Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Shibata, Goro; 9 of others*
Applied Physics Letters, 126(24), p.241902_1 - 241902_6, 2025/06
 CaOsO
CaOsO studied by O
studied by O  -edge resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and Raman spectroscopy
-edge resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and Raman spectroscopyOkamoto, Jun*; Shibata, Goro; Fujimori, Atsushi; 9 of others*
npj Quantum Materials (Internet), 10, p.44_1 - 44_8, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0Yoshida, Shuhei*; Gong, W.; 9 of others*
Acta Materialia, 283, p.120498_1 - 120498_15, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:63.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Zr +
Zr +  at 27 MeV/nucleon
at 27 MeV/nucleonHwang, J.*; Chillery, T.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; 49 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2024(9), p.093D03_1 - 093D03_12, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear transmutation emerges as a promising approach for reprocessing high-level waste, specifically treating long-lived nuclides like  Zr from spent fuel. It is essential to accumulate reaction data for these nuclei to advance this prominent treatment and to build a comprehensive understanding of reaction mechanisms. In this study, the residual production cross-sections resulting from proton-induced reactions on
Zr from spent fuel. It is essential to accumulate reaction data for these nuclei to advance this prominent treatment and to build a comprehensive understanding of reaction mechanisms. In this study, the residual production cross-sections resulting from proton-induced reactions on  Zr were measured at 27 MeV/nucleon in inverse kinematics. At the RIKEN-RIBF facility the OEDO beamline was used to deduce production cross-sections for isotopes,
Zr were measured at 27 MeV/nucleon in inverse kinematics. At the RIKEN-RIBF facility the OEDO beamline was used to deduce production cross-sections for isotopes, 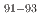 Nb,
Nb, 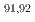 Zr, and
Zr, and 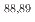 Y. Comparing the results from this study and prior research with calculated excitation functions, a moderate agreement is found with theoretical predictions derived from TALYS and CCONE. Despite the potential limitations of low-energy proton-induced reactions for
Y. Comparing the results from this study and prior research with calculated excitation functions, a moderate agreement is found with theoretical predictions derived from TALYS and CCONE. Despite the potential limitations of low-energy proton-induced reactions for  Zr transmutation, the measured cross-sections offer valuable insights for future considerations in nuclear-waste treatment facilities. This is particularly relevant for facilities exploring innovative methods, such as accelerator-driven systems.
Zr transmutation, the measured cross-sections offer valuable insights for future considerations in nuclear-waste treatment facilities. This is particularly relevant for facilities exploring innovative methods, such as accelerator-driven systems.
 Sn populated in the
Sn populated in the  decay of isomerically purified
decay of isomerically purified  In states
In statesBenito, J.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 93 of others*
Physical Review C, 110(1), p.014328_1 - 014328_19, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58.81(Physics, Nuclear) -delayed neutron emitters
-delayed neutron emitters 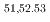 K
KXu, Z. Y.*; Grzywacz, R.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 49 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 133(4), p.042501_1 - 042501_7, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe O
O
Kawamoto, Yo*; Kikkawa, Takashi; Saito, Eiji; 9 of others*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(13), p.132406_1 - 132406_7, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:82.03(Physics, Applied)Zhou, X.*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; 9 of others*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(8), p.082103_1 - 082103_7, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:89.50(Physics, Applied)Zhang, Z.*; Gong, W.; Kawakita, Yukinobu; 9 of others*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(12), p.125402_1 - 125402_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Zr + d reaction cross sections measured at 28 MeV/nucleon
Zr + d reaction cross sections measured at 28 MeV/nucleonChillery, T.*; Hwang, J.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; 49 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2023(12), p.121D01_1 - 121D01_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:40.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The deuteron is a loosely bound system which can easily break up into its constituent proton and neutron whilst in the presence of Coulomb and nuclear fields. Previous experimental studies have shown that this breakup process has a significant impact on residual nucleus production from deuteron bombardment in the high energy range of 50 - 210 MeV/nucleon. However, there remains a lack of cross-section data at energies below 50 MeV/nucleon. The current study determined  Zr + d reaction cross sections under inverse kinematics at approximately 28 MeV/nucleon using the BigRIPS separator, OEDO beamline, and SHARAQ spectrometer. Cross sections from this research were compared with previous measurements and theoretical calculations. The experimental results show a large enhancement of the production cross sections of residual nuclei, especially those produced from a small number of particle emissions, compared to the proton-induced reaction data at similar bombarding energy. The DEURACS calculation, which quantitatively takes deuteron-breakup effects into account, reproduces the data well. As a long-lived fission product,
Zr + d reaction cross sections under inverse kinematics at approximately 28 MeV/nucleon using the BigRIPS separator, OEDO beamline, and SHARAQ spectrometer. Cross sections from this research were compared with previous measurements and theoretical calculations. The experimental results show a large enhancement of the production cross sections of residual nuclei, especially those produced from a small number of particle emissions, compared to the proton-induced reaction data at similar bombarding energy. The DEURACS calculation, which quantitatively takes deuteron-breakup effects into account, reproduces the data well. As a long-lived fission product,  Zr remains a challenge for nuclear waste disposal and treatment. This study's low-energy data may assist future consideration of nuclear-waste treatment facilities, where
Zr remains a challenge for nuclear waste disposal and treatment. This study's low-energy data may assist future consideration of nuclear-waste treatment facilities, where  Zr + d may feasibly transmute the waste into short-lived/stable nuclei.
Zr + d may feasibly transmute the waste into short-lived/stable nuclei.
Cubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 49 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 131(20), p.202501_1 - 202501_8, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:80.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary)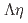 threshold in the
threshold in the 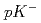 mass spectrum with
mass spectrum with 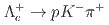 decays
decaysYang, S.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 196 of others*
Physical Review D, 108(3), p.L031104_1 - L031104_6, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.62(Astronomy & Astrophysics) N(n, p)
N(n, p) C cross section at the CERN n_TOF facility from subthermal energy to 800 keV
C cross section at the CERN n_TOF facility from subthermal energy to 800 keVTorres-S nchez, P.*; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; 129 of others*
nchez, P.*; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; 129 of others*
Physical Review C, 107(6), p.064617_1 - 064617_15, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:26.66(Physics, Nuclear)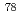 Cu
CuPedersen, L. G.*; Sahin, E.*; G rgen, A.*; Bello Garrote, F. L.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Niikura, Megumi*; Orlandi, R.; 59 of others*
rgen, A.*; Bello Garrote, F. L.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Niikura, Megumi*; Orlandi, R.; 59 of others*
Physical Review C, 107(4), p.044301_1 - 044301_10, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.98(Physics, Nuclear)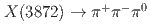 at Belle
at BelleYin, J. H.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 193 of others*
Physical Review D, 107(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_8, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:42.62(Astronomy & Astrophysics)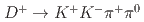 and
and 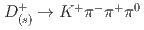 at Belle
at BelleLi, L. K.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 197 of others*
Physical Review D, 107(3), p.033003_1 - 033003_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)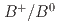 production ratio in
production ratio in 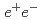 collisions at the
collisions at the 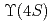 resonance using
resonance using 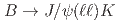 decays at Belle
decays at BelleChoudhury, S.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 198 of others*
Physical Review D, 107(3), p.L031102_1 - L031102_6, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:74.17(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Nakamura, Tomoki*; Osawa, Takahito; 219 of others*
Science, 379(6634), p.eabn8671_1 - eabn8671_14, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:208 Percentile:99.97(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Mineralogical, petrological, and physical properties of sixteen Ryugu particles measuring 1-8 mm indicate that they are most similar to CI chondrites. The presence of CO -bearing water in pyrrhotite indicates that the original parent asteroid formed beyond the H
-bearing water in pyrrhotite indicates that the original parent asteroid formed beyond the H O and CO
O and CO snow lines in the solar nebula, where, based on Ryugu mineralogy, very limited amounts of high-temperature objects including small chondrules and Ca, Al-rich inclusions were present. Fluid-rock reactions occurred at low-temperature, high pH, and reducing conditions at water/rock mass ratios smaller than 1 and changed an olivine-pyroxene rich lithology, remaining as the least-altered fragments in Ryugu samples, into phyllosilicate-carbonate rich lithologies, the predominant material of Ryugu samples. The solar nebula might have been still present when magnetite crystallized from the fluid in Ryugu's parent body.
snow lines in the solar nebula, where, based on Ryugu mineralogy, very limited amounts of high-temperature objects including small chondrules and Ca, Al-rich inclusions were present. Fluid-rock reactions occurred at low-temperature, high pH, and reducing conditions at water/rock mass ratios smaller than 1 and changed an olivine-pyroxene rich lithology, remaining as the least-altered fragments in Ryugu samples, into phyllosilicate-carbonate rich lithologies, the predominant material of Ryugu samples. The solar nebula might have been still present when magnetite crystallized from the fluid in Ryugu's parent body.
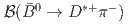 and
and 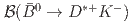 and tests of QCD factorization
and tests of QCD factorizationKrohn, J.-F.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 198 of others*
Physical Review D, 107(1), p.012003_1 - 012003_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.70(Astronomy & Astrophysics)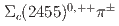
Li, Y. B.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 194 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 130(3), p.031901_1 - 031901_7, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:91.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)