Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 in a greenhouse for tomato cultivation
in a greenhouse for tomato cultivation石井 里美; 山崎 治明*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 河地 有木; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 93, 2016/02
Tomato is popularly grown in environmentally controlled system such as a greenhouse for improvement of bioproduction. It is important to control the condition in the greenhouse for increasing the translocation of fixed carbon from the leaves to the growing fruits. Elevation of CO concentration is widely employed for that purpose; however, it is difficult to estimate its effect quantitatively because tomato plants have too large inter-individual variations with developing fruits. In this study, we employed a PETIS which is a live-imaging system of nutrients in plant body using short-lived radioisotopes including
concentration is widely employed for that purpose; however, it is difficult to estimate its effect quantitatively because tomato plants have too large inter-individual variations with developing fruits. In this study, we employed a PETIS which is a live-imaging system of nutrients in plant body using short-lived radioisotopes including  C. We also established a closed cultivation system to feed a test plant with CO
C. We also established a closed cultivation system to feed a test plant with CO at set concentrations of 400, 1,500 and 3,000 ppm and a pulse of
at set concentrations of 400, 1,500 and 3,000 ppm and a pulse of  CO
CO .
.
 concentration in a closed cultivation system for the improvement of bioproduction in tomato fruits
concentration in a closed cultivation system for the improvement of bioproduction in tomato fruits山崎 治明*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
Plant Biotechnology, 32(1), p.31 - 37, 2015/04
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:53.52(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)To maximize fruit yield of tomatoes cultivated in a controlled, closed system such as a greenhouse or a plant factory at a limited cost, it is important to raise the translocation rate of fixed carbon to fruits by tuning the cultivation conditions. Elevation of atmospheric  CO
CO concentration is a good candidate. In this study, we employed a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS), which is a live-imaging technology for plant studies, and a short-lived radioisotope
concentration is a good candidate. In this study, we employed a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS), which is a live-imaging technology for plant studies, and a short-lived radioisotope  C to quantitatively analyze immediate responses of carbon fixation and translocation in tomatoes in elevated CO
C to quantitatively analyze immediate responses of carbon fixation and translocation in tomatoes in elevated CO conditions. We also developed a closed cultivation system to feed a test plant with CO
conditions. We also developed a closed cultivation system to feed a test plant with CO at concentrations of 400, 1500 and 3000 ppm and a pulse of
at concentrations of 400, 1500 and 3000 ppm and a pulse of  CO
CO . As a result, we obtained serial images of
. As a result, we obtained serial images of  C fixation by leaves and subsequent translocation into fruits. Carbon fixation was enhanced steadily by increasing the CO
C fixation by leaves and subsequent translocation into fruits. Carbon fixation was enhanced steadily by increasing the CO concentration, but the amount translocated into fruits saturated at 1500 ppm on average. The translocation rate had larger inter-individual variation and showed less consistent responses to external CO
concentration, but the amount translocated into fruits saturated at 1500 ppm on average. The translocation rate had larger inter-individual variation and showed less consistent responses to external CO conditions compared with carbon fixation.
conditions compared with carbon fixation.
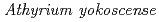 and tobacco plants
and tobacco plants吉原 利一*; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 北崎 真由*; 山崎 治明*; 北崎 一義*; 河地 有木; 尹 永根; 七夕 小百合*; 橋田 慎之介*; et al.
Plant, Cell & Environment, 37(5), p.1086 - 1096, 2014/05
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:65.61(Plant Sciences)Cadmium (Cd) accumulations in a Cd hyper-accumulator fern, 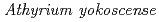 (
(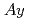 ), and tobacco,
), and tobacco, 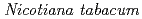 (
(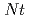 ), were kinetically analysed using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system under two medium conditions (basal and no-nutrient). In
), were kinetically analysed using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system under two medium conditions (basal and no-nutrient). In 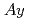 , maximumly 50% and 15% of the total Cd accumulated in the distal roots and the shoots under the basal condition, respectively. Interestingly, a portion of the Cd in the distal roots returned to the medium. In comparison with
, maximumly 50% and 15% of the total Cd accumulated in the distal roots and the shoots under the basal condition, respectively. Interestingly, a portion of the Cd in the distal roots returned to the medium. In comparison with 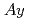 , a little fewer Cd accumulations in the distal roots and clearly higher Cd migration to the shoots were observed in
, a little fewer Cd accumulations in the distal roots and clearly higher Cd migration to the shoots were observed in 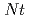 under the basal condition (maximumly 40% and 70% of the total Cd, respectively). The no-nutrient condition down-regulated the Cd migration in both species, although the regulation was highly stricter in
under the basal condition (maximumly 40% and 70% of the total Cd, respectively). The no-nutrient condition down-regulated the Cd migration in both species, although the regulation was highly stricter in 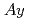 than in
than in 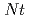 (almost no migration in
(almost no migration in 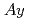 and around 20% migration in
and around 20% migration in 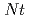 ). In addition, the present work enabled to estimate physical and physiological Cd accumulation capacities in the distal roots, and demonstrated condition-dependent changes especially in
). In addition, the present work enabled to estimate physical and physiological Cd accumulation capacities in the distal roots, and demonstrated condition-dependent changes especially in 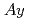 . These results clearly suggested occurrences of species-/condition-specific regulations in each observed parts. It is probable that integration of these properties govern the specific Cd tolerance/accumulation in
. These results clearly suggested occurrences of species-/condition-specific regulations in each observed parts. It is probable that integration of these properties govern the specific Cd tolerance/accumulation in 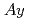 and
and 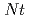 .
.
山崎 治明; 鈴井 伸郎; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 98, 2012/01
Improvement in crop yield is expected by understanding "source-sink regulation system" of higher plants. In this study, we analyzed the photoassimilate distribution system to two sink organs, the root and the shoot apex, using positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) and cold-girdling technique, which is known as a method to inhibit photoassimilate translocation.  CO
CO exposure and PETIS imaging were conducted two times with the same test plant. Cold-girdling was treated only in the second run by cooling the boundary region on the stem between shoot and root. Time-activity curves were generated from the regions of the root, shoot apex and source leaf in the PETIS data. Then, three indices were analyzed; the influx rates of photoassimilate into the two sink organs, the root and the shoot apex, and the efflux rate from the source leaf. As the results, the influx rate was decreased drastically into the root. On the other hand, influx into the shoot apex hardly changed. And the efflux rate from the leaf was decreased. These results suggest that the "source supply" is adjusted so as to keep influx rate of photoassimilate into the untreated sink.
exposure and PETIS imaging were conducted two times with the same test plant. Cold-girdling was treated only in the second run by cooling the boundary region on the stem between shoot and root. Time-activity curves were generated from the regions of the root, shoot apex and source leaf in the PETIS data. Then, three indices were analyzed; the influx rates of photoassimilate into the two sink organs, the root and the shoot apex, and the efflux rate from the source leaf. As the results, the influx rate was decreased drastically into the root. On the other hand, influx into the shoot apex hardly changed. And the efflux rate from the leaf was decreased. These results suggest that the "source supply" is adjusted so as to keep influx rate of photoassimilate into the untreated sink.
 Cを用いた光合成産物のイメージングによる植物の節の機能解析
Cを用いた光合成産物のイメージングによる植物の節の機能解析山崎 治明; 鈴井 伸郎; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 伊藤 小百合; 島田 浩章*; 石岡 典子; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
本研究では植物の節における元素分配メカニズムの解明を目的とし、まず節の機能を人為的に阻害する実験系の確立を目指した。今回、その候補として植物の一部を局所的に冷やす試みを行った。ダイズの葉柄、及びイネの茎基部に局所冷却を施し、それぞれの葉に CO
CO を投与した。次に、植物が
を投与した。次に、植物が CO
CO を吸収・固定し、
を吸収・固定し、 C-光合成産物として体内を移行・蓄積する様子を、PETISを用いてそれぞれ2時間撮像した。実験終了後、得られた動画像からダイズの節及びイネの茎基部における
C-光合成産物として体内を移行・蓄積する様子を、PETISを用いてそれぞれ2時間撮像した。実験終了後、得られた動画像からダイズの節及びイネの茎基部における C放射活性の経時変化を算出し、局所冷却を行わなかった場合と比較した。その結果、局所冷却を行ったダイズ、イネでは、ともに節での
C放射活性の経時変化を算出し、局所冷却を行わなかった場合と比較した。その結果、局所冷却を行ったダイズ、イネでは、ともに節での C-光合成産物の蓄積量に減少傾向が見られた。また、ダイズでは
C-光合成産物の蓄積量に減少傾向が見られた。また、ダイズでは C-光合成産物の節への到達時間に遅延が認められた。これらの結果より、局所冷却によって篩管内及び節での光合成産物の移行量が減少することが明らかとなり、節の機能を阻害する手段として局所冷却が有効である可能性が示された。
C-光合成産物の節への到達時間に遅延が認められた。これらの結果より、局所冷却によって篩管内及び節での光合成産物の移行量が減少することが明らかとなり、節の機能を阻害する手段として局所冷却が有効である可能性が示された。
 Cを用いた光合成産物のイメージングによる植物の節の機能解析
Cを用いた光合成産物のイメージングによる植物の節の機能解析山崎 治明; 鈴井 伸郎; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 伊藤 小百合; 島田 浩章*; 石岡 典子; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
本研究では植物の節における元素分配メカニズムの解明を目的とし、まず節の機能を人為的に阻害する実験系の確立を目指した。今回、その候補として植物の一部を局所的に冷やす試みを行った。ダイズの葉柄、及びイネの茎基部に局所冷却を施し、それぞれの葉に CO
CO を投与した。次に、植物が
を投与した。次に、植物が CO
CO を吸収・固定し、
を吸収・固定し、 C-光合成産物として体内を移行・蓄積する様子を、PETISを用いてそれぞれ2時間撮像した。実験終了後、得られた動画像からダイズの節及びイネの茎基部における
C-光合成産物として体内を移行・蓄積する様子を、PETISを用いてそれぞれ2時間撮像した。実験終了後、得られた動画像からダイズの節及びイネの茎基部における C放射活性の経時変化を算出し、局所冷却を行わなかった場合と比較した。その結果、局所冷却を行ったダイズ,イネでは、ともに節での
C放射活性の経時変化を算出し、局所冷却を行わなかった場合と比較した。その結果、局所冷却を行ったダイズ,イネでは、ともに節での C-光合成産物の蓄積量に減少傾向が見られた。また、ダイズでは
C-光合成産物の蓄積量に減少傾向が見られた。また、ダイズでは C-光合成産物の節への到達時間に遅延が認められた。これらの結果より、局所冷却によって篩管内及び節での光合成産物の移行量が減少することが明らかとなり、節の機能を阻害する手段として局所冷却が有効である可能性が示された。
C-光合成産物の節への到達時間に遅延が認められた。これらの結果より、局所冷却によって篩管内及び節での光合成産物の移行量が減少することが明らかとなり、節の機能を阻害する手段として局所冷却が有効である可能性が示された。
 Cを用いた光合成産物のイメージングによる高等植物のソース・シンクバランス制御機構の解明
Cを用いた光合成産物のイメージングによる高等植物のソース・シンクバランス制御機構の解明山崎 治明; 鈴井 伸郎; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
本研究では、ポジトロンイメージング技術(PETIS)を用いて、局所冷却による光合成産物の動態変化を解析することで、光合成産物の分配機構を解明することを目的とした。 CO
CO をダイズの地上部に投与し、
をダイズの地上部に投与し、 C-光合成産物が植物体内を移行する様子を、PETISを用いて120分間撮像した。次に、十分に
C-光合成産物が植物体内を移行する様子を、PETISを用いて120分間撮像した。次に、十分に C(半減期:20分)の減衰を待ったのち、地上部と根の境目を冷却し、同じ条件で
C(半減期:20分)の減衰を待ったのち、地上部と根の境目を冷却し、同じ条件で CO
CO の投与,撮像を行った。そして、得られた動画像をもとに光合成産物の移行速度、及びソース器官における光合成産物の送り出し、シンク器官への光合成産物の分配を比較した。その結果、局所冷却処理により、根に向かう光合成産物の移行速度が半分以下にまで遅くなったことを確認した。ソース器官における光合成産物の送り出しを比較したところ、すべての成熟葉で光合成産物の送り出しが抑制されていたが、一部では抑制の度合いが比較的小さかった。一方、シンク器官への分配を調べたところ、根での光合成産物の移行量は77%減少していたものの、茎頂部への移行量は15%の増加に留まっていた。以上の結果より、光合成産物の分配は葉の中で既に細分化されている可能性が示唆された。
の投与,撮像を行った。そして、得られた動画像をもとに光合成産物の移行速度、及びソース器官における光合成産物の送り出し、シンク器官への光合成産物の分配を比較した。その結果、局所冷却処理により、根に向かう光合成産物の移行速度が半分以下にまで遅くなったことを確認した。ソース器官における光合成産物の送り出しを比較したところ、すべての成熟葉で光合成産物の送り出しが抑制されていたが、一部では抑制の度合いが比較的小さかった。一方、シンク器官への分配を調べたところ、根での光合成産物の移行量は77%減少していたものの、茎頂部への移行量は15%の増加に留まっていた。以上の結果より、光合成産物の分配は葉の中で既に細分化されている可能性が示唆された。
吉原 利一*; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 橋田 慎之介*; 河地 有木; 山崎 治明; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
Positron-emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS)を用いて、Cd超耐性/超蓄積シダ植物「ヘビノネゴザ」のCdの吸収動態を解析した。まず、1/4MSと0.5mM CaCl の2種類の異なる培地をベースに、トレーサーとキャリアーを合わせて0.1
の2種類の異なる培地をベースに、トレーサーとキャリアーを合わせて0.1 MとなるようCdを混合し、ヘビノネゴザとタバコでCdの吸収・移行を比較した。その結果、ヘビノネゴザでは、0.5mM CaCl
MとなるようCdを混合し、ヘビノネゴザとタバコでCdの吸収・移行を比較した。その結果、ヘビノネゴザでは、0.5mM CaCl をベースにした場合、1/4MSに比べて根への取り込み量が少なく、取り込まれたCdが地上部に移行する割合も小さかった。一方、タバコでも同様に0.5mM CaCl
をベースにした場合、1/4MSに比べて根への取り込み量が少なく、取り込まれたCdが地上部に移行する割合も小さかった。一方、タバコでも同様に0.5mM CaCl をベースにした場合、1/4MSに比べて根への取り込み量が少なかったが、取り込まれたCdのかなりの割合が地上部に移行した。次にこれらの培地条件において、根を4
をベースにした場合、1/4MSに比べて根への取り込み量が少なかったが、取り込まれたCdのかなりの割合が地上部に移行した。次にこれらの培地条件において、根を4 Cに冷やした場合の変化を観察した。その結果、ヘビノネゴザでは、0.5mM CaCl
Cに冷やした場合の変化を観察した。その結果、ヘビノネゴザでは、0.5mM CaCl をベースにした場合、1/4MSに比べて根への取り込み量がある程度増加したが、取り込まれたCdはほとんど地上部に移行しなかった。一方、タバコでは同様に0.5mM CaCl
をベースにした場合、1/4MSに比べて根への取り込み量がある程度増加したが、取り込まれたCdはほとんど地上部に移行しなかった。一方、タバコでは同様に0.5mM CaCl をベースにした場合、1/4MSとほぼ同程度の根への取り込み量であったが地上部に移行する割合は若干多かった。これらの結果は、ヘビノネゴザとタバコにおけるCd吸収にかかわるトランスポーターの特性を明確に示している。
をベースにした場合、1/4MSとほぼ同程度の根への取り込み量であったが地上部に移行する割合は若干多かった。これらの結果は、ヘビノネゴザとタバコにおけるCd吸収にかかわるトランスポーターの特性を明確に示している。
小柳 淳*; 河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 尹 永根; 山崎 治明; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
シンク器官へ移行する炭素動態を解析することで、従来困難であった光合成産物の転流を、定量的に評価できることが示唆されてきた。そこで、ポジトロンイメージング技術を用いて、モデル植物であるシロイヌナズナ複数個体の体内の炭素の動きを、生育環境を妨害することなく同時に撮像し、得られた動画像から転流を定量することを目的とした。植物の成長に伴う光合成機能の個体差を抑え、またそれらを統計的に処理するため、同一シャーレ内で栽培した18個体の幼少期シロイヌナズナを供試植物とした。空気とトレーサガスの流出入を制御できる密閉容器を用いてC-11標識二酸化炭素を均一に投与する工夫を施した。植物体内を移動する炭素の動きを1時間連続で撮像し、得られた画像データを用いて数理的解析を行った。画像データ上に関心領域を設定し、各器官における炭素量の時間変化を解析し、炭素固定量及び転流率を定量した。さらに評価試験として、シンク部位における炭素栄養の需要量に差があると推察される、生育段階の異なる2つのシロイヌナズナの集団の転流率を定量し、本手法の有用性を示すことができた。今後は本手法を用いて、転流能が向上した形質転換体の系統を探索する予定である。
河地 有木; 小柳 淳*; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 尹 永根; 山崎 治明; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
光合成によって、葉で空気中の二酸化炭素から合成された炭素栄養は、根や果実といったシンク器官へと転流される。この炭素動態を解析することで、従来困難であった光合成機能の定量的な評価が可能であると示唆されてきた。そこで本研究では、ポジトロンイメージング技術を用いて、モデル植物であるシロイヌナズナ複数個体の体内の炭素の動きを、生育環境を妨害することなく同時に撮像し、光合成機能を定量することを目的とした。植物の成長に伴う光合成機能の個体差を抑え、またそれを統計的に処理するため、同一シャーレ内で栽培した18個体の幼少期シロイヌナズナを供試植物とした。空気とトレーサガスの流出入を制御できる密閉容器を用いてC-11標識二酸化炭素を均一に投与する工夫を施した。ポジトロンイメージング技術を用いて、植物体内を移動する炭素の動きを1時間撮像し、得られた画像データを用いて数理的な解析を行った。光合成機能に差があると推察される生育段階の異なる2つのシロイヌナズナの集団の炭素固定量と転流率を定量解析した結果、ともに生育段階が進んだ個体の方が向上していることがわかった。さらに、炭素固定量は葉身の新鮮重に比例して増加しており、この妥当な結果から本手法による高い信頼性を示すことができた。多数の幼少期シロイヌナズナの炭素固定と転流を同時に定量評価できる、ポジトロンイメージング技術を用いた手法の開発に成功した。
小柳 淳*; 河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 尹 永根; 山崎 治明*; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
ポジトロンイメージング技術を用いて、塩ストレスを与え、ソース葉に障害を受けた植物の光合成機能を定量し、シンク・ソースバランスを制御する機構を解明することを試みた。ナトリウム濃度が1, 5, 10, 20mMとなるように、塩化ナトリウムを添加した栄養培地を作製し、これら栄養培地で多数の野生型シロイヌナズナを20日間栽培した。植物にC-11標識二酸化炭素を投与し、植物体内を移動する炭素の動きを連続して撮像した。得られた画像データに対して数理的な解析を行い、各植物について炭素固定速度と転流率を算出した。その結果、炭素固定速度はナトリウム濃度10, 20mMの条件において低下した。一方、転流率はナトリウム濃度10mMの条件下で最大値を示し、20mMの条件下では顕著に低い値を示した。このことより、植物の炭素固定と転流において、塩ストレスに対する異なる感受性が示唆された。
鈴井 伸郎; 小柳 淳*; 河地 有木; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
Radiotracer imaging technologies allow us to know dynamic images of elements in living plants. In particular, a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS), which was specially designed for plant nutrition studies, has produced various imaging experiments for uptake and translocation of nutrition. In this study, we evaluated individual photosynthetic abilities of the small plant,  using
using  CO
CO tracer gas and PETIS. An agar plate including nine Arabidopsis plants (22 days after sown) was placed into an airtight cabinet, and approximately 40 MBq of
tracer gas and PETIS. An agar plate including nine Arabidopsis plants (22 days after sown) was placed into an airtight cabinet, and approximately 40 MBq of  CO
CO was introduced. The gas in the cabinet was flushed out after 10 minutes of contact, then the agar plate was mounted in the center of field of view of the imaging system, and a dynamic image of carbon distribution in the Arabidopsis plant was acquired for 1 hour. As a result, the average rate of carbon fixation in each Arabidopsis plant was estimated with only a few percent of coefficient of variance through a mathematical analysis. Furthermore, source and sink strength were successfully visualized by quantification of the increase or decrease rate of
was introduced. The gas in the cabinet was flushed out after 10 minutes of contact, then the agar plate was mounted in the center of field of view of the imaging system, and a dynamic image of carbon distribution in the Arabidopsis plant was acquired for 1 hour. As a result, the average rate of carbon fixation in each Arabidopsis plant was estimated with only a few percent of coefficient of variance through a mathematical analysis. Furthermore, source and sink strength were successfully visualized by quantification of the increase or decrease rate of  C-labeled compounds in each pixel of the dynamic image.
C-labeled compounds in each pixel of the dynamic image.
河地 有木; 小柳 淳*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
RIイメージング技術を用いた植物研究において、得られた動画像から生理機能値を解析し、これを統計的に評価することが重要である。そこで、ポジトロンイメージング技術を用いて、多数の幼植物個体の光合成機能を一括して定量解析する方法を開発した。本手法の有用性を示すため、個体生長と環境ストレスが炭素固定と光合成産物の転流に及ぼす影響の定量評価を試みた。代表的モデル植物であるシロイヌナズナの幼少期における光合成機能を定量するため、栽培したシャーレ内の生育環境を維持したまま、製造したC-11標識二酸化炭素トレーサガスを一様濃度で投与する実験装置を製作し、複数個体に対する炭素動態のイメージング実験を行った。塩化ナトリウムを添加した培地で栽培した個体を用いた実験で得られた画像データに対して動態解析と統計処理を行った結果、幼少期シロイヌナズナにおいて環境ストレスが光合成機能に及ぼす影響を、定量値として示すことができた。具体的には、寒天培地の塩化ナトリウム濃度に対する光合成機能の変化を定量した。この結果は、RIイメージング技術が植物の生理を統計的に解析・評価できること表しており、本手法の有用性を示している。
河地 有木; 小柳 淳*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
Using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS), we have been developing quantitative methods for analyzing the kinetics of carbon fixation and translocation within plants. In this study, our idea is to apply PETIS methods for a large number of Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings grown on petri dishes to minimize individual differences.  CO
CO must be administered uniformly to the plants on the petri dishes in a specially designed chamber to realize reliable estimation of carbon fixation rates from the PETIS image. Mathematical analysis of the image data must be established which can quantitate both carbon fixation rate from the amount of fixed
must be administered uniformly to the plants on the petri dishes in a specially designed chamber to realize reliable estimation of carbon fixation rates from the PETIS image. Mathematical analysis of the image data must be established which can quantitate both carbon fixation rate from the amount of fixed  C in each plant body, and translocation rate from the local decrease / increase of
C in each plant body, and translocation rate from the local decrease / increase of  C within it. The estimated parameters of fixation and translocation for the respective plants will be integrated and analyzed statistically. We applied the method to evaluation of the separate impact of salt stress on carbon fixation and translocation, and different susceptibility was suggested.
C within it. The estimated parameters of fixation and translocation for the respective plants will be integrated and analyzed statistically. We applied the method to evaluation of the separate impact of salt stress on carbon fixation and translocation, and different susceptibility was suggested.
藤巻 秀; 小柳 淳*; 河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 島田 浩章*
no journal, ,
Positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)と CO
CO を用いて、シロイヌナズナの幼少個体における光合成関連能力の定量的解析を行う系を開発した。固形培地プレートに一枚あたり9個体のシロイヌナズナを16日間あるいは20日間栽培したものを、専用に設計した照明付き気密キャビネット内に置き、約40MBqの
を用いて、シロイヌナズナの幼少個体における光合成関連能力の定量的解析を行う系を開発した。固形培地プレートに一枚あたり9個体のシロイヌナズナを16日間あるいは20日間栽培したものを、専用に設計した照明付き気密キャビネット内に置き、約40MBqの CO
CO を含む通常空気を導入した。10分間の投与の後、ガスを追い出し、取り出したプレートを人工気象器内に設置されたPETISにより計測して、植物体における
を含む通常空気を導入した。10分間の投与の後、ガスを追い出し、取り出したプレートを人工気象器内に設置されたPETISにより計測して、植物体における Cの分布の変化を1時間にわたり追跡して画像化した。動画像データの解析の結果、各個体のソース器官における炭素固定量とシンク器官への転流率を算出することに成功した。さらに、動画像データの画素毎に
Cの分布の変化を1時間にわたり追跡して画像化した。動画像データの解析の結果、各個体のソース器官における炭素固定量とシンク器官への転流率を算出することに成功した。さらに、動画像データの画素毎に Cの増減を定量することにより、ソース能とシンク能の植物体内における分布を「機能画像」として表せることも示した。この新しい手法は、特定の遺伝的改変や薬剤処理等が炭素固定と光合成産物の分配に及ぼす影響を定量的に解析するのに有効なものであると考えられる。
Cの増減を定量することにより、ソース能とシンク能の植物体内における分布を「機能画像」として表せることも示した。この新しい手法は、特定の遺伝的改変や薬剤処理等が炭素固定と光合成産物の分配に及ぼす影響を定量的に解析するのに有効なものであると考えられる。
 施用効果の評価; ポジトロンイメージング技術を用いた炭素栄養の動態解析
施用効果の評価; ポジトロンイメージング技術を用いた炭素栄養の動態解析鈴井 伸郎; 山崎 治明*; 尹 永根; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
炭素栄養の転流率の増加は果実収量の向上に直結するため、温室や植物工場などの閉鎖環境におけるトマト栽培では、転流率を増加させるための様々な条件検討がなされている。特にCO 施用濃度の最適化は転流率の増加に最も効果的であると言えるが、CO
施用濃度の最適化は転流率の増加に最も効果的であると言えるが、CO 濃度に対する転流率の応答を正確に評価することは技術的に困難であった。そこで本研究では、炭素11(半減期:20分)で標識したCO
濃度に対する転流率の応答を正確に評価することは技術的に困難であった。そこで本研究では、炭素11(半減期:20分)で標識したCO (
( CO
CO )とポジトロンイメージング技術を用いて、トマトの同一個体における異なるCO
)とポジトロンイメージング技術を用いて、トマトの同一個体における異なるCO 濃度での炭素動態をそれぞれ可視化し、CO
濃度での炭素動態をそれぞれ可視化し、CO 濃度の上昇に対する炭素の固定量と転流率の応答を解析した。まず、異なるCO
濃度の上昇に対する炭素の固定量と転流率の応答を解析した。まず、異なるCO 濃度の環境下でトマト(Micro-Tom)に
濃度の環境下でトマト(Micro-Tom)に CO
CO をパルス投与する実験システムを開発した。本実験システムを用いて、400, 1,500, 3,000ppmのCO
をパルス投与する実験システムを開発した。本実験システムを用いて、400, 1,500, 3,000ppmのCO 濃度の環境に曝されたトマトにおける
濃度の環境に曝されたトマトにおける C-光合成産物の動態画像を取得した。3段階のCO
C-光合成産物の動態画像を取得した。3段階のCO 濃度の環境に曝された6個体のトマトにおける動態画像を解析したところ、炭素固定量はCO
濃度の環境に曝された6個体のトマトにおける動態画像を解析したところ、炭素固定量はCO 濃度の上昇と共に単調に増加していたが、果実への炭素移行量は1,500ppmで飽和に達していた。果実への転流率(移行量/固定量)については、個体間で大きなばらつきが見られたものの、CO
濃度の上昇と共に単調に増加していたが、果実への炭素移行量は1,500ppmで飽和に達していた。果実への転流率(移行量/固定量)については、個体間で大きなばらつきが見られたものの、CO 濃度の上昇に伴って減少する傾向が認められた。
濃度の上昇に伴って減少する傾向が認められた。
 濃度環境によるシロイヌナズナの物質貯蔵関連遺伝子変異体への影響の解析
濃度環境によるシロイヌナズナの物質貯蔵関連遺伝子変異体への影響の解析石井 陽平*; 鈴井 伸郎; 河地 有木; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 栗田 圭輔; 藤巻 秀; 草野 博彰*; 島田 浩章*
no journal, ,
人間が食物として収穫する果実や根が同化産物を貯蔵する能力はシンク能力と呼ばれ、葉などが光合成を行う能力であるソース能力と対比して考えられている。ソース能力については生育との関係が多く研究されており、例えば、高CO 環境下では光合成が促進され生育速度が上がることが分かっている。一方、シンク能力については生育との関係があまり研究されていない。そこで本研究ではシンク能力に関係する遺伝子の変異株を高CO
環境下では光合成が促進され生育速度が上がることが分かっている。一方、シンク能力については生育との関係があまり研究されていない。そこで本研究ではシンク能力に関係する遺伝子の変異株を高CO 環境において生育させ、シンク能力と生育との関係に高CO
環境において生育させ、シンク能力と生育との関係に高CO が及ぼす影響を調べた。その結果、いくつかの変異株が野生型とは異なる生育を示したが、その差異はCO
が及ぼす影響を調べた。その結果、いくつかの変異株が野生型とは異なる生育を示したが、その差異はCO の濃度によって変化していた。よって、シンク能力と生育の相互関係の変化には、意外にも、外部のCO
の濃度によって変化していた。よって、シンク能力と生育の相互関係の変化には、意外にも、外部のCO 濃度が影響を及ぼすことが分かった。今後は高CO
濃度が影響を及ぼすことが分かった。今後は高CO におけるソース器官とシンク器官の関係を調べるために、PETISを用いて光合成によって生産される同化産物の動きを見く予定である。
におけるソース器官とシンク器官の関係を調べるために、PETISを用いて光合成によって生産される同化産物の動きを見く予定である。
河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 尹 永根; 栗田 圭輔; 石井 陽平*; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
放射線計測技術は、生命科学研究における一つの優れた分析技術である。これを用いた生体の生理機能を解析する様々な実験方法が生み出され、植物研究の分野において数多くの成果が生み出されてきた。特に、放射性同位元素を用いて、栄養元素もしくは環境汚染物質が植物体内を移行していく動きを追跡し、その動態を解明する技術は、現在も日々大きな進化を見せている。植物の吸収・移行・蓄積といった多様な物質動態が、様々な外的要因から受ける影響を明らかにすることが、農学上の植物研究の一つの目標となっている。この目標を達成できる強力なツールが放射線イメージング技術である。原子力機構で開発されてきた、「RIを生きた植物体に投与し、そのRIの分布と動きを、放射線計測技術を駆使して可視化する」というコンセプトを実現させた様々な放射線イメージング技術とその応用研究を本発表で紹介する。それぞれの測定原理を概説し、植物研究を目的とした放射線イメージング技術の今後のあるべき姿を展望したい。
石井 里美; 山崎 治明*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 河地 有木; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
トマトの生産性の向上のためには、温室等で栽培環境を制御し、炭素栄養の転流率を増加させる必要がある。このために、高濃度のCO を施用する方法が用いられているが、二酸化炭素濃度に対する転流率の応答を定量的に評価することは技術的に困難であった。そこで、本研究では、炭素11(半減期: 20分)で標識した二酸化炭素とポジトロンイメージング技術を用いて、同一個体のトマトにおける異なる二酸化炭素濃度での炭素動態を可視化し、二酸化炭素濃度の上昇に対する炭素の固定量と転流率の応答を解析した。
を施用する方法が用いられているが、二酸化炭素濃度に対する転流率の応答を定量的に評価することは技術的に困難であった。そこで、本研究では、炭素11(半減期: 20分)で標識した二酸化炭素とポジトロンイメージング技術を用いて、同一個体のトマトにおける異なる二酸化炭素濃度での炭素動態を可視化し、二酸化炭素濃度の上昇に対する炭素の固定量と転流率の応答を解析した。
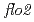 mutant of Arabidopsis using
mutant of Arabidopsis using  CO
CO and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)
and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)石井 陽平*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 栗田 圭輔; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
The gene 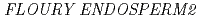 (
(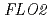 ) is widely distributed in plants. The
) is widely distributed in plants. The 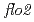 mutant of rice is known to have decreased expression of genes involved in production of storage starch. In this study, we analyzed the phenotype of
mutant of rice is known to have decreased expression of genes involved in production of storage starch. In this study, we analyzed the phenotype of 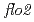 mutation in Arabidopsis from the aspect of carbon movement. 20 individuals each of
mutation in Arabidopsis from the aspect of carbon movement. 20 individuals each of 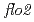 and WT (Col-0) were grown for 21 days. Starch accumulation in the whole plant of
and WT (Col-0) were grown for 21 days. Starch accumulation in the whole plant of 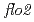 mutants was lower than WT. In contrast, the leaf areas and the fresh weights of
mutants was lower than WT. In contrast, the leaf areas and the fresh weights of 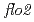 were larger and heavier than those of WT. We evaluated activity of carbon assimilation and source-to-sink translocation in
were larger and heavier than those of WT. We evaluated activity of carbon assimilation and source-to-sink translocation in 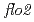 and WT using
and WT using  CO
CO tracer gas and PETIS, a noninvasive imaging system of radiotracers. As a result, the activity of carbon assimilation per leaf weight did not show difference between
tracer gas and PETIS, a noninvasive imaging system of radiotracers. As a result, the activity of carbon assimilation per leaf weight did not show difference between 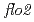 and WT; however, the carbon translocation rate from the leaves to sink tissues was lower in
and WT; however, the carbon translocation rate from the leaves to sink tissues was lower in 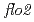 than in WT. These results imply the following mechanisms. Biosynthesis of starch in both of the source and sink tissues is decreased by
than in WT. These results imply the following mechanisms. Biosynthesis of starch in both of the source and sink tissues is decreased by 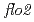 mutation. Sucrose accumulation in the sink tissue reduces the source-to-sink translocation. Excess sucrose in the source tissue causes the leaf expansion.
mutation. Sucrose accumulation in the sink tissue reduces the source-to-sink translocation. Excess sucrose in the source tissue causes the leaf expansion.