Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 experiment
experimentLee, D. H.*; 百々 拓; 羽賀 勝洋; 原田 正英; 長谷川 勝一; 春日井 好己; 木下 秀孝; 増田 志歩; 明午 伸一郎; 酒井 健二; et al.
European Physical Journal C, 84, p.409_1 - 409_6, 2024/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:41.24(Physics, Particles & Fields)JSNS (J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) is an experiment that searches for sterile neutrinos via the observation of
(J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) is an experiment that searches for sterile neutrinos via the observation of 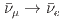 appearance oscillations using muon decay-at-rest neutrinos. The JSNS
appearance oscillations using muon decay-at-rest neutrinos. The JSNS experiment performed data taking from 2021. In this manuscript, a study of the accidental background is presented. The rate of the accidental background is (9.29
experiment performed data taking from 2021. In this manuscript, a study of the accidental background is presented. The rate of the accidental background is (9.29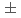 0.39)
0.39)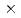 10
10 / spill with 0.75 MW beam power and comparable to the expected number of signal events.
/ spill with 0.75 MW beam power and comparable to the expected number of signal events.
西 隆博*; 橋本 直; 他46名*
Nature Physics, 19(6), p.788 - 793, 2023/06
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:88.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)According to quantum chromodynamics, vacuum is not an empty space, because it is filled with quark-antiquark pairs. The pair has the same quantum numbers as the vacuum and forms a condensate because the strong interaction of the quantum chromodynamics is too strong to leave the vacuum empty. This quark-antiquark condensation, the chiral condensate, breaks the chiral symmetry of the vacuum. The expectation value of the chiral condensate is an order parameter of the chiral symmetry, which is expected to decrease at high temperatures or high matter densities where the chiral symmetry is partially restored. Head-on collisions of nuclei at ultra-relativistic energies have explored the high-temperature regime, but experiments at high densities are rare. Here we measure the spectrum of pionic 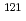 Sn atoms and study the interaction between the pion and the nucleus. We find that the expectation value of the chiral condensate is reduced at finite density compared to the value in vacuum. The reduction is linearly extrapolated to the nuclear saturation density and indicates that the chiral symmetry is partially restored due to the extremely high density of the nucleus.
Sn atoms and study the interaction between the pion and the nucleus. We find that the expectation value of the chiral condensate is reduced at finite density compared to the value in vacuum. The reduction is linearly extrapolated to the nuclear saturation density and indicates that the chiral symmetry is partially restored due to the extremely high density of the nucleus.
 hadrons in
hadrons in 
 Au and
Au and 

 collisions at
collisions at  GeV
GeVAdare, A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一; 永宮 正治; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他468名*
Physical Review C, 98(1), p.014912_1 - 014912_16, 2018/07
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:52.97(Physics, Nuclear)We present measurements of two-particle angular correlations between high-transverse-momentum (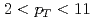 GeV/
GeV/ )
) 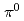 observed at midrapidity (
observed at midrapidity (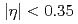 ) and particles produced either at forward (
) and particles produced either at forward (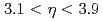 ) or backward (
) or backward (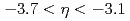 ) rapidity in
) rapidity in 
 Au and
Au and 

 collisions at
collisions at  GeV. The azimuthal angle correlations for particle pairs with this large rapidity gap in the Au-going direction exhibit a ridge-like structure that persists up to
GeV. The azimuthal angle correlations for particle pairs with this large rapidity gap in the Au-going direction exhibit a ridge-like structure that persists up to 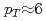 GeV/
GeV/ and which strongly depends on collision centrality, which is a similar characteristic to the hydrodynamical particle flow in A+A collisions. The ridge-like structure is absent in the
and which strongly depends on collision centrality, which is a similar characteristic to the hydrodynamical particle flow in A+A collisions. The ridge-like structure is absent in the  -going direction as well as in
-going direction as well as in 

 collisions, in the transverse-momentum range studied. The results indicate that the ridge-like structure is shifted in the Au-going direction toward more central collisions, similar to the charged-particle pseudorapidity distributions.
collisions, in the transverse-momentum range studied. The results indicate that the ridge-like structure is shifted in the Au-going direction toward more central collisions, similar to the charged-particle pseudorapidity distributions.
 + Au collisions at
+ Au collisions at 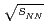 = 200, 62.4, 39, and 19.6 GeV
= 200, 62.4, 39, and 19.6 GeVAidala, C.*; 長谷川 勝一; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他246名*
Physical Review C, 96(6), p.064905_1 - 064905_21, 2017/12
被引用回数:36 パーセンタイル:91.47(Physics, Nuclear)We present measurements of the elliptic flow, 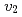 , as a function of transverse momentum (
, as a function of transverse momentum ( ), pseudorapidity (
), pseudorapidity ( ), and centrality in
), and centrality in 
 Au collisions at
Au collisions at 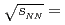 200, 62.4, 39, and 19.6 GeV. The beam-energy scan of
200, 62.4, 39, and 19.6 GeV. The beam-energy scan of 
 Au collisions provides a testing ground for the onset of flow signatures in small collision systems. We measure a nonzero
Au collisions provides a testing ground for the onset of flow signatures in small collision systems. We measure a nonzero 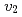 signal at all four collision energies, which, at midrapidity and low
signal at all four collision energies, which, at midrapidity and low  , is consistent with predictions from viscous hydrodynamic models. Comparisons with calculations from parton transport models (based on the
, is consistent with predictions from viscous hydrodynamic models. Comparisons with calculations from parton transport models (based on the 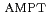 Monte Carlo generator) show good agreement with the data at midrapidity to forward (
Monte Carlo generator) show good agreement with the data at midrapidity to forward ( -going) rapidities and low
-going) rapidities and low  . At backward (Au-going) rapidities and
. At backward (Au-going) rapidities and 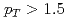 GeV/
GeV/ , the data diverges from
, the data diverges from 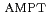 calculations of
calculations of 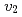 relative to the initial geometry, indicating the possible dominance of nongeometry related correlations, referred to as nonflow. We also present measurements of the charged-particle multiplicity (
relative to the initial geometry, indicating the possible dominance of nongeometry related correlations, referred to as nonflow. We also present measurements of the charged-particle multiplicity (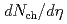 ) as a function of
) as a function of  in central
in central 
 Au collisions at the same energies. We find that in
Au collisions at the same energies. We find that in 
 Au collisions at
Au collisions at 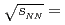 200 GeV the
200 GeV the 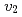 scales with
scales with 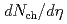 over all
over all  in the PHENIX acceptance. At
in the PHENIX acceptance. At 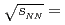 62.4, and 39 GeV,
62.4, and 39 GeV, 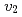 scales with
scales with 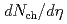 at midrapidity and forward rapidity, but falls off at backward rapidity. This departure from the
at midrapidity and forward rapidity, but falls off at backward rapidity. This departure from the 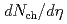 scaling may be a further indication of nonflow effects dominating at backward rapidity.
scaling may be a further indication of nonflow effects dominating at backward rapidity.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 510 GeV
= 510 GeVAdare, A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一; 永宮 正治; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他462名*
Physical Review D, 95(7), p.072002_1 - 072002_19, 2017/04
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:46.12(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Dihadron and isolated direct photon-hadron angular correlations are measured in  collisions at
collisions at  = 510 GeV. Correlations of charged hadrons of
= 510 GeV. Correlations of charged hadrons of 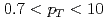 GeV/
GeV/ with
with 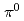 mesons of
mesons of  GeV/
GeV/ or isolated direct photons of
or isolated direct photons of 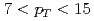 GeV/
GeV/ are used to study nonperturbative effects generated by initial-state partonic transverse momentum and final-state transverse momentum from fragmentation. The nonperturbative behavior is characterized by measuring the out-of-plane transverse momentum component
are used to study nonperturbative effects generated by initial-state partonic transverse momentum and final-state transverse momentum from fragmentation. The nonperturbative behavior is characterized by measuring the out-of-plane transverse momentum component 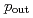 perpendicular to the axis of the trigger particle, which is the high-
perpendicular to the axis of the trigger particle, which is the high- direct photon or
direct photon or 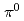 . Nonperturbative evolution effects are extracted from Gaussian fits to the away-side inclusive-charged-hadron yields for different trigger-particle transverse momenta (
. Nonperturbative evolution effects are extracted from Gaussian fits to the away-side inclusive-charged-hadron yields for different trigger-particle transverse momenta (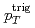 ). The Gaussian widths and root mean square of
). The Gaussian widths and root mean square of 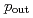 are reported as a function of the interaction hard scale
are reported as a function of the interaction hard scale 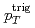 to investigate possible transverse-momentum-dependent evolution differences between the
to investigate possible transverse-momentum-dependent evolution differences between the 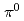 -
-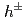 and direct photon-
and direct photon-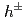 correlations and factorization breaking effects. The widths are found to decrease with
correlations and factorization breaking effects. The widths are found to decrease with 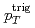 , which indicates that the Collins-Soper-Sterman soft factor is not driving the evolution with the hard scale in nearly back-to-back dihadron and direct photon-hadron production in
, which indicates that the Collins-Soper-Sterman soft factor is not driving the evolution with the hard scale in nearly back-to-back dihadron and direct photon-hadron production in  collisions. This behavior is in contrast to Drell-Yan and semi-inclusive deep-inelastic scattering measurements.
collisions. This behavior is in contrast to Drell-Yan and semi-inclusive deep-inelastic scattering measurements.
 and
and  mesons from protons in the photon energy range from 1.5 to 3.0 GeV
mesons from protons in the photon energy range from 1.5 to 3.0 GeV森野 雄平*; Hwang, S.; 今井 憲一; 谷田 聖; LEPS Collaboration*; 他46名*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(1), p.013D01_1 - 013D01_11, 2015/01
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:53.86(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report the measurement of differential cross sections for  and
and 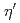 photoproduction from protons at backward angles (
photoproduction from protons at backward angles (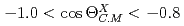 ) using linearly polarized photons at
) using linearly polarized photons at 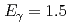 -
-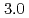 GeV. The differential cross sections for
GeV. The differential cross sections for  mesons are larger than the predicted
mesons are larger than the predicted 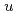 -channel contribution based on amplitude analysis in the energy range
-channel contribution based on amplitude analysis in the energy range 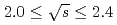 GeV. The differential cross sections for
GeV. The differential cross sections for  and
and 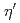 mesons become closer to the predicted
mesons become closer to the predicted 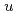 -channel contribution at
-channel contribution at 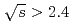 GeV. A bump structure in the
GeV. A bump structure in the 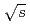 dependence of the differential cross sections for
dependence of the differential cross sections for  mesons was observed at
mesons was observed at 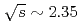 GeV.
GeV.