Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
和田 有希*; Bowers, G. S.*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 鴨川 仁*; 中村 佳敬*; 森本 健志*; Smith, D.*; 古田 禄大*; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 45(11), p.5700 - 5707, 2018/06
被引用回数:31 パーセンタイル:81.84(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)An on-ground observation program for high energy atmospheric phenomena in winter thunderstorms along Japan Sea has been performed via lightning measurements of  -ray radiation, atmospheric electric field and low-frequency radio band. On February 11, 2017, the radiation detectors recorded
-ray radiation, atmospheric electric field and low-frequency radio band. On February 11, 2017, the radiation detectors recorded  -ray emission lasting for 75 sec. The
-ray emission lasting for 75 sec. The  -ray spectrum extended up to 20 MeV and was reproduced by a cutoff power-law model with a photon index of 1.36
-ray spectrum extended up to 20 MeV and was reproduced by a cutoff power-law model with a photon index of 1.36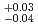 , being consistent with a Bremsstrahlung radiation from a thundercloud (as known as a
, being consistent with a Bremsstrahlung radiation from a thundercloud (as known as a  -ray glow). Then the
-ray glow). Then the  -ray glow was abruptly terminated with a nearby lightning discharge. The low-frequency radio monitors, installed
-ray glow was abruptly terminated with a nearby lightning discharge. The low-frequency radio monitors, installed  50 km away from Noto School, recorded intra/inter-cloud discharges spreading over
50 km away from Noto School, recorded intra/inter-cloud discharges spreading over  60km area with a
60km area with a  300 ms duration. The timing of the
300 ms duration. The timing of the  -ray termination coincided with the moment when a sequence of intra/inter-cloud discharges passed 0.7 km horizontally away from the radiation monitors. The atmospheric electric-field measurement presented that negative charge was located in the cloud base and not neutralized by the lightning discharge. This indicates that the
-ray termination coincided with the moment when a sequence of intra/inter-cloud discharges passed 0.7 km horizontally away from the radiation monitors. The atmospheric electric-field measurement presented that negative charge was located in the cloud base and not neutralized by the lightning discharge. This indicates that the  -ray source was located at an higher region than the cloud base.
-ray source was located at an higher region than the cloud base.
 中炭素成分の
中炭素成分の C分析
C分析山田 怜奈*; 池盛 文数*; 中村 俊夫*; 南 雅代*; 渡邊 隆広; 木ノ内 健人*; 松木 篤*
no journal, ,
炭素はエアロゾル粒子中の主な成分の一つであるが、その種類は多種多様であり、化学種を特定し、起源を推定することが困難とされる。しかし、 Cを用いることで、それらの発生源を推測することができる。
Cを用いることで、それらの発生源を推測することができる。 Cの半減期は5730年であり、化石燃料中には存在しない。このため
Cの半減期は5730年であり、化石燃料中には存在しない。このため C測定を行うことで化石燃料の寄与率を推定することができる。我々は能登半島の先端で、他の地域から長距離輸送された化石燃料由来物質、および自然環境やバイオマス燃料から排出された物質の寄与率を調べるため、能登半島でエアロゾル粒子を採集し、
C測定を行うことで化石燃料の寄与率を推定することができる。我々は能登半島の先端で、他の地域から長距離輸送された化石燃料由来物質、および自然環境やバイオマス燃料から排出された物質の寄与率を調べるため、能登半島でエアロゾル粒子を採集し、 C測定を行った。能登半島におけるPM
C測定を行った。能登半島におけるPM の放射性炭素濃度は、全ての試料で70pMC以上を示した。この結果は、中部日本遠隔地域のエアロゾルに含まれる炭素成分では、化石燃料由来の物質の寄与が小さく、相対的に現代の生物活動、もしくは人為的なバイオマス燃焼由来の物質の寄与が大きいことを示している。
の放射性炭素濃度は、全ての試料で70pMC以上を示した。この結果は、中部日本遠隔地域のエアロゾルに含まれる炭素成分では、化石燃料由来の物質の寄与が小さく、相対的に現代の生物活動、もしくは人為的なバイオマス燃焼由来の物質の寄与が大きいことを示している。
 at NOTO peninsula using
at NOTO peninsula using  C analysis
C analysis山田 怜奈*; 池盛 文数*; 中村 俊夫*; 南 雅代*; 渡邊 隆広; 木ノ内 健人*; 松木 篤*
no journal, ,
環境変動のメカニズムを理解するためにエアロゾル粒子中の主な成分の一つである炭素の寄与率と供給源を明らかにすることが必要である。著者らの最近の研究により、能登半島における微小なエアロゾル粒子には炭素成分がおおよそ50%以上含まれていることが明らかになっている。エアロゾル粒子に含まれる炭素成分は多様であり、それらの化学形態と供給源を推定することは困難であった。そこで、本研究では放射性・安定炭素同位体比を用いて、エアロゾル粒子中の炭素成分の分析を行った。能登半島の先端にある大気観測拠点(NOTOGRO)において、2014年6月26日から7月26日まで一週間ごとにPM ハイボリュームエアサンプラーを用いてエアロゾル粒子を採取し、炭素同位体比測定を行った。
ハイボリュームエアサンプラーを用いてエアロゾル粒子を採取し、炭素同位体比測定を行った。 C濃度測定は名古屋大学のタンデトロン加速器質量分析計、
C濃度測定は名古屋大学のタンデトロン加速器質量分析計、
 C測定には安定同位体比質量分析計を用いた。採取した4試料の放射性炭素濃度はそれぞれ約70pMC(パーセントモダンカーボン)であった。これらの結果は、化石燃料由来の物質のみではなく、現代の植物の影響や人為的なバイオマス燃焼由来物質の寄与が相対的に大きいことを示す。
C測定には安定同位体比質量分析計を用いた。採取した4試料の放射性炭素濃度はそれぞれ約70pMC(パーセントモダンカーボン)であった。これらの結果は、化石燃料由来の物質のみではなく、現代の植物の影響や人為的なバイオマス燃焼由来物質の寄与が相対的に大きいことを示す。