Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
片岡 隆浩*; 直江 翔太*; 村上 海斗*; 雪峰 諒平*; 藤本 有希*; 神崎 訓枝; 迫田 晃弘; 光延 文裕*; 山岡 聖典*
Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 70(2), p.154 - 159, 2022/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:57.52(Nutrition & Dietetics)Radon therapy has been reported to be effective in the management of rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease caused by immune cell imbalance. Although there are several reports that suggest that radon therapy induces Th17 cells, there are no studies on the effects of radon inhalation on Th1, Th2, and Th17 immune balance. The aim of this study, therefore, was to examine the changes in cytokine levels after radon inhalation. BALB/c mice were subjected to radon inhalation at a concentration of 2000 Bq/m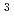 for 2 or 4 weeks, whereas SKG/Jcl mice were subjected to radon inhalation at a concentration of 2000 Bq/m
for 2 or 4 weeks, whereas SKG/Jcl mice were subjected to radon inhalation at a concentration of 2000 Bq/m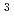 for 4 weeks after zymosan administration. For example, the results showed that radon inhalation for 4 weeks not only activated Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells but also modulated immune balance. This suggests that radon inhalation has different mechanisms of action in SKG/Jcl mice and normal BABL/c mice and that radon inhalation has immunomodulatory effects.
for 4 weeks after zymosan administration. For example, the results showed that radon inhalation for 4 weeks not only activated Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells but also modulated immune balance. This suggests that radon inhalation has different mechanisms of action in SKG/Jcl mice and normal BABL/c mice and that radon inhalation has immunomodulatory effects.