Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
池田 一貴*; 佐次田 頌*; 大友 季哉*; 大下 英敏*; 本田 孝志*; 羽合 孝文*; 齋藤 開*; 伊藤 晋一*; 横尾 哲也*; 榊 浩司*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51(Part A), p.79 - 87, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)Low-vanadium-concentration alloys have low durability, and their hydrogen absorption and desorption amounts decrease by 20% after 100 cycles. In this study, we conducted reverse Monte Carlo modeling on X-ray diffraction patterns and neutron pair distribution functions of the hydrogen-absorbed and desorbed samples of a V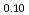 Ti
Ti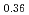 Cr
Cr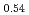 alloy to analyze the variations in the local structure. The local structure surrounding the hydrogen atom in the hydrogen-absorbed phase exhibited minimal changes. In contrast, hydrogen occupied both tetrahedral and octahedral sites of the hydrogen-desorbed phase almost equally during the early cycles; however, the amount of hydrogen occupying the tetrahedral sites increased with the number of cycles.
alloy to analyze the variations in the local structure. The local structure surrounding the hydrogen atom in the hydrogen-absorbed phase exhibited minimal changes. In contrast, hydrogen occupied both tetrahedral and octahedral sites of the hydrogen-desorbed phase almost equally during the early cycles; however, the amount of hydrogen occupying the tetrahedral sites increased with the number of cycles.
高木 寛貴*; 高木 里奈*; 見波 将*; 野本 拓也*; 大石 一城*; 鈴木 通人*; 柳 有起*; 平山 元昭*; Khanh, N.*; 軽部 皓介*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(7), p.961 - 968, 2023/07
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:96.03(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In ferromagnets, electric current generally induces a transverse Hall voltage in proportion to the internal magnetization. This effect is frequently used for electrical readout of the spin up and down states. While these properties are usually not expected in antiferromagnets, recent theoretical studies predicted that non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order with finite scalar spin chirality - meaning a solid angle spanned by neighboring spins - can induce a large spontaneous Hall effect even without net magnetization or external magnetic field. This phenomenon, the spontaneous topological Hall effect, can potentially be used for the efficient electrical readout of the antiferromagnetic states, but it has not been experimentally verified due to a lack of appropriate materials hosting such magnetism. Here, we report the discovery of all-in-all-out type non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order in triangular lattice compounds CoTa S
S and CoNb
and CoNb S
S . These compounds are reported to host unconventionally large spontaneous Hall effect despite their vanishingly small net magnetization, and our analysis reveals that it can be explained in terms of the topological Hall effect that originates from the fictitious magnetic field associated with scalar spin chirality. These results indicate that the scalar spin chirality mechanism offers a promising route to the realisation of giant spontaneous Hall response even in compensated antiferromagnets, and highlight intercalated van der Waals magnets as a promising quasi-two-dimensional material platform to enable various nontrivial ways of electrical reading and possible writing of non-coplanar antiferromagnetic domains.
. These compounds are reported to host unconventionally large spontaneous Hall effect despite their vanishingly small net magnetization, and our analysis reveals that it can be explained in terms of the topological Hall effect that originates from the fictitious magnetic field associated with scalar spin chirality. These results indicate that the scalar spin chirality mechanism offers a promising route to the realisation of giant spontaneous Hall response even in compensated antiferromagnets, and highlight intercalated van der Waals magnets as a promising quasi-two-dimensional material platform to enable various nontrivial ways of electrical reading and possible writing of non-coplanar antiferromagnetic domains.
高木 里奈*; 松山 直文*; Ukleev, V.*; Yu, L.*; White, J. S.*; Francoual, S.*; Mardegan, J. R. L.*; 速水 賢*; 齋藤 開*; 金子 耕士; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.1472_1 - 1472_7, 2022/03
被引用回数:55 パーセンタイル:99.61(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnetic skyrmions are topologically stable swirling spin textures with particle-like character, and have been intensively studied as a candidate of high-density information bit. While magnetic skyrmions were originally discovered in noncentrosymmetric systems, recently a nanometric skyrmion lattice has also been reported for centrosymmetric rare-earth compounds. For the latter systems, a novel skyrmion formation mechanism mediated by itinerant electrons has been proposed, and the search of a simpler model system allowing for a better understanding of their intricate magnetic phase diagram is highly demanded. Here, we report the discovery of square and rhombic lattices of nanometric skyrmions in a centrosymmetric binary compound EuAl , by performing small-angle neutron and resonant elastic X-ray scattering experiments. Unlike previously reported centrosymmetric skyrmion-hosting materials, EuAl
, by performing small-angle neutron and resonant elastic X-ray scattering experiments. Unlike previously reported centrosymmetric skyrmion-hosting materials, EuAl shows multiple-step reorientation of the fundamental magnetic modulation vector as a function of magnetic field, probably reflecting a delicate balance of associated itinerant-electron-mediated interactions. The present results demonstrate that a variety of distinctive skyrmion orders can be derived even in a simple centrosymmetric binary compound, which highlights rare-earth intermetallic systems as a promising platform to realize/control the competition of multiple topological magnetic phases in a single material.
shows multiple-step reorientation of the fundamental magnetic modulation vector as a function of magnetic field, probably reflecting a delicate balance of associated itinerant-electron-mediated interactions. The present results demonstrate that a variety of distinctive skyrmion orders can be derived even in a simple centrosymmetric binary compound, which highlights rare-earth intermetallic systems as a promising platform to realize/control the competition of multiple topological magnetic phases in a single material.
 with perovskite- and LiNbO
with perovskite- and LiNbO -type structures
-type structures稲熊 宜之*; 田中 樹恵*; 土谷 武史*; 森 大輔*; 勝又 哲裕*; 大場 友則*; 開 康一*; 高橋 利宏*; 齋藤 寛之
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 133(42), p.16920 - 16929, 2011/09
被引用回数:84 パーセンタイル:85.78(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We synthesized two high-pressure polymorphs PbNiO with different structures, a perovskite-type and a LiNbO
with different structures, a perovskite-type and a LiNbO -type structure, and investigated their formation behavior, detailed structure, structural transformation, thermal stability, valence state of cations, and magnetic and electronic properties. A perovskite-type PbNiO
-type structure, and investigated their formation behavior, detailed structure, structural transformation, thermal stability, valence state of cations, and magnetic and electronic properties. A perovskite-type PbNiO synthesized at 800
synthesized at 800 C under a pressure of 3 GPa crystallizes as an orthorhombic GdFeO
C under a pressure of 3 GPa crystallizes as an orthorhombic GdFeO -type structure with a space group Pnma. The reaction under high pressure was monitored by an in situ energy dispersive X-ray diffraction experiment, which revealed that a perovskit-type phase was formed even at 400
-type structure with a space group Pnma. The reaction under high pressure was monitored by an in situ energy dispersive X-ray diffraction experiment, which revealed that a perovskit-type phase was formed even at 400 C under 3 GPa.
C under 3 GPa.
 の磁場誘起相探査への応用
の磁場誘起相探査への応用渡辺 真朗; 中島 多朗*; 稲村 泰弘; 松井 一樹*; 神田 朋希*; 野本 哲也*; 大石 一城*; 河村 幸彦*; 齋藤 開*; 玉造 博夢; et al.
no journal, ,
近年パルス磁場中での精密測定技術の進歩により、高磁場中での新奇な磁気状態が開拓されてきている。我々はスーパーキャパシタを用いて発生したロングパルス磁場とJ-PARCのパルス中性子を組み合わせることで、多波長中性子パルスが試料を通過する時間幅(約10ミリ秒)よりも十分長い磁場を試料位置で発生させ、14テスラまでの磁場下で定常磁場中実験と同様に逆格子空間を網羅的に探査できる測定環境を構築した。この手法をフラストレート磁性体CuFeO の磁気相転移の探査に適用した。
の磁気相転移の探査に適用した。