Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
田中 真悟*; 横田 秀晴; 大野 宏和; 中山 雅; 藤田 朝雄; 瀧谷 啓晃*; 渡辺 直子*; 小崎 完*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2015/05
In-situ dipole tracer migration tests were conducted at the G.L.-250 m gallery of the Horonobe URL. Laboratory experiments were also conducted to determine the apparent diffusivity (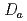 ) and sorption coefficients (
) and sorption coefficients (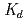 ) of cesium and water (HTO) in the rock taken at the gallery to evaluate the performance of Wakkanai formation as natural barrier. The breakthrough curves of non-sorbing tracer (Uranine) obtained at the in-situ dipole tracer migration tests were well described by a dual-channel model in which one-dimensional advection dispersion was taken in account. This suggests that the tracers migrate through at least two different pathways in the fracture. The breakthrough curves also indicated that the peak concentration of the sorbing tracer (cesium) was much smaller than that of the non-sorbing tracer (Uranine), suggesting that the Wakkanai Formation has a high sorptive and low diffusive properties for cesium. The
) of cesium and water (HTO) in the rock taken at the gallery to evaluate the performance of Wakkanai formation as natural barrier. The breakthrough curves of non-sorbing tracer (Uranine) obtained at the in-situ dipole tracer migration tests were well described by a dual-channel model in which one-dimensional advection dispersion was taken in account. This suggests that the tracers migrate through at least two different pathways in the fracture. The breakthrough curves also indicated that the peak concentration of the sorbing tracer (cesium) was much smaller than that of the non-sorbing tracer (Uranine), suggesting that the Wakkanai Formation has a high sorptive and low diffusive properties for cesium. The 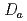 value obtained for cesium was about 3E-12 m
value obtained for cesium was about 3E-12 m /s, which is significantly smaller than that of water (3E-10 m
/s, which is significantly smaller than that of water (3E-10 m /s), and the
/s), and the 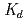 value of cesium was determined to be about 5E-2 ml/g.
value of cesium was determined to be about 5E-2 ml/g.
樋口 恭子*; 金井 雅武*; 土屋 将久*; 石井 春香*; 渋谷 尚史*; 藤田 直子*; 中村 保典*; 鈴井 伸郎; 藤巻 秀; 三輪 睿太郎*
Frontiers in Plant Science (Internet), 6, p.138_1 - 138_6, 2015/03
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:57.61(Plant Sciences)In a previous study, we reported that the common reed accumulates water-soluble Cd complexed with an  -glucan-like molecule, and that the synthesis of this molecule is induced in the stem of the common reed under Cd stress. We studied the metabolic background to ensure
-glucan-like molecule, and that the synthesis of this molecule is induced in the stem of the common reed under Cd stress. We studied the metabolic background to ensure  -glucan accumulation under the Cd stress conditions that generally inhibit photosynthesis. We found that the common reed maintained an adequate CO
-glucan accumulation under the Cd stress conditions that generally inhibit photosynthesis. We found that the common reed maintained an adequate CO assimilation rate, tended to allocate more assimilated
assimilation rate, tended to allocate more assimilated  C to the stem, and accumulated starch granules in its stem under Cd stress conditions. AGPase activity, which is the rate-limiting enzyme for starch synthesis, increased in the stem of common reed grown in the presence of Cd. Starch accumulation in the stem of common reed was not obvious under other excess metal conditions. Common reed may preferentially allocate assimilated carbon as the carbon source for the formation of Cd and
C to the stem, and accumulated starch granules in its stem under Cd stress conditions. AGPase activity, which is the rate-limiting enzyme for starch synthesis, increased in the stem of common reed grown in the presence of Cd. Starch accumulation in the stem of common reed was not obvious under other excess metal conditions. Common reed may preferentially allocate assimilated carbon as the carbon source for the formation of Cd and  -glucan complexes in its stem followed by prevention of Cd transfer to leaves acting as the photosynthetic organ. These responses may allow the common reed to grow even under severe Cd stress conditions.
-glucan complexes in its stem followed by prevention of Cd transfer to leaves acting as the photosynthetic organ. These responses may allow the common reed to grow even under severe Cd stress conditions.