Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Shibata, Takuya; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tanaka, Hirohisa*; Masaki, Sayaka*; Aotani, Takuro*; Inagawa, Kohei*; Iwata, Sogo*; Aida, Tatsuya*; Yamamoto, Tadasuke*; Kita, Tomoaki*; Ono, Hitomi*; Takenaka, Keisuke*; et al.
SAE Technical Paper 2022-01-0534 (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/03
Kato, Takuma*; Nagaoka, Mika; Guo, H.*; Fujita, Hiroki; Aida, Taku*; Smith, R. L. Jr.*
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(39), p.55725 - 55735, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)In this work, hydrothermal leaching was applied to simulated soils (clay minerals vermiculite, montmorillonite, kaolinite) and actual soils (Terunuma, Japan) to generate organic acids with the objective to develop an additive-free screening method for determination of Sr in soil. Stable strontium (SrCl ) was adsorbed onto soils for study and ten organic acids were evaluated for leaching Sr from simulated soils under hydrothermal conditions (120 to 200
) was adsorbed onto soils for study and ten organic acids were evaluated for leaching Sr from simulated soils under hydrothermal conditions (120 to 200 C) at concentrations up to 0.3 M. For strontium-adsorbed vermiculite (Sr-V), 0.1 M citric acid was found to be effective for leaching Sr at 150
C) at concentrations up to 0.3 M. For strontium-adsorbed vermiculite (Sr-V), 0.1 M citric acid was found to be effective for leaching Sr at 150 C and 1 h treatment time. Based on these results, the formation of organic acids from organic matter in Terunuma soil was studied. Hydrothermal treatment of Terunuma soil produced a maximum amount of organic acids at 200
C and 1 h treatment time. Based on these results, the formation of organic acids from organic matter in Terunuma soil was studied. Hydrothermal treatment of Terunuma soil produced a maximum amount of organic acids at 200 C and 0.5 h reaction time. To confirm the possibility for leaching of Sr from Terunuma soil, strontium-adsorbed Terunuma soil (Sr-S) was studied. For Sr-S, hydrothermal treatment at 200
C and 0.5 h reaction time. To confirm the possibility for leaching of Sr from Terunuma soil, strontium-adsorbed Terunuma soil (Sr-S) was studied. For Sr-S, hydrothermal treatment at 200 C for 0.5 h reaction time allowed 40% of the Sr to be leached at room temperature, thus demonstrating an additive-free method for screening of Sr in soil. The additive-free hydrothermal leaching method avoids calcination of solids in the first step of chemical analysis and has application to both routine monitoring of metals in soils and to emergency situations.
C for 0.5 h reaction time allowed 40% of the Sr to be leached at room temperature, thus demonstrating an additive-free method for screening of Sr in soil. The additive-free hydrothermal leaching method avoids calcination of solids in the first step of chemical analysis and has application to both routine monitoring of metals in soils and to emergency situations.
Takahashi, Atsushi*; Chiba, Mirei*; Tanahara, Akira*; Aida, Jun*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Murakami, Shinobu*; Koarai, Kazuma; Ono, Takumi*; Oka, Toshitaka; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.10355_1 - 10355_11, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Tamura, Koji; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.405 - 415, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:84.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Radiation dose rate effects on the properties of a compact fiber-optic laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system with a monolithic Nd:YAG/Cr:YAG composite ceramics were investigated for remote analysis in hazardous environment. To investigate radiation effects on the LIBS signal, properties related to the Nd:YAG laser operation such as oscillation threshold, output energy, oscillation timing, temporal pulse shape, and beam profile were measured as a function of the radiation dose rate from 0 to 10 kGy/hr in view of their influences to the signal. LIBS spectra of zirconium metal were measured under irradiation. Although signal intensity decreased considerably by irradiation, informative spectra were well obtained even at the maximum radiation dose rate. From the comparison of the LIBS-related parameters among the laser properties, signal reduction was mainly ascribed to the pulse energy reduction. Scintillation emission spectra were also measured from the ceramics during the irradiation, where the signal intensity increased linearly with the dose rate. The results show that the developed system.
Nagaoka, Mika; Fujita, Hiroki; Aida, Taku*; Guo, H.*; Smith, R. L. Jr.*
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 168, p.109465_1 - 109465_6, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The radioactivities in the environmental samples are analyzed to monitor the nuclear power facilities. The pretreatment of radioactive nuclides of alpha and beta emitters in the environmental samples is performed with acid to decompose organic matter and extract object nuclide such as  Sr, U and Pu. However, the pretreatment methods are time-consuming and used many concentrated acid solutions that are unsafe and hazardous. Therefore, we develop to the new pretreatment method using supercritical water instead of acid. Hydrothermal pretreatment of soils (Andosols) from Ibaraki prefecture (Japan) was used to improve methods for monitoring radioactive Sr and U. Calcined samples were pretreated with subcritical or supercritical water (SCW) followed by extraction with 0.5 M HNO
Sr, U and Pu. However, the pretreatment methods are time-consuming and used many concentrated acid solutions that are unsafe and hazardous. Therefore, we develop to the new pretreatment method using supercritical water instead of acid. Hydrothermal pretreatment of soils (Andosols) from Ibaraki prefecture (Japan) was used to improve methods for monitoring radioactive Sr and U. Calcined samples were pretreated with subcritical or supercritical water (SCW) followed by extraction with 0.5 M HNO solutions. With SCW pretreatment, recoveries of Sr and U were 70% and 40%, respectively. Experimental recoveries obtained can be described by a linear relationship in water density. The proposed method is robust and can lower environmental burden of routine analytical protocols.
solutions. With SCW pretreatment, recoveries of Sr and U were 70% and 40%, respectively. Experimental recoveries obtained can be described by a linear relationship in water density. The proposed method is robust and can lower environmental burden of routine analytical protocols.
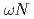 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.12(Physics, Nuclear)Kaida, Takuyo*; Ishizaki, Yoichi*; Okajima, Satoshi
Atsuryoku Gijutsu, 52(2), p.53 - 63, 2014/04
Probabilistic approach for Fitness-For-Service (FFS) assessment of pressure equipment in petroleum and petrochemical plant helps to quantify the safety margin and rationalize the assessment. As for local metal loss assessment, several studies have been made on reliability analysis of the damaged equipment by use of limit state function, denoted by deterministic FFS model in published standard. Stochastic properties of random variables are needed in the reliability analysis. Remaining thickness of the pressure equipment is one of the important variables in limit state function for metal loss assessment. The thickness readings on a prescribed grid, which characterize the remaining thickness and size of the region of metal loss, might be varied by each inspector. There has been, however, no studies on stochastic properties of thickness readings for the local metal loss assessment. In this study, the stochastic properties of thickness readings were investigated by analyzing of the results of Round-Robin test. The cause of variation of thickness readings was clarified for the purpose of either protection of failure by pressure or that of leakage. The results of investigation indicated that standard deviation of thickness readings in the region of metal loss was more than that of thickness away from metal loss. Finally, the reliability of pressure equipment with local metal loss was analyzed using stochastic properties.
Kurihara, Tomoyuki*; Kaida, Takuyo*; Okajima, Satoshi
Atsuryoku Gijutsu, 52(2), p.64 - 71, 2014/04
In Fitness-For-Service (FFS) assessment of pressure equipment, high reliability is needed in petroleum and petrochemical plant. Future Corrosion Allowance (FCA) is one of the most important factors in the metal loss assessment of FFS because it decides predicted value of the thickness during service periods. For the evaluation of FCA, the accurate corrosion rate from actual thinning data is needed and it is necessary to make a consideration of their variability of the thinning phenomena. In this study, the measured thickness data of the oil piping in the actual plant are collected and statistically analyzed as corrosion rate data which are classified by the operation condition. By the analysis, the probabilistic properties of corrosion rate are clarified in this piping system. Especially it is cleared that the corrosion rate of the air injection part is higher than that of the no air injection part. And the reliabilities of the protection of the failure by pressure and their change are quantitatively evaluated from the probabilistic properties of corrosion rate. From this case study, the procedure of FCA evaluation of FFS assessment was established and it's clear that the statistical analysis by the feature of thinning phenomena is important for accurate evaluation of corrosion data.
Okumura, Keisuke; Sato, Wakaei; Maeda, Hirobumi; Wakaida, Ikuo; Washiya, Tadahiro; Katakura, Junichi*
no journal, ,
In order to develop the evaluation technology of the most probable radiation source and dose rate distributions in the primary containment vessel (PCV), we evaluated the radiation source distribution based on the results of fuel burn-up calculation, activation calculation of structural materials and severe accident analysis. Then, we built a three-dimensional PCV model for the particle transport Monte Carlo calculation code PHITS. From the PHITS calculation, we obtained the response function of the dose rate distribution due to each unit radiation source.
Nagaoka, Mika; Fujita, Hiroki; Aida, Taku*; Smith, R.*
no journal, ,
Radioactivity concentration in environmental sample such as leaf, seaweed has been measured through chemical separation with organic matter decomposition and extraction of target element. However, the usual chemical treatment could affect worker's health, chemical hood and surrounding environment by usage of chemical regent. On the other hand, supercritical water reaction could decompose organic matter without health and environmental hazard caused by the regent. Therefore, we have tried to apply the supercritical water reaction to radioactivity analysis of environmental samples. In this research, organic matter content and strontium concentration in environmental sample were compared with between before and after the reaction. The organic matters were highly decomposed with the water reaction at higher temperature and for longer reaction time. However the strontium was not extracted into solution after the reaction.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Matsumoto, Ayumu; Miyabe, Masabumi; Ikeda, Yuji*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
For the decommissioning of "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS)", widely basic R&D and matting for actual application for decommissioning technology will be strongly required. CLADS/JAEA is one of the key institute for strategic promotion of Decommissioning Science on F1NPS. As for the development of rapid, easy, onsite and in-situ remote diagnostic/analysis techniques under extremely high radioactive condition, the concept of probing by light and diagnostic by light with radiation resistant optical fiber will be one of the simple, powerful and applicable choices as the innovative development based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) technology. Optical fiber based LIBS is developed for in-core and in-situ elemental analysis of debris and its activity is performed under severe environmental conditions such as high radiation field of about 10kGy/h and under water. Long pulse laser, microwave assisted LIBS and microchip laser are also introduced for more high sensitivity.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Ito, Chikara; Okumura, Keisuke; Katakura, Junichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori*; Ikeda, Yuji*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
Radiation resistant optical fiber based laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (Fiber LIBS) is developed for in-core and in-situ elemental analysis of debris and its activity is performed under severe environmental conditions such as high radiation field of about 10kGy/h and under water. Long pulse laser, microwave assisted LIBS for more high sensitivity and micro-chip Laser will be also introduced for In-Core use optical source.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Hironori; Ikeda, Yuji*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakaida, Ikuo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Oba, Hironori; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa; Matsumoto, Ayumu*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Ikeda, Yuji*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakaida, Ikuo; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Hironori; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Ikeda, Yuji*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
Shibata, Takuya; Oba, Hironori; Seko, Noriaki*; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English