Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shibata, Motoki*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Abe, Jun*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Shibayama, Mitsuhiro*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; et al.
Polymer Journal, 55(11), p.1165 - 1170, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.7(Polymer Science)
 H
H O
OFujihara, Masayoshi; Hagihara, Masato; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Murai, Naoki; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*
Physical Review B, 107(5), p.054435_1 - 054435_8, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The  = 1/2 Heisenberg linear chain antiferromagnet is the simplest spin model; nevertheless it serves as a platform for various quantum many-body phenomena. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of a quasi-one-dimensional antiferromagnet KCuPO
= 1/2 Heisenberg linear chain antiferromagnet is the simplest spin model; nevertheless it serves as a platform for various quantum many-body phenomena. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of a quasi-one-dimensional antiferromagnet KCuPO
 H
H O. A long-range commensurate antiferromagnetic order with ordered moment 0.31(1)
O. A long-range commensurate antiferromagnetic order with ordered moment 0.31(1) 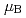 per spin occurs at
per spin occurs at 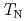 = 11.7(1) K. Above
= 11.7(1) K. Above 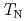 , the inelastic neutron excitation is characterized by a two spinon continuum. The intrachain interaction
, the inelastic neutron excitation is characterized by a two spinon continuum. The intrachain interaction  and interchain interaction
and interchain interaction 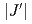 are estimated to be 172 K and 4.25(4) K, respectively; thus the ratio of the
are estimated to be 172 K and 4.25(4) K, respectively; thus the ratio of the 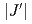 /
/ = 0.0247(3). At lower energies, below
= 0.0247(3). At lower energies, below 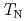 , a spin gap is observed in the dispersive excitations. These results are consistent with characteristics observed in weakly interacting
, a spin gap is observed in the dispersive excitations. These results are consistent with characteristics observed in weakly interacting  = 1/2 Heisenberg chain system.
= 1/2 Heisenberg chain system.
Saha, P. K.; Okabe, Kota; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Fumihiko; Okita, Hidefumi; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1 - 5, 2023/01
 Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg
O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain
chainFujihara, Masayoshi; Jeschke, H. O.*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(11), p.114408_1 - 114408_8, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)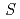 = 1/2 Heisenberg
= 1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd
chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and
O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and  SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the
SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the 
 -
-
 antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions
antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions 
 and
and 
 are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of
are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of 
 is two to three times larger than that of
is two to three times larger than that of 
 , thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of
, thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of 
 . The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K (
. The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K ( 0.036
0.036 
 ), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Saha, P. K.; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Okabe, Kota; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Fujirai, Kosuke; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Suganuma, Kazuaki
EPJ Techniques and Instrumentation (Internet), 8(1), p.9_1 - 9_9, 2021/07
The 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex supplies a high-intensity proton beam for neutron experiments. Various parameters are monitored to achieve a stable operation, and it was found that the oscillations of the charge-exchange efficiency and cooling water temperature were synchronized. We evaluated the orbit fluctuations at the injection point using a beam current of the injection dump, which is proportional to the number of particles that miss the foil and fail in the charge exchange, and profile of the injection beam. The total width of the fluctuations was approximately 0.072 mm. This value is negligible from the user operation viewpoint as our existing beam position monitors cannot detect such a small signal deviation. This displacement corresponds to a 1.63 10
10 variation in the dipole magnetic field. Conversely, the magnetic field variation in the L3BT dipole magnet, which was estimated by the temperature change directly, is 4.08
variation in the dipole magnetic field. Conversely, the magnetic field variation in the L3BT dipole magnet, which was estimated by the temperature change directly, is 4.08 10
10 . This result suggested that the change in the cooling water temperature is one of the major causes of the efficiency fluctuation.
. This result suggested that the change in the cooling water temperature is one of the major causes of the efficiency fluctuation.
Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kai, Tetsuya; Nakatani, Takeshi; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; Watanabe, Akihiko*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011151_1 - 011151_6, 2021/03
For safely and efficiently operating a spallation neutron source and a muon target, a general control system (GCS) operates within Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF), GCS administers operation processes and interlocks of many instruments for various operation statuses. It consists of several subsystems such as an integral control system (ICS), interlock systems (ILS), shared servers, network system, and timing distribution system (TDS). Although GCS is an independent system that controls the target stations, it works closely with the control systems of other facilities in J-PARC. Since the first beam injection in 2008, GCS has operated stably without any serious troubles after modification based on commissioning for operation and control. Then, significant improvements in GCS such as upgrade of ICS by changing its framework software and function enhancement of ILS were proceeded until 2015, in considering sustainable long-term operation and maintenance. In recent years, many instruments in GCS have replaced due to end of production and support of them. In this way, many modifications have been proceeded in the entire GCS after start of beam operation. Under these situation, it is important to comprehend upgrade history and present status of GCS in order to decide its upgrade plan for the coming ten years. This report will mention upgrade history, present status and future agenda of GCS.
 beam with orifice in J-PARC front-end
beam with orifice in J-PARC front-endShibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Nammo, Kesao*; Liu, Y.*; Otani, Masashi*; Naito, Fujio*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Okabe, Kota; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011010_1 - 011010_6, 2021/03
Together with the intensity upgrade in J-PARC Linac Front-End, improvement of RFQ transmission ratio is an important task. This RFQ transmission ratio depends strongly upon the solenoid current settings in the low energy beam transport line (LEBT). In the present study, high beam current cases (72 mA and 88 mA H beam current in LEBT) are investigated at a test-stand. Phase space distributions of the H
beam current in LEBT) are investigated at a test-stand. Phase space distributions of the H beam particles at the RFQ entrance are measured and compared with numerical results by Particle-In-Cell simulation. As a result, it has been clarified that a 15 mm
beam particles at the RFQ entrance are measured and compared with numerical results by Particle-In-Cell simulation. As a result, it has been clarified that a 15 mm  orifice for differential pumping of H
orifice for differential pumping of H gas coming from the ion source plays a role as a collimator in these beam conditions. This leads to change the beam emittance and Twiss parameters at the RFQ entrance. Especially in the condition with the beam current up to 88 mA in LEBT, the beam collimation contributes to optimize the phase space distribution to the RFQ acceptance with relatively low solenoid current settings. As a higher solenoid current setting would be necessary to suppress the beam expansion due to high space charge effect, these results suggest that current-saving of the solenoids can be possible even in the higher beam intensity operations.
gas coming from the ion source plays a role as a collimator in these beam conditions. This leads to change the beam emittance and Twiss parameters at the RFQ entrance. Especially in the condition with the beam current up to 88 mA in LEBT, the beam collimation contributes to optimize the phase space distribution to the RFQ acceptance with relatively low solenoid current settings. As a higher solenoid current setting would be necessary to suppress the beam expansion due to high space charge effect, these results suggest that current-saving of the solenoids can be possible even in the higher beam intensity operations.
Okabe, Kota; Liu, Y.*; Otani, Masashi*; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Chimura, Motoki*; Hirano, Koichiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kinsho, Michikazu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011011_1 - 011011_6, 2021/03
To realize more stable operation of the J-PARC accelerators, we have a re-design plan of an MEBT1 (Medium Energy Beam Transport). At the J-PARC Linac, the MEBT1 has transverse and longitudinal beam matching section for the DTLs. However there are some locally activated spots in DTL area at the current beam power level. To reduce beam loss during a beam acceleration at the DTLs is a most important task for a stable user operation. The first thing we should do is investigation a connection between beam quality in the MEBT1 and parameters of the upstream hardware. In this presentation, we will report a high intensity beam study results at the MEBT1.
Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Teshigawara, Makoto; Naoe, Takashi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Watanabe, Akihiko*
Journal of Neutron Research, 22(2-3), p.337 - 343, 2020/10
For operating a spallation neutron source and a muon target safely and efficiently, a general control system (GCS) operates within Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF). GCS administers operation and interlock processes of many instruments under various operation status. Since the first beam injection in 2008, it has operated stably without any serious troubles for more than ten years. GCS has a data storage server storing operational data on status around target stations. It has functioned well to detect and investigate unusual situations by checking data in this server. For continuing stable operation of MLF in future, however, introduction of abnormality sign determination system (ASDS) will be necessary for picking up potential abnormalities of target stations caused by radiation damages, time-related deterioration and so on. It will judge abnormalities from slight state transitions of target stations based on analysis with various operational data throughout proton beams, target stations, and secondary beams during long-term operations. This report mentions present status of GCS, conceptual design of ASDS, and installation of an integral data storage server which can deal with various data for ASDS integrally.
Fujihara, Masayoshi*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Mole, R.*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Toyama, Takami*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Yu, D.*; Sota, Shigetoshi*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3429_1 - 3429_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:90.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kamiya, Junichiro; Okabe, Kota; Kinsho, Michikazu; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Yamada, Ippei; Ogiwara, Norio*; Hikichi, Yusuke*; Wada, K.*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012149_1 - 012149_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:82.33(Physics, Particles & Fields)To obtain a getter effect to titanium vacuum duct surface, the method to remove the oxide on the surface by sputtering with ionized molecules has been developed. In the method, a sheet-shaped gas distribution with a uniform and high density is generated through a narrow slit by a small amount of gas. In this report, the gas density distribution was calculated by the Monte Carlo simulation code. As a result, it was found that a gas injection from both directions was effective to generate uniform density distribution. Furthermore, the gas injection method was applied to a non-destructive beam profile monitor, that detects ions generated by the interaction between gas molecules and beam. In this monitor, dependence of the beam profile on the injected gas amount was measured. A small amount of injected gas was found to be ideal for the beam profile measurements in the unsaturated and a high S/N ratio region.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.28(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Okabe, Kota; Kamiya, Junichiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012113_1 - 012113_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Particles & Fields)All holes on the chamber walls of synchrotrons should be filled with the radiofrequency (RF)-shields to suppress coupling impedances that excite beam instabilities. In a synchrotron, titanium nitride (TiN)-coated RF-shields are installed with collimators. If the holes, through which the collimator jaw enters and exits the chamber, are filled with such RF-shields, the shields may break down as the dynamic coefficient of TiN increases in vacuum. At the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), the RF-shields are eliminated from the collimator after demonstrating that the effect due to the RF-shields is negligible on the impedance at low frequencies.
Chimura, Motoki*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Okabe, Kota; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.728 - 732, 2019/07
The increase of space charge effect in high intensity beam causes the increase of the beam-loss. Beam loss limits beam intensity for accelerator equipment activation. Therefore, it is important to suppress the emittance growth due to the space charge effect. I focused on the low energy region in the linac where the space charge effect becomes remarkable. In order to identify the origin of the emittance growth due to the effect, a simulation was performed with a 3-D particle-in-cell simulation code, and evaluated the influence of the effects in the J-PARC medium energy beam transport line (MEBT1) entrance to DTL exit. As a result, it was confirmed that distortion of phase space distribution occurred due to nonlinear space charge force and that leading to emittance growth. I proposed to suppress the emittance growth by using an octupole magnet that gives nonlinear force to the beam. We report the new method and simulation results.
Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Okabe, Kota; Kamiya, Junichiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.163 - 166, 2019/06
All holes on the chamber walls of synchrotrons should be filled with the radiofrequency (RF)-shields to suppress coupling impedances that excite beam instabilities. In a synchrotron, titanium nitride (TiN)-coated RF-shields are installed with collimators. If the holes, through which the collimator jaw enters and exits the chamber, are filled with such RF-shields, the shields may break down as the dynamic coefficient of TiN increases in vacuum. At the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), the RF-shields are eliminated from the collimator after demonstrating that the effect due to the RF-shields is negligible on the impedance at low frequencies.
Moriya, Katsuhiro; Okabe, Kota; Liu, Y.*; Miura, Akihiko; Futatsukawa, Kenta*
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1081 - 1083, 2017/12
no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Asano, Hiroyuki*; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Ishiyama, Tatsuya; Ito, Takashi; Kawane, Yusuke; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Meigo, Shinichiro; Miura, Akihiko; et al.
Proceedings of 28th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2016) (Internet), p.298 - 300, 2017/05
We have constructed a linac for development of various accelerator components at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the RFQ is a used one in the J-PARC linac. The beam energy is 3 MeV and nominal beam current is 30 mA. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and the first development program, laser-charge-exchange experiment for the transmutation experimental facility, has been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Hirano, Koichiro; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ishiyama, Tatsuya; Ito, Takashi; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kawane, Yusuke; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Sato, Yoshikatsu; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.310 - 313, 2016/11
We have used a beam scraper with the incident angle of 65deg to reduce the beam power deposition density in the MEBT between a 324 MHz RFQ and a 50-MeV DTL of the J-PARC linac. The 65 scraper was irradiated by the H
scraper was irradiated by the H beam up to particle number of 1.47E22. We observed a lot of surface projections with several hundred micrometers high in the beam irradiation damage on the scraper by using the laser microscope. In order to study the limits of scrapers, we constructed a new 3 MeV linac at J-PARC. We will conduct the scraper irradiation test at the end of this year.
beam up to particle number of 1.47E22. We observed a lot of surface projections with several hundred micrometers high in the beam irradiation damage on the scraper by using the laser microscope. In order to study the limits of scrapers, we constructed a new 3 MeV linac at J-PARC. We will conduct the scraper irradiation test at the end of this year.