Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scattering
-synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scattering藤原 悟; 荒木 克哉*; 松尾 龍人; 八木 寿梓*; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫; 望月 秀樹*
PLOS ONE (Internet), 11(4), p.e0151447_1 - e0151447_17, 2016/04
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:64.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Filamentous aggregates (amyloid fibrils) of the protein  -synuclein (
-synuclein ( -Syn) are related to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. To understand the pathogenesis mechanism of this disease, the mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation of
-Syn) are related to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. To understand the pathogenesis mechanism of this disease, the mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation of  -Syn must be elucidated. As a first step toward this ultimate goal, dynamical behavior of
-Syn must be elucidated. As a first step toward this ultimate goal, dynamical behavior of  -Syn in the monomeric and the fibril states was investigated using quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS). Analysis of the QENS spectra of solution samples of
-Syn in the monomeric and the fibril states was investigated using quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS). Analysis of the QENS spectra of solution samples of  -Syn shows that diffusive global motions are observed in the monomeric state but largely suppressed in the fibril state. However, the amplitude of the side chain motion is shown to be larger in the fibril state than in the monomeric state. This implies that significant solvent space exists within the fibrils, which is attributed to the
-Syn shows that diffusive global motions are observed in the monomeric state but largely suppressed in the fibril state. However, the amplitude of the side chain motion is shown to be larger in the fibril state than in the monomeric state. This implies that significant solvent space exists within the fibrils, which is attributed to the  -Syn molecules within the fibrils having a distribution of conformations. The larger amplitude of the side chain motion in the fibril state than in the monomeric state implies that the fibril state is entropically favorable.
-Syn molecules within the fibrils having a distribution of conformations. The larger amplitude of the side chain motion in the fibril state than in the monomeric state implies that the fibril state is entropically favorable.
山下 孝子*; 勝山 仁哉; 佐藤 馨*; 水野 正隆*; 荒木 秀樹*; 白井 泰治*
鉄と鋼, 97(11), p.558 - 565, 2011/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Fe-Cu合金の硬さは熱時効に伴うCu析出物により増加することが知られている。以前にわれわれは、引張や冷間圧延により予歪導入された格子欠陥が、硬さが増加する時効温度を低下させ、Cu析出を促進させることを報告した。しかしながら、その機構は明らかにされていない。そこで本研究では、陽電子寿命法及び同時計数ドップラー幅広がり法により、冷間圧延後熱時効を施したFe-Cu合金における空孔,空孔複合体,転位等の格子欠陥の回復挙動及び、Cu原子の拡散挙動を分析した。その結果、冷間圧延により導入された空孔及び転位の熱時効による回復挙動について、空孔は300 Cで完全に回復する一方、転位は550
Cで完全に回復する一方、転位は550 Cでも一部残ることがわかった。またCuクラスターは、空孔の回復とともに析出し始め、おもに空孔のシンクスとなる転位の周辺に析出することがわかった。
Cでも一部残ることがわかった。またCuクラスターは、空孔の回復とともに析出し始め、おもに空孔のシンクスとなる転位の周辺に析出することがわかった。
中村 一男*; Jiang, Y.*; Liu, X.*; 御手洗 修*; 栗原 研一; 川俣 陽一; 末岡 通治; 長谷川 真*; 徳永 和俊*; 図子 秀樹*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.1080 - 1084, 2011/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:32.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)CCS (Cauchy Condition Surface) method is a numerical approach to reproduce plasma shape, which has good precision in conventional tokamak. In order to apply it in plasma shape reproduction of ST (Spherical Tokamak), the calculation precision of the CCS method in CPD (
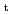 = 0.25 T,
= 0.25 T,  = 0.3 m,
= 0.3 m,  = 0.2 m) has been analyzed. The precision was confirmed also in ST and decided to be applied to QUEST (
= 0.2 m) has been analyzed. The precision was confirmed also in ST and decided to be applied to QUEST (
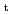 = 0.25 T,
= 0.25 T,  = 0.68 m,
= 0.68 m,  = 0.40 m). In present stage from the magnetic measurement, it is known that the eddy current effect is large in QUEST experiment, and there are no special magnetic measurements for eddy current now, so some proper model should be selected to evaluate the eddy current effect. The eddy current density by not only CS (Center Solenoid) coil but also plasma current is calculated using EDDYCAL (JAEA), the eddy currents are taken as unknown variables and solved together with plasma shape reconstruction. The result shows that the CCS method with eddy current adjustment achieves stable, accurate reconstruction of plasma shape in application to QUEST.
= 0.40 m). In present stage from the magnetic measurement, it is known that the eddy current effect is large in QUEST experiment, and there are no special magnetic measurements for eddy current now, so some proper model should be selected to evaluate the eddy current effect. The eddy current density by not only CS (Center Solenoid) coil but also plasma current is calculated using EDDYCAL (JAEA), the eddy currents are taken as unknown variables and solved together with plasma shape reconstruction. The result shows that the CCS method with eddy current adjustment achieves stable, accurate reconstruction of plasma shape in application to QUEST.
勝山 仁哉; 山野 裕子*; 山下 孝子*; 水野 正隆*; 荒木 秀樹*; 白井 泰治*
no journal, ,
圧力容器鋼の硬化や脆性に影響すると考えられるCu析出への予歪み効果について、陽電子寿命法,同時計数ドップラー幅拡がり(CDB)法及びビッカース硬さ測定により評価検討を行った。Fe-1.5mass%Cu合金に830 C、10分の溶体化処理を施し、その後冷間圧延により30%, 50%, 70%の予歪みを付加した試料を作製した。焼鈍温度200
C、10分の溶体化処理を施し、その後冷間圧延により30%, 50%, 70%の予歪みを付加した試料を作製した。焼鈍温度200 C
C 600
600 C(焼鈍時間15分)で等時焼鈍を行いつつ、室温下で陽電子寿命, CDB及びビッカース硬さを測定した。その結果、予歪みを付加すると転位がCu析出物の核生成サイトとなり、予歪付加直後からCu析出物により硬化することがわかった。その後の焼鈍過程では、予歪みにより導入された空孔クラスターが200
C(焼鈍時間15分)で等時焼鈍を行いつつ、室温下で陽電子寿命, CDB及びビッカース硬さを測定した。その結果、予歪みを付加すると転位がCu析出物の核生成サイトとなり、予歪付加直後からCu析出物により硬化することがわかった。その後の焼鈍過程では、予歪みにより導入された空孔クラスターが200 C近傍で移動・回復することによりCu原子が拡散し、Cu析出物が成長するため、合金はさらに硬化する。500
C近傍で移動・回復することによりCu原子が拡散し、Cu析出物が成長するため、合金はさらに硬化する。500 C以上の温度では熱平衡空孔が導入され、それらの移動により予歪を付加しない合金でも硬化することが明らかとなった。
C以上の温度では熱平衡空孔が導入され、それらの移動により予歪を付加しない合金でも硬化することが明らかとなった。
中村 一男*; Yi, J.*; Liu, X.*; 御手洗 修*; 栗原 研一; 川俣 陽一; 末岡 通治; 長谷川 真*; 徳永 和俊*; 図子 秀樹*; et al.
no journal, ,
JT-60で開発したプラズマ最外殻磁気面の同定法であるコーシー条件面(CCS)法は、真空場の解析解を基本とし、電磁気センサーの信号を用いて精度よくプラズマの断面形状を同定できる。このCCS法を九州大学の球状トカマク装置QUEST(Q-shu University Experiment with Steady-State Spherical Tokamak)のプラズマ断面形状再構成に適用し精度よく再構築できることを確認した。本発表では、球状トカマク装置QUESTにおけるプラズマ電流立上げや立下げ時の真空容器モデルに依存する渦電流分布の影響やコイル通電時の時定数の異なる渦電流の影響、さらに磁気プローブを設置した同定精度の向上など、これら一連の検討結果報告である。
Yi, J.*; 中村 一男*; Liu, X.*; 御手洗 修*; 栗原 研一; 川俣 陽一; 末岡 通治; 長谷川 真*; 徳永 和俊*; 図子 秀樹*; et al.
no journal, ,
JT-60で開発したプラズマ最外殻磁気面の同定法であるコーシー条件(CCS)法は真空場の解析解を基本とし、電磁気センサーの信号を用いて精度よくプラズマの断面形状を同定できる。このCCS法を九州大学の球状トカマク装置QEST(Q-shu University Experiment with Steady-State Spherical Tokamak)のプラズマ断面形状再構成に適用し精度よく再構築できることを確認した。本発表では、球状トカマク装置QUESTのプラズマ断面形状実時間再構成システムにおける、絶縁増幅器のオフセット電圧補正方法、プラズマ着火後のフィードバック制御によるプラズマ垂直位置不安定性の安定化、さらに一周電圧を用いた渦電流の解析など、これら一連の検討結果報告である。
 -synuclein and its relation to propensity for amyloid fibril formation
-synuclein and its relation to propensity for amyloid fibril formation藤原 悟; 荒木 克哉*; 松尾 龍人; 八木 寿梓*; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫; 望月 秀樹*
no journal, ,
A protein  -synuclein (
-synuclein ( -Syn), which is involved with pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease, forms amyloid fibrils. Propensity for amyloid fibril formation depends on environmental conditions such as pH. We employed neutron scattering to investigate the "dynamic" behavior of
-Syn), which is involved with pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease, forms amyloid fibrils. Propensity for amyloid fibril formation depends on environmental conditions such as pH. We employed neutron scattering to investigate the "dynamic" behavior of  -Syn at low and neutral pH, to investigate the relationship between the dynamics and propensity for amyloid fibril formation. We carried out the quasielastic neutron scattering experiments using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Analysis of the quasielasitc scattering spectra showed the increased flexibility of
-Syn at low and neutral pH, to investigate the relationship between the dynamics and propensity for amyloid fibril formation. We carried out the quasielastic neutron scattering experiments using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Analysis of the quasielasitc scattering spectra showed the increased flexibility of  -Syn at low pH. Since the increased flexibility is likely to arise from a wider distribution of conformational substates of
-Syn at low pH. Since the increased flexibility is likely to arise from a wider distribution of conformational substates of  -Syn, the results obtained suggest an entropy-driven mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation.
-Syn, the results obtained suggest an entropy-driven mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation.
 -synuclein; Implication for propensity for amyloid fibril formation
-synuclein; Implication for propensity for amyloid fibril formation藤原 悟; 荒木 克哉*; 松尾 龍人; 八木 寿梓*; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫; 望月 秀樹*
no journal, ,
A protein  -synuclein (
-synuclein ( -Syn) forms amyloid fibrils. This abnormal protein aggregation is related to pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease. Propensity for amyloid fibril formation depends on environmental conditions such as pH. We carried out quasielastic neutron scattering experiments to investigate the "dynamic" behavior of
-Syn) forms amyloid fibrils. This abnormal protein aggregation is related to pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease. Propensity for amyloid fibril formation depends on environmental conditions such as pH. We carried out quasielastic neutron scattering experiments to investigate the "dynamic" behavior of  -Syn to investigate the relationship between the dynamics and propensity for amyloid fibril formation. The measurements on the solution samples of
-Syn to investigate the relationship between the dynamics and propensity for amyloid fibril formation. The measurements on the solution samples of  -Syn in different pH were carried out using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Differences in flexibility of the protein were detected between the different conditions. Since the difference in flexibility is likely to arise from different distributions of conformational substates of
-Syn in different pH were carried out using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Differences in flexibility of the protein were detected between the different conditions. Since the difference in flexibility is likely to arise from different distributions of conformational substates of  -Syn, the results obtained suggest an entropy-driven mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation.
-Syn, the results obtained suggest an entropy-driven mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation.
 -synuclein detected by neutron scattering
-synuclein detected by neutron scattering藤原 悟; 荒木 克哉*; 松尾 龍人; 八木 寿梓*; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫; 望月 秀樹*
no journal, ,
The protein,  -synuclein (
-synuclein ( -Syn) forms amyloid fibrils. Formation of amyloid fibrils is associated with the pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease. In order to obtain insights into the role of the protein dynamics in the mechanism of amyloid fibril formation, we carried out quasielastic neutron scattering experiments and characterized the "dynamic" behavior of
-Syn) forms amyloid fibrils. Formation of amyloid fibrils is associated with the pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease. In order to obtain insights into the role of the protein dynamics in the mechanism of amyloid fibril formation, we carried out quasielastic neutron scattering experiments and characterized the "dynamic" behavior of  -Syn. The measurements on the solution samples of
-Syn. The measurements on the solution samples of  -Syn in the monomeric and fibril states were carried out using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Differences in the dynamical behavior of the protein were detected between the monomeric and fibril states. Analysis of the spectra obtained suggested an entropy-driven mechanism of amyloid fibril formation.
-Syn in the monomeric and fibril states were carried out using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Differences in the dynamical behavior of the protein were detected between the monomeric and fibril states. Analysis of the spectra obtained suggested an entropy-driven mechanism of amyloid fibril formation.