Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Atsushi*; Chiba, Mirei*; Tanahara, Akira*; Aida, Jun*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Murakami, Shinobu*; Koarai, Kazuma; Ono, Takumi*; Oka, Toshitaka; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.10355_1 - 10355_11, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:39.53(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Jung, K.; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2017-008, 26 Pages, 2017/08
We are developing an analytical method using laser ablation absorption spectroscopy (LAAS) to analyze radioactive waste mixed with zirconium, uranium and so on. It is essential to evaluate the characteristics of the plume formed by the objective particles for LAAS analysis. Therefore, in this study, titanium and hafnium whose chemical properties are similar to those of Zr were chosen as analytical object. And the difference in expanding behavior of the plume due to the weight of the particles was investigated. As a result of changing the height of the probe beam and applying the optical time-of-flight method to the plume, it was found that the influence of the background gas is larger for Ti than Hf. The meaning of the resonance absorption signal of the waste sample mixed with nuclear fuel materials and nuclear reactor materials was understood by this study and basic knowledge to optimize experimental conditions were also obtained.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Khumaeni, A.*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 134, p.42 - 51, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:91.69(Spectroscopy)Spectroscopic properties of atomic species of plutonium were investigated by combining laser ablation and resonance absorption techniques for the analysis of a plutonium oxide sample. For 17 transitions of Pu atoms and ions, the absorbance, isotope shift, and hyperfine splitting were determined via Voigt profile fitting of the recorded absorption spectra. Three transitions were selected as candidates for analytical use. Using these transitions, we investigated the analytical performance that was attainable and determined a correlation coefficient R2 between the absorbance and plutonium concentration of 0.9999, a limit of detection of 30-130 ppm, and a relative standard deviation of approximately 6% for an abundance of  Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Yamada, Rui*; Tsubaki, Shinki*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Sato, Shigeo*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Machida, Akihiko; Saida, Junji*
Metals, 6(1), p.12_1 - 12_11, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Elastic deformation behaviors of as-cast and annealed eutectic and hypoeutectic Zr-Cu-Al bulk metallic glasses (BMGs) were investigated on a basis of different strain-scales determined by X-ray scattering and the strain gauge. The microscopic strains determined by Direct-space method (DSM) and Q-space method (QSM) were compared with the macroscopic strain measured by the strain gauge, and the difference in the deformation mechanism between eutectic and hypoeutectic Zr-Cu-Al BMGs was investigated by their correlation. The eutectic Zr Cu
Cu Al
Al BMG obtains more homogeneous microstructure by free-volume annihilation after annealing, improving a resistance to deformation but degrading ductility because of a decrease in the volume fraction of WBRs (Weakly-Bonded Regions) with relatively high mobility. On the other hand, the as-cast hypoeutectic Zr
BMG obtains more homogeneous microstructure by free-volume annihilation after annealing, improving a resistance to deformation but degrading ductility because of a decrease in the volume fraction of WBRs (Weakly-Bonded Regions) with relatively high mobility. On the other hand, the as-cast hypoeutectic Zr Cu
Cu Al
Al BMG originally has homogeneous microstructure, but loses its structural and elastic homogeneities because of nanocluster formation after annealing. Such structural changes after annealing might develop unique mechanical properties showing no degradations of ductility and toughness for the structural-relaxed hypoeutectic BMGs.
BMG originally has homogeneous microstructure, but loses its structural and elastic homogeneities because of nanocluster formation after annealing. Such structural changes after annealing might develop unique mechanical properties showing no degradations of ductility and toughness for the structural-relaxed hypoeutectic BMGs.
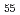 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu bulk metallic glass containing ZrC particles by synchrotron X-ray diffraction
bulk metallic glass containing ZrC particles by synchrotron X-ray diffractionSuzuki, Hiroshi; Saida, Junji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Katsuyama, Jinya; Kato, Hidemi*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Sato, Shigeo*
Scripta Materialia, 66(10), p.801 - 804, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.71(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Compressive deformation mechanism of a Zr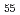 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu bulk metallic glass containing 10vol.%ZrC (ZrC-BMG) was evaluated by measuring the residual strains in the compressive deformed samples using the synchrotron X-ray diffraction and also evaluating the localized deformation behavior around the ZrC particles by the finite element analysis. Phase stress shared by the metallic glass matrix was increased before macroscopic yielding due to local plastic deformation around the ZrC particles. After macroscopic yielding, the phase stress shared by the ZrC phase was drastically increased, and finally the ZrC-BMG was fractured by breaking the ZrC particles reaching its fracture strength.
bulk metallic glass containing 10vol.%ZrC (ZrC-BMG) was evaluated by measuring the residual strains in the compressive deformed samples using the synchrotron X-ray diffraction and also evaluating the localized deformation behavior around the ZrC particles by the finite element analysis. Phase stress shared by the metallic glass matrix was increased before macroscopic yielding due to local plastic deformation around the ZrC particles. After macroscopic yielding, the phase stress shared by the ZrC phase was drastically increased, and finally the ZrC-BMG was fractured by breaking the ZrC particles reaching its fracture strength.
Sato, Yuki; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Terasaka, Yuta; Saegusa, Jun; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Iwata, Yoshihiro*; Jung, K.*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
For the radioactivity evaluation regarding to the accident of TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, time-consuming and skills-required sample pretreatments for  Sr analysis (radiometric or ICP-MS analyses) is serious issue. We are developing a ultra-sensitive and rapid analytical technique for
Sr analysis (radiometric or ICP-MS analyses) is serious issue. We are developing a ultra-sensitive and rapid analytical technique for  Sr by combining resonance ionization spectroscopy, in which only the atoms of specific isotope can be ionized using the slight difference in level energy, and ion trap technique, in which only the ions of specific isotope can be trapped for a long duration to observe them with high sensitivity. In this study, we applied a continuous-wave isolated-core excitation technique (cw-ICE) for the first time to search for highly efficient and isotope-selective ionization schemes, especially for the Rydberg series converging to the 5
Sr by combining resonance ionization spectroscopy, in which only the atoms of specific isotope can be ionized using the slight difference in level energy, and ion trap technique, in which only the ions of specific isotope can be trapped for a long duration to observe them with high sensitivity. In this study, we applied a continuous-wave isolated-core excitation technique (cw-ICE) for the first time to search for highly efficient and isotope-selective ionization schemes, especially for the Rydberg series converging to the 5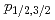 ionic levels, of which information is quite scarce. As a result, we have revealed a detailed level-structure of autoionizing 5
ionic levels, of which information is quite scarce. As a result, we have revealed a detailed level-structure of autoionizing 5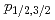 (nl) series of Sr atoms.
(nl) series of Sr atoms.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
In order to analyze isotopic composition of fuel debris generated in melted reactor core, a remote analytical method is developed based on laser ablation technique. In this method, the interaction between ablated and gas species affects time evolution of the plume structure, which also affects on analytical performance. Thus we investigate time evolution of ablated and gas species using resonance fluorescence and absorption techniques. As a result, it was found that the interaction between gas and ablated species leads complicated three dimensional structure. In particular, in the case of atmospheric air condition, it was found that many particulates and clusters are produced at the contact layer between gas and plume, and the neutral atoms stays near the center of the clusters. These findings is of great importance for future development of various laser-ablation-based analytical techniques.
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Saida, Junji*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Sato, Shigeo*
no journal, ,
Residual stress measurements using neutron and X-ray diffractions are applicable to crystalline materials whereas the strain measurement in amorphous materials had been difficult. Recently, Q-space method, which can evaluate the strain from peak shift of 1st halo peak measured by synchrotron X-ray, and Direct space method, which can evaluate the strain from changes in local structures obtained by the radial distribution function, have been reported by Poulsed et al. In this study, the evaluation of tensile deformation in Zr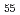 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu metallic glass using Q-space method was discussed by using neutron diffraction.
metallic glass using Q-space method was discussed by using neutron diffraction.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Ito, Chikara; Okumura, Keisuke; Katakura, Junichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Saida, Junji*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*
no journal, ,
Residual stress and deformation behavior on a Zr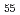 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu bulk metallic glass containing 10vol%ZrC particles were measured using neutron diffraction. Elastic deformation behavior under uniaxial tensile loading can be predicted by the Self-Consistent model. Since phase stress transferred to the metallic glass matrix is 5% less than applied stresses and the residual stress in the matrix is approximately 100MPa in tension, the compressive strength of the composite bulk metallic glass would be higher than that of monolithic one.
bulk metallic glass containing 10vol%ZrC particles were measured using neutron diffraction. Elastic deformation behavior under uniaxial tensile loading can be predicted by the Self-Consistent model. Since phase stress transferred to the metallic glass matrix is 5% less than applied stresses and the residual stress in the matrix is approximately 100MPa in tension, the compressive strength of the composite bulk metallic glass would be higher than that of monolithic one.
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Saida, Junji*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Setyawan, A. D.*; Kato, Hidemi*; Sato, Shigeo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Saida, Junji*; Kato, Hidemi*; Sato, Shigeo*; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Shobu, Takahisa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Koarai, Kazuma; Ono, Takumi*; Tamaki, Hiroaki*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Chiba, Mirei*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Releases of the radioactive materials from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident result in an ionization exposure to people and animals, the precise dosimetry is required. To estimate the external dose due to the accident, we utilize electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy which is a powerful tool for the dosimetry of external dose. The detection limit of this technique was 146 mGy, so that we have to improve the detection limit for the precise dosimetry. In this work, we developed a novel enamel-dentine separation technique and improved the detection limit down to 43 mGy, and estimated the external dose for Japanese macaque and Procyon lotor collected in Fukushima prefecture.
Jung, K.; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Imafuku, Muneyuki*; Saida, Junji*; Setyawan, A. D.*; Kato, Hidemi*
no journal, ,
Deformation behavior on a Zr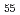 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu bulk metallic glass containing 10 vol%ZrC particles were measured using neutron diffraction. Elastic deformation behavior under uniaxial tensile loading can be predicted by the Self-Consistent model. Higher strength in compressive deformation in this sample is originated from the thermal tensile residual stresses, and from the phase stresses transferred to the metallic glass matrix which are 5% less than the applied stresses under uniaxial loading.
bulk metallic glass containing 10 vol%ZrC particles were measured using neutron diffraction. Elastic deformation behavior under uniaxial tensile loading can be predicted by the Self-Consistent model. Higher strength in compressive deformation in this sample is originated from the thermal tensile residual stresses, and from the phase stresses transferred to the metallic glass matrix which are 5% less than the applied stresses under uniaxial loading.
Sato, Yuki; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Terasaka, Yuta; Saegusa, Jun; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
The development of radiation measurement methods in the high dose-rate environment is requested to accelerate implementation of decommissioning of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). We are now developing the technology which can measure the distribution of the contamination level with radioactive substances inside the building of FDNPP. Light-weight portable gamma camera is to be developed, and is used for drones that can remotely measure the radiation distributions in the high radioactive fields where workers are not allowed to enter and remain there.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Jung, K.; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
Remote isotopic analysis for highly radioactive fuel debris containing various actinides, fission products and the other reactor materials is expected to be needed for the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan. This is because the information on the amount of fissile materials in the debris is of great importance for the purpose of safeguard verification and prevention of re-criticality accident. However, to decrease radiation dose to the analytical workers handling the debris, traditional analytical techniques such as radiometric and radiochemical methods are inadequate and an alternative technique is needed. For this reason, we are developing remote spectroscopic techniques (LIBS and LAAS) for debris analysis using laser ablation process. Laser ablation absorption spectroscopy (LAAS) is the technique by combining resonance absorption spectroscopy and laser ablation. In this technique for nuclear fuel materials, one uses the probe laser whose frequency is tuned to the resonance line of the specific isotope of U or Pu and determines the isotopic abundance from the measured absorbance. For realization of highly sensitive and isotope-selective analysis, it is necessary to optimize experimental conditions to decrease kinetic energy of the ablated species and the number of ionic species so as to reduce Doppler and Stark effects. For this optimization, we have studied the temporal and spatial variations in the density distribution under various background gas conditions. Using the optimum conditions, we have measured isotope-selective absorption spectra of U and Pu and evaluated several analytical performances of LAAS.
Okumura, Keisuke; Sato, Wakaei; Maeda, Hirobumi; Wakaida, Ikuo; Washiya, Tadahiro; Katakura, Junichi*
no journal, ,
In order to develop the evaluation technology of the most probable radiation source and dose rate distributions in the primary containment vessel (PCV), we evaluated the radiation source distribution based on the results of fuel burn-up calculation, activation calculation of structural materials and severe accident analysis. Then, we built a three-dimensional PCV model for the particle transport Monte Carlo calculation code PHITS. From the PHITS calculation, we obtained the response function of the dose rate distribution due to each unit radiation source.