Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
粟飯原 はるか; 渡部 創; 柴田 淳広; Mahardiani, L.*; 大友 亮一*; 神谷 裕一*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 139, p.103872_1 - 103872_9, 2021/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:31.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)To prevent unexpected accidents at nuclear facilities caused by accumulated ammonium nitrate in an aqueous liquid waste containing ammonium salts and nitric acid, NH 
 in the liquid waste must be decomposed under mild reaction conditions. In this study, we investigated the oxidative decomposition of NH
in the liquid waste must be decomposed under mild reaction conditions. In this study, we investigated the oxidative decomposition of NH 
 with O
with O at 333 K in the presence of a homogeneous Co
at 333 K in the presence of a homogeneous Co catalyst and Cl
catalyst and Cl in the wide pH range of the test solution. The reaction behavior was greatly affected by pH of the test solution. In a basic solution at pH 12, high conversion of NH
in the wide pH range of the test solution. The reaction behavior was greatly affected by pH of the test solution. In a basic solution at pH 12, high conversion of NH 
 was obtained even in the absence of Co
was obtained even in the absence of Co and Cl
and Cl and the main product was NO
and the main product was NO 
 . However, Co
. However, Co and Cl
and Cl in the solution greatly enhanced the decomposition rate of NH
in the solution greatly enhanced the decomposition rate of NH 
 in acidic to mild basic solutions (pH 1-8), while only low conversion of NH
in acidic to mild basic solutions (pH 1-8), while only low conversion of NH 
 was observed unless both Co
was observed unless both Co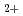 and Cl
and Cl were present. For the reaction with Co
were present. For the reaction with Co and Cl
and Cl in the solutions, NH
in the solutions, NH
 was transformed mainly into chloramines (NH
was transformed mainly into chloramines (NH  Cl
Cl  , x = 1-3) by the reaction with HClO, which was formed by the reaction of Cl
, x = 1-3) by the reaction with HClO, which was formed by the reaction of Cl with O
with O catalyzed by the homogeneous Co
catalyzed by the homogeneous Co catalyst, and led to the high decomposition rate of NH
catalyst, and led to the high decomposition rate of NH
 . Cl
. Cl suppressed the formation of the precipitate CoO(OH) during the reaction and consequently the Co
suppressed the formation of the precipitate CoO(OH) during the reaction and consequently the Co catalyst stably existed in the reaction solution, which was another reason for the high decomposition rate of NH
catalyst stably existed in the reaction solution, which was another reason for the high decomposition rate of NH
 in the presence of Cl
in the presence of Cl . Owing to the swift decomposition of NH
. Owing to the swift decomposition of NH
 under mild reaction conditions and small formation of secondary waste, the oxidative decomposition of NH
under mild reaction conditions and small formation of secondary waste, the oxidative decomposition of NH
 in the presence of the homogeneous Co
in the presence of the homogeneous Co catalyst and Cl
catalyst and Cl is suitable and applicable for the treatment of the aqueous liquid waste containing ammonium salts and nitric acid.
is suitable and applicable for the treatment of the aqueous liquid waste containing ammonium salts and nitric acid.
渡部 創; 小木 浩通*; 荒井 陽一; 粟飯原 はるか; 高畠 容子; 柴田 淳広; 野村 和則; 神谷 裕一*; 浅沼 徳子*; 松浦 治明*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 117, p.103090_1 - 103090_8, 2019/11
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:77.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new collaborative research project for systematic treatments of radioactive liquid wastes containing various reagents generating in nuclear facilities was started from 2018 initiated by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The project was named as STRAD (Systematic Treatments of RAdioactive liquid wastes for Decommissioning) project. Tentative targets to be studied under the project are aqueous and organic liquid wastes which have been generated by experiments and analyses in a reprocessing experimental laboratory of JAEA. Currently fundamental studies for treatments of the liquid wastes with complicated compositions are underway. In the STRAD project, process flow for treatment of ammonium ion involved in aqueous waste was designed though the inactive experiments, and decomposition of ammonium ion using catalysis will be carried out soon. Adsorbents for recovery of U and Pu from spent solvent were also developed. Demonstration experiments on genuine spent solvent is under planning.
 baking method for degassing of a kicker magnet in accelerator beam line
baking method for degassing of a kicker magnet in accelerator beam line神谷 潤一郎; 荻原 徳男; 柳橋 亨*; 金正 倫計; 安田 裕一*
Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology A, 34(2), p.021604_1 - 021604_10, 2016/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:14.94(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)J-PARC RCSビーム出射用キッカー電磁石の脱ガスを加速器のビームライン上で、すなわち で行うため手法を開発した。その手法とはヒーターと熱輻射遮蔽板をキッカー電磁石と真空容器間に設置し、熱束の多くをキッカー電磁石へ向けることで、真空容器の熱膨張を発生させずにキッカー電磁石を昇温、脱ガスする手法である。フェライトを120
で行うため手法を開発した。その手法とはヒーターと熱輻射遮蔽板をキッカー電磁石と真空容器間に設置し、熱束の多くをキッカー電磁石へ向けることで、真空容器の熱膨張を発生させずにキッカー電磁石を昇温、脱ガスする手法である。フェライトを120 C以上へ昇温すること、及び真空容器の温度上昇を30
C以上へ昇温すること、及び真空容器の温度上昇を30 C以下へ抑えることを目標としてヒーター導入式の脱ガス手法の開発を行った。まず、原理実験を行い、本手法で真空内のキッカー電磁石を昇温できることを確認した。その後、実機への適応を見据え、ヒーターの選択、昇温試験を行い良好な結果を得た。
C以下へ抑えることを目標としてヒーター導入式の脱ガス手法の開発を行った。まず、原理実験を行い、本手法で真空内のキッカー電磁石を昇温できることを確認した。その後、実機への適応を見据え、ヒーターの選択、昇温試験を行い良好な結果を得た。
横田 渉; 佐藤 隆博; 神谷 富裕; 奥村 進; 倉島 俊; 宮脇 信正; 柏木 啓次; 吉田 健一; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2014-018, 103 Pages, 2014/09
日本原子力研究開発機構高崎量子応用研究所のイオン照射研究施設(TIARA)では、イオンビームを利用する主要な研究課題である生物細胞放射線影響評価研究と宇宙用半導体耐放射線性評価研究を推進するため、TIARAのサイクロトロンで加速した数百MeV重イオンビームを磁気レンズで集束させて直径1 m以下のマイクロビームに形成する技術を世界で初めて実現した。更に、これを用いて1個のイオンをビーム径の空間精度で照準するシングルイオンヒットを可能にした。この過程で、TIARAの静電加速器で完成した数MeVイオンのマイクロビーム形成・シングルイオンヒット技術を活かしたビーム集束装置、ビーム照準・計測技術や、1
m以下のマイクロビームに形成する技術を世界で初めて実現した。更に、これを用いて1個のイオンをビーム径の空間精度で照準するシングルイオンヒットを可能にした。この過程で、TIARAの静電加速器で完成した数MeVイオンのマイクロビーム形成・シングルイオンヒット技術を活かしたビーム集束装置、ビーム照準・計測技術や、1 mへの集束に必要なエネルギー幅の狭い数百MeV重イオンビームを加速するためのサイクロトロンに特有な技術を開発した。また、開発途中に利用研究の実験に試用することにより、本技術の適用性を適宜評価しその改良を行うことで、利用研究の試用実験を軌道に乗せることができた。本報告書は、およそ10年に亘るこれらの技術・装置開発の過程及び成果を、試用実験における評価とともにまとめたものである。
mへの集束に必要なエネルギー幅の狭い数百MeV重イオンビームを加速するためのサイクロトロンに特有な技術を開発した。また、開発途中に利用研究の実験に試用することにより、本技術の適用性を適宜評価しその改良を行うことで、利用研究の試用実験を軌道に乗せることができた。本報告書は、およそ10年に亘るこれらの技術・装置開発の過程及び成果を、試用実験における評価とともにまとめたものである。
舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 及川 将一*; 佐藤 隆博; 横田 裕一郎; 和田 成一*; 神谷 富裕; 横田 渉; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
原子力機構・高崎量子応用研究所・TIARAではAVFサイクロトロンの垂直ビームラインにコリメーション式マイクロビーム装置を設置し、バイスタンダー効果研究などで成果を挙げてきた。しかし、コリメーションによるマイクロビーム形成では、形成できるビームサイズに限界がある。現在のマイクロビーム利用研究では、細胞そのものに加え、細胞内小器官への放射線障害が細胞死に与える影響にも関心が高まっており、より径の小さいビームが求められている。そこで、磁気レンズによる集束式マイクロビーム装置を従来の装置とは異なるビームラインに新規に設置した。集束式ビームはサブミクロンのビームが形成可能でかつコリメーター周辺部による散乱がない。加えて、ビームスキャナでビームの高速なスキャンを行うことで、細胞への高速連続照射が実現可能になる。この集束式マイクロビーム装置を用いて、直径1 m以下のビームを真空中で形成することに成功した。形成したビームを大気中に取り出し、CR39を照射してビームの分布を測定したところ、大気中でも、従来のマイクロビーム装置よりも微細な5
m以下のビームを真空中で形成することに成功した。形成したビームを大気中に取り出し、CR39を照射してビームの分布を測定したところ、大気中でも、従来のマイクロビーム装置よりも微細な5 m径以下のビームを得ることができた。
m径以下のビームを得ることができた。
舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 佐藤 隆博; 深本 花菜; 倉島 俊; 横田 裕一郎; 横田 渉; 神谷 富裕; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
私たちは、原子力機構・高崎量子応用研究所・TIARAのAVFサイクロトロンにコリメーション式重イオンマイクロビームを設置し、これを用いることで、生物の重イオン照射効果研究を進めてきた。その一方で、コリメーション式マイクロビームでは実現できない照射を行うために、新たなビームラインに集束式重イオンマイクロビーム装置を設置し、それを用いた生物照射技術の開発を進めている。集束式重イオンマイクロビーム装置は、既存のコリメーション式マイクロビーム装置では不可避であったコリメータエッジでの散乱イオンの発生を回避することができるため、従来よりも微細なビームで細胞を正確に照射することができる。現在、昨年度までに設置された細胞照射用ステーションを用いて大気中で顕微鏡観察下の試料への照準照射技術の開発を進めている。また、従来から用いられてきたコリメーション式マイクロビームでも、コリメーション式マイクロビームの特徴である高フルエンス照射を活かした新たな照射を実現できるようにするための細胞照準照射系の新規設計とシステム更新を行うなどの改良を施した。
坂下 哲哉; 舟山 知夫; 佐藤 隆博; 浜田 信行*; 深本 花菜; 横田 裕一郎; 鈴木 芳代; 横田 渉; 神谷 富裕; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
日本原子力研究開発機構では、生物の特定組織の機能を解析するためのラジオサージャリ技術の開発、及びがん治療や長期宇宙飛行において重要な重粒子線被ばくの生物影響を明らかにすることを目的として、重イオンマイクロビーム細胞照射装置を開発してきた。本装置により、加速器を用いて得られる重イオンビームをマイクロビーム化し生体組織の微小領域に照射することが可能である。本発表では、重イオンマイクロビーム細胞照射装置の概要とそれを用いた生物学研究への適用例について紹介した。
粟飯原 はるか; 渡部 創; 野村 和則; 神谷 裕一*
no journal, ,
放射性廃液の処理手法を開発するSTRADプロジェクトの一環として、分析廃液の処理技術の開発を行っている。多様な成分を含む分析廃液中のアンモニウムの処理を目的として、蒸留等による分離と酸化分解を組み合わせた工程の開発に着手した。ここではコバルトイオンを均一系触媒として添加したオゾン酸化によって、アンモニウムイオンの分解ができることを確認した。試験液成分をパラメータとして振ることにより初期pHに依存して反応機構が異なり、pHの影響や塩化物イオンの反応への寄与が明らかとなった。本技術を適用することにより、固液分離等の必要のない簡便な操作でアンモニウムイオンが分解可能である。
粟飯原 はるか; 渡部 創; 野村 和則; 神谷 裕一*
no journal, ,
An effective decomposition method of ammonium ion in radioactive analytical waste solutions containing U, Pu and nitric acid has been developed to suppress formation of ammonium nitrate. Oxidative decomposition was examined using ozone gas with existence of cobalt ions as homogeneous catalyst. Reduction in concentration of ammonium ion was achieved by combination of the ozone gas oxidation with the catalyst, and the behavior distinctly depend on compositions of the initial solution.
渡部 創; 小木 浩通*; 荒井 陽一; 粟飯原 はるか; 柴田 淳広; 野村 和則; 神谷 裕一*; 浅沼 徳子*; 松浦 治明*; 久保田 俊夫*; et al.
no journal, ,
A new collaborative research project for systematic treatments of radioactive liquid wastes containing various reagents generating in nuclear facilities was started from 2018 initiated by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The project was named as STRAD (Systematic Treatments of RAdioactive liquid wastes for Decommissioning) project. Tentative targets to be studied under the project are aqueous and organic liquid wastes which have been generated by experiments and analyses in a reprocessing experimental laboratory of JAEA. Currently fundamental studies for treatments of the liquid wastes with complicated compositions are underway.
粟飯原 はるか; 渡部 創; 柴田 淳広; 神谷 裕一*
no journal, ,
Treatment of accumulated radioactive liquid waste in laboratories is urgent task not only for effective utilization of the research fields but also for safety management of the facilities. Since the liquid waste has to be treated inside shielded devices such as concrete cell or grove box due to its radioactivity, easy operations for the treatment are preferred to prevent any unexpected accidents during the treatment. Decomposition of ammonium ion under mild reaction conditions has been successfully achieved in the presence of Co O
O 4, which acts as a heterogeneous catalyst. We have demonstrated that cobalt(II) nitrate acted as a homogeneous catalyst for the reaction and chloride ion in water was indispensable for the catalyst to effective promote the reaction. In-situ XAFS were measured during blowing ozone. Conversion ratio of ammonium ion was significantly increased when both cobalt and chloride ions existed. Cobalt ion was keeping divalent, these ion assumed to produce OH radical to decompose ammonium ion.
4, which acts as a heterogeneous catalyst. We have demonstrated that cobalt(II) nitrate acted as a homogeneous catalyst for the reaction and chloride ion in water was indispensable for the catalyst to effective promote the reaction. In-situ XAFS were measured during blowing ozone. Conversion ratio of ammonium ion was significantly increased when both cobalt and chloride ions existed. Cobalt ion was keeping divalent, these ion assumed to produce OH radical to decompose ammonium ion.
 -HCO
-HCO H反応
H反応Wei, J.*; 山田 千波*; 粟飯原 はるか; 渡部 創; 大友 亮一*; 神谷 裕一*
no journal, ,
本研究では高濃度硝酸含有廃水の浄化を目指し、HCO Hとの反応でHNO
Hとの反応でHNO を分解するHNO
を分解するHNO -HCO
-HCO H反応に対する多孔性炭素の触媒作用を調べた。活性炭および多孔性炭素はHNO
H反応に対する多孔性炭素の触媒作用を調べた。活性炭および多孔性炭素はHNO -HCO
-HCO H反応の触媒として作用した。HNO
H反応の触媒として作用した。HNO に対して2等量のHCO
に対して2等量のHCO Hを添加し、触媒量の多孔性炭素存在下、90
Hを添加し、触媒量の多孔性炭素存在下、90 Cで反応したところ、反応開始から8時間で85%以上のHNO
Cで反応したところ、反応開始から8時間で85%以上のHNO が分解された。HNO
が分解された。HNO もしくはHCO
もしくはHCO H中で加熱処理した多孔性炭素のTPDの結果から、HNO
H中で加熱処理した多孔性炭素のTPDの結果から、HNO -HCO
-HCO H反応は酸化還元機構で進行すると推定された。
H反応は酸化還元機構で進行すると推定された。