Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01023_1 - 01023_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron, lead, and bismuth have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics. The measured TTNYs and DDXs were compared with calculations by the Monte Carlo transport code PHITS with its default physics model of INCL version 4.6 combined with GEM and those with the JENDL-4.0/HE nuclear data library.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
Yogo, Akifumi*; Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; Mori, Takato*; Golovin, D.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Iwata, Natsumi*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:88.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary) rays in the
rays in the 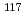 Sn(
Sn( )
)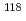 Sn reaction
Sn reactionEndo, Shunsuke; Okudaira, Takuya*; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Oku, Takayuki; Sakai, Kenji; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064601_1 - 064601_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.69(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, p.129 - 133, 2022/11
For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors composed of the NE213 liquid organic scintillators and photomultiplier tubes, which were connected to a multi-channel digitizer mounted with a field-programmable gate array (FPGA), for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination applying the gate integration method to the FPGA. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics.
 Ni and
Ni and  Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV
Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeVTakeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 527, p.17 - 27, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)To improve accuracy of nuclear design of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems and so on, nuclide production cross sections on Ni and Zr were measured for GeV energy protons. The measured results were compared with PHITS calculations, JENDL/HE-2007 and so on.
 Lu target irradiated with 0.4-, 1.3-, 2.2-, and 3.0-GeV protons
Lu target irradiated with 0.4-, 1.3-, 2.2-, and 3.0-GeV protonsTakeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.207 - 212, 2022/03
Prediction of nuclide production of spallation products by high-energy proton injection plays a fundamental and important role in shielding design of high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as accelerator driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS). Since the prediction accuracy of the nuclear reaction models used in the production quantity prediction simulation is insufficient, it is necessary to improve the nuclear reaction models. We have measured nuclide production cross sections for various target materials with the aim of acquiring experimental data and improving nuclear reaction models. In this study, 1.3-, 2.2- and 3.0-GeV proton beams were irradiated to  Lu target, and nuclide production cross-section data were acquired by the activation method. The measured data were compared with several nuclear reaction models used in Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes to grasp the current prediction accuracy and to study how the nuclear reaction model could be improved.
Lu target, and nuclide production cross-section data were acquired by the activation method. The measured data were compared with several nuclear reaction models used in Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes to grasp the current prediction accuracy and to study how the nuclear reaction model could be improved.
Takeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.30 - 41, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:65.59(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nuclide production cross sections for proton-induced reactions on Mn and Co at incident energies of 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV were measured by the activation method at the J-PARC. In total, 143 production cross sections of reaction products were obtained. Among them, the cross sections of  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) S and
S and  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
 beam with orifice in J-PARC front-end
beam with orifice in J-PARC front-endShibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Nammo, Kesao*; Liu, Y.*; Otani, Masashi*; Naito, Fujio*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Okabe, Kota; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011010_1 - 011010_6, 2021/03
Together with the intensity upgrade in J-PARC Linac Front-End, improvement of RFQ transmission ratio is an important task. This RFQ transmission ratio depends strongly upon the solenoid current settings in the low energy beam transport line (LEBT). In the present study, high beam current cases (72 mA and 88 mA H beam current in LEBT) are investigated at a test-stand. Phase space distributions of the H
beam current in LEBT) are investigated at a test-stand. Phase space distributions of the H beam particles at the RFQ entrance are measured and compared with numerical results by Particle-In-Cell simulation. As a result, it has been clarified that a 15 mm
beam particles at the RFQ entrance are measured and compared with numerical results by Particle-In-Cell simulation. As a result, it has been clarified that a 15 mm  orifice for differential pumping of H
orifice for differential pumping of H gas coming from the ion source plays a role as a collimator in these beam conditions. This leads to change the beam emittance and Twiss parameters at the RFQ entrance. Especially in the condition with the beam current up to 88 mA in LEBT, the beam collimation contributes to optimize the phase space distribution to the RFQ acceptance with relatively low solenoid current settings. As a higher solenoid current setting would be necessary to suppress the beam expansion due to high space charge effect, these results suggest that current-saving of the solenoids can be possible even in the higher beam intensity operations.
gas coming from the ion source plays a role as a collimator in these beam conditions. This leads to change the beam emittance and Twiss parameters at the RFQ entrance. Especially in the condition with the beam current up to 88 mA in LEBT, the beam collimation contributes to optimize the phase space distribution to the RFQ acceptance with relatively low solenoid current settings. As a higher solenoid current setting would be necessary to suppress the beam expansion due to high space charge effect, these results suggest that current-saving of the solenoids can be possible even in the higher beam intensity operations.
Takeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011045_1 - 011045_6, 2021/03
To improve accuracy of nuclear design of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems, nuclide production cross sections on Ni and Zr, which were candidate materials to be used in ADS, were measured for GeV energy protons. The measured results were compared with PHITS calculations and JENDL/HE-2007.
Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kawane, Yusuke; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Miura, Akihiko; Morishita, Takatoshi; Sawabe, Yuki; Sugimura, Takashi*; Naito, Fujio*; Fang, Z.*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.944 - 947, 2015/09
Two RF-deflecting cavities as a chopper and a beam scraper have been used in the MEBT1 between a 324 MHz RFQ and a 50-MeV DTL of the J-PARC Linac. We replaced with a newly fabricated RF chopper to decrease beam loss for the operation with 50 mA. We installed two new scrapers to absorb the higher power of the deflected beam by the RF chopper. This paper describes the RF chopper system and beam irradiation test results of the scraper.
Oguri, Hidetomo; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ao, Hiroyuki; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.389 - 393, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Kenji; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Seki, Masakazu; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; Naoe, Takashi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Tatsumoto, Hideki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-039, 121 Pages, 2012/03
This report investigates the behavior, damage and restoration of a neutron source station of the MLF at the Great East Japan Earthquake and verified the safety design for emergency accidents in the neutron source station. In the MLF, after an occurrence of the Earthquake, strong quakes were detected at the instruments, the external power supply was lost, all of the circulators shut down automatically, and the hydrogen gas was released. The leakages of mercury, hydrogen and radio-activation gases did not occur. While, the quakes made gaps between the shield blocks and ruptured external pipe lines by subsidence around the building. But significant damages to the components were not found though the pressure drop of compressed air lines influenced on a target trolley lock system and so on. These results substantiated the validity of the safety design for emergency accidents in the source station, and suggested several points of improvement.
Sakai, Kenji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Takada, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Seki, Masakazu; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of 20th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-20) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/03
This report investigates behaviors and damages of each component in a neutron target station of the MLF at the J-PARC at the time of the Great East Japan Earthquake (GEJE). At the date of the GEJE, in the MLF, strong quakes were detected at several instruments, an external power supply were lost, all of the circulation systems were shut down automatically, and a hydrogen gas was released as planned. Leakage of activation liquids and gases did not occur. While, the quakes made gaps between shield blocks and ruptured external pipe lines for air and water by subsidence. But significant damages on the components of the target station were not found though a loss of compressed air supply affected lock systems with air cylinders and pneumatic operation values. These results substantiated a validity of safety design on the target station for emergency accidents.
 and TbVO
and TbVO under high pressure
under high pressureBizen, Daisuke*; Nakao, Hironori*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Fujioka, Jun*; Yasue, Toshio*; Miyasaka, Shigeki*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(2), p.024715_1 - 024715_6, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.8(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic phase diagrams for  VO
VO (
( = Y, Tb) were determined by low temperature and high pressure neutron-diffraction techniques. We found that the magnetic ground state in TbVO
= Y, Tb) were determined by low temperature and high pressure neutron-diffraction techniques. We found that the magnetic ground state in TbVO changes from
changes from 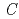 -type spin ordering (
-type spin ordering (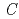 -SO) to
-SO) to  -type spin ordering (
-type spin ordering ( -SO) on application of pressure. The transition of the magnetic ground state also indicates that the ground state of the orbital ordering changes from
-SO) on application of pressure. The transition of the magnetic ground state also indicates that the ground state of the orbital ordering changes from  -type orbital ordering (
-type orbital ordering ( -OO) to
-OO) to 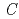 -type orbital ordering (
-type orbital ordering (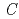 -OO). In YVO
-OO). In YVO , the
, the  -SO and
-SO and 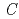 -OO phases set in simultaneously up to 6.2 GPa, and the disorder-[
-OO phases set in simultaneously up to 6.2 GPa, and the disorder-[ -SO,
-SO, 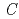 -OO] phase transition appears above 6 GPa. This is the first observation of a simultaneous spin and orbital order-disorder phase transition in perovskite-type transition-metal oxides
-OO] phase transition appears above 6 GPa. This is the first observation of a simultaneous spin and orbital order-disorder phase transition in perovskite-type transition-metal oxides  MO
MO . The [
. The [ -SO,
-SO, 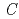 -OO] phase is strongly stabilized with increasing pressure, and both the covalency effect and the superexchange interaction play roles in this stabilization.
-OO] phase is strongly stabilized with increasing pressure, and both the covalency effect and the superexchange interaction play roles in this stabilization.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Aizawa, Kazuya; Suzuya, Kentaro; Shibata, Kaoru; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.B), p.SB028_1 - SB028_6, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:125 Percentile:95.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)AMATERAS is a cold-neutron disk-chopper spectrometer in MLF, J-PARC. The construction of main part of the spectrometer has been completed in spring of 2009. Soon after that, we have started the commissioning work on AMATERAS. The performance of AMATERAS has been examined by test experiments in the course of commissioning. In parallel to these works, we have started the user program on AMATERAS from December 2009 and we are getting scientific results from our spectrometer. In this presentation, we will report the current status of AMATERAS including the results of performance tests and some of examples of scientific outputs.
Maekawa, Fujio; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Teshigawara, Makoto; Kai, Tetsuya; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Takada, Hiroshi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 620(2-3), p.159 - 165, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:97.59(Instruments & Instrumentation)The J-PARC 1-MW pulsed spallation neutron source JSNS was successfully launched on 30th of May 2008. To demonstrate the unique features of the moderator design and the neutronic performance of JSNS the neutron spectral intensity, absolute neutron flux, and time structure of the neutron pulse shapes etc have been measured using several neutron instruments since then. The measured energy spectra clearly revealed the feature of the para-hydrogen, as expected when designing the moderator. The measured neutron flux below 0.4 eV agreed with the corresponding design value within  20%, thus suggesting that the JSNS design calculations to have been reliable. World-class high-resolution diffraction data could be recorded due to the suitability of design of the moderators and the instruments. Another world-class high-intensity neutron flux was also capable of being demonstrated due to the unique design of the large cylindrical coupled moderator.
20%, thus suggesting that the JSNS design calculations to have been reliable. World-class high-resolution diffraction data could be recorded due to the suitability of design of the moderators and the instruments. Another world-class high-intensity neutron flux was also capable of being demonstrated due to the unique design of the large cylindrical coupled moderator.
Maekawa, Fujio; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Kai, Tetsuya; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Watanabe, Noboru*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-19) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/07
Efforts have been made to characterize neutronic performance of JSNS. A NOBORU instrument was mainly used for this purpose while some other instruments were used when needed. The followings were confirmed. (1) Judging from a measured spectral shape, a para-hydrogen fraction in the hydrogen moderator was very close to unity as expected due to introduction of catalyst in a hydrogen circulation system. (2) Measured data for absolute spectral intensity and pulse shapes agreed very well with simulation calculations, and suggested adequacy of the neutron source designs. (3) The world's highest resolution of 0.035 % was recorded at the powder diffractometer SuperHRPD. (4) A total neutron flux of 3  10
10 n/s/cm
n/s/cm was confirmed at the chopper instrument 4SEASONS when it was normalized to 1 MW. The flux is the world's highest among existing spallation neutron sources, and is comparable to fluxes at intense reactor sources even in time-averaged value.
was confirmed at the chopper instrument 4SEASONS when it was normalized to 1 MW. The flux is the world's highest among existing spallation neutron sources, and is comparable to fluxes at intense reactor sources even in time-averaged value.
Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Watanabe, Noboru*
Proceedings of 19th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-19) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/07
To validate the neutronics design of JSNS, we measured neutron spectra at all available neutron beam lines by CTOF method. Measured values were in good agreement with evaluated ones for beam lines without guide tubes. Some discrepancies in spectral intensity were found in some of beam lines using a neutron guide tube. This result indicates that the CTOF method is very effective for checking initial installation of beam lines because neutron spectral intensity can be measured systematically in a short time. Furthermore, by measuring neutron spectral intensity with the CTOF method, we studied change of neutronic performance due to changes of operation conditions of JSNS such as incident proton beam conditions (position, profile and energy) and moderator temperature. These operation parameter dependences on neutronic performance were compared with calculated ones, and confirmed good agreements between them. This indicated reliability of neutronics design of JSNS.
Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Oi, Motoki; Kai, Tetsuya; Sakai, Kenji; Maekawa, Fujio; Watanabe, Noboru*; Shinohara, Takenao; Takata, Shinichi
Proceedings of 19th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2010/07
A neutron beam line NOBORU built at MLF in J-PARC is suitable for imaging experiments due to a large beam size, a short distance from the moderator to the sample position and an adequate experimental room. In order to evaluate suitability for the imaging experiments, we measured neutron spectral intensities and flux distributions at the sample position of NOBORU. We also measured those quantities with use of some filters, collimators and slits equipped on NOBORU. As preliminary experiments for imaging, we measured Bragg edge transmission of some alloys and resonance absorption of some elements. The result showed welded and non-welded areas in an alloy could be clearly distinguished by the Bragg edge transmission. It was also found that several elements in the sample could be distinguished clearly by the resonance absorption method. It could be concluded that NOBORU was very suitable for the imaging experiments at J-PARC.