Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
古株 弘樹*; Yoon, S.*; Lee, H.*; 中嶋 薫*; 松田 誠; 左高 正雄*; 辻本 将彦*; Toulemonde, M.*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 460, p.34 - 37, 2019/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)Gold and platinum nanoparticles of few-nm size were deposited on amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiN) films. These samples were irradiated with 380 MeV Au ions at grazing incident angles (
 =2
=2 -5
-5 ) to a fluence of ~1
) to a fluence of ~1 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . The irradiated samples were observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Ion tracks were clearly observed as long bright lines. Nanoparticles were found to be desorbed from long and narrow regions along the ion tracks. The surface temperature at the thermal spike produced by the ion impact was evaluated from the observed nanoparticle desorption. The observed temperature distribution is qualitatively explained by a one-dimensional two temperature model (1D-TTM) although there are some discrepancies which may be attributed to the surface effects which are not taken into account in 1D-TTM.
. The irradiated samples were observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Ion tracks were clearly observed as long bright lines. Nanoparticles were found to be desorbed from long and narrow regions along the ion tracks. The surface temperature at the thermal spike produced by the ion impact was evaluated from the observed nanoparticle desorption. The observed temperature distribution is qualitatively explained by a one-dimensional two temperature model (1D-TTM) although there are some discrepancies which may be attributed to the surface effects which are not taken into account in 1D-TTM.
松崎 勝太*; 林 宏明*; 中嶋 薫*; 松田 誠; 左高 正雄*; 辻本 将彦*; Toulemonde, M.*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 406(Part B), p.456 - 459, 2017/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:37.06(Instruments & Instrumentation)Few-nm sized gold, platinum and palladium nanoparticles were deposited on amorphous silicon nitride films. These films were irradiated with 420 MeV Au and 100 MeV Xe ions. Temperature distributions of thermal spikes produced by these ions were evaluated by observing desorption of the nanoparticles from the target surfaces upon ion impact. It was found that the temperature of the thermal spike produced by 420 MeV Au is higher than 100 MeV Xe. The observed temperature of the thermal spike at the entrance surface is slightly lower than that at the exit surface both for 420 MeV Au and 100 MeV Xe ions. These results can be well explained by the inelastic thermal spike model.
中嶋 薫*; 北山 巧*; 林 宏明*; 松田 誠; 左高 正雄*; 辻本 将彦*; Toulemonde, M.*; Bouffard, S.*; 木村 健二*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 5, p.13363_1 - 13363_8, 2015/08
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:41.15(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Irradiation of materials with either swift heavy ions or slow highly charged ions leads to ultrafast heating on a timescale of several picosecond in a region of several nanometer. This ultrafast local heating result in formation of nanostructures, which provide a number of potential applications in nanotechnologies. These nanostructures are believed to be formed when the local temperature rises beyond the melting or boiling point of the material. Conventional techniques, however, are not applicable to measure temperature in such a localized region in a short time period. Here, we propose a novel method for tracing temperature in a nanometer region in a picosecond time period by utilizing desorption of gold nanoparticles around the ion impact position. The feasibility is examined by comparing with the temperature evolution predicted by a theoretical model.
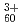 impacts
impacts北山 巧*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 松田 誠; 左高 正雄*; 辻本 将彦*; 磯田 正二*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 354, p.183 - 186, 2015/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:17.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)According to an inelastic-thermal-spike (i-TS) model, which is regarded as the most promising among several models proposed to explain the formation of an ion track, a part of the energy deposited to electrons in a solid by a swift heavy ion is gradually transferred to target atoms via electron-phonon coupling. The temperature of target atoms rises along the ion path and consequently an ion track is formed when the temperature exceeds the melting point. Therefore, the temperature of target atoms along the ion path is regarded as a key parameter for the i-TS model; however, such a spatiotemporally-localized temperature is difficult to measure because the processes involved occur in a very short period ( 10
10 s) and in a very localized area. In this study, the temperature of target atoms along the ion path is estimated experimentally with transmission-electron-microscope (TEM) observation of desorption of Au nanoclusters (the melting point
s) and in a very localized area. In this study, the temperature of target atoms along the ion path is estimated experimentally with transmission-electron-microscope (TEM) observation of desorption of Au nanoclusters (the melting point  1300 K) on an amorphous Si
1300 K) on an amorphous Si N
N thin film under 1.1-MeV C
thin film under 1.1-MeV C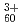 -ion irradiation to the fluence of
-ion irradiation to the fluence of  5
5 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . TEM images show that Au nanoclusters, deposited at the areal density of 1.16
. TEM images show that Au nanoclusters, deposited at the areal density of 1.16 10
10 particles/cm
particles/cm , disappear in a surface area with a diameter of
, disappear in a surface area with a diameter of  20 nm around each ion track, whose diameter is
20 nm around each ion track, whose diameter is  4 nm, after irradiation. This indicates that the temperature at the film surface rises locally to at least 1300 K by the ion bombardment.
4 nm, after irradiation. This indicates that the temperature at the film surface rises locally to at least 1300 K by the ion bombardment.

 ions observed using high-resolution Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy
ions observed using high-resolution Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy中嶋 薫*; 森田 陽亮*; 北山 巧*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 辻本 将彦*; 磯田 正二*; 藤居 義和*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 332, p.117 - 121, 2014/08
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:48.36(Instruments & Instrumentation)Our previous observation that an impact of sub-MeV C ion makes an ion track in a thin amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiN) film suggests emission of thousands of atoms from the cylindrical region. Sputtering yields of a-SiN films by C
ion makes an ion track in a thin amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiN) film suggests emission of thousands of atoms from the cylindrical region. Sputtering yields of a-SiN films by C ions were evaluated in order to confirm this observation. A-SiN films deposited on Si(001) were irradiated with 540-keV C
ions were evaluated in order to confirm this observation. A-SiN films deposited on Si(001) were irradiated with 540-keV C
 ions at fluences from 2.5
ions at fluences from 2.5 10
10 to 1
to 1 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . The compositional depth profiles of the irradiated samples were measured with high-resolution Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy, and the sputtering yields were estimated at 3900
. The compositional depth profiles of the irradiated samples were measured with high-resolution Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy, and the sputtering yields were estimated at 3900  500 N atoms/ion and 1500
500 N atoms/ion and 1500  1000 Si atoms/ion. The sputtering yield of N was two orders of magnitude larger than the elastic sputtering yield by the SRIM code or than the measured electronic sputtering yield of a-SiN by 50-MeV Cu ions previously reported. Such a large sputtering yield cannot be explained either by the elastic sputtering or by the electronic sputtering. However, an estimation of the synergistic effect based on the inelastic thermal spike model roughly explains the observed large sputtering yield, indicating that the synergistic effect of the nuclear and electronic stopping powers plays an important role.
1000 Si atoms/ion. The sputtering yield of N was two orders of magnitude larger than the elastic sputtering yield by the SRIM code or than the measured electronic sputtering yield of a-SiN by 50-MeV Cu ions previously reported. Such a large sputtering yield cannot be explained either by the elastic sputtering or by the electronic sputtering. However, an estimation of the synergistic effect based on the inelastic thermal spike model roughly explains the observed large sputtering yield, indicating that the synergistic effect of the nuclear and electronic stopping powers plays an important role.
 N
N films
films森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 石川 法人; 北條 喜一; 辻本 将彦*; 磯田 正二*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 315, p.142 - 145, 2013/11
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:69.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)Thin films of amorphous Si N
N (thickness 5-30 nm) were irradiated with 360-720 keV C
(thickness 5-30 nm) were irradiated with 360-720 keV C
 ions in order to investigate ion track formation. Ion tracks were observed with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM). The length and the radial density profile of the track were measured for various combinations of the film thickness and the energy of C
ions in order to investigate ion track formation. Ion tracks were observed with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM). The length and the radial density profile of the track were measured for various combinations of the film thickness and the energy of C
 ions. The length of the ion track produced in a 30-nm film was found shorter than that in a 20-nm film for the same projectile energy, which indicates that there is surface effect on track formation. This can be qualitatively understood in terms of the energy dissipation process. The observed radial density profile also depends on the film thickness: The apparent density reduction increases with decreasing film thickness. The result can be explained by surface cratering.
ions. The length of the ion track produced in a 30-nm film was found shorter than that in a 20-nm film for the same projectile energy, which indicates that there is surface effect on track formation. This can be qualitatively understood in terms of the energy dissipation process. The observed radial density profile also depends on the film thickness: The apparent density reduction increases with decreasing film thickness. The result can be explained by surface cratering.
 イオン照射によって形成された非晶質SiN薄膜中のイオントラックの膜厚依存性
イオン照射によって形成された非晶質SiN薄膜中のイオントラックの膜厚依存性中嶋 薫*; 森田 陽亮*; 北山 巧*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 辻本 将彦*; 磯田 正二*
no journal, ,
物質にイオンを照射すると、入射イオンの経路やその周辺領域において物質の密度や構造が変化することがある。こうしたイオン照射痕跡をイオントラックと呼ぶ。これまでのイオントラックに関する研究は、その形成に大きなエネルギー付与を必要とするため数百MeVからGeVに及ぶ極めて高いエネルギーの重イオンを用いて行われてきた。また、イオントラックの直径などの形状観察を行う場合には、単結晶試料を使い、照射による結晶性の変化を透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)などで観察する手法が主であった。これに対して、最近我々は数百keVのC イオンを非晶質のSiN薄膜、SiO
イオンを非晶質のSiN薄膜、SiO 薄膜に照射(阻止能は200MeVのAuイオンの場合にほぼ相当する)し、形成されたイオントラックをTEMで直接観察することに成功した。さらに高角度暗視野走査型透過電子顕微鏡(HAADF-STEM)観察により、そのイオントラックの密度が中心部で大きく低下する一方、周辺部でわずかに上昇しているコア-シェル構造であることを明らかにした。本発表では、SiN薄膜に形成されたイオントラックの長さに着目し、その膜厚に対する依存性を調べた結果、照射したC
薄膜に照射(阻止能は200MeVのAuイオンの場合にほぼ相当する)し、形成されたイオントラックをTEMで直接観察することに成功した。さらに高角度暗視野走査型透過電子顕微鏡(HAADF-STEM)観察により、そのイオントラックの密度が中心部で大きく低下する一方、周辺部でわずかに上昇しているコア-シェル構造であることを明らかにした。本発表では、SiN薄膜に形成されたイオントラックの長さに着目し、その膜厚に対する依存性を調べた結果、照射したC イオンのエネルギーが同じでも、膜が厚いほどイオントラックが短くなる傾向が観測されたことを報告する。この傾向は、イオンが与えたエネルギーが熱化した際、膜の厚さによってトラック末端での熱伝導が異なることに起因しているものと考えられる。
イオンのエネルギーが同じでも、膜が厚いほどイオントラックが短くなる傾向が観測されたことを報告する。この傾向は、イオンが与えたエネルギーが熱化した際、膜の厚さによってトラック末端での熱伝導が異なることに起因しているものと考えられる。
中嶋 薫*; 森田 陽亮*; 北山 巧*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 石川 法人; 北條 喜一; 辻本 将彦*; et al.
no journal, ,
物質にイオンを照射すると、イオンの経路やその周囲の領域で物質の密度変化や構造変化が生じることがあり、物質中に形成されたこのような痕跡をイオントラックと呼ぶ。イオントラックに関する研究では、その形状や大きさ、トラック内の原子密度の分布などを知ることが課題となるため、透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)や高角度暗視野走査型透過電子顕微鏡(HAADF-STEM)などの空間的な分解能をもつ手法で観察することが望まれる。しかし、結晶性の物質中に形成されるイオントラックは結晶性の変化として捉えることができ、TEMによる直接観察が容易であるのに対して、非晶質物質中に形成されるイオントラックはTEM像にコントラストの差がつきにくいことなどから、TEMによる直接観察はほとんど試みられなかった。我々は、非晶質中に形成されるイオントラックの構造等を明らかにするために、厚さ20nmの非晶質SiN薄膜、非晶質SiO 薄膜に120-720keVのC
薄膜に120-720keVのC
 , C
, C
 イオンを照射した試料に対してTEMによる直接観察を行った。その結果、非晶質絶縁体中に形成されたイオントラックをTEMで直接観察することに初めて成功した。さらに、トラック内の密度分布を定量的に評価するためにHAADF-STEMによる観察を行い、イオントラックの中心部は密度が約20%低下し、それに対して周辺部は約1
イオンを照射した試料に対してTEMによる直接観察を行った。その結果、非晶質絶縁体中に形成されたイオントラックをTEMで直接観察することに初めて成功した。さらに、トラック内の密度分布を定量的に評価するためにHAADF-STEMによる観察を行い、イオントラックの中心部は密度が約20%低下し、それに対して周辺部は約1 2%密度が上昇していることを明らかにした。
2%密度が上昇していることを明らかにした。

 照射による非晶質SiNのスパッタリング
照射による非晶質SiNのスパッタリング北山 巧*; 森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 松田 誠; 左高 正雄*; 辻本 将彦*; et al.
no journal, ,
サブMeV C イオン照射によって非晶質SiN膜中に形成されるイオントラックの微細構造を調べる研究の過程で、C
イオン照射によって非晶質SiN膜中に形成されるイオントラックの微細構造を調べる研究の過程で、C イオン1個で数千個の標的原子がスパッタリングされることを示唆する実験結果を得た。そこで、この現象を詳細に調べるために、Si基板上の非晶質SiN膜(厚さ30nm)に540keV C
イオン1個で数千個の標的原子がスパッタリングされることを示唆する実験結果を得た。そこで、この現象を詳細に調べるために、Si基板上の非晶質SiN膜(厚さ30nm)に540keV C
 イオンを照射し、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱(RBS)法によってそのスパッタリング収量を評価した結果、およそ5000atoms/ionであった。一方、弾性衝突によるスパッタリングを模擬するSRIMコードで計算すると約80atoms/ionである。このことは、本研究で考えるスパッタリングが単純な弾性衝突によるスパッタリングでは説明できないことを示している。また、SiNの電子的阻止能が540keV C
イオンを照射し、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱(RBS)法によってそのスパッタリング収量を評価した結果、およそ5000atoms/ionであった。一方、弾性衝突によるスパッタリングを模擬するSRIMコードで計算すると約80atoms/ionである。このことは、本研究で考えるスパッタリングが単純な弾性衝突によるスパッタリングでは説明できないことを示している。また、SiNの電子的阻止能が540keV C
 イオンに対する値(8keV/nm)よりも大きい19keV/nmの100MeV Xe
イオンに対する値(8keV/nm)よりも大きい19keV/nmの100MeV Xe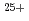 によるスパッタリング収量を同様の方法で測定すると、C
によるスパッタリング収量を同様の方法で測定すると、C 照射に比べて非常に小さくなり、電子的阻止能のみによる単純な電子的スパッタリングでも、540keV C
照射に比べて非常に小さくなり、電子的阻止能のみによる単純な電子的スパッタリングでも、540keV C
 によるスパッタリング収量は説明できない。そこで、本発表では電子的阻止能と核的阻止能の相乗効果により説明が可能であることを議論する。
によるスパッタリング収量は説明できない。そこで、本発表では電子的阻止能と核的阻止能の相乗効果により説明が可能であることを議論する。

 irradiation
irradiation北山 巧*; 森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 松田 誠; 左高 正雄*; 辻本 将彦*; 磯田 正二*; et al.
no journal, ,
Our previous observation of an ion track by sub-MeV C -ion bombardment of a thin amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiN) film with transmission-electron microscopy has shown a large density reduction in the core region, and it suggests emission of thousands of atoms from the cylindrical region. Sputtering yields of a-SiN films by C
-ion bombardment of a thin amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiN) film with transmission-electron microscopy has shown a large density reduction in the core region, and it suggests emission of thousands of atoms from the cylindrical region. Sputtering yields of a-SiN films by C ions were evaluated in order to confirm this suggestion. A-SiN films deposited on Si(001) were irradiated with 540-keV C
ions were evaluated in order to confirm this suggestion. A-SiN films deposited on Si(001) were irradiated with 540-keV C
 ions at fluences up to 1
ions at fluences up to 1 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . The sputtering yields were estimated to be 3900
. The sputtering yields were estimated to be 3900 500 N atoms/ion and 1500
500 N atoms/ion and 1500 1000 Si atoms/ion from the compositional depth profiles measured with high-resolution Rutherford-backscattering spectroscopy. The sputtering yield of N was two orders of magnitude larger than the elastic sputtering yield by the SRIM code, indicating that the observed sputtering yield cannot be explained by elastic collisions. The sputtering yield of an a-SiN film by 100-MeV Xe
1000 Si atoms/ion from the compositional depth profiles measured with high-resolution Rutherford-backscattering spectroscopy. The sputtering yield of N was two orders of magnitude larger than the elastic sputtering yield by the SRIM code, indicating that the observed sputtering yield cannot be explained by elastic collisions. The sputtering yield of an a-SiN film by 100-MeV Xe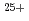 ions was also measured in order to confirm a possibility of electronic sputtering. Although the electronic stopping power for 100-MeV Xe is more than twice larger than that for 540-keV C
ions was also measured in order to confirm a possibility of electronic sputtering. Although the electronic stopping power for 100-MeV Xe is more than twice larger than that for 540-keV C , the observed sputtering yield was only
, the observed sputtering yield was only  500
500 200 atoms/ion. This indicates that the huge sputtering yield for the impact of C
200 atoms/ion. This indicates that the huge sputtering yield for the impact of C cannot be explained by the simple electronic sputtering, either. A possible explanation might be a synergistic effect of the nuclear and electronic stopping powers.
cannot be explained by the simple electronic sputtering, either. A possible explanation might be a synergistic effect of the nuclear and electronic stopping powers.
林 宏昭*; 北山 巧*; 森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 松田 誠; 左高 正雄*; 辻本 将彦*; 磯田 正二*; et al.
no journal, ,
固体に高速重イオンを照射すると、イオンの軌跡に沿って直径数nmの円筒状の照射痕(イオントラック)が生成する場合がある。このイオントラックは、固体内の電子励起に伴うイオン軌跡近傍の温度上昇によるものと考えられている。しかし、イオン軌跡近傍の温度上昇は数ピコ秒の極短時間に数nmの極めて狭い領域で生じるため、温度の直接測定はこれまで非常に困難であった。そこで本研究では、試料表面上の金ナノ粒子が、表面温度が金の融点(約1300K)を超えると表面から脱離することを利用して局所的な温度を測定する手法を提案する。表面に金ナノ粒子を蒸着した非晶質窒化ケイ素薄膜に1.11MeVのC イオンを照射した後、薄膜を透過型電子顕微鏡で観察した結果、各イオントラックの周囲数nmにわたって金ナノ粒子が消失している領域が観察され、照射によってイオントラック近傍の温度が少なくとも金の融点を超えたことが明らかになった。イオントラック形成機構を説明するモデルの中で現在最も有力と考えられている非弾性熱スパイクモデルを用いて、照射点近傍の温度分布を計算した結果、金の融点を超える領域は金ナノ粒子が消失した領域とおおよそ一致した。この結果より本手法が局所的な温度を測定する方法として適切なものであると結論した。
イオンを照射した後、薄膜を透過型電子顕微鏡で観察した結果、各イオントラックの周囲数nmにわたって金ナノ粒子が消失している領域が観察され、照射によってイオントラック近傍の温度が少なくとも金の融点を超えたことが明らかになった。イオントラック形成機構を説明するモデルの中で現在最も有力と考えられている非弾性熱スパイクモデルを用いて、照射点近傍の温度分布を計算した結果、金の融点を超える領域は金ナノ粒子が消失した領域とおおよそ一致した。この結果より本手法が局所的な温度を測定する方法として適切なものであると結論した。