Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Urano, Hajime; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 56(1), p.016005_1 - 016005_8, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:33.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dependence of pedestal structure on collisionality at fixed beta has been investigated in JT-60U. In the ITER-relevant low collisionality regime, the pedestal width does not change with edge collisionality. In the high collisionality regime, the pedestal width broadens with increased edge collisionality. The pedestal pressure gradient and width are not significantly changed when the pedestal is close to an intermediate  peeling-ballooning mode boundary at low collisionality. The experimental result indicates that conventional pedestal models where the pedestal width is independent of collisionality and is determined by
peeling-ballooning mode boundary at low collisionality. The experimental result indicates that conventional pedestal models where the pedestal width is independent of collisionality and is determined by 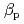 at the pedestal is not a bad assumption in the ITER-relevant low collisionality regime. On the other hand, the pressure gradient decreases and the pedestal width increases at high collisionality. The pedestal broadening becomes significant when the pedestal is marginal to be unstable at high
at the pedestal is not a bad assumption in the ITER-relevant low collisionality regime. On the other hand, the pressure gradient decreases and the pedestal width increases at high collisionality. The pedestal broadening becomes significant when the pedestal is marginal to be unstable at high  ballooning mode in high collisionality regime.
ballooning mode in high collisionality regime.
Shinohara, Koji; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Miyato, Naoaki; Urano, Hajime; Aiba, Nobuyuki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 91(12), p.797 - 800, 2015/12
no abstracts in English
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Hirota, Makoto*
Physics of Plasmas, 22(8), p.082512_1 - 082512_9, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.24(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A mechanism exciting magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) instabilities in rotating tokamak plasmas is found numerically for the first time. This mechanism is the interplay between a resistive wall mode (RWM) and a stable MHD mode. When the plasma has a stable discrete eigenmode, a reversed shear Alfv n eigenmode (RSAE) for example, a MHD mode is destabilized when plasma equilibrium rotation frequency is similar to the frequency of this stable eigenmode in a static equilibrium. This destabilization is also observed even when the eigenmode couples with Alfv
n eigenmode (RSAE) for example, a MHD mode is destabilized when plasma equilibrium rotation frequency is similar to the frequency of this stable eigenmode in a static equilibrium. This destabilization is also observed even when the eigenmode couples with Alfv n continua. This result suggests that for steady state high beta tokamaks, like DEMO, it is necessary to shape the safety factor profile in such a way that no stable eigenmode exists in the band of rotation frequency. With a dispersion relation, it was shown explicitly that plasma rotation switches the unstable mode from the RWM to the ideal MHD mode destabilized by wall resistivity.
n continua. This result suggests that for steady state high beta tokamaks, like DEMO, it is necessary to shape the safety factor profile in such a way that no stable eigenmode exists in the band of rotation frequency. With a dispersion relation, it was shown explicitly that plasma rotation switches the unstable mode from the RWM to the ideal MHD mode destabilized by wall resistivity.
Urano, Hajime; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 39E, p.P5.146_1 - P5.146_4, 2015/06
no abstracts in English
Cooper, W. A.*; Brunetti, D.*; Faustin, J. M.*; Graves, J. P.*; Pfefferl , D.*; Raghunathan, M.*; Sauter, O.*; Tran, T. M.*; Chapman, I. T.*; Ham, C. J.*; et al.
, D.*; Raghunathan, M.*; Sauter, O.*; Tran, T. M.*; Chapman, I. T.*; Ham, C. J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(6), p.063032_1 - 063032_8, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.24(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)An approximate model for a single fluid 3D MHD equilibrium with pure isothermal toroidal flow with imposed nested magnetic flux surfaces is proposed. It recovers the rigorous toroidal rotation equilibrium description in the axisymmetric limit. The approximation is valid under conditions of nearly rigid or vanishing toroidal rotation in regions with 3D deformation of the equilibrium flux surfaces. Bifurcated helical core equilibrium simulations of long-lived modes in the MAST device demonstrate that the magnetic structure is only weakly affected by the flow but that the 3D pressure distortion is important. The pressure is displaced away from the major axis and therefore is not as noticeably helically deformed as the toroidal magnetic flux under the subsonic flow conditions. Fast particle confinement is investigated with the VENUS code. In the presence of toroidal flow, the drift orbit equations depend on the electrostatic potential associated with the rotation and quasineutrality at lowest order in Larmor radius. When the equilibrium has 3D deformations, geometrical terms appear from the evaluation of Ohm's Law that considerably complicates the description of fast particle confinement.
Urano, Hajime; Nakata, Motoki; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Honda, Mitsuru; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Yoshida, Maiko; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 55(3), p.033010_1 - 033010_9, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:89.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Physics picture of improving energy confinement with argon seeding at high density has been investigated in JT-60U. Better confinement is sustained at high density by argon seeding accompanied by higher core and pedestal temperatures. Peaked density profiles are kept with argon seeding. Density peaking and dilution effects lower the pedestal density at a given averaged density. The pedestal density in the argon seeded plasmas which is relatively lower than that in a single deuterium puff enables the pedestal temperature to be higher. The density peaking is a key factor of sustaining better confinement in argon seeded H-mode plasmas.
Giroud, C.*; Jachmich, S.*; Jacquet, P.*; J rvinen, A.*; Lerche, E.*; Rimini, F.*; Aho-Mantila, L.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Balboa, I.*; Belo, P.*; et al.
rvinen, A.*; Lerche, E.*; Rimini, F.*; Aho-Mantila, L.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Balboa, I.*; Belo, P.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(3), p.035004_1 - 035004_20, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:95.51(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper reports the progress made at JET-ILW on integrating the requirements of the reference ITER baseline scenario with normalized confinement factor of 1, at a normalized pressure of 1.8 together with partially detached divertor whilst maintaining these conditions over many energy confinement times. The 2.5 MA high triangularity ELMy H-modes are studied with two different divertor configurations with D-gas injection and nitrogen seeding. The power load reduction with N seeding is reported. The relationship between an increase in energy confinement and pedestal pressure with triangularity is investigated. The operational space of both plasma configurations is studied together with the ELM energy losses and stability of the pedestal of unseeded and seeded plasmas.
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Hirota, Makoto*
Physical Review Letters, 114(6), p.065001_1 - 065001_5, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A mechanism exciting magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) instabilities in rotating tokamak plasmas is found numerically for the first time. This mechanism is the interplay between a resistive wall mode (RWM) and a stable MHD mode. When the plasma has a stable discrete eigenmode, a reversed shear Alfv n eigenmode (RSAE) for example, a MHD mode is destabilized when plasma equilibrium rotation frequency is similar to the frequency of this stable eigenmode in a static equilibrium. This destabilization is also observed even when the eigenmode couples with Alfv
n eigenmode (RSAE) for example, a MHD mode is destabilized when plasma equilibrium rotation frequency is similar to the frequency of this stable eigenmode in a static equilibrium. This destabilization is also observed even when the eigenmode couples with Alfv n continua. This result suggests that for steady state high beta tokamaks, like DEMO, it is necessary to shape the safety factor profile in such a way that no stable eigenmode exists in the band of rotation frequency.
n continua. This result suggests that for steady state high beta tokamaks, like DEMO, it is necessary to shape the safety factor profile in such a way that no stable eigenmode exists in the band of rotation frequency.
 n acoustic channel for ion energy in high-beta tokamak plasmas
n acoustic channel for ion energy in high-beta tokamak plasmasBierwage, A.; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji
Physical Review Letters, 114(1), p.015002_1 - 015002_5, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:60.82(Physics, Multidisciplinary) n acoustic channel for ion energy in high-beta tokamak plasmas revisited with a linear gyrokinetic model (LIGKA)
n acoustic channel for ion energy in high-beta tokamak plasmas revisited with a linear gyrokinetic model (LIGKA)Bierwage, A.; Lauber, P.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 14th IAEA Technical Meeting on Energetic Particles in Magnetic Confinement Systems (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/00
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Urano, Hajime
Nuclear Fusion, 54(11), p.114007_1 - 114007_9, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.11(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 shear Alfv
shear Alfv n modes driven by energetic N-NB ions in JT-60U
n modes driven by energetic N-NB ions in JT-60UBierwage, A.; Todo, Yasushi*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji
Nuclear Fusion, 54(10), p.104001_1 - 104001_14, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:66.24(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Aiba, Nobuyuki; Hirota, Makoto*; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Shiraishi, Junya; Bierwage, A.
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
A mechanism exciting magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) instabilities in rotating tokamak plasmas is found numerically for the first time. This mechanism is the interplay between a resistive wall mode (RWM) and a stable MHD mode. When the plasma has a stable discrete eigenmode, a reversed shear Alfv n eigenmode (RSAE) for example, a MHD mode is destabilized when plasma equilibrium rotation frequency is similar to the frequency of this stable eigenmode in a static equilibrium. This destabilization is also observed even when the eigenmode couples with Alfv
n eigenmode (RSAE) for example, a MHD mode is destabilized when plasma equilibrium rotation frequency is similar to the frequency of this stable eigenmode in a static equilibrium. This destabilization is also observed even when the eigenmode couples with Alfv n continua. This result suggests that for steady state high beta tokamaks, like DEMO, it is necessary to shape the safety factor profile in such a way that no stable eigenmode exists in the band of rotation frequency.
n continua. This result suggests that for steady state high beta tokamaks, like DEMO, it is necessary to shape the safety factor profile in such a way that no stable eigenmode exists in the band of rotation frequency.
Cooper, W. A.*; Hirshman, S. P.*; Chapman, I. T.*; Brunetti, D.*; Faustin, J. M.*; Graves, J. P.*; Pfefferl , D.*; Raghunathan, M.*; Sauter, O.*; Tran, T. M.*; et al.
, D.*; Raghunathan, M.*; Sauter, O.*; Tran, T. M.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 56(9), p.094004_1 - 094004_8, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.11(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)An approximate model for a single fluid three-dimensional (3D) magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) equilibrium with pure isothermal toroidal flow with imposed nested magnetic flux surfaces is proposed. It recovers the rigorous toroidal rotation equilibrium description in the axisymmetric limit. The approximation is valid under conditions of nearly rigid or vanishing toroidal rotation in regions with significant 3D deformation of the equilibrium flux surfaces. Bifurcated helical core equilibrium simulations of long-lived modes in the MAST device demonstrate that the magnetic structure is only weakly affected by the flow but that the 3D pressure distortion is important. The pressure is displaced away from the major axis and therefore is not as noticeably helically deformed as the toroidal magnetic flux under the subsonic flow conditions measured in the experiment.
Shiraishi, Junya; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Miyato, Naoaki; Yagi, Masatoshi
Nuclear Fusion, 54(8), p.083008_1 - 083008_8, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Toroidal rotation effects are self-consistently taken into account not only in the linear magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stability analysis but also in the equilibrium calculation. The MHD equilibrium computation is affected by centrifugal force due to the toroidal rotation. To study the toroidal rotation effects on resistive wall modes (RWMs), a new code has been developed. The RWMaC modules, which solve the electromagnetic dynamics in vacuum and the resistive wall, have been implemented in the MINERVA code, which solves the Frieman-Rotenberg equation that describes the linear ideal MHD dynamics in a rotating plasma. It is shown that modification of MHD equilibrium by the centrifugal force significantly reduces growth rates of RWMs. Moreover, it can open a stable window which does not exist under the assumption that the rotation affects only the linear dynamics.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Oyama, Naoyuki
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 54(4-6), p.599 - 604, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Urano, Hajime; Nakata, Motoki; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Honda, Mitsuru; Yoshida, Maiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 38F, p.P4.018_1 - P4.018_4, 2014/06
This paper reports the analysis result of heat transport and pedestal structure in H-mode plasmas with and without argon seeding on JT-60U.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Shinohara, Koji; Honda, Mitsuru
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 90(6), p.352 - 355, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
Nakata, Motoki; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Maeyama, Shinya; Nunami, Masanori*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 9, p.1403029_1 - 1403029_12, 2014/04
A local gyrokinetic Vlasov simulation code GKV is extended to incorporate realistic tokamak equilibria including up-down asymmetry, which are produced by a free-boundary 2D Grad-Shafranov equation solver MEUDAS. The developed codes have been verified by a cross-code benchmark test using Cyclone-base-case like MHD equilibrium, where good agreement in the dispersion relation of ion temperature gradient (ITG) driven mode has been confirmed. The extended GKV is applied to two types of shaped plasmas expected in JT-60SA tokamak devices, i.e., ITER-like and highly-shaped plasmas, and ITG-mode stability and residual zonal-flow level are investigated. Through the detailed comparisons, more favorable stability properties against the ITG mode are revealed for the highly-shaped case, where the lower ITG-mode growth rate and higher residual zonal-flow levels compared to the ITER-like case are identified.