Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 decay near doubly magic
decay near doubly magic  Sn
SnHeideman, J.*; Grzywacz, R.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Madurga, M.*; Escher, J. E.*; 河野 俊彦*; Algora, A.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 他41名*
Physical Review C, 108(2), p.024311_1 - 024311_9, 2023/08
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:57.48(Physics, Nuclear) -delayed neutron emission was observed in the study of the
-delayed neutron emission was observed in the study of the  decay of
decay of  In at ISOLDE CERN. Neutron emission probabilities from the unbound states in
In at ISOLDE CERN. Neutron emission probabilities from the unbound states in  Sn to known low-lying, single-particle states in
Sn to known low-lying, single-particle states in  Sn were measured. The neutron energies were determined using the time-of-flight technique and the decay from excited states in
Sn were measured. The neutron energies were determined using the time-of-flight technique and the decay from excited states in  Sn was studied by detecting its
Sn was studied by detecting its  rays. Individual
rays. Individual  -delayed neutron emission probabilities were determined by correlating the relative intensities and energies of neutrons and
-delayed neutron emission probabilities were determined by correlating the relative intensities and energies of neutrons and  rays. The new results suggest the violation of the assumption that neutrons are emitted statistically via the intermediate compound nucleus. This impacts the neutron-emission probabilities and other properties of nuclei participating in the
rays. The new results suggest the violation of the assumption that neutrons are emitted statistically via the intermediate compound nucleus. This impacts the neutron-emission probabilities and other properties of nuclei participating in the  -process. A model of neutron emission, which links the observed neutron emission probabilities to nuclear shell effects, is proposed.
-process. A model of neutron emission, which links the observed neutron emission probabilities to nuclear shell effects, is proposed.
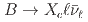 decays with the Belle II experiment
decays with the Belle II experimentAbudin n, F.*; 谷田 聖; Belle II Collaboration*; 他413名*
n, F.*; 谷田 聖; Belle II Collaboration*; 他413名*
Physical Review D, 107(7), p.072002_1 - 072002_24, 2023/04
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:76.22(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We present measurements of the first to fourth moments of the lepton mass squared 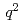 of
of 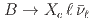 decays for
decays for 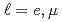 and with
and with 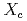 a hadronic system containing a charm quark. These results use a sample of electron-positron collisions at the
a hadronic system containing a charm quark. These results use a sample of electron-positron collisions at the 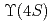 resonance corresponding to
resonance corresponding to 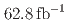 of integrated luminosity and collected by the Belle II experiment in 2019 and 2020. To identify the
of integrated luminosity and collected by the Belle II experiment in 2019 and 2020. To identify the 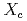 system and reconstruct
system and reconstruct 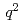 , one of the
, one of the  mesons from an
mesons from an 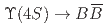 decay is fully reconstructed in a hadronic decay mode using a multivariate
decay is fully reconstructed in a hadronic decay mode using a multivariate  tagging algorithm. We report raw and central moments for
tagging algorithm. We report raw and central moments for 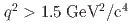 up to
up to 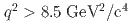 , probing up to 77% of the accessible
, probing up to 77% of the accessible 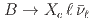 phase space. This is the first measurement of moments in the experimentally challenging range of
phase space. This is the first measurement of moments in the experimentally challenging range of ![$$[ 1.5, 2.5 ] , mathrm{GeV^2/c^4}$$](/search/images/ERNSAMJOGUWCAMROGUQF0IC2FQQFY1LBORUHE1L1I3SVMXRSF3RV2ND3EQ.gif) .
.
 =126 shell closure
=126 shell closureDay Goodacre, T.*; Afanasjev, A. V.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Nies, L.*; Marsh, B. A.*; Sels, S.*; Perera, U. C.*; Ring, P.*; Wienholz, F.*; Andreyev, A. N.; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(5), p.054322_1 - 054322_18, 2021/11
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:86.03(Physics, Nuclear)Combining laser spectroscopy with Penning-trap mass spectroscopy at the Isolde facility at CERN, the charge radii of neutron-rich mercury isotopes 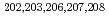 Hg were successfully measured. Furthermore, more precise values for the masses of
Hg were successfully measured. Furthermore, more precise values for the masses of 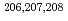 Hg was obtained, as well as the magnetic moment of
Hg was obtained, as well as the magnetic moment of  Hg. These results were used to understand the systematics of Hg isotopes across the
Hg. These results were used to understand the systematics of Hg isotopes across the  =126 shell closure. Comparison with covariant density functional theory calculations revealed that in particular the 1
=126 shell closure. Comparison with covariant density functional theory calculations revealed that in particular the 1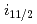 and 2
and 2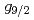 neutron orbitals affect the evolution of charge radii.
neutron orbitals affect the evolution of charge radii.
Marsh, B. A.*; Day Goodacre, T.*; 角田 佑介*; Andreyev, A. N.; 他41名*
Nature Physics, 14(12), p.1163 - 1167, 2018/12
被引用回数:127 パーセンタイル:96.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In rare cases, the removal of a single proton (Z) or neutron (N) from an atomic nucleus leads to a dramatic shape change. These instances are crucial for understanding the components of the nuclear interactions that drive deformation. The mercuryisotopes (Z = 80) are a striking example: their close neighbours, the lead isotopes (Z = 82), are spherical and steadily shrink with decreasing N. The even-mass (A = N + Z) mercury isotopes follow this trend. The odd-mass mercury isotopes 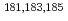 Hg, however, exhibit noticeably larger charge radii. Due to the experimental difficulties of probing extremely neutron-deficient systems, and the computational complexity of modelling such heavy nuclides, the microscopic origin of this unique shape staggering has remained unclear. Here, by applying resonance ionization spectroscopy, mass spectrometry and nuclear spectroscopy as far as
Hg, however, exhibit noticeably larger charge radii. Due to the experimental difficulties of probing extremely neutron-deficient systems, and the computational complexity of modelling such heavy nuclides, the microscopic origin of this unique shape staggering has remained unclear. Here, by applying resonance ionization spectroscopy, mass spectrometry and nuclear spectroscopy as far as  Hg, we determine
Hg, we determine  Hg as the shape-staggering endpoint. By combining our experimental measurements with Monte Carlo shell model calculations, we conclude that this phenomenon results from the interplay between monopole and quadrupole interactions driving a quantum phase transition, for which we identify the participating orbitals. Although shape staggering in the mercury isotopes is a unique and localized feature in the nuclear chart, it nicely illustrates the concurrence of single-particle and collective degrees of freedom at play in atomic nuclei.
Hg as the shape-staggering endpoint. By combining our experimental measurements with Monte Carlo shell model calculations, we conclude that this phenomenon results from the interplay between monopole and quadrupole interactions driving a quantum phase transition, for which we identify the participating orbitals. Although shape staggering in the mercury isotopes is a unique and localized feature in the nuclear chart, it nicely illustrates the concurrence of single-particle and collective degrees of freedom at play in atomic nuclei.
 -delayed
-delayed  decay of
decay of  N and implications for the
N and implications for the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O astrophysical reaction rate
O astrophysical reaction rateKirsebom, O. S.*; Tengblad, O.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 他41名*
Physical Review Letters, 121(14), p.142701_1 - 142701_6, 2018/10
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:46.75(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction plays a central role in astrophysics, but its cross section at energies relevant for astrophysical applications is only poorly constrained by laboratory data. The reduced
O reaction plays a central role in astrophysics, but its cross section at energies relevant for astrophysical applications is only poorly constrained by laboratory data. The reduced  width,
width,  , of the bound 1
, of the bound 1 level in
level in  O is particularly important to determine the cross section. The magnitude of
O is particularly important to determine the cross section. The magnitude of 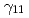 is determined via sub-Coulomb
is determined via sub-Coulomb  -transfer reactions or the
-transfer reactions or the  -delayed
-delayed  decay of
decay of  N, but the latter approach is presently hampered by the lack of sufficiently precise data on the
N, but the latter approach is presently hampered by the lack of sufficiently precise data on the  -decay branching ratios. Here we report improved branching ratios for the bound 1
-decay branching ratios. Here we report improved branching ratios for the bound 1 level (
level (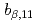 ) and for
) and for  -delayed
-delayed  emission (
emission (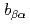 ). Our value for
). Our value for 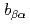 is 33
is 33  larger than previously held, leading to a substantial increase in
larger than previously held, leading to a substantial increase in 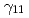 . Our revised value for
. Our revised value for 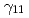 is in good agreement with the value obtained in
is in good agreement with the value obtained in  -transfer studies and the weighted average of the two gives a robust and precise determination of
-transfer studies and the weighted average of the two gives a robust and precise determination of 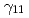 , which provides significantly improved constraints on the
, which provides significantly improved constraints on the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O cross section in the energy range relevant to hydro static He burning.
O cross section in the energy range relevant to hydro static He burning.
Gunsing, F.*; 原田 秀郎; 木村 敦; n_TOF Collaboration*; 他141名*
European Physical Journal Plus (Internet), 131(10), p.371_1 - 371_13, 2016/10
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:58.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear data in general, and neutron-induced reaction cross sections in particular, are important for a wide variety of research fields. They play a key role in the safety and criticality assessment of nuclear technology, not only for existing power reactors but also for radiation dosimetry, medical applications, the transmutation of nuclear waste, accelerator-driven systems, fuel cycle investigations and future reactor systems as in Generation IV. Applications of nuclear data are also related to research fields as the study of nuclear level densities and stellar nucleosynthesis. Simulations and calculations of nuclear technology applications largely rely on evaluated nuclear data libraries. The evaluations in these libraries are based both on experimental data and theoretical models. CERN's neutron time-of-flight facility, n_TOF, has produced a considerable amount of experimental data since it has become fully operational with the start of the scientific measurement program in 2001. While for a long period a single measurement station (EAR1) located at 185 m from the neutron production target was available, the construction of a second beam line at 20 m (EAR2) in 2014 has substantially increased the measurement capabilities of the facility. An outline of the experimental nuclear data activities at n_TOF will be presented.
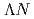 interaction;
interaction;  -ray spectroscopy of
-ray spectroscopy of 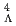 He
He山本 剛史*; 長谷川 勝一; 早川 修平; 細見 健二; Hwang, S.; 市川 裕大; 今井 憲一; 金原 慎二; 中田 祥之; 佐甲 博之; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 115(22), p.222501_1 - 222501_5, 2015/11
被引用回数:74 パーセンタイル:92.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The energy spacing between the spin-doublet bound state of 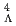 He
He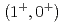 was determined to be
was determined to be 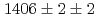 keV, by measuring
keV, by measuring  rays for the
rays for the 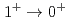 transition with a high efficiency germanium detector array in coincidence with the
transition with a high efficiency germanium detector array in coincidence with the 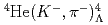 He reaction at J-PARC. In comparison to the corresponding energy spacing in the mirror hypernucleus
He reaction at J-PARC. In comparison to the corresponding energy spacing in the mirror hypernucleus 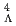 H, the present result clearly indicates the existence of charge symmetry breaking (CSB) in
H, the present result clearly indicates the existence of charge symmetry breaking (CSB) in 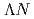 interaction. By combining the energy spacings with the known ground-state binding energies, it is also found that the CSB effect is large in the
interaction. By combining the energy spacings with the known ground-state binding energies, it is also found that the CSB effect is large in the 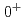 ground state but is vanishingly small in the
ground state but is vanishingly small in the 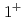 excited state, demonstrating that the
excited state, demonstrating that the 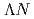 CSB interaction has spin dependence.
CSB interaction has spin dependence.
菊池 満; Medvedev, S.*; 滝塚 知典*; Fasoli, A.*; Wu, Y.*; Diamond, P. H.*; Duan, X.*; 岸本 泰明*; 花田 和明*; 他41名*
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 39E, p.P4.179_1 - P4.179_4, 2015/06
核融合炉における熱粒子制御は挑戦的課題である。定常的な熱負荷とエルムによる過渡的熱負荷を緩和する新しい方策として負三角度トカマクを評価している。これまで、負三角度は磁気丘であるにもかかわらず、ダブルヌルでは炉に使えるレベルの規格化ベータ値3以上が安定であることを見いだしている。本論文では、シングルヌル平衡配位とその理想電磁流体安定性を報告する。