Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oikawa, Kenichi; Sato, Hirotaka*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Su, Y. H.; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Hasemi, Hiroyuki
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012013_1 - 012013_6, 2023/10
Osawa, Takahito; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Wada, Taiga*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Terada, Kentaro*; et al.
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 7(4), p.699 - 711, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:92.07(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The concentrations of carbon and other major elements in asteroid samples provide very important information on the birth of life on the Earth and the solar-system evolution. Elemental analysis using muonic X-rays is one of the best analytical methods to determine the elemental composition of solid materials, and notably, is the only method to determine the concentration of light elements in bulk samples in a non-destructive manner. We developed a new analysis system using muonic X-rays to measure the concentrations of carbon and other major elements in precious and expectedly tiny samples recovered from the asteroid Ryugu by spacecraft Hayabusa2. Here we report the development process of the system in 4 stages and their system configurations, The analysis system is composed of a stainless-steel analysis chamber, an acrylic glove box for manipulating asteroid samples in a clean environment, and Ge semiconductor detectors arranged to surround the analysis chamber. The performance of the analysis system, including the background level, which is crucial for the measurement, was greatly improved from the first stage to the later ones. Our feasibility study showed that the latest model of our muonic X-ray analysis system is capable of determining the carbon concentration in Hayabusa2's sample model with an uncertainty of less than 10 percent in a 6-day measurement.
 Fe
Fe intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundCao, Y.*; Zhou, H.*; Khmelevskyi, S.*; Lin, K.*; Avdeev, M.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Wang, B.*; Hu, F.*; Kato, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 35(8), p.3249 - 3255, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:45.8(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrostatic and chemical pressure are efficient stimuli to alter the crystal structure and are commonly used for tuning electronic and magnetic properties in materials science. However, chemical pressure is difficult to quantify and a clear correspondence between these two types of pressure is still lacking. Here, we study intermetallic candidates for a permanent magnet with a negative thermal expansion (NTE). Based on in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, negative chemical pressure is revealed in Ho Fe
Fe on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Abe, Yutaka*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:99.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
Akuzawa, Tadashi*; Kim, S.-Y.*; Kubota, Masahiko*; Wu, H.*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Arai, Tsuyoshi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(12), p.5851 - 5858, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:66.21(Chemistry, Analytical) Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg
O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain
chainFujihara, Masayoshi; Jeschke, H. O.*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(11), p.114408_1 - 114408_8, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)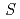 = 1/2 Heisenberg
= 1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd
chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and
O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and  SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the
SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the 
 -
-
 antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions
antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions 
 and
and 
 are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of
are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of 
 is two to three times larger than that of
is two to three times larger than that of 
 , thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of
, thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of 
 . The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K (
. The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K ( 0.036
0.036 
 ), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Jeon, H.*; Hou, Y.*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Aze, Takahiro*; Miyairi, Yosuke*; Yokoyama, Yusuke*; Ogawa, Hiroshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 527, p.1 - 6, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The measurement the radiocarbon of dissolved organic matter (DO C) in seawater can provide information about a timescale of the dynamics of dissolved organic matter as well as about its sources in the ocean. Due to the low DOC concentration in seawater, in spite of the development of accelerator mass spectrometry, a relatively large volume of seawater (
C) in seawater can provide information about a timescale of the dynamics of dissolved organic matter as well as about its sources in the ocean. Due to the low DOC concentration in seawater, in spite of the development of accelerator mass spectrometry, a relatively large volume of seawater ( 1 L) is required for that analysis. In addition, complicated processing such as UV irradiation that emits high heat is required. In this study, we have developed a safer and easier method to analyze DO
1 L) is required for that analysis. In addition, complicated processing such as UV irradiation that emits high heat is required. In this study, we have developed a safer and easier method to analyze DO C in seawater than the conventional method. A particularly significant change was the adoption of a low-pressure mercury lamp in the decomposition system, which enabled direct decomposition of organic matter at lower temperatures. We also propose a method to quantitatively evaluate the accuracy of this system by analyzing simulated seawater consists of a soluble reference material of organic matter and sodium chloride. This method is expected to be applied not only to carbon isotope ratio analysis but also to analysis of trace elements and isotopes of various dissolved organic substances.
C in seawater than the conventional method. A particularly significant change was the adoption of a low-pressure mercury lamp in the decomposition system, which enabled direct decomposition of organic matter at lower temperatures. We also propose a method to quantitatively evaluate the accuracy of this system by analyzing simulated seawater consists of a soluble reference material of organic matter and sodium chloride. This method is expected to be applied not only to carbon isotope ratio analysis but also to analysis of trace elements and isotopes of various dissolved organic substances.
Nguyen, T. H.*; Le Ba, T.*; Tran, C. T.*; Nguyen, T. T.*; Doan, T. T. T.*; Do, V. K.; Watanabe, Masayuki; Pham, Q. M.*; Hoang, S. T.*; Nguyen, D. V.*; et al.
Hydrometallurgy, 213, p.105933_1 - 105933_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:81.6(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)A continuous counter-current extraction for the selective recovery of thorium (Th) and uranium (U) from the Yen Phu (Vietnam) rare earth concentrate leach solutions was systematically studied. The primary amine N1923 was used as an extractant which was prepared in the isoparaffin IP-2028 diluent. Thorium and uranium were selectively recovered in a hydrometallurgical circuit established by continuous mixer-settler extraction, scrubbing, and back-extraction at the laboratory scale. The desired purity of Th and U can be achieved by managing the volume ratio of organic to aqueous phase (O/A ratio) in the corresponding steps. Highly pure Th and U were recovered from the pregnant back-extraction liquor and the raffinate, respectively, which have satisfactory properties for further processing of the subsequent nuclear materials.
Endo, Shunsuke; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Zen, H.*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Omer, M.; Kawamura, Shiori*; Abe, Ryota*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*
UVSOR-49, P. 38, 2022/08
Sasada, Seiji*; Takahashi, Yoshihito*; Takeuchi, Keisuke*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Shinohara, Takenao; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Uritani, Akira*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 61(4), p.046004_1 - 046004_8, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:80.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Saito, Shimpei*; De Rosis, A.*; Fei, L.*; Luo, K. H.*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Kaneko, Akiko*; Abe, Yutaka*
Physics of Fluids, 33(2), p.023307_1 - 023307_21, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:98.3(Mechanics)A Boiling phenomenon in a liquid flow field is known as forced-convection boiling. We numerically investigated the boiling system on a cylinder in a flow at a saturated condition. To deal with such a phenomenon, we developed a numerical scheme based on the pseudopotential lattice Boltzmann method. The collision was performed in the space of central moments (CMs) to enhance stability for high Reynolds numbers. Furthermore, additional terms for thermodynamic consistency were derived in a CMs framework. The effectiveness of the model was tested against some boiling processes, including nucleation, growth, and departure of a vapor bubble for high Reynolds numbers. Our model can reproduce all the boiling regimes without the artificial initial vapor phase. We found that the Nukiyama curve appears even though the focused system is the forced-convection system. Also, our simulations support experimental observations of intermittent direct solid-liquid contact even in the film-boiling regime.
Ratliff, H.; Matsuda, Norihiro; Abe, Shinichiro; Miura, Takamitsu*; Furuta, Takuya; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 484, p.29 - 41, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:81.27(Instruments & Instrumentation) Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy
scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopyFujimori, Kosuke*; Kitaura, Mamoru*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Fujimoto, Masaki*; Zen, H.*; Watanabe, Shinta*; Kamada, Kei*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Kato, Masahiro*; Hosaka, Masahito*; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 13(8), p.085505_1 - 085505_4, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:32.24(Physics, Applied)To clarify the existence of cation vacancies in Ce-doped Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O (Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y
(Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y Al
Al O
O , the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg
, the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
Fujihara, Masayoshi*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Mole, R.*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Toyama, Takami*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Yu, D.*; Sota, Shigetoshi*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3429_1 - 3429_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:92.14(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targets
Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targetsSun, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Aikawa, Masayuki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; Kawakami, Shunsuke*; Koyama, Shumpei*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064623_1 - 064623_12, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:51.79(Physics, Nuclear)The spallation and fragmentation reactions of  Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
 F from
F from  O
O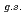 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:73.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 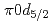 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O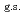 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
 Np and
Np and  Am by accelerator-driven system at Kyoto University Critical Assembly
Am by accelerator-driven system at Kyoto University Critical AssemblyPyeon, C. H.*; Yamanaka, Masao*; Oizumi, Akito; Fukushima, Masahiro; Chiba, Go*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Van Rooijen, W. G.*; Hashimoto, Kengo*; Sakon, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(8), p.684 - 689, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:79.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study demonstrates, for the first time, the principle of nuclear transmutation of minor actinide (MA) by the accelerator-driven system (ADS) through the injection of high-energy neutrons into the subcritical core at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly. The main objective of the experiments is to confirm fission reactions of neptunium-237 ( Np) and americium-241 (
Np) and americium-241 ( Am), and capture reactions of
Am), and capture reactions of  Np. Subcritical irradiation of
Np. Subcritical irradiation of  Np and
Np and  Am foils is conducted in a hard spectrum core with the use of the back-to-back fission chamber that obtains simultaneously two signals from specially installed test (
Am foils is conducted in a hard spectrum core with the use of the back-to-back fission chamber that obtains simultaneously two signals from specially installed test ( Np or
Np or  Am) and reference (uranium-235) foils. The first nuclear transmutation of
Am) and reference (uranium-235) foils. The first nuclear transmutation of  Np and
Np and  Am by ADS soundly implemented by combining the subcritical core and the 100 MeV proton accelerator, and the use of a lead-bismuth target, is conclusively demonstrated through the experimental results of fission and capture reaction events.
Am by ADS soundly implemented by combining the subcritical core and the 100 MeV proton accelerator, and the use of a lead-bismuth target, is conclusively demonstrated through the experimental results of fission and capture reaction events.