Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sn nanodot
Sn nanodot佐藤 佑磨*; 竹内 祐太郎*; 山根 結太*; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 大野 英男*; 深見 俊輔*
Applied Physics Letters, 122(12), p.122404_1 - 122404_5, 2023/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:54.89(Physics, Applied)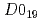 -Mn
-Mn Sn, an antiferromagnet having a non-collinear spin structure in a kagome lattice, has attracted great attention owing to various intriguing properties such as large anomalous Hall effect. Stability of magnetic state against thermal fluctuation, characterized in general by the thermal stability factor
Sn, an antiferromagnet having a non-collinear spin structure in a kagome lattice, has attracted great attention owing to various intriguing properties such as large anomalous Hall effect. Stability of magnetic state against thermal fluctuation, characterized in general by the thermal stability factor  , has been well studied in ferromagnetic systems but not for antiferromagnets. Here we study
, has been well studied in ferromagnetic systems but not for antiferromagnets. Here we study  of the antiferromagnetic Mn
of the antiferromagnetic Mn Sn nanodots as a function of their diameter
Sn nanodots as a function of their diameter  . To obtain
. To obtain  , we measure the switching probability as a function of pulse-field amplitude and analyze the results based on a model developed by accounting for two and six-fold magnetic anisotropies in the kagome plane. We observe no significant change in
, we measure the switching probability as a function of pulse-field amplitude and analyze the results based on a model developed by accounting for two and six-fold magnetic anisotropies in the kagome plane. We observe no significant change in  down to
down to 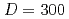 nm below which it decreases with
nm below which it decreases with  . The obtained
. The obtained  dependence is well explained by a single-domain and nucleation-mediated reversal models. These findings provide a basis to understand the thermal fluctuation and reversal mechanism of antiferromagnets for device application.
dependence is well explained by a single-domain and nucleation-mediated reversal models. These findings provide a basis to understand the thermal fluctuation and reversal mechanism of antiferromagnets for device application.
舩津 拓也*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 深見 俊輔*; 大野 英男*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.4079_1 - 4079_8, 2022/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:34.67(Multidisciplinary Sciences)外部摂動によるエネルギー配置の変調は、アレニウスの法則によって記述されるさまざまな熱活性化現象を支配している。スピン移行トルク(STT)によるナノスケールの磁気トンネル接合の熱ゆらぎの利用は、非従来型計算機の可能性を示しているものの、ネール・アレニウス則に基づくその厳密な表現については未解明な点がある。特に、その中の熱的に活性化されるスイッチング速度の指数は、10年の長い保持時間を持つ従来の熱的に安定なナノ磁石では到達できなかった。本研究では、外部摂動に対して高い感度を持つ超常磁性トンネル接合を利用することで、STTによるネール・アレニウス則に迫り、強磁性共鳴のホモダイン検出,ナノ秒STTスイッチング,ランダム電信ノイズなどのいくつかの独立した測定を通じて指数を決定する。さらに、結果がさまざまな物理システムで観察された局所分岐の概念によって包括的に記述されていることを示す。調査結果は、統計物理学の有用なテスターとしての超常磁性トンネル接合の能力、および厳密な数学的基盤を備えた確率的コンピューティングハードウェアの高度なエンジニアリングの可能性を示している。
 Sn thin films by magneto-optical Kerr effect
Sn thin films by magneto-optical Kerr effect内村 友宏*; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 佐藤 佑磨*; 竹内 祐太郎*; 金井 駿*; 武智 涼太*; 岸 桂輔*; 山根 結太*; DuttaGupta, S.*; 家田 淳一; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 120(17), p.172405_1 - 172405_5, 2022/04
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:83.82(Physics, Applied)We perform a hysteresis-loop measurement and domain imaging for 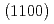 -oriented
-oriented 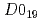 -Mn
-Mn Sn
Sn
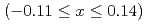 thin films using magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) and compare it with the anomalous Hall effect (AHE) measurement. We obtain a large Kerr rotation angle of 10 mdeg., comparable with bulk single-crystal Mn
thin films using magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) and compare it with the anomalous Hall effect (AHE) measurement. We obtain a large Kerr rotation angle of 10 mdeg., comparable with bulk single-crystal Mn Sn. The composition
Sn. The composition  dependence of AHE and MOKE shows a similar trend, suggesting the same origin, i.e., the non-vanishing Berry curvature in the momentum space. Magnetic domain observation at the saturated state shows that x dependence of AHE and MOKE is explained by an amount of reversible area that crucially depends on the crystalline structure of the film. Furthermore, in-depth observation of the reversal process reveals that the reversal starts with nucleation of sub-micrometer-scale domains dispersed in the film, followed by a domain expansion, where the domain wall preferentially propagates along the
dependence of AHE and MOKE shows a similar trend, suggesting the same origin, i.e., the non-vanishing Berry curvature in the momentum space. Magnetic domain observation at the saturated state shows that x dependence of AHE and MOKE is explained by an amount of reversible area that crucially depends on the crystalline structure of the film. Furthermore, in-depth observation of the reversal process reveals that the reversal starts with nucleation of sub-micrometer-scale domains dispersed in the film, followed by a domain expansion, where the domain wall preferentially propagates along the ![$$[11bar{2}0]$$](/search/images/ERNTCMK2MJQXE4ZSPUYF0JA.gif) direction. Our study provides a basic understanding of the spatial evolution of the reversal of chiral-spin structure in non-collinear antiferromagnetic thin films.
direction. Our study provides a basic understanding of the spatial evolution of the reversal of chiral-spin structure in non-collinear antiferromagnetic thin films.
竹内 祐太郎*; 山根 結太*; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 伊藤 隆一*; 陣内 佛霖*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 深見 俊輔*; 大野 英男*
Nature Materials, 20(10), p.1364 - 1370, 2021/10
被引用回数:81 パーセンタイル:98.79(Chemistry, Physical)Electrical manipulation of magnetic materials by current-induced spin torque constitutes the basis of spintronics. Recent studies have demonstrated electrical controls of ferromagnets and collinear antiferromagnets by spin-orbit torque (SOT). Here we show an unconventional response to SOT of a non-collinear antiferromagnet, which has recently attracted great attention owing to large anomalous Hall effect despite vanishingly small net magnetization. In heterostructures with epitaxial non-collinear antiferromagnet Mn Sn, we observe a characteristic fluctuation of Hall resistance, which is attributed to a persistent rotation of chiral-spin structure of Mn
Sn, we observe a characteristic fluctuation of Hall resistance, which is attributed to a persistent rotation of chiral-spin structure of Mn Sn driven by SOT. We find that level of the fluctuation that varies with sample size represents the number of magnetic domains of Mn
Sn driven by SOT. We find that level of the fluctuation that varies with sample size represents the number of magnetic domains of Mn Sn. In addition, Mn
Sn. In addition, Mn Sn thickness dependence of critical current reveals that SOT generated by small current density below 20 MA cm
Sn thickness dependence of critical current reveals that SOT generated by small current density below 20 MA cm effectively acts on the chiral-spin structure even in thick Mn
effectively acts on the chiral-spin structure even in thick Mn Sn above 20 nm. The results provide unprecedented pathways of electrical manipulation of magnetic materials, offering new-concept spintronics devices with unconventional functionalities and low-power consumption.
Sn above 20 nm. The results provide unprecedented pathways of electrical manipulation of magnetic materials, offering new-concept spintronics devices with unconventional functionalities and low-power consumption.
 Sn
Sn thin films
thin filmsYoon, J.-Y.*; 竹内 祐太郎*; DuttaGupta, S.*; 山根 結太*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 大野 英男*; 深見 俊輔*
AIP Advances (Internet), 11(6), p.065318_1 - 065318_6, 2021/06
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:79.58(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)We investigate the relationship between structural parameters, magnetic ordering, and the anomalous Hall effect (AHE) of Mn Sn
Sn (
(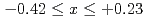 ) thin films annealed at various temperature
) thin films annealed at various temperature 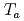 . The crystal structure changes with
. The crystal structure changes with  and
and 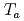 and at
and at 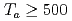
 C near the stoichiometric composition (
C near the stoichiometric composition (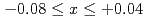 ) epitaxial single-phase
) epitaxial single-phase  0
0 -Mn
-Mn Sn
Sn (
(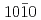 ) is obtained. At room temperature, a larger AHE is obtained when the single-phase epitaxial Mn
) is obtained. At room temperature, a larger AHE is obtained when the single-phase epitaxial Mn Sn with the lattice constant closer to that of bulk is formed. The temperature dependence of the AHE shows different behaviors depending on
Sn with the lattice constant closer to that of bulk is formed. The temperature dependence of the AHE shows different behaviors depending on 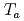 and can be explained by considering the variation of magnetic ordering. A close inspection into the temperature and composition dependence suggests a variation of magnetic phase transition temperature with composition and/or a possible correlation between the AHE and Fermi level position with respect to the Weyl points. Our comprehensive study would provide the basis for utilizing the unique functionalities of non-collinear antiferromagnetic materials.
and can be explained by considering the variation of magnetic ordering. A close inspection into the temperature and composition dependence suggests a variation of magnetic phase transition temperature with composition and/or a possible correlation between the AHE and Fermi level position with respect to the Weyl points. Our comprehensive study would provide the basis for utilizing the unique functionalities of non-collinear antiferromagnetic materials.
岡田 篤*; He, S.*; Gu, B.; 金井 駿*; Soumyanarayanan, A.*; Lim, S. T.*; Tran, M.*; 森 道康; 前川 禎通; 松倉 文礼*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 144(15), p.3815 - 3820, 2017/04
Studies of magnetization dynamics have incessantly facilitated the discovery of fundamentally novel physical phenomena, making steady headway in the development of magnetic and spintronics devices. The dynamics can be induced and detected electrically, offering new functionalities in advanced electronics at the nanoscale. However, its scattering mechanism is still disputed. Understanding the mechanism in thin films is especially important, because most spintronics devices are made from stacks of multilayers with nanometer thickness. The stacks are known to possess interfacial magnetic anisotropy, a central property for applications, whose influence on the dynamics remains unknown. Here, we investigate the impact of interfacial anisotropy by adopting CoFeB/MgO as a model system. Through systematic and complementary measurements of ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) on a series of thin films, we identify narrower FMR linewidths at higher temperatures. We explicitly rule out the temperature dependence of intrinsic damping as a possible cause, and it is also not expected from existing extrinsic scattering mechanisms for ferromagnets. We ascribe this observation to motional narrowing, an old concept so far neglected in the analyses of FMR spectra. The effect is confirmed to originate from interfacial anisotropy, impacting the practical technology of spin-based nanodevices up to room temperature.
家田 淳一
竹内 祐太朗*; 深見 俊輔*; 山根 結太*; Yoon J.-Y.*; 陣内 佛霖*; 金井 駿*; 大野 英男*
【課題】 外部磁場が不要であり、比較的大きな読み出し信号の出力が可能な乱数生成素子、メモリ素子として使用することが可能であり、また、出力/入力周波数の可変性を備えた発振/検波素子としても使用することが可能である電子デバイスを提供することを目的とする。 【解決手段】 本体と、入力端子と、出力端子と、を備え、前記本体は、基板上にスピントルク生成層とノンコリニア反強磁性層がこの順、または逆順の積層方向に積層されて構成されるものであり、前記入力端子は、前記スピントルク生成層の積層面と平行な任意の一方向の両端に配置され、前記ノンコリニア反強磁性層は、前記任意の一方向と前記積層方向が成す平面においてノンコリニアな磁気秩序を有することを特徴とする電子デバイス。
家田 淳一
竹内 祐太朗*; 深見 俊輔*; 山根 結太*; Yoon J.-Y.*; 陣内 佛霖*; 金井 駿*; 大野 英男*
外部磁場が不要であり、比較的大きな読み出し信号の出力が可能な乱数生成素子、メモリ素子として使用することが可能であり、また、出力/入力周波数の可変性を備えた発振/検波素子としても使用することが可能である電子デバイスを提供することを目的とする。 本体と、入力端子と、出力端子と、を備え、前記本体は、基板上にスピントルク生成層とノンコリニア反強磁性層がこの順、または逆順の積層方向に積層されて構成されるものであり、前記入力端子は、前記スピントルク生成層の積層面と平行な任意の一方向の両端に配置され、前記ノンコリニア反強磁性層は、前記任意の一方向と前記積層方向が成す平面においてノンコリニアな磁気秩序を有することを特徴とする電子デバイス。
家田 淳一
竹内 祐太朗*; 深見 俊輔*; 山根 結太*; Yoon J.-Y.*; 陣内 佛霖*; 金井 駿*; 大野 英男*
外部磁場が不要であり、比較的大きな読み出し信号の出力が可能な乱数生成素子、メモリ素子として使用することが可能であり、また、出力/入力周波数の可変性を備えた発振/検波素子としても使用することが可能である電子デバイスを提供することを目的とする。 本体と、入力端子と、出力端子と、を備え、前記本体は、基板上にスピントルク生成層とノンコリニア反強磁性層がこの順、または逆順の積層方向に積層されて構成されるものであり、前記入力端子は、前記スピントルク生成層の積層面と平行な任意の一方向の両端に配置され、前記ノンコリニア反強磁性層は、前記任意の一方向と前記積層方向が成す平面においてノンコリニアな磁気秩序を有することを特徴とする電子デバイス。