow temperature because random Coulomb collisions are suppressed. It gradually increases after the collapse of the ordered state by perturbation, and comes to a peak when the beam reaches a liquid phase. The dependence of the heating behavior on the beam line density and betatron tune is explored systematically. The effect of lattice imperfection on the stability of crystalline beams is also confirmed.
杉本 寛*; 岡本 宏巳*; Wei, J.*; 百合 庸介; Sessler, A. M.*
Proceedings of 5th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 33rd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.436 - 438, 2008/00
加速器中のビームを冷却すると、ビームは最終的にクーロン結晶状態になると予見されている。そのエミッタンスはゼロであり、高エネルギー衝突実験に利用すれば非常に大きなルミノシティが期待される。ビームを結晶化させるためには、ベータトロン振動数 とラティスの超周期数
とラティスの超周期数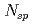 は
は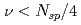 を満たしている必要がある。また、結晶化したビームを安定に周回させるためにはビームエネルギー
を満たしている必要がある。また、結晶化したビームを安定に周回させるためにはビームエネルギー はトランジションエネルギー
はトランジションエネルギー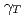 を超えてはならない。本研究では
を超えてはならない。本研究では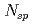 と
と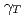 が大きい蓄積リングを想定し、結晶化ビームの安定性とビームのエネルギーの関係を理論及び分子動力学シミュレーションにより検討した。その結果、
が大きい蓄積リングを想定し、結晶化ビームの安定性とビームのエネルギーの関係を理論及び分子動力学シミュレーションにより検討した。その結果、 が
が を超えると結晶は不安定になることがわかった。これは
を超えると結晶は不安定になることがわかった。これは の増加に伴い結晶化ビームの感じる実効的な集束力が弱くなることが原因であると考えられる。ただし、比較的低密度のひも状結晶は
の増加に伴い結晶化ビームの感じる実効的な集束力が弱くなることが原因であると考えられる。ただし、比較的低密度のひも状結晶は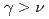 の場合にも安定に周回した。以上の結果から、高エネルギーの多次元結晶化ビームを安定に周回させるためには、ベータトロン振動数と超周期数が大きなリングが必要であることがわかった。
の場合にも安定に周回した。以上の結果から、高エネルギーの多次元結晶化ビームを安定に周回させるためには、ベータトロン振動数と超周期数が大きなリングが必要であることがわかった。
Wei, J.*; 岡本 宏巳*; 杉本 寛*; 百合 庸介; Sessler, A. M.*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '07), p.91 - 95, 2007/09
Recent theoretical investigations of beam crystallization using computer modeling based on the method of molecular dynamics (MD) and analytical approach based on the phonon theory are motivated by the study of colliding crystalline beams. In order to investigate the stability of 1D crystals at high energies, we present a newly developed phonon theory in a time-dependent Hamiltonian system representing the actual alternating-gradient focusing ring. Using the theory, we explore ring lattices appropriate for beam crystallization at high energies. In comparison, we study both 1D and multi-dimensional high-energy crystals using the MD method. Both theoretical and numerical results show that it is possible to form 1D crystalline beams at high energies in rings that have high (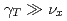 ) and imaginary (
) and imaginary (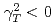 ) transition energy. Finally, we present examples of ion-ion and electron-ion colliders with 1D ordered ions.
) transition energy. Finally, we present examples of ion-ion and electron-ion colliders with 1D ordered ions.
白井 敏之*; 田辺 幹夫*; 想田 光*; 池上 将弘*; 藤本 慎司*; 頓宮 拓*; 野田 章*; 野田 耕司*; 渋谷 真二*; 藤本 哲也*; et al.
Proceedings of 9th Symposium on Accelerator and Related Technology for Application, p.19 - 22, 2007/06
The ion storage ring, S-LSR has an electron beam cooler and a laser cooling system. The electron cooler for S-LSR was designed to maximize the effective cooling length in the limited drift space of the ring. Various experiments have been carried out using the electron beam cooling, such as the sweep electron cooling, the one-dimensional ordering experiment of protons, and the short bunch generation. The laser cooling experiment is also currently in progress. Concerning the one-dimensional ordering experiment, the first proton ordering was successfully confirmed. An abrupt drop in the momentum spread and the Schottky noise power have been observed at the proton number of 2000 with electron currents of 25 mA. The transition temperature of the proton ordering is 0.17 meV in the longitudinal direction.