Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Masato; Nakamichi, Shinya; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Ishii, Katsunori
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(2), p.51 - 58, 2023/04
Uranium and Plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) pellets used as fast reactor fuels have been produced from several raw materials by mechanical blending method through processes of ball milling, additive blending, granulation, pressing, sintering and so on. It is essential to control the pellet density which is one of the important fuel specifications, but it is difficult to understand relationships among many parameters in the production. Database for MOX production was prepared from production results in Japan, and input data of eighteen types were chosen from production process and made a data set. Machine learning model to predict sintered density of MOX pellet was derived by gradient boosting regressor, and represented the measured sintered density with coefficient of determination of R =0.996
=0.996
 ceramics
ceramicsVauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Ceramics International, 49(2), p.3058 - 3065, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:75.06(Materials Science, Ceramics) (001) surface with supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beam
(001) surface with supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beamKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Inami, Eiichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abe, Masayuki*
Vacuum and Surface Science, 65(11), p.526 - 530, 2022/11
The oxidation of oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO (001) was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic O
(001) was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic O beam (SSMB). The oxygen vacancies at the top surface and subsurface could be eliminated by the supply of hyperthermal oxygen molecules. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO
beam (SSMB). The oxygen vacancies at the top surface and subsurface could be eliminated by the supply of hyperthermal oxygen molecules. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO (001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the ambient condition, could also be effectively eliminated by using oxygen SSMB. This result is promising as a surface processing for various functional oxides.
(001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the ambient condition, could also be effectively eliminated by using oxygen SSMB. This result is promising as a surface processing for various functional oxides.
Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
Maeyama, Shinya*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Asahi, Yuichi; Ishizawa, Akihiro*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.3166_1 - 3166_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:93.39(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Turbulent transport is a key physics process for confining magnetic fusion plasma. Recent theoretical and experimental studies of existing fusion experimental devices revealed the existence of cross-scale interactions between small (electron)-scale and large (ion)-scale turbulence. Since conventional turbulent transport modelling lacks cross-scale interactions, it should be clarified whether cross-scale interactions are needed to be considered in future experiments on burning plasma, whose high electron temperature is sustained with fusion-born alpha particle heating. Here, we present supercomputer simulations showing that electron scale turbulence in high electron temperature plasma can affect the turbulent transport of not only electrons but also fuels and ash. Electron-scale turbulence disturbs the trajectories of resonant electrons responsible for ion-scale micro-instability and suppresses large-scale turbulent fluctuations. Simultaneously, ion-scale turbulent eddies also suppress electron-scale turbulence. These results indicate a mutually exclusive nature of turbulence with disparate scales. We demonstrate the possibility of reduced heat flux via cross-scale interactions.
 (001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beam
(001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beamKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Takayanagi, Shuhei*; Ojima, Shoki*; Maeda, Motoyasu*; Origuchi, Naoki*; Ogawa, Arata*; Ikeda, Natsuki*; Aoyagi, Yoshihide*; Kabutoya, Yuito*; et al.
Langmuir, 37(42), p.12313 - 12317, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the oxidation of oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO (001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO
(001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO (001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
(001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:79.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Watanabe, Takahiro; Ishii, Chikako; Ishizaka, Chika; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sawai, Yuki*; Tsuchiya, Noriyoshi*; Matsunaka, Tetsuya*; Ochiai, Shinya*; Nara, Fumiko*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 116(3), p.140 - 158, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:51.59(Mineralogy)A portable energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (potable XRF) can be an effective tool for detecting chemical elements in various materials, such as geological, and environmental samples. In this study, working curves were confirmed using reference materials, such as igneous rocks and other geochemical standards, distributed by national and international organizations. Subsequently, quantification and semi-quantification analyses were performed by the portable XRF for inorganic elements in (A) fault rocks, (B) lake sediments from the middle Japan, and (C) soils with paleotsunami deposits from the Pacific coast of northeast Japan. Twenty-four elements (Mg-U) in these geological samples were measured by potable XRF using our working curves. Measured values by the portable XRF of the samples were good agreement with the reported values in almost cases.
Maeyama, Shinya*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*
Computer Physics Communications, 235, p.9 - 15, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:46.27(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)We have implemented the Sugama collision operator in the gyrokinetic Vlasov simulation code, GKV, with an implicit time-integration scheme. The new method is versatile and independent of the details of the linearized collision operator, by means of an operator splitting, an implicit time integrator, and an iterative Krylov subspace solver. Numerical tests demonstrate stable computation over the time step size restricted by the collision term. An efficient implementation for parallel computation on distributed memory systems is realized by using the data transpose communication, which makes the iterative solver free from inter-node communications during iteration. Consequently, the present approach achieves enhancement of computational efficiency and reduction of computational time to solution simultaneously, and significantly accelerates the total performance of the application.
Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Watanabe, Naoko*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Sakaguchi, Aya*; Fan, Q.*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Geochemical Journal, 52(2), p.173 - 185, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.3(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We analyzed riverbed sediments collected at two sites, Yamakiya and Kuroiwa, in Fukushima after the Fukushima accident. The size distributions of K, Rb, and  Csreflected the mineralogy of sediments, where primary host minerals for these alkali elements would be biotite, K-feldspar, and clay minerals. Silt-size fractions contained high
Csreflected the mineralogy of sediments, where primary host minerals for these alkali elements would be biotite, K-feldspar, and clay minerals. Silt-size fractions contained high  Cs and
Cs and  Cs concentrations possibly due to adsorption on clay minerals. Their concentrations decreased with particle size at the Yamakiya site. In contrast, coarse and very coarse sand fractions from the Kuroiwa site showed higher
Cs concentrations possibly due to adsorption on clay minerals. Their concentrations decreased with particle size at the Yamakiya site. In contrast, coarse and very coarse sand fractions from the Kuroiwa site showed higher  Cs and
Cs and  Cs concentrations in comparison to fine - medium sand fractions. The coarse sand fractions contained many weathered biotite grains. Overall, the size distributions of
Cs concentrations in comparison to fine - medium sand fractions. The coarse sand fractions contained many weathered biotite grains. Overall, the size distributions of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs were similar in the sediments, suggesting that the Fukushima-derived radiocesium was distributed into each particle size fraction in response to the distribution of the stable Cs that was controlled by mineralogical composition.
Cs were similar in the sediments, suggesting that the Fukushima-derived radiocesium was distributed into each particle size fraction in response to the distribution of the stable Cs that was controlled by mineralogical composition.
Maeyama, Shinya*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Nakata, Motoki*; Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Nunami, Masanori*
Nuclear Fusion, 57(6), p.066036_1 - 066036_10, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:65.83(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Multi-scale plasma turbulence including electron and ion temperature gradient (ETG/ITG) modes has been investigated by means of electromagnetic gyrokinetic simulations. Triad transfer analyses on nonlinear mode coupling reveal cross-scale interactions between electron and ion scales. One of the interactions is suppression of electron-scale turbulence by ion- scale turbulence, where ITG-driven short-wavelength eddies act like shear flows and suppress ETG turbulence. Another cross-scale interaction is enhancement of ion-scale turbulence in the presence of electron-scale turbulence. This is caused via short-wavelength zonal flows, which are created by the response of passing kinetic electrons in ITG turbulence, suppress ITG turbulence by their shearing, and are damped by ETG turbulence. In both cases, sub-ion-scale structures between electron and ion scales play important roles in the cross-scale interactions.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Maeyama, Shinya; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Nakata, Motoki; Nunami, Masanori*; Ishizawa, Akihiro*
Parallel Computing, 49, p.1 - 12, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:52.84(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)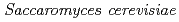
Onuki, Toshihiko; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Kozai, Naofumi; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Watanabe, Naoko*; Kozaki, Tamotsu*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 144, p.127 - 133, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:27.12(Environmental Sciences)The accumulation of Cs by unicellular fungus of 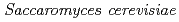 in the presence of minerals has been studied to elucidate the role of microorganisms in the migration of radioactive Cs in the environment. In the presence of minerals in the agar medium, the radioactivity in the yeast cells was in the order of mica
in the presence of minerals has been studied to elucidate the role of microorganisms in the migration of radioactive Cs in the environment. In the presence of minerals in the agar medium, the radioactivity in the yeast cells was in the order of mica  smectite, illite
smectite, illite 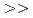 vermiculite, phlogopite, zeolite. This order is inversely correlated to the ratio of the concentration of radioactive Cs between the minerals and the medium solution. These results strongly suggest that the yeast accumulates radioactive Cs competitively with minerals.
vermiculite, phlogopite, zeolite. This order is inversely correlated to the ratio of the concentration of radioactive Cs between the minerals and the medium solution. These results strongly suggest that the yeast accumulates radioactive Cs competitively with minerals.
Maeyama, Shinya*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Nakata, Motoki*; Yagi, Masatoshi; Miyato, Naoaki; Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Nunami, Masanori*
Physical Review Letters, 114(25), p.255002_1 - 255002_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:92 Percentile:95.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Multiscale gyrokinetic turbulence simulations with the real ion-to-electron mass ratio and  value are realized for the first time, where the
value are realized for the first time, where the  value is given by the ratio of plasma pressure to magnetic pressure and characterizes electromagnetic effects on microinstabilities. Numerical analysis at both the electron scale and the ion scale is used to reveal the mechanism of their cross-scale interactions. Even with the real- mass scale separation, ion-scale turbulence eliminates electron-scale streamers and dominates heat transport, not only of ions but also of electrons. When the ion-scale modes are stabilized by finite-
value is given by the ratio of plasma pressure to magnetic pressure and characterizes electromagnetic effects on microinstabilities. Numerical analysis at both the electron scale and the ion scale is used to reveal the mechanism of their cross-scale interactions. Even with the real- mass scale separation, ion-scale turbulence eliminates electron-scale streamers and dominates heat transport, not only of ions but also of electrons. When the ion-scale modes are stabilized by finite- effects, the contribution of the electron-scale dynamics to the turbulent transport becomes non-negligible and turns out to enhance ion-scale turbulent transport.
effects, the contribution of the electron-scale dynamics to the turbulent transport becomes non-negligible and turns out to enhance ion-scale turbulent transport.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Maeyama, Shinya; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Sugama, Hideo*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*
Journal of Plasma Physics, 81(2), p.435810203_1 - 435810203_41, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:81.53(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Abe, Shinya; Katada, Inao; Hoshino, Masato; Tokunaga, Hiroaki*; Horikoshi, Hidehiko*
JAEA-Review 2014-034, 81 Pages, 2014/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Center conducts research and development to enhance the reliability of geological disposal technology, indicate the margin of technical safety for legally decided depth of repository, improve understanding of the deep geological environment, and promote greater public understanding for geological disposal technology. "YUME chisoukan" ceased its role as an exhibition facility as of end August 2012 as part of an administrative reform under the then Democratic Party rule, and came to be focused on disclosing the underground drifts to ascertain that JAEA is true to its tripartite agreement signed between the Hokkaido Prefecture, Town of Horonobe and JAEA (i.e., no nuclear materials will be used, etc.). It is also used as the facility to provide information on the research results of the Center. This report presents the statistical results of a questionnaire (2,566 responses) conducted from April to October 2013.
Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Maeyama, Shinya; Nakata, Motoki; Sugama, Hideo*; Nunami, Masanori*; Ishizawa, Akihiro*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 510, p.012045_1 - 012045_11, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:49.83(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)Plasma turbulence accompanied with fluctuations of the distribution function and the electromagnetic fields develops on the phase space composed of the configuration space and the velocity space. Detailed structures of the distribution function in magnetic fusion plasmas are investigated by means of gyrokinetic simulations performed on massively parallel supercomputers. The gyrokinetic simulations of drift wave turbulence have demonstrated entropy transfer in the phase space, zonal flow enhancement by helical fields and the resultant transport reduction. The state-of-the-art high performance computing is utilized for a multi- scale turbulence simulation covering ion- and electron-scales and for a global-scale simulation of turbulent transport in a sub-ITER sized plasma.