Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Di Palma, A.; Adamo, P.*; Dohi, Terumi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Kitamura, Akihiro; Sakoda, Akihiro; Sato, Kazuhiko; Iijima, Kazuki
Chemosphere, 308, Part 1, p.136179_1 - 136179_13, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.53(Environmental Sciences)The present study shows the use of mosses transplanted in bags, called as moss bags, as biosensors of airborne radioactive dusts in the environment of the evacuated zone of Fukushima. A standardized protocol was applied and three moss species were used. Background sites of Okayama Prefecture were used for comparison. In the Fukushima area, the moss bags were able to accumulate radiocaesium in all exposure sites and periods, with Sphagnum palustre moss acting as the most performant moss. The radiocaesium activity concentrations dectected in mosses were in strong agreement with the Cs deposition levels and decontamination status of each exposure site. The accumulation of soil-derived radiocaesium by moss bags was supported by autoradiography and electron microscopy analyses. The linear dependency of Cs accumulation with the exposure time allowed a radiocaesium quantitative assessment.
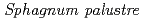 (Mosses); Towards a unified protocol of biomonitoring of airborne heavy metal pollution
(Mosses); Towards a unified protocol of biomonitoring of airborne heavy metal pollutionDi Palma, A.; Gonz lez, A. G.*; Adamo, P.*; Giordano, S.*; Reski, R.*; Pokrovsky, O. S.*
lez, A. G.*; Adamo, P.*; Giordano, S.*; Reski, R.*; Pokrovsky, O. S.*
Chemosphere, 236, p.124375_1 - 124375_9, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.34(Environmental Sciences)Di Palma, A.; Dohi, Terumi; Adamo, P.*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kitamura, Akihiro; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
We present the application of the moss bag methodology for the monitoring of  Cs-bearing airborne dusts. The moss bags will be exposed in the evacuated areas of Fukushima Prefecture and inside the FDNPP to monitor dust resuspension during decommissioning activities. Uncontaminated sites of the Japan territory will be also monitored as background-control areas. In addition, the moss heavy metal content and PM entrapped by the biomonitor will be also analysed to investigate the nature of
Cs-bearing airborne dusts. The moss bags will be exposed in the evacuated areas of Fukushima Prefecture and inside the FDNPP to monitor dust resuspension during decommissioning activities. Uncontaminated sites of the Japan territory will be also monitored as background-control areas. In addition, the moss heavy metal content and PM entrapped by the biomonitor will be also analysed to investigate the nature of  Cs-bearing particles. Finally, the biomonitoring protocol for radioactive dusts and parameters (e.g. duration of exposure, selection of the most performant moss specie) will be optimized and data compared with those provided by conventional dust sampling methods.
Cs-bearing particles. Finally, the biomonitoring protocol for radioactive dusts and parameters (e.g. duration of exposure, selection of the most performant moss specie) will be optimized and data compared with those provided by conventional dust sampling methods.
Dohi, Terumi; Di Palma, A.*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Adamo, P.*; Kusano, Keiichi*; Kimura, Shigeru*; Kanno, Futoshi*; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
In the surrounding area of the FDNPS, dust samplers have been used as a means of monitoring the radionuclides concentration in the air. However, the installation of dust samplers requires a power supply, which limits the number and location of the samplers. We aim to establish a method to evaluate the radiocaesium concentration and behavior in the air using moss bags, which have been used in air pollution research. Since the moss bags can be easily installed at any place and time, the establishment of the evaluation method using the moss bags will be effective in creating a sense of security among the local governments and their residents around the FDNPS. In this study, we investigated the applicability of moss bags to the evaluation of the concentration and behavior of radiocaesium in the air.
Di Palma, A.*; Adamo, P.*; Dohi, Terumi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,