Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Hirohisa*; Masaki, Sayaka*; Aotani, Takuro*; Inagawa, Kohei*; Iwata, Sogo*; Aida, Tatsuya*; Yamamoto, Tadasuke*; Kita, Tomoaki*; Ono, Hitomi*; Takenaka, Keisuke*; et al.
SAE Technical Paper 2022-01-0534 (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/03
Naganuma, Masayuki; Aida, Tatsuya*; Hayashi, Hideyuki
JAEA-Research 2006-087, 72 Pages, 2007/02
In the core and fuel design of sodium-cooled MOX fuel FR of FS, core designs with pellet fuel were mainly evaluated. However, vibro-packed fuel and sphere-pac fuel are also considered one of the candidates. Besides, the design must be affected by difference of the fuel behavior, however, the influence had not yet been evaluated adequately. Thus, authors examined the fuel thermal design model and evaluated the influences to the core and fuel design quantitatively. As a result, in the fuel thermal design model, selection of restructuring conditions was found to be important. Proper values were evaluated from the viewpoint of fitting PIE results. In applying this model, limitation of the stationary LHR was reduced to 390 W/cm. For FS phase-II reference cores, though it is required to modify specifications due to the decrease of LHR, the influence to nuclear performance is found to be benign. Therefore, the design that meets the requirements and targets of FS is possible for those fuels.
Oki, Shigeo; Sugino, Kazuteru; Ogawa, Takashi; Aida, Tatsuya*; Hayashi, Hideyuki
JAEA-Research 2006-077, 86 Pages, 2006/11
Core and fuel design study of 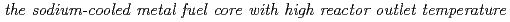 was performed. The reference specification of the large-scale (1,500 MWe) and the middle-scale (750 MWe) cores were proposed as a final result of
was performed. The reference specification of the large-scale (1,500 MWe) and the middle-scale (750 MWe) cores were proposed as a final result of 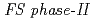 . Since the local conversion ratio of any of the core points is made close to unity with single Pu enrichment, it is possible to minimize the necessary coolant flow rate for the core region and then, accept high reactor outlet temperature of 550
. Since the local conversion ratio of any of the core points is made close to unity with single Pu enrichment, it is possible to minimize the necessary coolant flow rate for the core region and then, accept high reactor outlet temperature of 550 C. By the rationalization of hot spot factors, the coolant flow distribution design can be optimized to 5 regions for the large-scale core and 8 regions for the middle-scale core, respectively. It was also confirmed that the core specification met the criteria of fuel-assembly integrity, as well as those of shielding design. For further improvement on the reactor outlet temperature condition, the reduction of the maximum cladding inner-wall temperature was investigated with the reflection of the actual control rod insertion depth and the rationalization of the excess-reactivity uncertainty. An alternative core design was investigated by adopting the PNC-FMS steel as the cladding material instead of the ODS steel. As a result of the investigation of extending the control rod lifetime, three-cycle lifetime (which is the same as fuel assemblies) could be possible by means of the reductions in
C. By the rationalization of hot spot factors, the coolant flow distribution design can be optimized to 5 regions for the large-scale core and 8 regions for the middle-scale core, respectively. It was also confirmed that the core specification met the criteria of fuel-assembly integrity, as well as those of shielding design. For further improvement on the reactor outlet temperature condition, the reduction of the maximum cladding inner-wall temperature was investigated with the reflection of the actual control rod insertion depth and the rationalization of the excess-reactivity uncertainty. An alternative core design was investigated by adopting the PNC-FMS steel as the cladding material instead of the ODS steel. As a result of the investigation of extending the control rod lifetime, three-cycle lifetime (which is the same as fuel assemblies) could be possible by means of the reductions in  B enrichment and B
B enrichment and B C pellet diameter.
C pellet diameter.
Naganuma, Masayuki; Aida, Tatsuya*; Hayashi, Hideyuki
JAEA-Research 2006-063, 97 Pages, 2006/09
In the Feasibility Study in Japan (FS), transmutation technology of LLFP using commercial fast reactors has been studied to reduce the environmental burden. In this report, loading type of LLFP target assembly, transmutation performances of FS designed cores and capability of transmutation core with high SF (transmutation / production ratio) are studied. Design studies for two loading types cores (in-core and ex-core loading type) were conducted for comparison. The in-core loading type core was found to decrease LLFP inventories significantly, thus, that was selected as the reference of FS. For FS phase-II designed cores, LLFP transmutation performances were evaluated. Every core was confirmed to have the capability to attain SF  1.0. Then, we conducted sensitivity evaluations of design conditions to SF for transmutation core with high SF. Since sensitivities of every condition were found to be small, we concluded that large SF may be impossible for the commercial reactors.
1.0. Then, we conducted sensitivity evaluations of design conditions to SF for transmutation core with high SF. Since sensitivities of every condition were found to be small, we concluded that large SF may be impossible for the commercial reactors.
Ogawa, Takashi; Sato, Isamu; Naganuma, Masayuki; Aida, Tatsuya*; Sugino, Kazuteru; Hayashi, Hideyuki
JAEA-Research 2006-061, 54 Pages, 2006/09
Sodium cooled fast reactor with mixed oxide fueled core is one of the promising candidates in "Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System" in Japan. The results of the study on the reactor core and fuel design in the JFY2005 are reported. (1)Design studies of high internal conversion (HIC) type core: (i)Influence of TRU composition variation on the HIC type core and fuel designs was evaluated. (ii)In adopting PNC-FMS steel as alternative cladding material of ODS steel, influence to the reactor core and fuel design was evaluated for the large-scale HIC type core. (iii)Shielding property of the large-scale HIC type core was evaluated. (iv)Some measures to extend the lifetime of control rod were studied for the large-scale HIC type core. (2)Design study on high breeding performance: The core design corresponding to a requirement of high breeding performance was studied based on the large-scale compact type core designed in the JFY2004.
Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Ogawa, Takashi; Naganuma, Masayuki; Aida, Tatsuya
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
Conceptual design studies of sodium cooled fast reactor core are performed. Oxide fuel core is studied to construct advanced core concepts. As regards the core, an advanced concept of large diameter fuel pin is applied to obtain high internal conversion ratio. This leads to the break even breeding core, in which the breeding ratio is just above 1.0, without radial blanket, which has economical advantage due to high burnup of about 100GWd/t in refueling batch average including blanket. This advanced concept has economical advantage by consistently achieving high burnup and breeding with small amount of blanket.
Naganuma, Masayuki; Takaki, Naoyuki*; Aida, Tatsuya; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
In this paper, promising loading method of LLFP target assemblies and LLFP transmutation performances of typical cores designed in phase-II of FS are described. As for loading method, in-core loading type is found to be most promising in LLFP inventory. LLFP transmutation performances are evaluated by applying the in-core loading method. As a result, every core is confirmed to have capability to transmute LLFP amount more than generated one for 99Tc and 129I in keeping the breeding performance.
Naganuma, Masayuki; Sugino, Kazuteru; Aida, Tatsuya; Ogawa, Takashi; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JNC TN9400 2005-051, 239 Pages, 2005/09
Sodium cooled fast reactor (mixed oxide and metal fuel core) is one of promising candidates in Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System in Japan (FS). Its design study has been conducted thorough FS. In JFY2004's mixed oxide fuel core design study, a core with improved FAIDUS (Fuel Assembly with Inner Duct Structure) type fuel assemblies was examined. In the core design study, two types of core concepts were examined as well as JFY2003's study. One is "Compact type" that follows a conventional type core and the other is "High internal conversion type (HIC type)". As a result, the HIC type core is revealed to attain higher total discharge average burn-up and longer operation cycle length compaired with the "Compact type" core, which decreases the fuel cycle cost and increases the availability factor. The HIC type core was selected from this as representatives of large scale (1500 MWe) and medium scale (750 MWe) reactors of FS phase II. In the metal fuel core design study, a core with "High core outlet temperature type" was investigated for improving economics. "High core outlet temperature" core is aimed at achieving the identical core outlet and inlet temperatures to those of sodium cooled mixed oxide fuel cores (550C/395C). In the new measure for flatting the radial power distribution, Pu-enrichment and fuel pin-diameter are unified and the levels of Zr-contents and fuel smeared densities of metal fuel are changed in the radial direction. For avoiding the difficulty in the fuel fabrication compared with conventional core, the Zr-content was set less than 10wt%. This new measure produced cores with smaller core size compared with the mixed oxide fuel "Compact type" cores. The results of maximum cladding temperature were 650C for large-scale core and 652C for middle-scale core, which nearly satisfied the design limit of 650C. Rationalization of hot spot factor has a pottential for further increase of the core outlet temperature.
Okano, Yasushi; Aida, Tatsuya; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JNC TN9400 2005-031, 173 Pages, 2005/07
He-cooled fast reactor employing coated-particle nitride fuel has been taken an interest as a part of feasibility study projects in JNC. Hexagonal-block fuel assembly configuration has been considered as a candidate, where mass of CPs packed in a SiC matrix are indirectly cooled using ascending flow in penetrating tubes. This manuscript describes technical keys for neutronics/thermal-hydraulics performance enhancements of the hexagonal-block fuel concepts, and the best-to-date core designs for taking the feasibility study Phase-II qualification, as an annual report of JFY2004.
Naganuma, Masayuki; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Aida, Tatsuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English