Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Np and
Np and  Am by accelerator-driven system at Kyoto University Critical Assembly
Am by accelerator-driven system at Kyoto University Critical AssemblyPyeon, C. H.*; Yamanaka, Masao*; Oizumi, Akito; Fukushima, Masahiro; Chiba, Go*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Van Rooijen, W. G.*; Hashimoto, Kengo*; Sakon, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(8), p.684 - 689, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:80.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study demonstrates, for the first time, the principle of nuclear transmutation of minor actinide (MA) by the accelerator-driven system (ADS) through the injection of high-energy neutrons into the subcritical core at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly. The main objective of the experiments is to confirm fission reactions of neptunium-237 ( Np) and americium-241 (
Np) and americium-241 ( Am), and capture reactions of
Am), and capture reactions of  Np. Subcritical irradiation of
Np. Subcritical irradiation of  Np and
Np and  Am foils is conducted in a hard spectrum core with the use of the back-to-back fission chamber that obtains simultaneously two signals from specially installed test (
Am foils is conducted in a hard spectrum core with the use of the back-to-back fission chamber that obtains simultaneously two signals from specially installed test ( Np or
Np or  Am) and reference (uranium-235) foils. The first nuclear transmutation of
Am) and reference (uranium-235) foils. The first nuclear transmutation of  Np and
Np and  Am by ADS soundly implemented by combining the subcritical core and the 100 MeV proton accelerator, and the use of a lead-bismuth target, is conclusively demonstrated through the experimental results of fission and capture reaction events.
Am by ADS soundly implemented by combining the subcritical core and the 100 MeV proton accelerator, and the use of a lead-bismuth target, is conclusively demonstrated through the experimental results of fission and capture reaction events.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Masaya; Nakata, Masahito; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Abe, Kazuyuki; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-072, 144 Pages, 2010/03
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from FY2006 in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupled irradiations or single irradiation by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 thermal reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we summarized about the overall plan, the work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Koga, Tadanori*; Hashimoto, Takeji; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Amino, Naoya*; Nakamura, Masao*; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Koizumi, Satoshi
Macromolecules, 41(2), p.453 - 464, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:112 Percentile:95.04(Polymer Science)Using a combined ultra-small-angle and small-angle scattering method of neutrons and X-rays, we investigated hierarchical structures of carbon black (CB) highly loaded in polyisoprene (PI) and poly-(styrene-random-butadiene) copolymer (SBR) under mechanical field (defined respectively as CB/PI and CB/SBR) as well as in toluene under a sonic field (defined as CB/toluene). Comparison of the scattering profiles from CB/PI and CB/SBR with CB/toluene clarified that (1) the smallest structure elements of CB in PI and SBR were composed of the several unbreakable units bounded together by polymer chains (defined as "dispersible units") and (2) sizes and shapes of the dispersible units depended on the polymer matrix. (3) Moreover, the enlarged size of the dispersible unit in PI was found to enlarge the upper cutoff length of the mass-fractal structure in PI, while the mass-fractal dimensions themselves remained unchanged between PI and SBR.
 He for neutron detection
He for neutron detectionNakamura, Tatsuya; Masaoka, Sei; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Tanaka, Hiroki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 539(1-2), p.363 - 371, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)We evaluated the neutron-detection performance of a capillary plate under high-pressure helium-3 in terms of the gas gain and the distribution of pulse heights, with the aim of using the device as a neutron detector and a gas preamplification device. The capillary plate exhibited a gas gain of more than 1000 up to a gas pressure of 6 atm with a 5% mixture of ethane, confirming an adequate gas gain as a neutron detector. It was also found that the rise times of the signal pulses were correlated with the range and the emission angle of the secondary particles, protons and tritons, thereby providing useful information for developing a system with position-sensitive readouts with a high spatial resolution and a low background.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Masaoka, Sei; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 51(4), p.1519 - 1523, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.41(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A capillary plate (CP) comprising an assembly of fine glass tubes was applied as a pre-gas-amplification device for a microstrip gas chamber (MSGC) operating under high-gas pressure of helium-3 for use in neutron detection. The collection efficiency of the electrons between the CP and MSGC was maximally 17% using neutrons. The effective gas gain of the detector system was  600 at a gas pressure of 3 atm with a 10% mixture of ethane with helium-3, confirming the feasibility of the CP as a pre-gas-amplification device. Moreover, we demonstrated that the coincidence measurement of the signals between the CP and the anodes of MSGC decreased the background levels of electronics noise, electronic discharges, and
600 at a gas pressure of 3 atm with a 10% mixture of ethane with helium-3, confirming the feasibility of the CP as a pre-gas-amplification device. Moreover, we demonstrated that the coincidence measurement of the signals between the CP and the anodes of MSGC decreased the background levels of electronics noise, electronic discharges, and  -rays, indicating that a detector system with a low background can be constructed using the CP.
-rays, indicating that a detector system with a low background can be constructed using the CP.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Masaoka, Sei; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.336 - 341, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)A microstrip gas chamber (MSGC) with a capability of track discrimination for neutron detection was developed whilst ensuring the stability of the MSGC and fulfilling the specifications required for detectors using in high-flux reactors and high-intensity pulsed-neutron sources. The developed two-dimensional detector system comprises a MSGC with individual signal channel read-outs and a new instrument system with a capability of secondary-particle discrimination (InSPaD). The InSPaD identifies the particles -proton and triton- created in the nuclear reaction 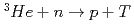 by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as
by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as 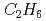 with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
Yamagishi, Hideshi; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Masaoka, Sei; Aizawa, Kazuya
Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(7), p.2340 - 2345, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:46.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new instrument system with the capability of secondary-particle discrimination (InSPaD) was studied for the development of two-dimensional neutron detectors (2D-ND) filled with helium-3 gas and with high spatial resolution. The InSPaD can discriminate between the tracks of a proton and a triton created in the nuclear reaction  He(
He( ,
, )
) by simply setting the level of discriminators appropriately in each signal channel, and the system exhibits a high spatial resolution, high counting rate, low background, and stability. The simulations of the 2D-ND equipped with the InSPaD revealed spatial resolutions of 0.46 mm in full width at half maximum for a 10% mixture of C
by simply setting the level of discriminators appropriately in each signal channel, and the system exhibits a high spatial resolution, high counting rate, low background, and stability. The simulations of the 2D-ND equipped with the InSPaD revealed spatial resolutions of 0.46 mm in full width at half maximum for a 10% mixture of C H
H with helium-3 at 0.3 MPa. The results of neutron-detection experiments using a microstrip gas chamber, including the range of the secondary particles and the pulse-height distribution, agreed well with the simulated results, indicating the feasibility of the InSPaD.
with helium-3 at 0.3 MPa. The results of neutron-detection experiments using a microstrip gas chamber, including the range of the secondary particles and the pulse-height distribution, agreed well with the simulated results, indicating the feasibility of the InSPaD.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Masaoka, Sei; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 1, p.441 - 446, 2003/07
Development of a Micro-Strip Gas Chamber(MSGC) in JAERI is presented. The performances we aim at are counting rate  10
10
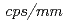
 , position resolution
, position resolution  1
1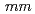 , detection efficiency
, detection efficiency  60% at thermal neutron and good n/gamma discrimination. Our two-dimensional gas detector consists of a micro strip plate printed on a polyimide substrate and a high pressure gas chamber which has all the signal lines are directly taken out (256ch individual readout) and withstands the pressure of 10bar
60% at thermal neutron and good n/gamma discrimination. Our two-dimensional gas detector consists of a micro strip plate printed on a polyimide substrate and a high pressure gas chamber which has all the signal lines are directly taken out (256ch individual readout) and withstands the pressure of 10bar 
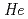 . The individual signal readout opens the way to realize high counting rate and high position resolution at the same time. We carried out range measurements of secondary particles to confirm the range measuring power of the MSGC with that read out method. The measured ranges in the gas of 3bar helium mixed with
. The individual signal readout opens the way to realize high counting rate and high position resolution at the same time. We carried out range measurements of secondary particles to confirm the range measuring power of the MSGC with that read out method. The measured ranges in the gas of 3bar helium mixed with 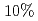 ethane is 3mm, 9.5mm for triton and proton, respectively. Those values are well agreed with theoretical estimation and we could show the feasibility of the precise measurement of the ranges by the MSGC.
ethane is 3mm, 9.5mm for triton and proton, respectively. Those values are well agreed with theoretical estimation and we could show the feasibility of the precise measurement of the ranges by the MSGC.
Ishigaki, Toru; Harjo, S.; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Mori, Kazuhiro*; Mochiku, Takashi*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; Ebata, Kazuhiro*; Takano, Yoshiki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Matsui, Yoshinori; Sasajima, Fumio; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Aizawa, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishigaki, Toru; Hoshikawa, Akinori; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Sakuma, Takashi*; Tomota, Yo*; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
Ibaraki prefecture, the local goverment of the area for J-PARC site, was decided to build a versatile neutron diffractometer (IBARAKI Materials Design Diffractometer) to promote a industrial application for neutron beam in J-PARC. This diffractometer is planned to be a high throughput diffractometer so that materials engineers and scientists can use it like the chemical analytical instruments in their materials development process. It covers in d range 0.18  d (
d ( )
)  5 with
5 with 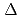
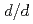 = 0.16% at high resolution bank, and covers 5
= 0.16% at high resolution bank, and covers 5  d (
d ( )
)  800 with gradually changing resolution at three detector bank (90 degree, low angle and small angle). Typical measuring time to obtain a "Rietveld-quality" data is several minutes with the sample size of laboratory X-ray diffractometer. To promote industrial application, a utilization system for this diffractometer is required. We will establish a support system for both academic and industrial users who are willing to use neutron but have not been familiar with neutron diffraction. The construction of this instrument was already begun and will be compleated in the beggining of 2008, as one of day-one instruments for J-PARC.
800 with gradually changing resolution at three detector bank (90 degree, low angle and small angle). Typical measuring time to obtain a "Rietveld-quality" data is several minutes with the sample size of laboratory X-ray diffractometer. To promote industrial application, a utilization system for this diffractometer is required. We will establish a support system for both academic and industrial users who are willing to use neutron but have not been familiar with neutron diffraction. The construction of this instrument was already begun and will be compleated in the beggining of 2008, as one of day-one instruments for J-PARC.
Ishigaki, Toru; Hoshikawa, Akinori; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Mori, Kazuhiro*; Mochiku, Takashi*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; Ebata, Kazuhiro*; Takano, Yoshiki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishigaki, Toru; Hoshikawa, Akinori; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Sakuma, Takashi*; Tomota, Yo*; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; Hayashi, Makoto*; et al.
no journal, ,
Ibaraki prefecture, the local government of the area for J-PARC site, was decided to build a versatile neutron diffractometer (IBARAKI Materials Design Diffractometer) to promote an industrial application for neutron beam in J-PARC. This diffractometer is planned to be a high throughput diffractometer so that materials engineers and scientists can use it like the chemical analytical instruments in their materials development process. It covers in d range 0.18  d (
d ( )
)  5 with
5 with  d/d = 0.16 % at high resolution bank, and covers
d/d = 0.16 % at high resolution bank, and covers  d (
d ( )
)  800 with gradually changing resolution at three detector bank (90 degree, low angle and small angle). Typical measuring time to obtain a "Rietveld-quality" data is several minutes with the sample size of laboratory X-ray diffractometer. To promote industrial application, a utilization system for this diffractometer is required. We will establish a support system for both academic and industrial users who are willing to use neutron but have not been familiar with neutron diffraction. The construction of this instrument was already beginning and will be completed in the beginning of 2008, as one of day-one instruments for J-PARC. The current status for this instrument also will be reported.
800 with gradually changing resolution at three detector bank (90 degree, low angle and small angle). Typical measuring time to obtain a "Rietveld-quality" data is several minutes with the sample size of laboratory X-ray diffractometer. To promote industrial application, a utilization system for this diffractometer is required. We will establish a support system for both academic and industrial users who are willing to use neutron but have not been familiar with neutron diffraction. The construction of this instrument was already beginning and will be completed in the beginning of 2008, as one of day-one instruments for J-PARC. The current status for this instrument also will be reported.
Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Umeda, Miki; Sasajima, Hideo; Udagawa, Yutaka; Fuketa, Toyoshi; Aizawa, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsui, Yoshinori; Nabeya, Hideaki; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Aizawa, Masao; Nakata, Masahito; Numata, Masami; Usami, Koji; Endo, Shinya; Ito, Kazuhiro; et al.
no journal, ,
We are proceeding with the study of "R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant". For the study, it is important that the irradiated specimens are gotten by the coupling of JRR-3 and JOYO. This reports the total irradiation plan in the study, and the executed work for the coupling irradiation (JRR-3 and JOYO) including the Hot facilities work of Tokai and Oarai in the 2006 fiscal year.
Ito, Takayoshi; Harjo, S.; Arima, Hiroshi; Abe, Jun; Moriai, Atsushi; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; Nakatani, Takeshi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aso, Tomokazu; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Munakata, Koji*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kawamura, Seiko; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Watanabe, Masao; Takata, Shinichi; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
no journal, ,
In FY2013, the SE team was officially organized in Technology Development Section in MLF with succeeding the previous ad hoc SE team. We are working on operation of so-called beam-line (BL)-common SE equipment and development of the SE devices as well as the previous SE team. We have already prepared a vertical-field superconducting magnet, a dilution refrigerator insert, a furnace with Nb heater and 2K cryostat as the BL-common SE equipment. In this fiscal year, a bottom-loading type  He cryostat will be introduced. Moreover, we have just started developing high pressure system by collaborating with High Pressure Group in MLF, to comply with users' requests. We have also discussed the general purpose of apparatus for pulse magnet and for hydrogen environment. We plan to prepare more working area for the SE equipment, whose number gradually increases, and sample preparation and characterization rooms for users in the new building, which is under construction.
He cryostat will be introduced. Moreover, we have just started developing high pressure system by collaborating with High Pressure Group in MLF, to comply with users' requests. We have also discussed the general purpose of apparatus for pulse magnet and for hydrogen environment. We plan to prepare more working area for the SE equipment, whose number gradually increases, and sample preparation and characterization rooms for users in the new building, which is under construction.
Aso, Tomokazu; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Munakata, Koji*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kawamura, Seiko; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Watanabe, Masao; Takata, Shinichi; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
no journal, ,
In FY2013, the SE team was officially organized in Technology Development Section in MLF with succeeding the previous ad hoc SE team. We are working on operation of so-called beam-line (BL)-common SE equipment and development of the SE devices as well as the previous SE team. We have already prepared a vertical-field superconducting magnet, a dilution refrigerator insert, a furnace with Nb heater and 2K cryostat as the BL-common SE equipment. In this fiscal year, a bottom-loading type  He cryostat will be introduced. Moreover, we have just started developing high pressure system by collaborating with High Pressure Group in MLF, to comply with users' requests. We have also discussed the general purpose of apparatus for pulse magnet and for hydrogen environment. We plan to prepare more working area for the SE equipment, whose number gradually increases, and sample preparation and characterization rooms for users in the new building, which is under construction.
He cryostat will be introduced. Moreover, we have just started developing high pressure system by collaborating with High Pressure Group in MLF, to comply with users' requests. We have also discussed the general purpose of apparatus for pulse magnet and for hydrogen environment. We plan to prepare more working area for the SE equipment, whose number gradually increases, and sample preparation and characterization rooms for users in the new building, which is under construction.