Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
平原 徹*; Otrokov, M. M.*; 佐々木 泰祐*; 角田 一樹*; 友弘 雄太*; 日下 翔太郎*; 奥山 裕磨*; 一ノ倉 聖*; 小林 正起*; 竹田 幸治; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.4821_1 - 4821_8, 2020/09
被引用回数:41 パーセンタイル:93.11(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We fabricate a novel magnetic topological heterostructure Mn Bi
Bi Te
Te /Bi
/Bi Te
Te where multiple magnetic layers are inserted into the topmost quintuple layer of the original topological insulator Bi
where multiple magnetic layers are inserted into the topmost quintuple layer of the original topological insulator Bi Te
Te . A massive Dirac cone (DC) with a gap of 40-75 meV at 16 K is observed. By tracing the temperature evolution, this gap is shown to gradually decrease with increasing temperature and a blunt transition from a massive to a massless DC occurs around 200-250 K. Magnetic measurements show that there are two distinct Mn components in the system that corresponds to the two heterostructures; MnBi
. A massive Dirac cone (DC) with a gap of 40-75 meV at 16 K is observed. By tracing the temperature evolution, this gap is shown to gradually decrease with increasing temperature and a blunt transition from a massive to a massless DC occurs around 200-250 K. Magnetic measurements show that there are two distinct Mn components in the system that corresponds to the two heterostructures; MnBi Te
Te /Bi
/Bi Te
Te is paramagnetic at 6 K while Mn
is paramagnetic at 6 K while Mn Bi
Bi Te
Te /Bi
/Bi Te
Te is ferromagnetic with a negative hysteresis (critical temperature 20 K). This novel heterostructure is potentially important for future device applications.
is ferromagnetic with a negative hysteresis (critical temperature 20 K). This novel heterostructure is potentially important for future device applications.
久保田 正人; 児子 精祐*; 加藤 誠一*; 雨宮 健太*
AIP Advances (Internet), 9(9), p.095050_1 - 095050_4, 2019/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:4.41(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)アルミ酸化膜のメモリ機能と微視的な物性の関係を明らかにするために、放射光吸収測定を行い、電気特性の変化に伴う酸素サイトの電子状態の変化を直接的に捉えることに成功した。
雨宮 健太*; 酒巻 真粧子*; 水沢 まり*; 武田 全康
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034004_1 - 034004_6, 2015/09
The canted magnetic moment around the interface between ferromagnetic Ni and antiferromagnetic FeMn films is observed, and its dependence on the in-plane magnetic field is revealed by means of the polarized neutron reflectivity. The Ni magnetic moment at the interface to the FeMn film is suggested to be canted to the in-plane direction, while that in the inner Ni layers remains rather perpendicular to the film at weak magnetic fields. The interface moment easily rotates to the in-plane direction as increasing the magnetic field, and finally the inner layer moment also aligns in the in-plane direction at higher magnetic fields.
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 小出 明広*; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 藤川 高志*; 境 誠司
Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 1(35), p.5533 - 5537, 2013/09
被引用回数:32 パーセンタイル:76.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The spin-electronic structures across the interface between single-layer graphene and a Ni(111) thin film are explored by employing the depth-resolved X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy with the atomic layer resolution. The depth-resolved Ni L-edge analysis clarifies that the Ni atomic layers adjacent to the interface show a transition of the spin orientation to the perpendicular one in contrast with the in-plane one in the bulk region. The C K-edge analysis reveals the intensifying of the spin-orbital interactions induced by the 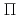 -d hybridization at the interface as well as out-of-plane spin polarization at the
-d hybridization at the interface as well as out-of-plane spin polarization at the 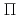 band region of graphene. The present study indicates the importance of the interface design at the atomic layer level for graphene-based spintronics.
band region of graphene. The present study indicates the importance of the interface design at the atomic layer level for graphene-based spintronics.
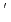 -iodobiphenyl molecular crystal on GeS(001)
-iodobiphenyl molecular crystal on GeS(001)隅井 良平*; 酒巻 真粧子*; 松本 吉弘; 雨宮 健太*; 金井 要*; 関 一彦*
Surface Science, 604(13-14), p.1100 - 1104, 2010/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:17.17(Chemistry, Physical)The electronic and atomic structures of 4-cyano-4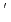 -iodobiphenyl (CIB) during the growth of a molecular crystal on a GeS(001) substrate were studied by ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (UPS), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. AFM images suggest that the CIB molecule grows as a microcrystal at a nominal thickness of 80
-iodobiphenyl (CIB) during the growth of a molecular crystal on a GeS(001) substrate were studied by ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (UPS), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy. AFM images suggest that the CIB molecule grows as a microcrystal at a nominal thickness of 80 . The microcrystal grows with the crystal plane parallel to the surface and isotropic crystal axis orientation. EXAFS analysis suggests that a CIB crystal forms by strong N-I interaction, called halogen bonding. The formation of the intermolecular N-I bond was demonstrated by EXAFS analyses in which the N-I distance was determined to be 3.29
. The microcrystal grows with the crystal plane parallel to the surface and isotropic crystal axis orientation. EXAFS analysis suggests that a CIB crystal forms by strong N-I interaction, called halogen bonding. The formation of the intermolecular N-I bond was demonstrated by EXAFS analyses in which the N-I distance was determined to be 3.29 . An upward shift of the highest occupied molecular orbital level was observed by UPS and can be attributed to the aggregation of CIB molecules caused by halogen bonding.
. An upward shift of the highest occupied molecular orbital level was observed by UPS and can be attributed to the aggregation of CIB molecules caused by halogen bonding.
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
グラフェンへの効率的なスピン注入を実現するために重要となる強磁性金属との界面近傍の電子・スピン状態を明らかにすることを目的とし、超高真空中での化学気相成長によりNi上に作製した単層・二層グラフェン試料について、X線吸収分光とX線磁気円二色性分光を用いた解析を行った。単層・二層グラフェンともに、285eV付近に鋭い
 軌道由来のピークが、293eV近傍に
軌道由来のピークが、293eV近傍に
 軌道由来のブロードな構造が観測された。二層グラフェンの場合、
軌道由来のブロードな構造が観測された。二層グラフェンの場合、
 近傍で炭素原子のスピン偏極状態(軌道磁気モーメント成分)の大きさを反映するXMCD信号が検出されたが、単層グラフェンの場合にはXMCD信号はほとんど観測されなかった。ラマン分光測定から、単層グラフェンではNiとの間に強い相互作用(
近傍で炭素原子のスピン偏極状態(軌道磁気モーメント成分)の大きさを反映するXMCD信号が検出されたが、単層グラフェンの場合にはXMCD信号はほとんど観測されなかった。ラマン分光測定から、単層グラフェンではNiとの間に強い相互作用( -d混成軌道形成)が生じていることがわかっており、同相互作用により軌道磁気モーメント成分が減衰したものと考えられる。この結果は、Dedkovらが先に行った、単層グラフェン/Ni(111)試料についてのXMCD測定結果とは異なっており、下地のNiとの相互作用の違いに起因するものと推察される。
-d混成軌道形成)が生じていることがわかっており、同相互作用により軌道磁気モーメント成分が減衰したものと考えられる。この結果は、Dedkovらが先に行った、単層グラフェン/Ni(111)試料についてのXMCD測定結果とは異なっており、下地のNiとの相互作用の違いに起因するものと推察される。
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
グラフェンへの効率的なスピン注入を実現するために重要となる強磁性金属との界面近傍の電子・スピン状態を明らかにすることを目的とし、超高真空中での化学気相成長によりNi上に作製した単層・二層グラフェン試料について、X線吸収分光とX線磁気円二色性分光を用いた解析を行った。単層・二層グラフェンともに、285eV付近に鋭い
 軌道由来のピークが、293eV近傍に
軌道由来のピークが、293eV近傍に
 軌道由来のブロードな構造が観測された。二層グラフェンの場合、
軌道由来のブロードな構造が観測された。二層グラフェンの場合、
 近傍で炭素原子のスピン偏極状態(軌道磁気モーメント成分)の大きさを反映するXMCD信号が検出されたが、単層グラフェンの場合にはXMCD信号はほとんど観測されなかった。ラマン分光測定から、単層グラフェンではNiとの間に強い相互作用(
近傍で炭素原子のスピン偏極状態(軌道磁気モーメント成分)の大きさを反映するXMCD信号が検出されたが、単層グラフェンの場合にはXMCD信号はほとんど観測されなかった。ラマン分光測定から、単層グラフェンではNiとの間に強い相互作用( -d混成軌道形成)が生じていることがわかっており、同相互作用により軌道磁気モーメント成分が減衰したものと考えられる。この結果は、Dedkovらが先に行った、単層グラフェン/Ni(111)試料についてのXMCD測定結果とは異なっており、下地のNiとの相互作用の違いに起因するものと推察される。
-d混成軌道形成)が生じていることがわかっており、同相互作用により軌道磁気モーメント成分が減衰したものと考えられる。この結果は、Dedkovらが先に行った、単層グラフェン/Ni(111)試料についてのXMCD測定結果とは異なっており、下地のNiとの相互作用の違いに起因するものと推察される。
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
Graphene-based materials are attractive for molecular spintronics applications because their high mobility and small spin-orbit coupling are expected to give rise to long spin-relaxation length. In the present work, the depth-resolved X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) spectroscopy has been applied to the single layer graphene grown on the Ni(111) substrate by chemical vapor deposition method. As a result, the XMCD signals corresponding to the spin-polarization of graphene were detected clearly. On the other hand, the XMCD signal attributed to carbon atoms dissolved in Ni are also found near the graphene/Ni interface, and its direction is in the inverse orientation to those of graphene. This implies that it is necessary to prepare the chemically sharp hetero-interface to realize the efficient spin-injection from ferromagnetic metal to a graphene layer.
大伴 真名歩; 松本 吉弘; Avramov, P.; 圓谷 志郎; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
六方晶窒化ホウ素(h-BN)は層状の積層構造を持ち、よく規定された単原子層の絶縁体層を作製できるため、スピントロニクス素子の界面バリア層として有望である。本研究ではX線吸収磁気円二色性(XMCD)分光により、強磁性金属薄膜上のh-BN単原子層の電子・スピン状態を調べた。伝導帯最下位に位置する、N  軌道とNi 3d軌道の反結合的な混成によって生成した軌道に、強いMCDシグナルが観測された。この結果は密度汎関数法で計算したスピン依存バンド構造とも一致し、h-BN/Ni(111)界面にスピン偏極準位ができていることが明らかになった。このことは、h-BNをバリア層としてスピン注入を行う際、同準位がスピンフィルターとして働く可能性を示唆する。
軌道とNi 3d軌道の反結合的な混成によって生成した軌道に、強いMCDシグナルが観測された。この結果は密度汎関数法で計算したスピン依存バンド構造とも一致し、h-BN/Ni(111)界面にスピン偏極準位ができていることが明らかになった。このことは、h-BNをバリア層としてスピン注入を行う際、同準位がスピンフィルターとして働く可能性を示唆する。
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
本研究ではスピン注入効率に支配的な寄与を及ぼすことが考えられるグラフェンと強磁性金属電極の界面の電子・スピン状態の解明を目的に、単層グラフェン(SLG)をNi(111)薄膜上に成長した積層構造について深さ分解したX線磁気円二色性(XMCD)分光の実験を行った。結果として、自由表面に近いSLGの状態をより強く反映する e=0.5nm付近のスペクトルにおいて、
e=0.5nm付近のスペクトルにおいて、 軌道の領域(約290eV以下)に強いXMCD信号が観測された。これは、Ni(111)薄膜の磁化方向に応じてSLGのフェルミレベル近傍の状態にスピン偏極が誘起されていることを示している。さらに、検出深さの増大に伴いXMCD信号の符号が逆転する奇妙な振る舞いが観測された。同現象の原因は現時点では不明であるが、深さ分解を行っていない先行研究で報告された弱いXMCD信号は、深さに伴う信号強度の変化が相殺した結果と考えられる。
軌道の領域(約290eV以下)に強いXMCD信号が観測された。これは、Ni(111)薄膜の磁化方向に応じてSLGのフェルミレベル近傍の状態にスピン偏極が誘起されていることを示している。さらに、検出深さの増大に伴いXMCD信号の符号が逆転する奇妙な振る舞いが観測された。同現象の原因は現時点では不明であるが、深さ分解を行っていない先行研究で報告された弱いXMCD信号は、深さに伴う信号強度の変化が相殺した結果と考えられる。
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
The graphene-metal interaction is not only of fundamental interest but also of technological importance in view of spintronic applications. For the purpose of clarifying the electronic and magnetic states of graphene / ferromagnetic metal structure, depth-resolved X-ray absorption and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) spectroscopy are performed on the single- and bi-layer graphene /Ni(111) structures. An intense XMCD signal is observed in the C K-edge XMCD spectrum taken under the surface sensitive condition. This indicates that there exists the Ni-induced spin polarization in the  -orbitals of graphene even at room temperature. The depth-resolved analysis of the Ni L-edge XMCD spectrum makes clear that the magnetization of Ni is decreased by 20-30% within a few atomic layers from the interface with single-layer graphen, possibly associated with the formation of C-Ni bonds.
-orbitals of graphene even at room temperature. The depth-resolved analysis of the Ni L-edge XMCD spectrum makes clear that the magnetization of Ni is decreased by 20-30% within a few atomic layers from the interface with single-layer graphen, possibly associated with the formation of C-Ni bonds.
大伴 真名歩; 松本 吉弘; 山村 野百合*; 圓谷 志郎; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 藤川 高志*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
グラフェンはスピントロニクス材料として有望であるが、グラフェンへのスピン注入には酸化アルミニウム・酸化マグネシウムなどのトンネルバリアの挿入が不可欠である。本研究では酸化アルミニウム・酸化マグネシウムよりも成膜時のダメージが少ないバリア層材料として六方晶窒化ホウ素(h-BN)を提案し、その電子・スピン状態をX線吸収分光・X線吸収磁気円二色性測定により解析した。ホウ素のK吸収端と窒素のK吸収端において解析した結果、それぞれにおいてXMCDシグナルが観測された。多重散乱理論を用いたシミュレーション結果と照らし合わせた結果、窒素原子のみにスピン軌道相互作用を持たせても十分な大きさのXMCDシグナルが得られないことがわかった。これは周辺のNi原子の交換ポテンシャルによる散乱などの効果を考慮に入れなければならないことを示している。
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
The electronic and magnetic properties of the single-layer graphene (SLG)/Ni(111) and bilayer graphene (BLG)/Ni(111) structures are investigated by using the X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) spectroscopy. For the SLG/Ni(111) structure, an intense XMCD signal was observed in the C K-edge XMCD spectrum measured by reversing the remanent magnetization of Ni(111). This indicates that spin polarization is induced in the  -orbitals of SLG by the contact with Ni(111) even at room temperature. More interestingly, the BLG/Ni(111) structure is found to show the C K-edge XMCD signal whose intensity changes dramatically with the probing depth. On the other hand, Ni L-edge XMCD spectrum demonstrated that the magnetization of Ni decreases by 20-30% within a few atomic layers from the SLG/Ni(111) interfaces, possibly associated with the formation of C-Ni bonds.
-orbitals of SLG by the contact with Ni(111) even at room temperature. More interestingly, the BLG/Ni(111) structure is found to show the C K-edge XMCD signal whose intensity changes dramatically with the probing depth. On the other hand, Ni L-edge XMCD spectrum demonstrated that the magnetization of Ni decreases by 20-30% within a few atomic layers from the SLG/Ni(111) interfaces, possibly associated with the formation of C-Ni bonds.
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
本研究では、グラフェン/磁性金属界面の電子・スピン状態を明らかにするために、Ni(111)面上に成長させた単層グラフェン構造(SLG/Ni(111))と二層グラフェン構造(BLG/Ni(111)構造)について深さ分解X線磁気円二色性(XMCD)分光手法による解析を行った。SLG/Ni(111)構造では、Ni(111)層の残留磁化方向を反転させることで明瞭な炭素K端励起XMCD信号が室温下で観測された。これはNi(111)面とSLGが接触することで、SLGの 軌道にスピン偏極が誘起されていることを示している。さらに興味深い点として、BLG/Ni(111)構造では観測される炭素K端励起XMCD信号の強度が検出深さによって大きく変化することが明らかとなった。一方で、Ni L端励起XMCD測定からは、グラフェンとの界面近傍に存在する数層程度のNi原子層の磁化が、約20-30%程度減少していることが分かり、C-Ni結合形成によるものと推測された。
軌道にスピン偏極が誘起されていることを示している。さらに興味深い点として、BLG/Ni(111)構造では観測される炭素K端励起XMCD信号の強度が検出深さによって大きく変化することが明らかとなった。一方で、Ni L端励起XMCD測定からは、グラフェンとの界面近傍に存在する数層程度のNi原子層の磁化が、約20-30%程度減少していることが分かり、C-Ni結合形成によるものと推測された。
大伴 真名歩; 松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
グラフェンはスピントロニクス材料として有望であるが、グラフェンへのスピン注入には酸化アルミニウム・酸化マグネシウムなどのトンネルバリアの挿入が不可欠である。本研究では酸化アルミニウム・酸化マグネシウムよりも成膜時のダメージが少ないバリア層材料として六方晶窒化ホウ素(h-BN)を提案し、その電子・スピン状態をX線吸収分光・X線吸収磁気円二色性測定により解析した。ホウ素のK吸収端と窒素のK吸収端において解析した結果、それぞれにおいてXMCDシグナルが観測された。多重散乱理論を用いたシミュレーション結果と照らし合わせた結果、窒素原子のみにスピン軌道相互作用を持たせても十分な大きさのXMCDシグナルが得られないことがわかった。これは周辺のNi原子の交換ポテンシャルによる散乱などの効果を考慮に入れなければならないことを示している。
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
グラフェン-金属間の相互作用は、グラフェンのデバイス応用を実現するうえでの基礎的・技術的な観点から非常に興味深い。本研究では、グラフェン/強磁性金属界面の電子スピン状態を明らかにするため、Ni(111)面上に超高真空化学気相成長法により作成した単層グラフェン(SLG)構造について、深さ分解X線吸収(XAS)と磁気円二色性(XMCD)分光を用いた分光解析を行った。結果として、SLG由来の強いXMCD信号の検出に成功した。これは、Ni磁化によりSLG中にスピン偏極が誘起されていることを示唆する結果である。さらに、XMCD信号強度が検出深さに依存して大きく変化することも明らかとなった。Niの場合、界面に近いNi原子層の磁気モーメントが、試料内部のNi原子層の磁気モーメントと比べ2-3割減少していることが明らかとなった。これはC-Ni結合が形成されることで界面近くのNi原子層の磁気状態が大きく変化したことによるものと考えられる。
大伴 真名歩; 山内 泰*; 山村 野百合*; Avramov, P.; 松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 小出 明広*; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 藤川 高志*; et al.
no journal, ,
グラフェンはスピントロニクス材料として有望であるが、グラフェンへのスピン注入には酸化アルミニウム・酸化マグネシウムなどのトンネルバリアの挿入が不可欠である。本研究では酸化アルミニウム・酸化マグネシウムよりも成膜時のダメージが少ないバリア層材料として六方晶窒化ホウ素(h-BN)を提案し、その電子・スピン状態をX線吸収分光・X線吸収磁気円二色性測定により解析した。ホウ素のK吸収端と窒素のK吸収端において解析した結果、それぞれにおいてXMCDシグナルが観測された。多重散乱理論を用いたシミュレーション結果と照らし合わせた結果、窒素原子のみにスピン軌道相互作用を持たせても十分な大きさのXMCDシグナルが得られないことがわかった。これは周辺のNi原子の交換ポテンシャルによる散乱などの効果を考慮に入れなければならないことを示している。
松本 吉弘; 圓谷 志郎; 小出 明広*; 大伴 真名歩; Avramov, P.; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 藤川 高志*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
The spin-polarized electronic structures across the interface between single-layer graphene and a Ni(111) thin film are explored by employing the depth-resolved X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy with the atomic layer resolution. The depth-resolved Ni L-edge analysis clarifies that the Ni atomic layers adjacent to the interface show a transition of the spin orientation to the perpendicular one in contrast with the in-plane one in the bulk region. The C K-edge analysis reveals the intensifying of the spin-orbital interactions induced by the  -d hybridization at the interface as well as out-of-plane spin polarization at the
-d hybridization at the interface as well as out-of-plane spin polarization at the  band region of graphene. The present study indicates the importance of the interface design at the atomic layer level for graphene-based spintronics.
band region of graphene. The present study indicates the importance of the interface design at the atomic layer level for graphene-based spintronics.
境 誠司; 松本 吉弘*; 圓谷 志郎; 楢本 洋*; 小出 明広*; 藤川 高志*; 山内 泰*; 雨宮 健太*
no journal, ,
グラフェンは、長距離スピン輸送の実現や分子性材料をスピントロニクスに用いるためのベース材料として注目されている。本研究では、グラフェン基デバイスの基本構造であるグラフェン/磁性金属界面の電子スピン状態を、原子層スケールの深さ分解能を有する深さ分解X線磁気円二色性分光とスピン偏極He原子線による最表面スピン検出法を用いて調べた。その結果、単層グラフェン(SLG)/Ni(111)界面から数原子層の領域で、Ni薄膜の容易磁化方向が面内から面直方向に変化することが明らかになった。一方、SLGは、界面のNi原子層との相互作用により伝導を担う バンドの電子状態が変化しNiと逆向きのスピン偏極を生じることやスピン軌道相互作用の増大が生じることが分かった。
バンドの電子状態が変化しNiと逆向きのスピン偏極を生じることやスピン軌道相互作用の増大が生じることが分かった。
松本 吉弘*; 圓谷 志郎; 小出 明広*; 大伴 真名歩*; Avramov, P.*; 楢本 洋*; 雨宮 健太*; 藤川 高志*; 境 誠司
no journal, ,
グラフェン基スピントロニクスデバイスの特性を司るグラフェン/磁性金属界面の電子・スピン状態について、深さ分解X線磁気円二色性分光による調査を行った。その結果、グラフェン/ニッケル界面においてニッケル中の電子スピン(磁化)の安定な配置が面直方向に変化する特異な物性(界面誘起垂直磁気異方性)が生じることが明らかになった。さらに、界面における相互作用によりグラフェンの電子状態が変化し磁性を帯びることも分かった。